Indian Economy
Rising Share of Personal Income Tax and Indirect Tax
- 06 May 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Income Tax, Direct Taxes, Indirect Taxes, GST.
For Mains: Reforms, Issues and Challenges in the Taxation system in India, Budget 2023.
Why in News?
Amidst ongoing political debates and controversies surrounding socio-economic policies, recent tax data released by the Ministry of Finance sheds light on significant trends in India's tax landscape.
- As per the report, the collection of personal income tax and indirect taxes have increased, while collections from corporate taxes have reduced.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Growth in Direct Tax Collection:
- India’s net direct tax collections grew 17.7% in 2023-24 to hit Rs.19.58 lakh crores.
- This can be attributed to a surge in personal income taxes whose share of the tax rose to 53.3% from 50.06% in the previous year.
- The data also show that revenues from personal income tax and securities transaction tax (STT) grew at almost double the pace compared to revenues from corporate taxes last year.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT) is a tax levied on the purchase and sale of securities such as stocks, derivatives, and equity-oriented mutual funds. It was introduced in India in 2004 as a part of the Finance Act, 2004.
- The purpose of STT is to collect revenue for the government and to discourage speculative trading by adding a small tax on each transaction.
- Direct Tax: A direct tax is a tax that an individual or organisation pays directly to the entity that imposed it. It is a “progressive tax” because those who earn less are taxed less and vice-versa.
- Types of Direct Taxes:
- Income Tax: It is based on an individual’s or organisation’s earnings.
- Property Tax: Property tax is assessed on real estate properties (land, buildings, etc.).
- Types of Direct Taxes:
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT) is a tax levied on the purchase and sale of securities such as stocks, derivatives, and equity-oriented mutual funds. It was introduced in India in 2004 as a part of the Finance Act, 2004.
- India’s net direct tax collections grew 17.7% in 2023-24 to hit Rs.19.58 lakh crores.
- Dip in Corporate Tax:
- Share of Corporate Taxes contribution to overall tax collection dipped to 46.5% from 49.6% in 2022-23.
- Corporate taxes refer to taxes imposed on the profits of corporations by governmental entities. These taxes are typically based on the net income of a corporation after accounting for various deductions and credits.
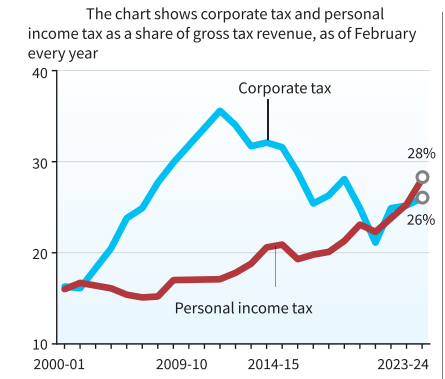
- The share of corporate tax has been on a decreasing trend, while that of personal income tax has been increasing.
- The sharp fall in corporate tax after FY19 can be attributed to the deep corporate tax cuts introduced by the ruling government in September 2019.
- As of February 2024, the gap between the two tax shares further increased, with income tax forming 28% of the gross tax- a new peak and corporate tax at 26%.
- Share of Corporate Taxes contribution to overall tax collection dipped to 46.5% from 49.6% in 2022-23.
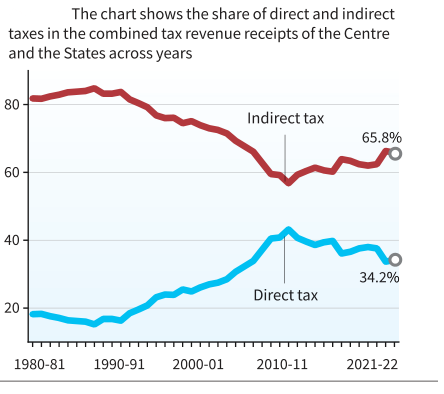
- Decrease in Share of Direct Taxes, and Increase in Share of Indirect Taxes:
- Indirect taxes, which include union excise duties and the Goods and Services Tax are considered “regressive” as all consumers, regardless of their income levels, pay the same amount.
- The share of Indirect taxes, which had been falling steadily since the 1980s, has increased from 2010-11 onwards.
- The increasing share of indirect taxes implies a heavier burden on lower-income individuals.
- On the other hand, the share of Direct taxes, which had been increasing till 2010-11, has consistently recorded a downturn in recent years.
- Thus, the increased tax burden on poorer citizens and those in the middle-class category is a result of the growing proportion of personal income tax and indirect taxes within the overall.
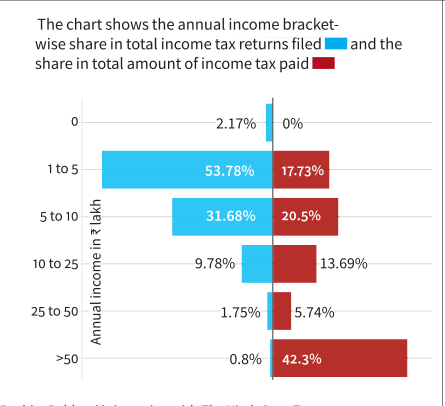
- Relation Between Annual Income Vs Income Tax Returns Filed:
- The majority (53.78%) of individuals filing personal income tax have an annual income ranging from Rs 1 lakh to Rs. 5 lakh and they contribute 17.73% in total value income tax paid.
- There are only a small number (0.84%) of wealthier individuals earning more than Rs. 50 lakh and they have the highest share in the total value of income tax paid (42.3%).
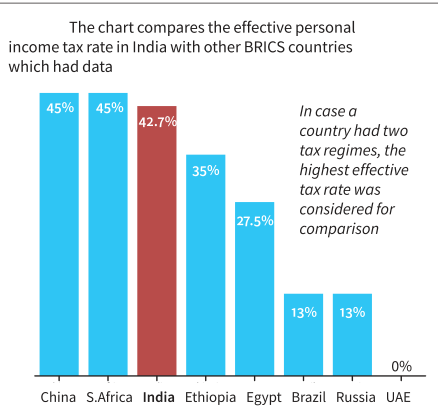
- Effective Personal Income Tax Rate:
- A comparison of India with BRICS economies shows that India has among the highest effective personal income tax rates.
- The effective personal income tax rate is the percentage of an individual's income that they actually pay in taxes after accounting for deductions, credits, exemptions, and other factors that affect their tax liability.
- A comparison of India with BRICS economies shows that India has among the highest effective personal income tax rates.
Why is Rising Share of Personal Income Tax and Indirect Taxes a Matter of Concern?
- Income Inequality: If personal income tax is a significant portion of government revenue, it may disproportionately burden lower and middle-income individuals, exacerbating income inequality.
- This can occur if the tax system is not progressive enough or if there are loopholes that allow the wealthy to avoid paying their fair share.
- Consumer Burden: Indirect taxes are typically regressive as they take a higher percentage of income from low-income individuals compared to high-income individuals.
- This can place a heavier burden on those with lower incomes, potentially leading to decreased consumer spending and economic activity.
- Economic Efficiency: High personal income tax rates can discourage work, savings, and investment, leading to a less efficient allocation of resources in the economy.
- Also, excessive reliance on indirect taxes may distort consumer behaviour and lead to market inefficiencies.
- Tax Evasion and Avoidance: As personal income tax rates rise, individuals may be more incentivised to engage in tax evasion or avoidance strategies to reduce their tax liabilities.
- This can undermine the integrity of the tax system and reduce overall government revenue.
- Macroeconomic Stability: Heavy reliance on personal income tax and indirect tax revenue can make government finances vulnerable to economic downturns.
- During periods of recession or high unemployment, personal income tax revenues may decline, leading to budget deficits or cuts in essential services.
What are the Steps Taken by the Government to Boost the Direct-Tax Collection?
- Promoting Voluntary Income-tax Compliance:
- Vivad se Vishwas Scheme: Under Vivad se Vishwas, declarations for settling pending tax disputes are filed.
- This will benefit the Government by generating timely revenue and to the taxpayers by bringing down mounting litigation costs.
- Focus on Digital Transactions: The government is promoting digital payments to discourage cash-based transactions that are harder to track for tax purposes.
- For Personal Income Tax: The Finance Act, 2020 has provided an option to individuals and co-operatives to pay income tax at concessional rates if they do not avail of specified exemptions and incentives.
- Increased Scrutiny and Compliance Measures: Tax authorities have intensified scrutiny and compliance measures, including tax audits, surveys, and data analytics, to identify tax evaders and non-compliant taxpayers.
- Awareness and Education Campaigns: The government conducts awareness and education campaigns to promote tax compliance and deter tax evasion.
- These campaigns aim to inform taxpayers about their rights and responsibilities, the consequences of non-compliance, and the benefits of participating in the formal economy.
- Expansion of scope of TDS/TCS: To widen the tax base, several new transactions were brought into the ambit of Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) and Tax Collection at Source (TCS).
- These transactions include huge cash withdrawals, foreign remittances, purchase of luxury cars, e-commerce participants, sale of goods, acquisition of immovable property, etc.
- Tax Deduction at Source (TDS): A person (deductor) who is liable to make payment of a specified nature to any other person (deductee) shall deduct tax at source and remit the same into the account of the Central Government.
- Tax Collection at Source (TCS): It is an additional amount collected as tax by a seller of specified goods from the buyer at the time of sale over and above the sale amount and is remitted to the government account.
- These transactions include huge cash withdrawals, foreign remittances, purchase of luxury cars, e-commerce participants, sale of goods, acquisition of immovable property, etc.
- Transparent Taxation - Honoring The Honest Platform: It is aimed at bringing transparency in income tax systems and empowering taxpayers.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does the tax system promote compliance in India? What are some recent developments in the Indian taxation system? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following effects of creation of black money in India has been the main cause of worry to the Government of India? (2021)
(a) Diversion of resources to the purchase of real estate and investment in luxury housing.
(b) Investment in unproductive activities and purchase of precious stones, jewellery, gold, etc.
(c) Large donations to political parties and growth of regionalism.
(d) Loss of revenue to the State Exchequer due to tax evasion.
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. What is the meaning of the term ‘tax expenditure’? Taking the housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences the budgetary policies of the government. (2013)