Biodiversity & Environment
Mangroves in India
- 02 Aug 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem, UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Indian State Forest Report 2021, Sundarbans, Royal Bengal tiger, Irrawady Dolphin, MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes), Sustainable Aquaculture In Mangrove Ecosystem (SAIME) initiative.
For Mains: Significance of Mangroves, Challenges Related to Mangroves in India
Why in News?
On the International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem, West Bengal, which is home to approximately 40% of India's mangrove forests, unveiled plans to establish a dedicated 'Mangrove Cell' to streamline mangrove management efforts.
International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem
- The International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem is celebrated every year on 26 July and aims to raise awareness of the importance of mangrove ecosystems as “a unique, special and vulnerable ecosystem” and to promote solutions for their sustainable management, conservation and uses.
- This International Day was adopted by the General Conference of the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2015.
What is the Status of Mangroves in India?
- About:
- Mangroves are a unique type of coastal ecosystem found in tropical and subtropical regions. They are dense forests of salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that thrive in intertidal zones, where land meets the sea.
- These ecosystems are characterized by their ability to withstand harsh conditions, such as saline water, tidal fluctuations, and muddy, oxygen-poor soils.
- Characteristics:
- Mangroves exhibit Viviparity mode of reproduction, where seeds germinate within the tree before falling to the ground. This is an adaptive mechanism to overcome the challenge of germination in saline water.
- Some mangrove species secrete excess salt through their leaves, while others block the absorption of salt at their roots.
- Mangrove plants have special roots like prop roots and pneumatophores, which help impede water flow and provide support in the challenging tidal environment.
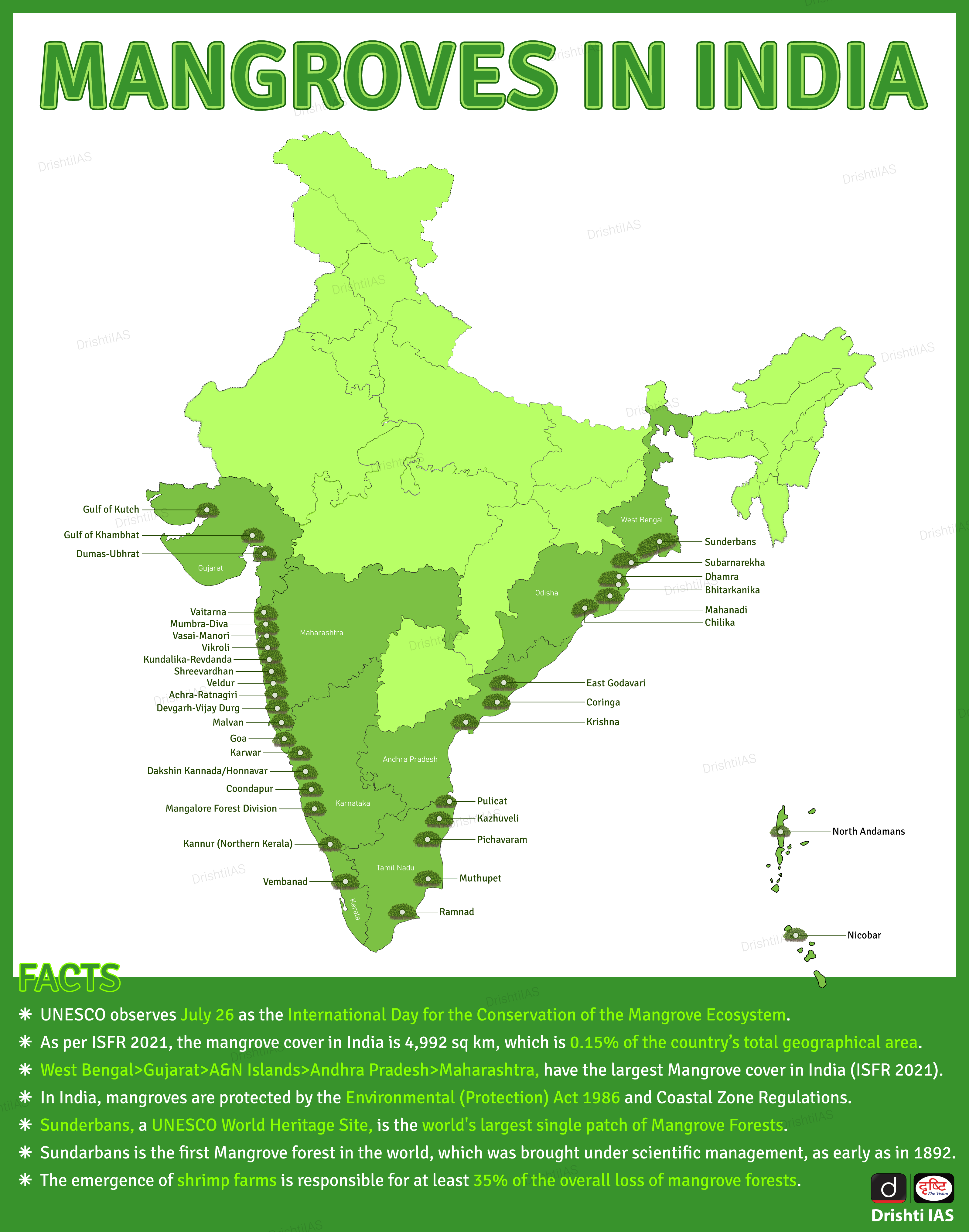
- Mangrove Cover in India:
- According to the Indian State Forest Report 2021, Mangrove cover in India is 4992 sq. Km which is 0.15% of the country's total geographical area.
- Sundarbans in West Bengal are the largest mangrove forest regions in the world. It is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Besides the Sundarbans, the Andamans region, the Kachchh and Jamnagar areas in Gujarat too have substantial mangrove cover.
- Significance:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Mangroves provide a unique habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, serving as breeding, nursery, and feeding grounds for numerous marine and terrestrial organisms.
- For example, sundarban hosts the Royal Bengal tiger, Irrawady Dolphin, Rhesus macaque, Leopard cats, Small Indian civet.
- Coastal Protection: Mangroves act as natural buffers against coastal erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis.
- Their dense root systems and tangled network of prop roots stabilize shorelines and reduce the impact of waves and currents.
- During hurricanes and cyclones, mangroves can absorb and dissipate a significant amount of energy, protecting inland areas and human settlements from devastating damage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Mangroves are highly efficient carbon sinks, sequestering large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass and sediments.
- Fisheries and Livelihoods: Mangroves support fisheries by providing nursery areas for fish and shellfish, enhancing fishery productivity and contributing to livelihood and local food security.
- Water Quality Improvement: Mangroves act as natural filters, trapping and removing pollutants and excess nutrients from coastal waters before they reach the open ocean.
- Their role in purifying water contributes to the health of marine ecosystems and helps maintain the balance of fragile coastal ecosystems.
- Tourism and Recreation: Mangroves offer recreational opportunities such as eco-tourism, birdwatching, kayaking, and nature-based activities, which can promote sustainable economic growth for local communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Mangroves provide a unique habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, serving as breeding, nursery, and feeding grounds for numerous marine and terrestrial organisms.
- Challenges:
- Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation: Mangroves are often cleared for various purposes, including agriculture, urbanization, aquaculture, and infrastructure development.
- Such activities lead to the fragmentation and loss of mangrove habitats, disrupting their ecosystem functioning and biodiversity.
- The conversion of mangroves into shrimp farms and other commercial uses is a significant concern.
- Climate Change and Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels due to climate change pose a significant threat to mangroves.
- Climate change also brings about extreme weather events, such as cyclones and storms, which can cause severe damage to mangrove forests.
- Pollution and Contamination: Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and improper waste disposal contaminate mangrove habitats.
- Heavy metals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect the flora and fauna of these ecosystems.
- Lack of Integrated Management: Often, mangroves are managed in isolation, without considering their interconnectedness with adjacent ecosystems like coral reefs and seagrass beds.
- Integrated management approaches that consider the broader coastal ecosystem are necessary for effective conservation.
- Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation: Mangroves are often cleared for various purposes, including agriculture, urbanization, aquaculture, and infrastructure development.
- Government Initiatives Related to Mangrove Conservation:
Way Forward
- Drone Monitoring and AI: Employ drone technology equipped with high-resolution cameras and AI algorithms to monitor mangrove health and detect illegal activities such as encroachment or illegal logging.
- This approach can help in efficient and timely surveillance over vast areas.
- Mangrove Adoption Program: Launch a public-driven initiative where individuals, corporates, and institutions can "adopt" a patch of mangroves.
- Participants would be responsible for the maintenance, protection, and restoration of their adopted area, fostering a sense of ownership and collective responsibility.
- Mangrove Research and Development: Invest in research to explore novel applications of mangroves, such as phytoremediation to clean polluted water or developing new medicines from mangrove plant extracts.
- This could lead to innovative ways to leverage mangroves' unique properties for sustainable development.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest? (2015)
(a) North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
(b) South-West Bengal
(c) Southern Saurashtra
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and explain their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. (2019)