Social Justice
Persistent Issue of Violence Against Women in India
For Prelims: Indian Medical Association, Fifteenth Finance Commission, Concurrent list, National Crime Records Bureau, First Information Report, PoSH Act, Vishakha guidelines, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme, Ujjawala Scheme, NIRBHAYA Fund
For Mains: Women's Safety in India and Legal Reforms, Issues Related to Women, Role of societal norms and women empowerment
Why in News?
The recent rape and murder of a trainee doctor in Kolkata have reignited nationwide concerns about women's safety and intensified protests by healthcare workers, who are now calling for a Central law to protect them.
- Despite stricter laws, crimes against women persist and continue to rise, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive reforms.
What are the Demands of Healthcare Workers?
- Demands:
- Central Protection Act: The Indian Medical Association (IMA) is advocating for the Implementation of a nationwide law to ensure the safety of healthcare professionals, similar to global examples like the United Kingdom's National Health Service (NHS) zero-tolerance policy and the United States's felony (crime that is serious enough to be punishable) classifications for assaults.
- In the US, felonies are categorised into classes based on their maximum prison sentences.
- Ranging from Class A felonies, the most serious, carry a maximum sentence of life imprisonment or death to Class E felonies range from more than 1 year to less than 5 years.
- In the US, felonies are categorised into classes based on their maximum prison sentences.
- Enhanced Safety Measures: Better lighting, security guards, and monitored security cameras in hospitals and medical facilities.
- Ensuring safer working and living conditions for doctors, including well-lit corridors and secure wards.
- Installation of security systems and emergency response mechanisms in healthcare settings.
- Central Protection Act: The Indian Medical Association (IMA) is advocating for the Implementation of a nationwide law to ensure the safety of healthcare professionals, similar to global examples like the United Kingdom's National Health Service (NHS) zero-tolerance policy and the United States's felony (crime that is serious enough to be punishable) classifications for assaults.
- Current Provisions:
- State Responsibilities: Health and law and order are primarily State subjects, with the Union government lacking centralised data on attacks on medical professionals.
- N.K. Singh, Chairman of the Fifteenth Finance Commission, suggested that health should be shifted to the Concurrent list under the Constitution, as it is currently under the State List.
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Order: Mandates filing of a First Information Report(FIR) within six hours of any violence against healthcare workers.
- National Medical Commission (NMC) Directives: Requires medical colleges to develop policies for safe work environments and timely reporting of incidents.
- State Responsibilities: Health and law and order are primarily State subjects, with the Union government lacking centralised data on attacks on medical professionals.
- Central Government Response for Demands: The Health Ministry has stated that the Kolkata incident is covered under existing legal provisions and that a Central Protection Act is unnecessary, as 26 States and Union Territories already have laws protecting healthcare workers.
- These State laws define violence against healthcare personnel as cognisable and non-bailable, encompassing doctors, nurses, and paramedical staff.
What do the Crime Statistics Reveal About Women's Safety in India?
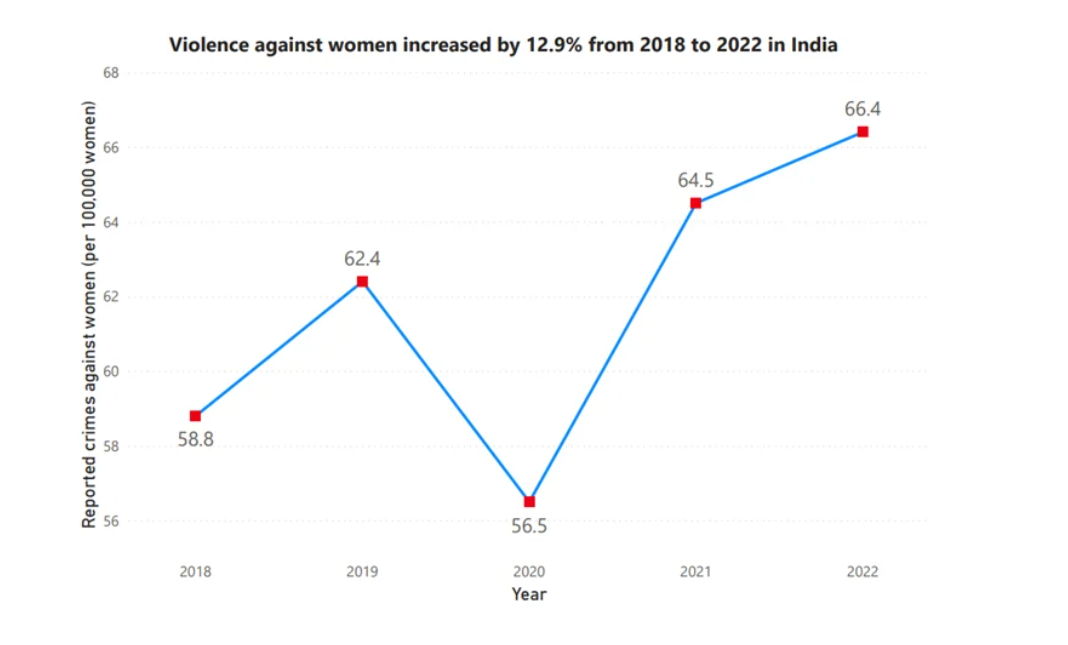
- Rising Crime Rates: The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported 445,256 cases of crime against women in 2022.
- From 2018 to 2022, reported crimes against women rose by 12.9%, reflecting both increased incidents and improved reporting.
- The Women and Men in India 2023 report shows a rise from 359,849 cases in 2017 to over 445,000 in 2022, averaging 1,220 cases daily, averaging 51 First Information Report (FIRs) per hour.
- The National Family Health Survey-5 found that nearly one-third of women aged 15-49 in India have experienced some form of violence.
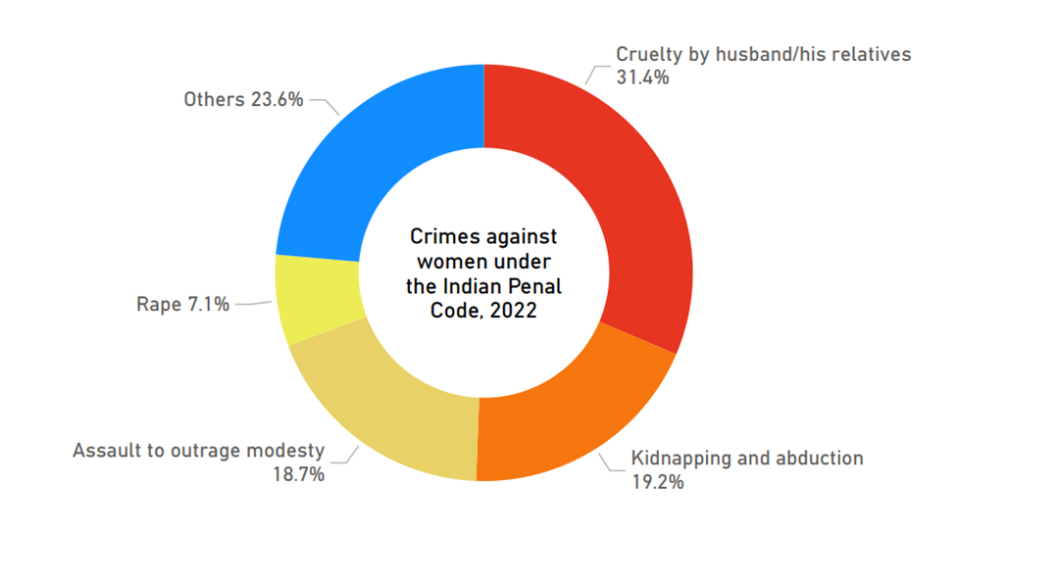
- Types of Crimes: The most common crimes include cruelty by husbands or in-laws (31.4%), kidnapping and abduction (19.2%), assault to outrage modesty (18.7%), and rape (7.1%).
- These figures underscore the persistent threats women face, even within their homes.
- Persistently High Rape Cases: The number of reported rapes remains alarmingly high, with annual reports consistently exceeding 30,000 cases since 2012, except for a decline during the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020.
- Attacks peaked at nearly 39,000 in 2016. By 2018, one woman was reporting a rape every 15 minutes across the country, highlighting the alarming frequency of these crimes.
- In 2022, over 31,000 rape cases were reported, reflecting the ongoing severity of the issue.
- Despite tougher laws, conviction rates for rape have remained low, fluctuating between 27%-28% from 2018 to 2022.
- Impact of the Pandemic: The Covid-19 pandemic exacerbated violence against women, with the crime rate jumping from 56.5 per 100,000 women in 2020 to 64.5 in 2021. Factors such as economic strain, social isolation, and reverse migration contributed to this surge.
- Workplace Harassment: Despite the enactment of the Protection of Women from Sexual Harassment Act, 2013 (POSH Act), sexual harassment in the workplace remains a concern, with cases increasing slightly from 402 in 2018 to 422 in 2022.
- However, these numbers are likely underreported due to societal biases and fear of repercussions.
- Index on Women's Safety: According to the Georgetown Institute 2023 Women Peace and Security Index, India scored 0.595 out of 1 point, placing it in rank 128 among 177 countries in terms of women's inclusion, justice, and security.
- The index also states that India is among the top 10 worst countries for political violence targeting women in 2022.
What are India's Initiatives Related Women Safety?
- Legislations:
- International Conventions: India ratified key international conventions, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) in 1993.
- India also endorsed the Mexico Plan of Action (1975) aimed at full gender equality and ending gender discrimination and the UN General Assembly Session on Gender Equality and Development and Peace for the 21st century.
- The Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956: Prohibits commercial sex work and trafficking of persons for prostitution.
- Indecent Representation of Women Act, 1986: Prohibits indecent representation of women in advertisements and publications.
- National Policy for the Empowerment of Women, 2001: Aims for women's advancement and empowerment, addressing violence against women and providing mechanisms for prevention, assistance, and action.
- Eleventh Five-Year Plan (2007-2012): Acknowledges violence against women (VAW) as a major issue, focusing on domestic violence and rape.
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005: Provides support for women victims of domestic violence, including shelter and medical facilities, with mandatory Protection Officers.
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) (PoSH) Act, 2013: The POSH Act addresses sexual harassment faced by women in the workplace, aiming to ensure a safe work environment.
- It defines sexual harassment to include unwelcome physical contact, sexual advances, demands for sexual favours, sexually coloured remarks, and showing pornography.
- The Act is based on the Vishakha guidelines established by the Supreme Court in the case of Vishakha & Others v. State of Rajasthan, 1997 which addressed workplace harassment.
- It draws from the Indian Constitution’s Article 15 and international norms like CEDAW.
- Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2013: Enacted for effective legal deterrence against sexual offences.
- Further, the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2018 was enacted to prescribe even more stringent penal provisions including the death penalty for the rape of a girl below the age of 12 years.
- Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM): Recommends incorporating gender considerations in urban development to enhance safety for women.
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012: Protects children from sexual offences, providing a legal framework for their protection and ensuring strict penalties for offenders.
- International Conventions: India ratified key international conventions, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) in 1993.
- Strategies and Measures:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme: Focuses on preventing gender-biased sex selection and ensuring the survival, protection, and education of the girl child.
- Ujjawala Scheme: Aims at preventing trafficking, rescuing and rehabilitating victims of trafficking and commercial sexual exploitation.
- NIRBHAYA Fund: Aims at supporting initiatives for the safety and security of women, including setting up emergency response systems and improving public infrastructure.
- Ministry of Women and Child Development Initiatives: Administers schemes like Swadhar Greh Scheme, provides short stay homes for women in difficult circumstances, and conducts awareness programs.
- Women Safety in Trains: Introduction of the 182 Security helpline, CCTV cameras in ladies' compartments, and the 'R-Mitra' mobile app for emergencies.
- Safety and Security for Women Tourists: Measures include the 'Incredible India Help Line,' Code of Conduct for Safe Tourism, and directives for state governments to ensure a secure environment for tourists.
- Safety of Women in Metro: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) has dedicated women-only coaches, reserved seats, and dedicated Central Industrial Security Force staff for safety.
- Scheme for Universalisation of Women Helpline: Provides 24-hour emergency and non-emergency response through a publicized helpline.
- Mobile Apps:
- Suraksha: Designed to provide women with a quick and easy way to send distress signals and their location to the police in case of an emergency.
- Amrita Personal Safety System (APSS): Wearable device for communication with family and police.
- VithU: Emergency app that sends alerts to contacts.
Why are Laws and Regulations Falling Short for Women Safety?
- Implementation Gaps: Strict laws enacted after the 2012 Nirbhaya case, like the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2013, enforcement remains inconsistent across different regions and police jurisdictions.
- Implementation of regulations, like establishing Internal Complaints Committees (ICC) in organizations, remains inadequate.
- Additionally, in 2018 the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) requires listed companies to report cases of sexual harassment annually, but data remains inconsistent and scattered.
- Systemic Issues: Corruption within the legal and law enforcement systems can undermine efforts to address crimes against women. Bribery and misconduct can result in cases being mishandled or dismissed.
- Many incidents of violence are not reported due to fear of retaliation, lack of trust in the system, or perceived inefficacy of the legal process.
- Cultural and Social Norms: Deeply ingrained societal attitudes and norms can undermine legal protections. In some communities, violence against women may be normalised or not taken seriously.
- Cultural attitudes and victim-blaming can discourage women from reporting crimes or seeking help, fearing stigma and societal judgement.
- Legal Challenges: Victims often face a high burden of proof, which can lead to low conviction rates. The requirement for substantial evidence and the legal complexity of cases can deter victims from pursuing justice.
- The judicial process can be cumbersome, leading to prolonged trials and delayed justice for victims. This can also discourage survivors from reporting crimes.
- Economic Dependence: Economic factors can also play a significant role. Women who are financially dependent on their abusers may find it difficult to leave abusive relationships, even if legal protections are in place.
- Resistance to Change: Resistance to reform within institutions and among policymakers can delay or obstruct efforts to improve laws and regulations.
- Legal frameworks may not evolve quickly enough to address emerging forms of violence or changes in societal attitudes.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: There is often limited awareness among women about their legal rights and available support services. This lack of knowledge can prevent them from accessing justice and support.
International Approaches in Promoting Women's Safety
- Key International Initiatives:
- International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women: The United Nations observes 25th November as the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women every year.
- United Nations Women Safe Cities and Safe Public Spaces for Women and Girls: Aimed at creating safe and inclusive public spaces for women and girls. It recognizes that public spaces are essential for women's participation in society, but they can also be places of fear and harassment.
- Focuses on integrating gender perspectives into safety strategies, developing tools to combat violence against women, and promoting women's participation in urban planning.
- Gender Inclusive Cities Programme: It is funded by the UN Trust Fund in Support of Actions to Eliminate Violence Against Women.
- This initiative aims to improve women's safety in cities like Dar es Salaam, Delhi, Rosario, and Petrozavodsk by promoting equal access to public spaces.
- UN Development Fund for Women (UNIFEM): It provides financial and technical assistance to promote gender equality and women's empowerment.
- National Approaches:
- United Kingdom: The London Authority’s strategy tackles violence against women and girls by boosting Safer Transport Teams, running awareness campaigns, and enhancing enforcement.
- Latin America: Cities like Bogota have developed safety strategies, including women-only subway cars and police stations.
Way Forward
- Nationwide Protection Law: Advocate for a Central Protection Act that mirrors the UK's zero-tolerance policy (protection from violence and intimidation for assaults).
- This legislation should provide uniform protection for all working professionals, ensuring consistent and comprehensive safeguards across the country.
- Strengthen the monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with existing laws such as the PoSH Act, 2013. Regular audits and reports should be mandated to track effectiveness and compliance.
- Fast-Track Courts: Establish fast-track courts and enhance punishment for grave cases like rape, as recommended by Justice Verma Committee. Increase women's representation in the judiciary.
- Local Security Measures: Implementing specialised police units like SHE Teams to address and prevent violence against women.
- SHE Teams is a division of Telangana Police for enhanced safety and security of women. The She Teams have successfully provided security and support to women, helping victims of sexual harassment for offences ranging from online stalking to physical harassment and violence.
- Safe City Designs: Integrating safety features into urban planning, such as improved street lighting and secure public spaces.
- Support Systems: Strengthen support systems for victims, including counselling services and legal aid. Ensure victims have access to resources without additional barriers.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch nationwide campaigns to raise awareness about women's rights, workplace safety, and available legal recourse using media, educational institutions, and community organizations.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Despite existing legal provisions, crimes against women in India persist. Critically evaluate the reasons for the high rates of violence and suggest comprehensive reforms to address these issues. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)
Biodiversity & Environment
Climate Change Impact on Panama Canal
For Prelims: Panama Canal, Lake Gatun, GDP, Isthmus of Panama, Tectonic Plates, Evaporation, Humidity, Precipitation, Algal Bloom, Ocean Currents, Mangroves, Drip Irrigation.
For Mains: Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Mitigation Strategies.
Why in News?
The Panama Canal, a critical global shipping lane, is facing significant challenges due to prolonged drought conditions exacerbated by climate change.
- This situation has led to reduced water levels in Lake Gatun, prompting discussions about long-term solutions to sustain the Panama canal’s operations.
What is the Impact of Climate Change on the Panama Canal?
- Drought and Reduced Passage of Ships: The Panama Canal is experiencing a prolonged drought that began in early 2023.
- Rainfall in October 2023 was 43% below average, making it the driest October since the 1950s.
- Traffic through the canal dropped to as low as 22 ships per day in December 2023, down from the usual 36 to 38 ships, due to low water levels in Lake Gatun.
- Restriction on Size of Ships: Lower water levels restrict the size of ships that can pass through the canal, as larger, heavier vessels are at higher risk of running aground in shallower waters.
- Large ships also require more lake water to lift them in the locks.
- Effect on Global Trade: The Panama Canal accounts for 5% of global shipping, so disruptions here affect the worldwide supply chain, resulting in delayed shipments, more fuel usage, and GDP losses.
- Ships are forced to take the long way around i.e., travelling down to the southern points of South America.
What are Key Facts about the Panama Canal?
- About Panama Canal:
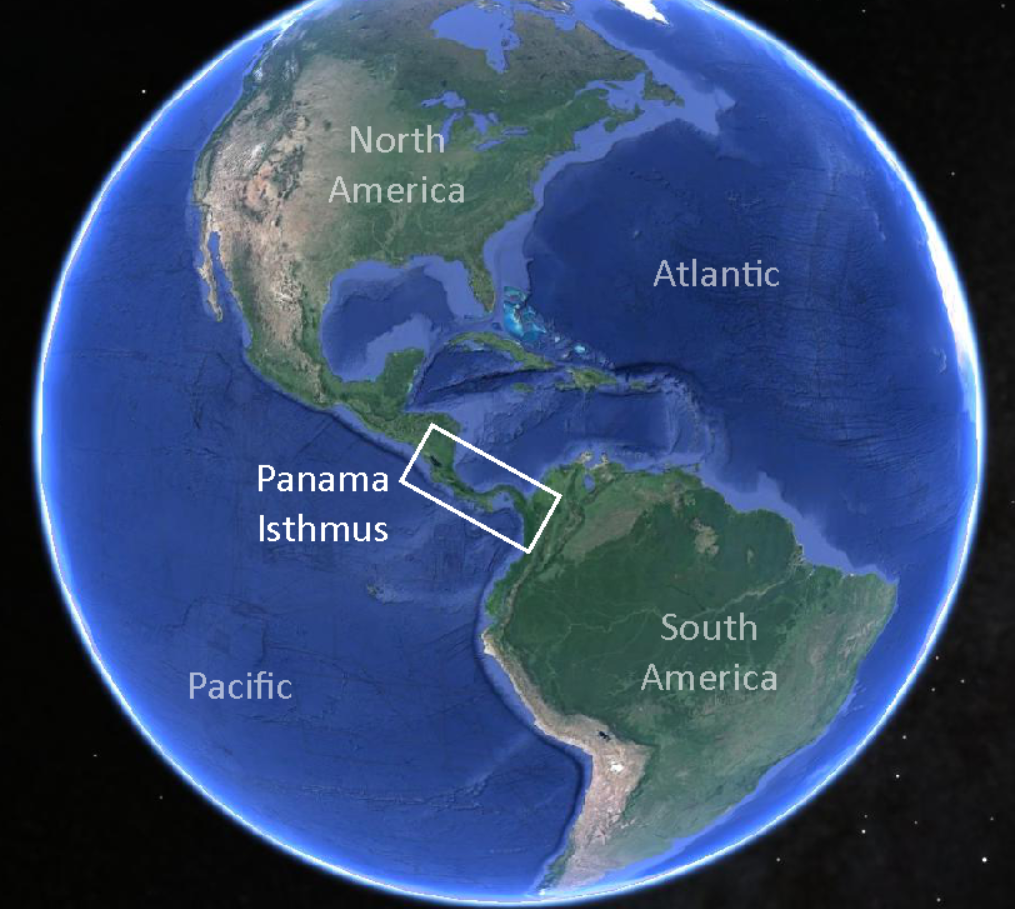
- It is an artificial 82 kilometers waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean.
- It cuts across the Isthmus of Panama, and is a conduit for maritime trade.
- It saves approximately 12,600 km in a trip between New York and San Francisco.
- The first ship passed through the Panama Canal on 15th August 1914.
- It is an artificial 82 kilometers waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean.
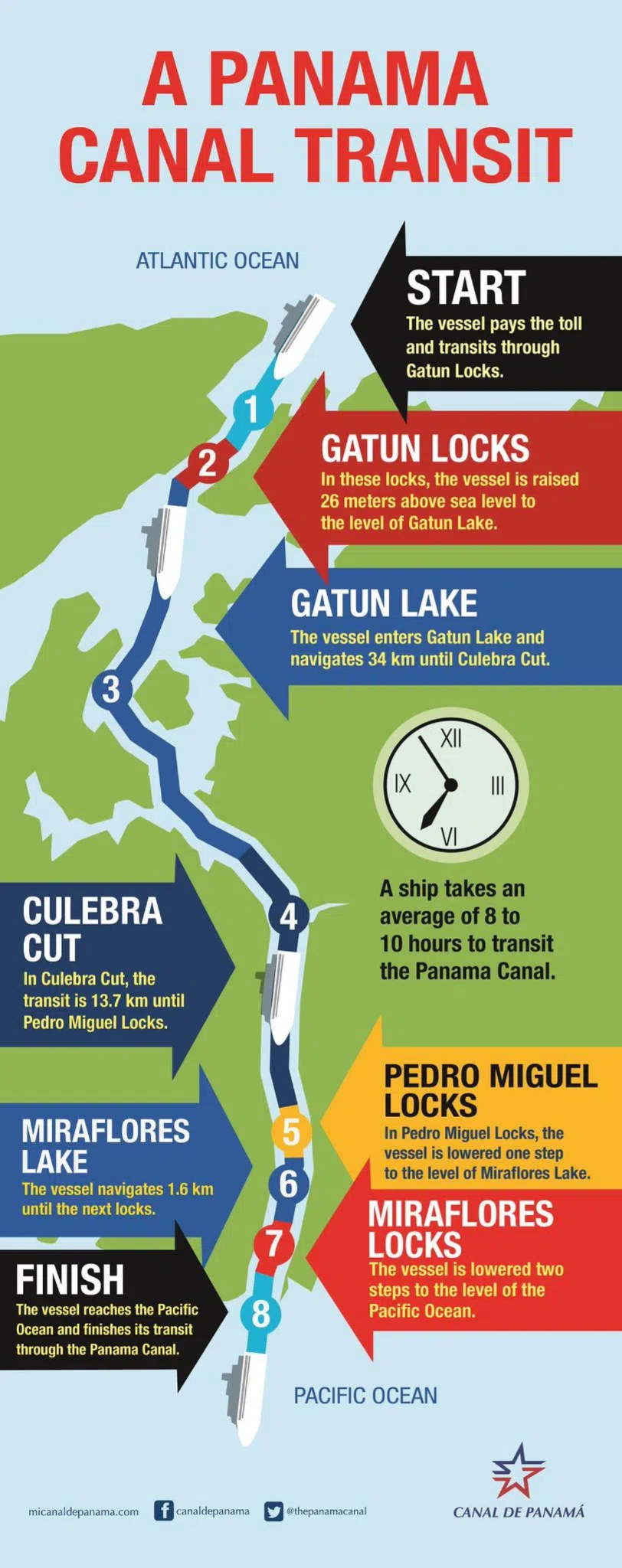
- Functioning of Panama Canal:
- It is a sophisticated, highly-engineered system which uses a system of locks and elevators to take ships from one end to the other.
- This is needed because the two oceans that the Panama Canal connects do not lie at the same elevation, with the Pacific slightly higher than the Atlantic.
- For a ship entering the canal through the Atlantic, it needs to gain elevation during its journey to the Pacific. This is achieved using a lock system that lifts and drops vessels to the required sea level at either end of the canal.
- Locks are either flooded (to gain elevation) or drained (to lose elevation), and act as water elevators.
- In total, the system comprises 12 locks in total which are serviced using artificial lakes and channels.
- It is a sophisticated, highly-engineered system which uses a system of locks and elevators to take ships from one end to the other.
Isthmus of Panama
- An isthmus is a narrow strip of land that connects two larger landmasses and separates two bodies of water.
- They are natural sites for ports and canals linking terrestrial and aquatic trade routes.
- The Isthmus of Panama links the continents of North and South America, and separates the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- It was formed when the Caribbean tectonic plate got pushed between the North and South American Plates. The resultant tectonic activity raised the seafloor.
Note:
- A strait is a narrow waterway between two pieces of land that connects two large bodies of water e.g., Strait of Gibraltar links the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Straits are important transportation routes since they allow ships to pass from one body of water to another.
What are other Important Canals Around the World?
- Suez Canal: The canal connects the Gulf of Suez and the Mediterranean Sea, separating Asia from Africa. It extends between Port Said in the north and Suez in the south.
- It separates Asia from the African continent and provides the shortest maritime route between Europe and the regions around the Indian Ocean and the Western Pacific Ocean.
- Kiel Canal: It connects the Baltic Sea with the North Sea. Opened in 1895, the 98 km-long Kiel Canal helps vessels bypass the longer route that goes via Denmark (peninsula of Jutland).
- Corinth Canal: The Corinth Canal in Greece is considered the world's narrowest canal. It connects the Corinthian Gulf of the Ionian Sea and the Saronic Gulf of the Aegean Sea.
- Kra Isthmus Canal (Thai Canal): It is a proposed canal that would connect the Andaman Sea to the Gulf of Thailand across the Kra Isthmus in southern Thailand.
- The canal would provide a shortcut to routes between India and China, avoiding the Strait of Malacca.
- Great Lakes Seaway Navigation System: In the United States, the five Great Lakes, their connecting channels, and the St. Lawrence River forms one of the longest navigation systems in the world. The waterway flows from west to east and drains into the Atlantic Ocean via the St. Lawrence River.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Discuss the impact of Climate Change on water channels? How canals are inevitable for the smooth flow of global trade? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Between India and East Asia, the navigation-time and distance can be greatly reduced by which of the following? (2011)
- Deepening the Malacca straits between Malaysia and Indonesia.
- Opening a new canal across the Kra isthmus between the Gulf of Siam and Andaman Sea.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What is water stress? How and why does it differ regionally in India? (2019)
Q.“The ideal solution of depleting groundwater resources in India is the water harvesting system”. How can it be made effective in urban areas? (2018)
Q. In what way micro-watershed development projects help in water conservation in drought-prone and semi-arid regions of India? (2014)
Social Issues
Rising Cancer Concerns
For Prelims: Cancer, Global Burden of Cancer, World Health Organisation (WHO)
For Mains: Issues relating to the development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Rising Cases of Different forms of Cancer in India and its impact on the Health Sector.
Why in News?
A recent study published in the journal Cancer predicts that global cancer cases in men will increase by 84.3% and the number of cancer deaths will increase by 93.2% by 2050 compared to the 2022 estimate.
- This alarming trend underscores a significant public health challenge that requires urgent attention.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Projected Increase in Cancer Cases and Deaths: The study predicts that cancer cases among men will rise to 19 million by 2050 while cancer deaths are expected to reach 10.5 million.
- Projection of Specific Cancer Types: From 2022 to 2050, mesothelioma (the most common kind of lung cancer) cases are expected to increase by 105.5%, prostate cancer deaths by 136.4%, while testicular cancer will see the smallest rises, with incidents up by 22.7% and deaths by 40%.
- Dominance of Lung Cancer: Lung cancer is expected to remain the leading type of cancer in both incidence and mortality, with a projected increase of over 87% compared to 2022.
- Disparities Across Age and Regions: The report notes significant disparities in cancer rates by age and region, with about 10.3 million cases and 5.4 million deaths among men globally in 2022.
- Nearly two-thirds of these cases were in adults aged 65 and older.
- Impact of Human Development Index (HDI): The report predicts that cancer cases will increase by 50.2% in very high HDI countries and by 138.6% in low HDI countries from 2022 to 2050.
- Cancer deaths are expected to rise by 63.9% in very high HDI countries and 141.6% in low HDI countries.
- High Mortality-to-Incidence Ratios: The report highlights high mortality-to-incidence ratios, with older men at 61% and low HDI countries at 74%. Rare cancers like pancreatic cancer have an even higher ratio of 91%, indicating poor survival outcomes.
- The Mortality-to-Incidence Ratio (MIR) is a measure that compares the number of cancer deaths (mortality) to the number of new cancer cases (incidence) over a specified period.
What is the State of Cancer Prevalence in India?
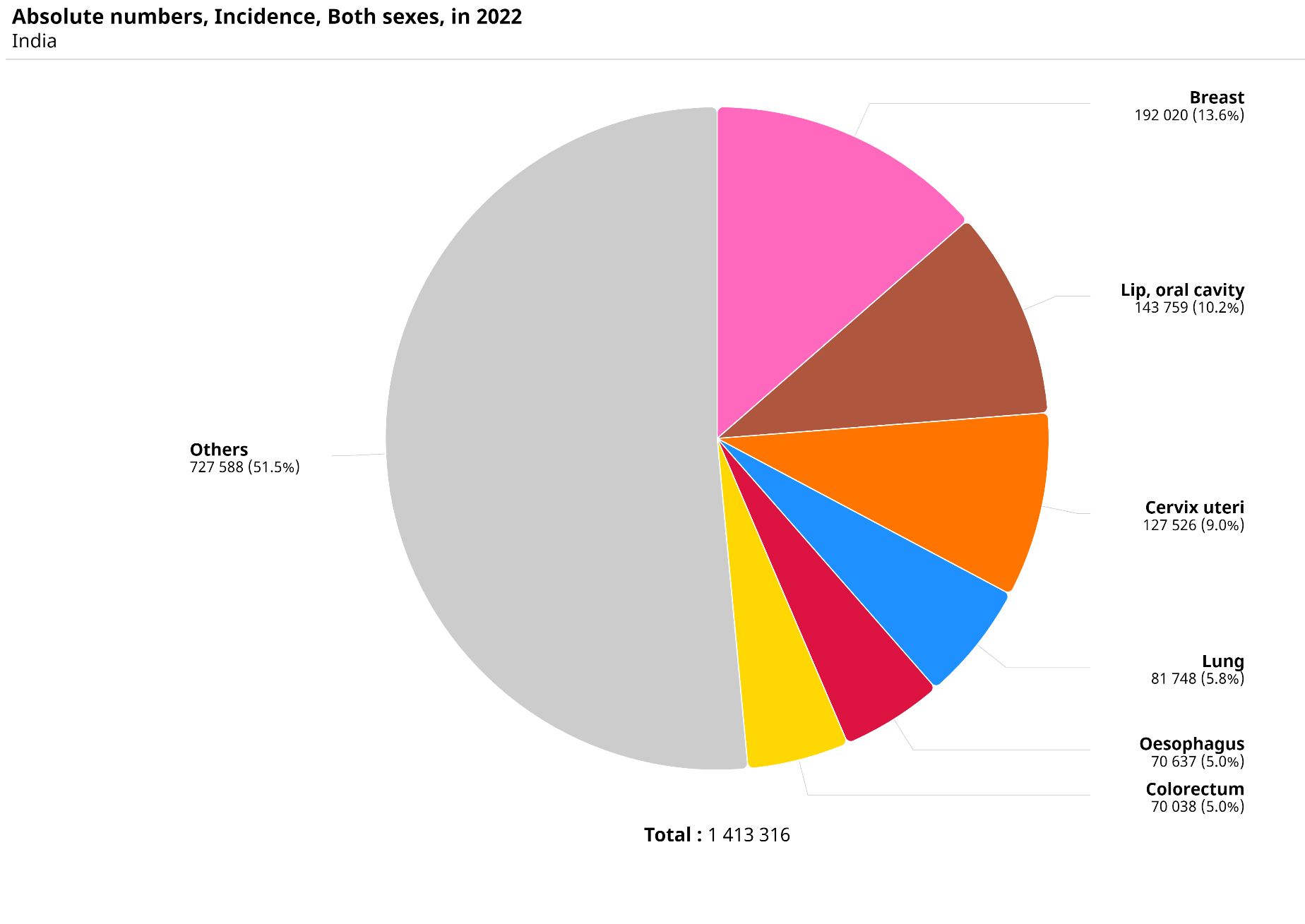
- India reported 1,413,316 new cases in 2022 with a higher proportion of female patients (691,178 men and 722,138 women).
- Breast cancer had the highest proportion in the country, with 192,020 new cases, accounting for 13.6% of all patients and over 26% in women.
- In India, breast cancer was followed by lip and oral cavity (143,759 new cases, 10.2%), cervix and uterine, lung, and esophageal cancers.
- A recent study by WHO assessing the cancer burden in Asia, published in The Lancet Regional Health, found that India alone accounted for 32.9% of global deaths and 28.1% of new cases of lip and oral cavity cancer in 2019.
- This was on account of the widespread consumption of smokeless tobacco (SMT) such as khaini, gutkha, betel quid and paan masala in South Asian countries like India, Bangladesh and Nepal.
- Worldwide, SMT is responsible for 50% of the oral cancer burden.
- As per the Lancet Global Health 2023, India accounted for 23% of deaths that occurred due to cervical cancer globally.
- In India, cervical cancer’s five-year survival rate was 51.7% which is lower compared to high-income countries such as the United States.
Cancer
- It is a complex and broad term used to describe a group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These abnormal cells, known as cancer cells, have the ability to invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, allowing for the normal functioning of tissues and organs.
- However, in the case of cancer, certain genetic mutations or abnormalities disrupt this normal cell cycle, causing cells to divide and grow uncontrollably.
What are the Government Initiatives for Cancer Control In India?
- In the Union Budget 2024-25, the government exempted 3 cancer medicines- Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, and Durvalumab from customs duty.
- The Interim Budget 2024-25 encouraged the vaccination of girls aged 9-14 years to prevent cervical cancer.
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke
- National Cancer Grid
- National Cancer Awareness Day
- HPV Vaccine
- Ayushman Bharat- Health & Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs)
What are the Key Highlights of the NITI Aayog Report on Early Cancer Detection in India?
- Cancer Screening Gap: According to NITI Ayog’s Report, there is a significant shortfall in cancer screening at Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs).
- Less than 10% of these centres had conducted even a single round of screening for non-communicable diseases, including cancer.
- Screening Practices:
- Breast Cancer: Screening is performed via self-examination.
- Cervical Cancer: Screening has not been fully implemented.
- Oral Cancer: Screening is conducted on a case-by-case basis, depending on visible symptoms.
- Infrastructure and Resources: HWCs lacked basic infrastructure, devices, medicines, and diagnostic tests as per operational guidelines.
- Staff Training and Awareness: There is inadequate training and monitoring of Auxiliary Nurses and Midwives (ANMs) on screening methods.
- Additionally, HWC staff had limited awareness of the need for annual screening for hypertension and diabetes.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of early detection and screening in cancer control strategies and evaluate the effectiveness of India's current cancer control policies in addressing the growing burden of the disease. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) Immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) Construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to the treatment of cancerous tumours, a tool called cyberknife has been making the news. In this context, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2010)
(a) It is a robotic image guided system
(b) It delivers an extremely precise dose of radiation
(c) It has the capability of achieving sub-millimetre accuracy
(d) It can map the spread of tumour in the body
Ans: (d)
Q. ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why? (2019)
- It is used in developing gene-silencing therapies.
- It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer.
- It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies.
- It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q.1 What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q.2 What do you understand by nanotechnology and how is it helping in the health sector? (2020)
Facts for UPSC Mains
Key Reforms Needed for India's Economic Growth
Why in News?
India's path to becoming a developed economy was highlighted by the Deputy Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), who emphasised the need for reforms in domestic resource mobilisation, infrastructure investment, and increasing women’s workforce participation.
What Key Reforms are Needed for India's Economic Growth?
- Simplification of GST: India can increase revenues-to-Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through Goods and Services Tax (GST) by simplifying the tax structure, having fewer tax rates, and broadening the tax base by reducing exceptions, which could potentially raise an additional 1% point of GDP in revenue.
- The revenues-to-GDP ratio is a way to measure a country's tax revenue relative to the size of its economy, as measured by GDP.
- It can provide insight into a country's tax policy, potential taxation, and international comparisons between tax revenues.
- Countries would need to rely on domestic resource mobilisation, as money from international institutions or multilateral development banks will be a fraction of the spending needed.
- In India's case, increasing fiscal space should occur through raising revenues-to-GDP rather than reducing overall spending.
- The revenues-to-GDP ratio is a way to measure a country's tax revenue relative to the size of its economy, as measured by GDP.
- Broaden Personal Income Tax Base: Expanding the personal income tax base, reducing loopholes in tax exemptions, and improving property tax collection through better technology are crucial for ensuring sufficient progressivity and enhancing revenue generation in India's taxation system.
- Additionally, effective collection of capital gains and property taxes is essential for bolstering fiscal resources.
- Targeted Subsidy Reforms: India can also save money by targeting benefits and subsidies more effectively, such as through tailored fertiliser subsidies based on farm size, as being done as a pilot project in Karnataka.
- Ensuring subsidies reach the right beneficiaries can significantly impact revenue savings.
- Skilled Workforce and Education: Enhancing the quality of education and developing a more skilled workforce are essential for India’s economic advancement. This includes improving formal education and skill acquisition to ensure a competitive workforce, especially in comparison to G20 peers.
- Women’s Labour Force Participation: Women's participation needs to increase from the current 35% to achieve high-income status.
- This requires not only creating more opportunities for women but also ensuring their safety in the workplace.
- Job Creation and Employment Policies: India needs to create between 10 to 24 million jobs annually over the next decade. This requires substantial efforts in job creation across diverse sectors.
- Focus on inclusive growth that spans multiple sectors, not just a few industries, to ensure broad-based employment opportunities.
- Land and Labour Reforms: Land and labour reforms are also essential for transitioning to a high-income country.
- Greater flexibility in labour markets is needed. The 2019 labour codes offer a balance between flexibility and worker protection, but their effective implementation is vital.
- Ease of Doing Business: Improving the regulatory environment, enhancing the efficiency of the judicial system, and simplifying business procedures are essential to fostering a conducive environment for economic activity.
- Openness to Trade and Lower Tariffs: India must reduce its average tariff rates and become more open to international trade.
- Lowering trade barriers will enable India to integrate better into global supply chains and enhance its position on the world stage.
- Investment in Infrastructure: While India has made significant progress in public and digital infrastructure, there remains a considerable gap. Continued investment in this area is necessary for sustaining economic growth.
Current Economic Status of India
- India aims to become a "developed nation" by 2047 under the banner of "Viksit Bharat 2047."
- India has surpassed the UK to become the fifth-largest economy globally. Analysts from Morgan Stanley project that India could overtake Japan and Germany to reach the third spot by 2027.
- India has grown well, being the fastest-growing major economy at 7%, but the challenge is to maintain and further increase the momentum to raise per capita incomes and become an advanced economy.
- India's digital governance reforms have enhanced financial inclusion, streamlined public service delivery, and reduced corruption to a significant extent. The digital payments ecosystem has expanded significantly, allowing millions to transact with ease.
- Current Economic Indicators:
- Nominal GDP: USD 3.54 trillion for FY24, reflecting strong growth.
- Real GDP Growth: Estimated at 8.2% for FY24.
- World Bank Classifications by Income Level: Until 2006, the World Bank categorised India as a low-income nation. In 2007, India transitioned to the lower-middle income group and has remained in that classification since then.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. What are the critical reforms needed for India to transition from a lower-middle-income to a developed economy? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Normally countries shift from agriculture to industry and then later to services, but India shifted directly from agriculture to services. What are the reasons for the huge growth of services vis-a-vis the industry in the country? Can India become a developed country without a strong industrial base? (2014)
Important Facts For Prelims
Hayflick limit
Why in News?
The recent death of Leonard Hayflick, a prominent biomedical researcher has brought renewed attention to his groundbreaking discovery, known as the Hayflick limit.
- This discovery fundamentally altered the understanding of ageing, challenging the previous belief that ageing was solely influenced by external factors such as disease, and environmental conditions.
What is the Hayflick Limit?
- About: Leonard Hayflick, in the 1960s discovered that somatic (non-reproductive) cells can only divide approximately 40-60 times before they stop dividing, a phenomenon known as cellular senescence (those that have stopped dividing).
- This cessation (ceasing) of cell division, which leads to the accumulation of senescent cells, is posited to be a key factor in ageing. As more cells stop dividing, the body begins to age and experience decline.
- The Hayflick limit suggests that there is an inherent cellular clock in organisms, including humans, determining the maximum lifespan.
- For humans, this limit is estimated to be around 125 years, beyond which no external factors or genetic modifications can extend life.
- Comparison of Species: Hayflick and other scientists documented the Hayflick limits in various animals.
- For example, cells of Galapagos turtles, which can live for over 200 years, divide approximately 110 times before reaching senescence.
- In contrast, laboratory mice cells become senescent after just 15 divisions, correlating with their much shorter lifespans.
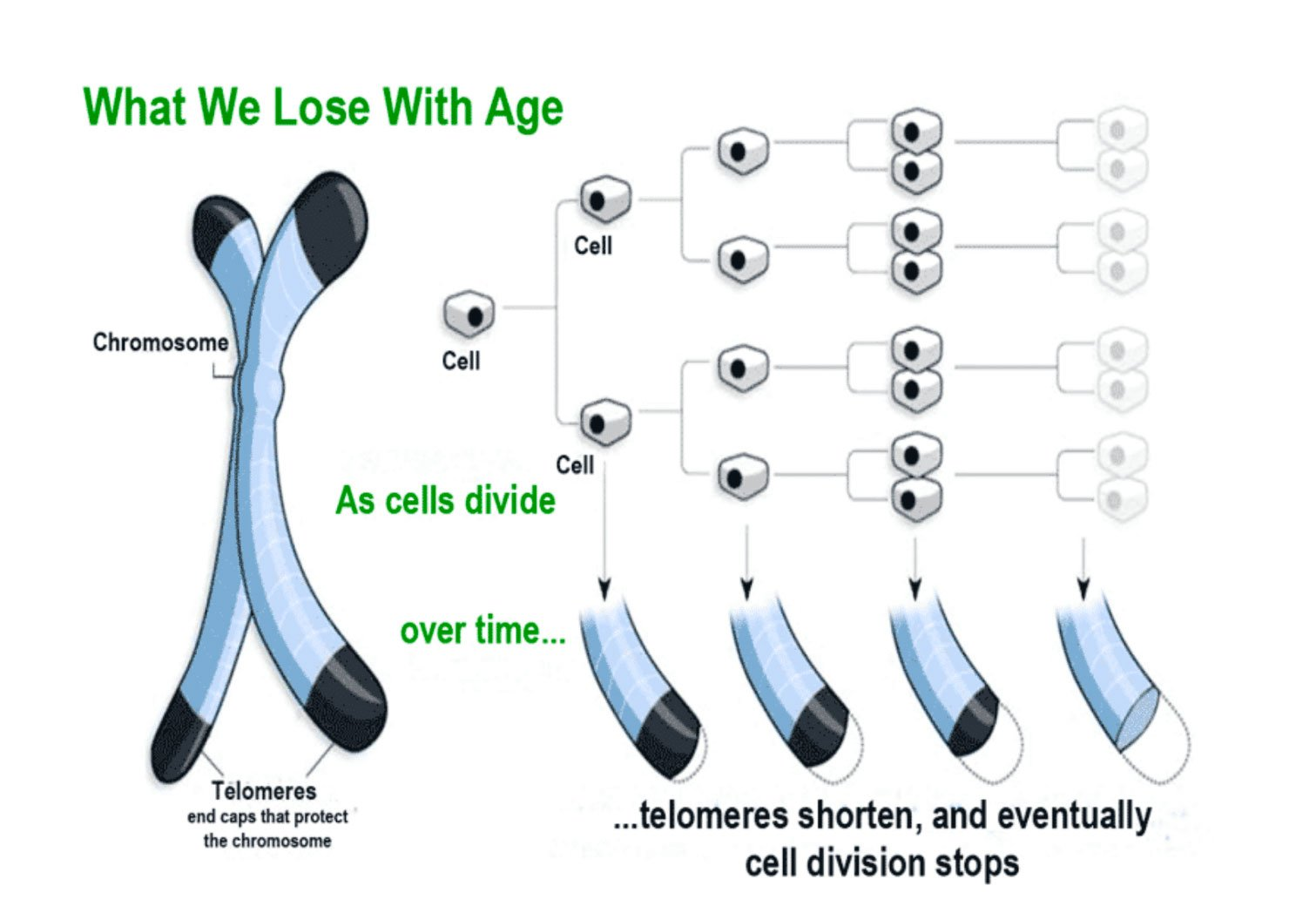
- Further Studies: In the 1970s, researchers discovered telomeres, which are repetitive Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) sequences at the end of chromosomes that protect them during cell division.
-
With each cell division, telomeres become shorter until they reach a critical length, signalling the end of cell division and contributing to ageing.
- While telomere shortening is linked to ageing, the exact correlation between telomere length and lifespan is not straightforward. For instance, Mice have longer telomeres than humans but live significantly shorter lives.
- Some researchers argue that telomere loss and the Hayflick limit are not direct causes of ageing but symptoms of the ageing process.
-
Note: In the 1980s, scientists discovered a protein called telomerase that can produce new telomeres. This protein is active in cancer cells, allowing them to bypass the Hayflick limit and continue dividing indefinitely. This is why, as Hayflick himself said, cancer cells are not subject to the Hayflick Limit.
- However, telomerase is primarily active in cancer cells, complicating its potential use in healthy cells.
- Although scientists have synthesised telomerase and some in vitro studies have indicated they may slow down telomere loss in normal human cells, practical application remains distant.
What is Cell Division?
- About: Cell division is a fundamental biological process where a parent cell divides to form two or more daughter cells. This process is critical for growth, repair, and reproduction in living organisms.
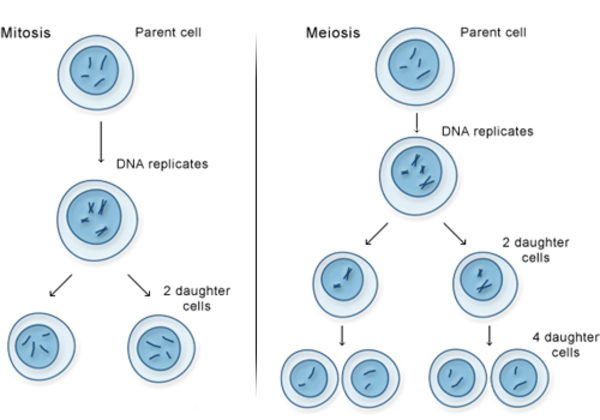
- Cell division in humans occurs through two main processes: mitosis and meiosis.
- Mitosis: This is the process through which somatic (body) cells divide.
- Mitosis results in two daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. It is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
- Mitosis is a highly regulated process that ensures genetic consistency in somatic cells.
- Meiosis: This type of cell division is specific to the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells).
- Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four non-identical daughter cells, each with 23 chromosomes.
- This reduction is essential for maintaining the species' chromosome number across generations.
- Meiosis also introduces genetic variation through processes like crossing over and independent assortment (different genes independently separate from one another during the development of reproductive cells).
- Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four non-identical daughter cells, each with 23 chromosomes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body?(2022)
(a) They protect the environmental allergens. body
(b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
(c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
(d) They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Ans: (d)
Important Facts For Prelims
National Film Awards 2022
Why in News?
Recently, the winners of the 70th National Film Awards for 2022 were announced by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
What were the Key Awards Presented at the 70th National Film Awards?
- Best Feature Film: Aattam (The Play), directed by Anand Ekarshi.
- Best Non-Feature Film: Ayena (Mirror), directed by Siddhant Sarin.
- Best Popular Film Providing Wholesome Entertainment: Kantara.
- Best Actor in a Leading Role: Rishab Shetty for Kantara.
- Best Actress in a Leading Role: Nithya Menen for Thiruchitrambalam.
- Best Supporting Actor: Pavan Raj Malhotra.
- Best Supporting Actress: Neena Gupta.
- Best Film in AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects Gaming & Comic): BRAHMASTRA-PART 1: SHIVA.
- Best Book on Cinema: “Kishore Kumar: The Ultimate Biography”, authored by Anirudha Bhattacharjee & Parthiv Dhar.
What are the National Film Awards?
- About: Established in 1954, it has been administered, along with the International Film Festival of India and the Indian Panorama, by the Indian government's Directorate of Film Festivals since 1973.
- Winners receive a Medallion, a cash prize, and a certificate of merit.
- Six categories from Feature Films, and two each from Non-Feature Films and Best Writing on Cinema are eligible for the Swarna Kamal (Golden Lotus Award).
- The remaining categories are eligible for the Rajat Kamal (Silver Lotus Award).
- Categories:
- Feature Films: Encourages the production of films with aesthetic and technical excellence.
- Promotes understanding and appreciation of regional cultures and national unity.
- Swarna Kamal Award receiving 6 Categories under this:
- Best Feature Film, Best Direction, Best Children’s Film, Best Popular Film providing wholesome entertainment and Best Film in AVGC.
- Non-Feature Films: Aims to produce films of social relevance and technical quality.
- Swarna Kamal Award for Best non-feature film and Best Debut film of a Director.
- Contributes to the appreciation of diverse cultural representations.
- Best Writing on Cinema: Encourages study and critical appreciation of cinema as an art form.
- Swarna Kamal Award for Best Book on Cinema and Award for Best Film Critic.
- Promotes dissemination of information through books, articles, reviews, and studies.
- Feature Films: Encourages the production of films with aesthetic and technical excellence.
- Eligibility criteria: Films must be produced in India, with the director and makers being Indian nationals. Co-productions with foreign entities must meet specific conditions.
- Films should be certified by the Central Board of Film Certification between 1st January and 31st December each year.
- Over 100 films from across the country are entered in each category (Feature and Non-Feature).
- The juries, appointed by the Directorate of Film Festivals, have strict criteria for eligibility and are not influenced by the Government or Directorate.
What is Dadasaheb Phalke Award?
- About:
- It is part of the National Film Awards, a highly coveted collection of honours in the film industry.
- The Award is named after Dhundiraj Govind Phalke, the pioneering filmmaker who gave India its first film– ‘Raja Harishchandra’, in 1913.
- It is awarded for “its outstanding contribution to the growth and development of Indian cinema.
- It is part of the National Film Awards, a highly coveted collection of honours in the film industry.
- Overview:
- The award was instituted by the government in 1969 and consists of a ‘Swarna Kamal’, a cash prize of Rs 10 lakh, a certificate, a silk roll, and a shawl.
- The President of India presents the award.
- The first recipient of the award was Devika Rani Roerich in 1969.
- The award was instituted by the government in 1969 and consists of a ‘Swarna Kamal’, a cash prize of Rs 10 lakh, a certificate, a silk roll, and a shawl.
Read More: National Film Awards, Dadasaheb Phalke Award
Rapid Fire
Bank Strategies to Attract Depositors Amid Declining Growth
Amidst a slowdown in deposit growth and increased competition from capital markets, banks in India are introducing special schemes to attract depositors and meet credit demands.
- Major banks like State Bank of India (SBI) have reported a drop in deposits, with SBI's Current Account and Savings Account (CASA) deposits falling from Rs 19.14 lakh crore to Rs 19.41 lakh crore, and overall deposits decreasing from Rs 49.16 lakh crore to Rs 49.01 lakh crore.
- Credit growth rose by 15.1% while deposit growth declined to 10.6%, highlighting a significant gap.
- Customers are increasingly opting for capital markets over bank deposits for better returns, leading to a decline in traditional deposit growth.
- To counter declining deposits, banks like SBI and Bank of Baroda introduced special deposit schemes offering competitive interest rates (e.g., 7.25% for 444 days).
- These schemes are designed to attract depositors looking for higher returns in a low-interest environment.
- Banks are targeting specific segments like senior citizens and women, offering attractive rates and additional perks to mobilise deposits effectively.
- The Finance Minister stressed the importance of mobilizing small deposits rather than focusing solely on large sums.
Rapid Fire
New Parliamentary Committees Formed for 2024-25
The recent constitution of six new Parliamentary Committees by Lok Sabha Speaker marks a strategic move in overseeing government functions.
- These committees include the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) (overseeing government expenditure), Estimates Committee (examining government spending and ensuring efficiency), Public Undertakings Committee (focusing on the performance of public sector enterprises), and committees focused on the welfare of Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Scheduled Castes (SCs), and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
- The newly constituted committees have a tenure of one year and include members from both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha.
- Unlike the previous Lok Sabha, where committee formation often involved elections, the committees in the 18th Lok Sabha have been primarily formed through consensus.
- Parliamentary committees, originating from the British Parliament, in India derive their authority from the Indian Constitution under Article 105 (powers and privileges) and Article 118 (regulation of business).
- Parliamentary Committees in India are of two kinds: Standing committees and Ad hoc committees.
- Standing committees are permanent committees that are constituted by the Parliament to deal with specific areas of public policy or administration.
- Ad Hoc Committees are temporary Committees formed for specific tasks or to review particular bills. Dissolved after completing their objectives.
Rapid Fire
BHAVISHYA
Recently, to address delays, clerical errors, and financial loss in pension processing, the DOPPW (Department of Pension & Pensioners' Welfare) introduced 'Bhavishya,' a centralized pension processing software for all central government Ministries/Departments.
- "Bhavishya" became mandatory for all central ministries and at present 99 ministries/departments are on board.
- It ranked 3rd in NeSDA(National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment), 2021.
- Best Practices of Bhavishya:
- Automatic registration of retirees with pre-filled data, self-registration for stakeholders, and auto-calculation of retirement benefits.
- Enforces strict timelines for pension processing, ensuring transparency, accountability, and easy identification of delays.
- Provides real-time updates via email/SMS; integrated with PFMS (Public Financial Management System) for electronic PPOs, making the process paperless.
- Integrated with banks for post-retirement services; ePPOs (Pension Payment Orders) are stored in Digilocker for easy access.
- Issue of Pensioners' Identity cards through Bhavishya.
Read More: Integration of e-PPO with Digi Locker, Old Pension Scheme, National Pension System and Atal Pension Yojana, System for Pension Administration Raksha (SPARSH)
Rapid Fire
Catastrophe Bonds
Catastrophe bonds, which have delivered substantial returns for investors, are now under scrutiny due to concerns that their risk-reward dynamics might unfairly disadvantage issuers, particularly in the Caribbean.
- Catastrophe bonds or CAT bonds are financial instruments that pay high returns to investors in exchange for bearing the risk of significant disasters. These bonds are typically issued by insurers, or governments to obtain additional coverage for catastrophic events like hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods.
- Catastrophe bonds allow investors to receive periodic interest payments, but if a predefined catastrophic event occurs, the bond's principal is used to cover the issuer's losses.
- Payout conditions are based on triggers defined in the bond contract, which can be parametric (e.g. wind speed, seismic activity ) or indemnity (e.g. actual loss figures reported by insurers).
- Recently, in Jamaica Catastrophe bonds have delivered double-digit returns, averaging around 15%, while issuers face significantly increased costs.
- The bond issued by Jamaica was not triggered despite the island being declared a disaster area after Hurricane Beryl, raising questions about the bond's terms.
- Caribbean heads of government are seeking an examination of catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities to assess their fairness and market selection.
Read more: Catastrophe Bonds
Rapid Fire
RBI Issues Framework for SROs in Financial Markets
The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) issued a framework for recognition of self-regulatory organizations (SROs) in the financial markets to strengthen compliance culture and provide a consultative platform for policy making.
- The proposed SROs can play a vital role in developing industry standards and best practices and ensuring member adherence.
- Under the new framework SROs must be not-for-profit companies (registered under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013) with a minimum net worth of Rs 10 crore, shareholding must be diversified, with no single entity holding 10% or more of the paid-up share capital.
- SROs regulate their respective industries or sectors, often in collaboration with government regulators.
- The SRO will act as a bridge between its members and the regulator. It will ensure better compliance with regulatory guidelines, development of early warning signals, protection of stakeholder interests, and foster innovation.
Read more: Omnibus SRO Framework