Indian Economy
India’s Remittance Trends 2024
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India, Remittance, Gulf Cooperation Council, Rupee Drawing Arrangement, Liberalized Remittance Scheme
For Mains: Remittances trends, Influence of global economic shifts on remittance inflows, foreign exchange
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 6th Round of India’s Remittances Survey (2023-24) highlights that Advanced economies (AEs), particularly the US and the United Kingdom (UK), have overtaken Gulf nations as the top contributors to remittances in India.
What are the Key Findings of the 6th Round of India’s Remittances Survey?
- Shift in Source of Remittances: India’s total remittances have more than doubled, rising from USD 55.6 billion in 2010-11 to USD 118.7 billion in 2023-24.
- The US led remittances at 27.7% in 2023-24, followed by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at 19.2%.
- AEs, including the UK, Singapore, Canada, and Australia, contributed over 50%.
- The U.K.’s share rose to 10.8% from 3.4% (2016-17), driven by increased Indian emigration and Australia emerged as a key source with 2.3%.
- The overall share of Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain) stands at 38% (2023-24), down from around 47% (2016-17).
- State-wise Distribution of Remittances: Maharashtra (20.5%) remained the top recipient, followed by Kerala (19.7%).
- Other major states include Tamil Nadu (10.4%), Telangana (8.1%), and Karnataka (7.7%). Rising trends were seen in Punjab, and Haryana.
- Mode of Remittance Transfers: Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA) remains the dominant channel for inward remittances, followed by direct Vostro transfers and fintech platforms.
- Digital remittances are rising, accounting for 73.5% of total transactions in 2023-24.
What are the Reasons for the Shift in Source of Remittances to India?
- Stronger Job Markets in AEs: The US, UK, Canada, and Australia offer high-paying jobs, especially for skilled Indian migrants.
- The US job market recovered post Covid-19, leading to higher remittances from Indian professionals.
- The UK-India Migration and Mobility Partnership (MMP) made it easier for Indians to get work visas, as a result, Indian migration to the UK tripled from 76,000 in 2020 to 250,000 in 2023.
- Canada’s Express Entry and Australia’s immigration system favor skilled Indian professionals, leading to high-paying jobs and increased remittances.
- Declining Job Opportunities in GCC: Many Indian migrants who returned from the Gulf during Covid-19 and later moved to AEs for better financial opportunities.
- Additionally, economic diversification and automation have reduced demand for low-skilled Indian labor in the Gulf’s construction sector.
- Meanwhile, nationalization policies like Nitaqat (Saudi Arabia) and Emiratization (UAE) favor local workers, further limiting job prospects for migrants.
- Changing Migration Patterns in India: Southern states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana now prefer AEs over the Gulf.
- Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Rajasthan continue to send large numbers of workers to the Gulf, lower educational attainment compared to southern states, reducing eligibility for skilled jobs in AEs.
- Rise in Education-Driven Migration & Remittances: The growing number of Indian students in AEs has also boosted remittances. Many students stay back for work, sending money home.
- Canada hosts 32% of Indian students abroad, followed by the US (25.3%), the UK (13.9%), and Australia (9.2%).
Remittance
- About: Remittances are funds sent by overseas workers to support families back home, playing a key role in household income and the economy.
- In 2024, India received a record USD 129.1 billion in remittances, the highest ever for any country in a single year, accounting for 14.3% of global remittances. Mexico and China followed as the next largest recipients.
- Regulatory Framework: The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999 regulates all foreign exchange transactions in India.
- Under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS), a part of FEMA, Indian residents can remit up to USD 250,000 per year for personal and investment purposes, with higher amounts requiring RBI approval.
- However, LRS prohibits remittances for gambling, speculative trading, and terrorist financing.
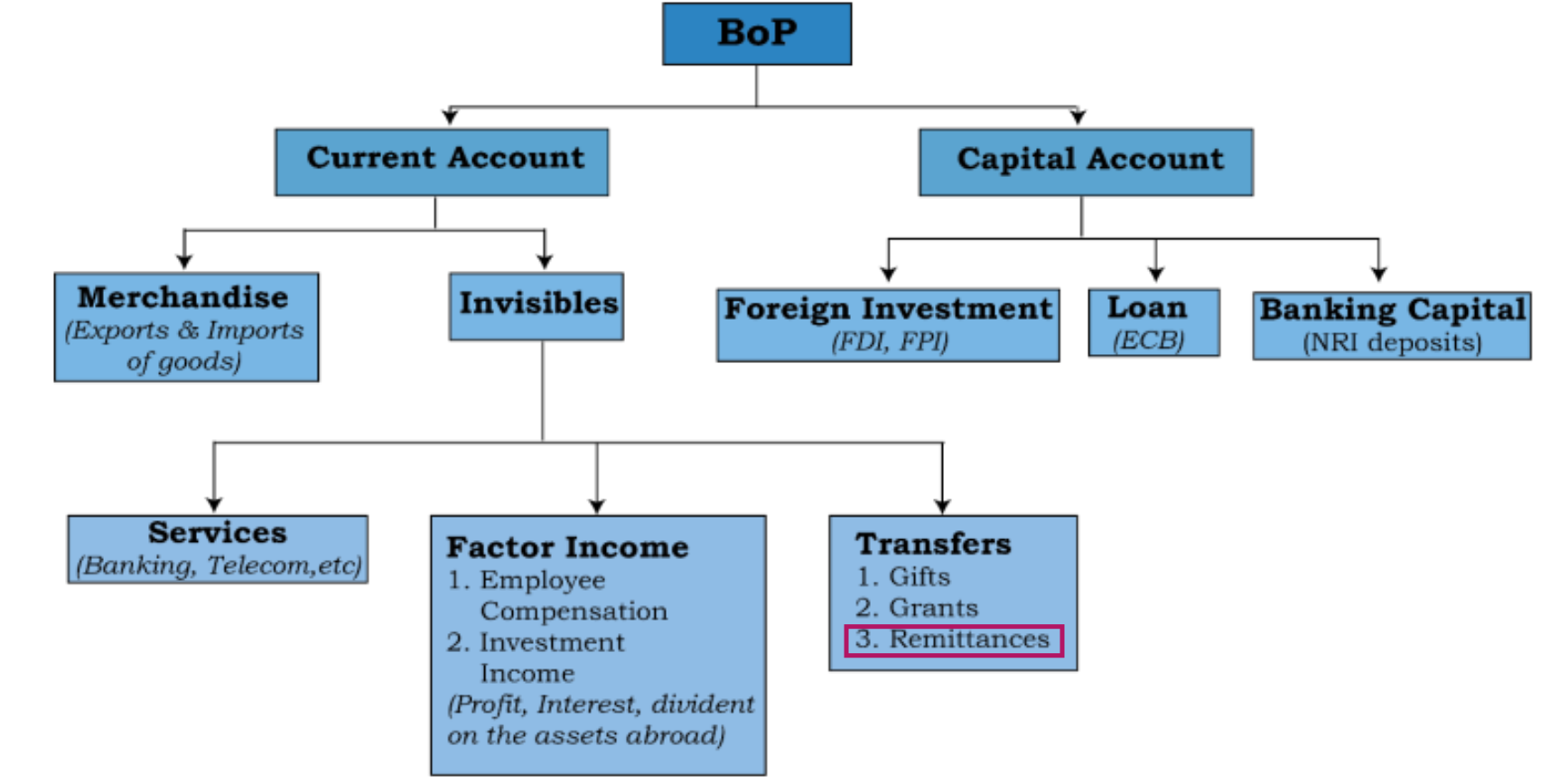
- Remittances are recorded under the current account of the Balance of Payments (BoP) as unilateral transfers. They represent foreign income inflows that do not create liabilities.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the impact of shifting migration trends on India’s Remittances and domestic labor market. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Prelims
Q1. Which of the following constitute Capital Account? (2013)
- Foreign Loans
- Foreign Direct Investment
- Private Remittances
- Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q3. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (2017)
(a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
(b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades.
(c) FDI inflows will drastically increase.
(d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘Indian diaspora has a decisive role to play in the politics and economy of America and European Countries’. Comment with examples. (2020)


Economy
De-Dollarization and India
For Prelims: BRICS+, De-dollarisation, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), Bank for International Settlements (BIS), 16th Kazan BRICS summit 2024, Cryptocurrencies, Exchange Rate, Currency Devaluation, Blockchain Payment, UPI, RuPay, IMF, SDRs, Sovereign Wealth Funds, G20.
For Mains: De-dollarisation and its impacts on Indian and global economy.
Why in News?
Recent financial and currency initiatives, particularly within the BRICS+ framework, seek to lessen dependence on the US dollar-dominated system (de-dollarisation) and establish alternative mechanisms for global trade and finance.
De-dollarization
- It refers to the process of reducing the dominance of the US dollar in global trade, finance, and foreign exchange reserves.
- It involves substituting the US dollar with other currencies or assets (such as gold, cryptocurrencies, or regional currencies) for international transactions, commodity trading (like oil), and reserve holdings.
What are the Recent Financial and Currency Initiatives for De-dollarisation?
- mBridge Project: It is a digital cross-border payment system using Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). It was initially promoted by the central banks of several countries like China, Thailand, with support from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
- Speculation suggests the BIS withdrew under US pressure to protect dollar dominance.
- BRICS+ Initiatives: BRICS Bridge and BRICS Clear are proposed financial systems for setting up a payment and clearing system among Brics+ countries.
- BRICS+ group includes original BRICS nations i.e., Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa along with new members i.e., Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, United Arab Emirates, and Indonesia.
- Petro-Yuan Market: Shanghai International Energy Exchange (2018) handles 10.5% of global oil trade and 14.4% of global oil futures.
- Saudi Arabia and the UAE's non-dollar oil trades boost the petro-yuan by increasing demand and enhancing its credibility as a stable alternative to the US dollar.
- BRICS Currency: At the 16th Kazan BRICS summit 2024, an agreement in principle was reached to use a new settlement currency called the "Unit," backed by 40% gold and 60% local currencies of member countries.
What are Global Benefits of De-Dollarization?
- Reduced Geopolitical Risks: Countries can insulate themselves from US sanctions and foreign policy decisions that leverage the dollar's dominance (e.g., freezing assets or restricting access to the global financial system).
- E.g., After Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine, the West froze over USD 300 billion in Russian assets.
- Diversification: De-dollarization promotes multi-currency use, reducing reliance on one currency and balancing global finance.
- E.g., rise of the petro-yuan and Indian rupee to create an alternative payment system.
- Strengthening Regional Currencies: Countries can boost their currencies in trade, strengthening economic sovereignty and reducing exchange rate risks.
- E.g., India trading oil with the UAE in rupees.
- Reduced Vulnerability: Countries become less impacted by US monetary policy (e.g., interest rate changes), avoiding effects like capital flight and currency devaluation.
- Increased Use of Gold: De-dollarization has led to a resurgence in gold as a reserve asset, providing a stable alternative to fiat currencies.
- Promotion of Digital Currencies: De-dollarization speeds up digital currency and blockchain payment development, driving financial innovation.
- E.g., China's digital yuan (e-CNY) and India’s Digital Rupee (e₹).
What Concerns are Associated with Global De-dollarization?
- Short-Term Instability: Sudden shifts in currency reserves or trade agreements could create volatility in global markets, as the dollar remains the backbone of international trade and finance.
- Limited Acceptance of Alternatives: Many alternative currencies (e.g., the yuan, rupee, or ruble) lack the liquidity, stability, and global trust that the US dollar enjoys.
- Risk of Fragmentation: De-dollarization could lead to the formation of competing currency blocs, fragmenting the global economy and complicating international trade and investment.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The US may respond aggressively to de-dollarization efforts, potentially escalating trade wars, sanctions, or other forms of economic retaliation.
- E.fg., US tariffs threats to BRICS countries attempting to reduce dollar dependency.
- Global Repercussions: A decline in the dollar's reserve status could lead to reduced demand for US debt, and economic instability in the US, which could have global repercussions, as the US being the largest economy.
- Exchange Rate Determination Problem: Without the US Dollar as a global benchmark, countries must use alternatives like a multi-currency basket, complicating exchange rates.
- E.g., India and Russia are still negotiating a currency exchange rate based on their local currencies.
What is India’s Stand on De-Dollarization and it Impacts India?
- India’s Stand on De-Dollarization: India engages in BRICS+ currency discussions but remains cautious, affirming it has no intent to undermine the US dollar, seeing it as key to global stability.
Benefits
- Promotion of the Indian Rupee: It encourages the use of the Indian rupee in bilateral and multilateral trade agreements. E.g., India’s trade with Russia in rupees for oil imports.
- Greater Monetary Policy Autonomy: Reducing dollar reliance gives India greater control over monetary policy to manage inflation, and interest rates, without being impacted by US policy shifts.
- Diversification of Reserves: De-dollarization helps India diversify reserves into other currencies (e.g., euro, yen, yuan) or gold, reducing dollar devaluation risks.
- Reduced Exposure to US Sanctions: It reduces India’s vulnerability to US-led sanctions providing greater geopolitical flexibility.
- It reduces reliance on the US-centric SWIFT system, shielding India’s financial system from risks and sanctions.
Concerns
- Impact on Foreign Investment: Moving away from the dollar could deter foreign investors who prefer the stability and predictability of dollar-denominated assets.
- Challenges in Diversifying Reserves: Alternative currencies or assets like gold may expose India to new risks, such as currency depreciation or price fluctuations in commodities.
- India risks over-reliance on the Chinese yuan, bringing geopolitical and economic challenges.
- Impact on Remittances: De-dollarization may disrupt India's dollar-denominated remittances, impacting millions of families.
What Lies Ahead for India?
- Strengthening Rupee: Expand bilateral trade in rupees, such as India-UAE oil trade, while promoting currency swaps and regional frameworks like BRICS+ initiatives.
- Diversifying Reserves: Reduce USD reliance by diversifying reserves into Euro, Yen, Yuan, gold, and IMF SDRs while developing sovereign wealth funds and commodity reserves for stability.
- Managing Risks: Maintain a multi-currency trade system, strengthen ties with ASEAN, EU, and Africa for diversified trade, and ensure investor confidence in Rupee.
- Strengthening India’s Financial Position: Position Mumbai as a global financial hub, boost bond market liquidity, and advocate for a multi-currency system through IMF, G20, and other bodies.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the concept of de-dollarization and its implications for India’s economy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Most of India’s external debt is owed by governmental entities.
- All of India’s external debt is denominated in US dollars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. Recently, which one of the following currencies has been proposed to be added to the basket of IMF’s SDR? (2016)
(a) Rouble
(b) Indian Rupee
(c) Rand
(d) Renminbi
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India? (2018)
Q. Craze for gold in Indians has led to surge in import of gold in recent years and put pressure on balance of payments and external value of rupee. In view of this, examine the merits of Gold Monetization scheme. (2015)


Important Facts For Prelims
Return of Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams from ISS
Why in News?
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) astronauts Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams have returned to Earth after an unexpectedly long 286-day mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
- Initially planned for a 8-day mission, their return was delayed due to issues with Boeing's Starliner spacecraft. They finally came back via SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, highlighting the technological and health challenges of prolonged space travel.
What are the Key Facts About Starliner Spacecraft and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon?
- Starliner Spacecraft: Developed by Boeing in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP), was designed to transport astronauts to and from low Earth orbit (LEO).
- Boeing's Starliner took Williams and Wilmore to the ISS in 2024 but propulsion issues delayed their return.
- SpaceX’s Crew Dragon: Crew Dragon is one of the two variants of SpaceX’s Dragon 2 spacecraft, featuring a reusable capsule and launching atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Developed under NASA’s CCP, it primarily ferries astronauts to the ISS. The other variant, Cargo Dragon, transports cargo to the station.
- NASA's SpaceX Crew-9 mission returned Williams and Wilmore from the ISS aboard the Crew Dragon spacecraft named Freedom.
What are the Health Implications of Space Travel?
- Space Anemia: A condition where astronauts experience a drop in red blood cell count due to fluid shifts in microgravity, leading to fatigue, dizziness, and cardiovascular risks post-mission.
- Spaceflight-Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome (SANS): It is a vision impairment caused by fluid shifts in microgravity, leading to optic disc swelling and farsightedness.
- Baby Feet Syndrome: It refers to the hypersensitivity of the soles and difficulty in walking experienced by astronauts after prolonged space missions.
- In microgravity, the lack of weight-bearing activity causes foot calluses to disappear, making the skin soft and sensitive upon return to Earth.
- Bone Density Loss: NASA studies show that astronauts lose around 2% of bone density per month in space. Without proper countermeasures like exercise, this loss can lead to osteoporosis-like conditions.
- Risks of Cosmic Radiation Exposure: In space, astronauts face direct exposure to cosmic rays and solar radiation, unlike on Earth, where the atmosphere and magnetic field provide protection.
- This can cause DNA damage, genetic mutations, and increased cancer risk.
- Deep-space missions to Mars and the Moon pose higher risks due to prolonged exposure.
India's Gaganyaan Mission and Bhartiya Antriksh Station (BAS)
- Gaganyaan Mission: Aims to send three astronauts on a 3-day mission to a 400 km orbit and return them safely to Earth. This would place India alongside the US, Russia, and China in human spaceflight.
- The Gaganyaan mission's short-term goal is to demonstrate human spaceflight to Low Earth Orbit, with a long-term aim of establishing a sustained Indian human space exploration program.
- Bhartiya Antriksh Station: The BAS is India's planned space station, set to orbit 400–450 km above Earth.
- The first module, the Base Module, will be launched in 2028, with full operationalization by 2035.
- It will support human spaceflight, Earth observation, and microgravity research while fostering technological innovations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. What is the purpose of the US Space Agency’s Themis Mission, which was recently in the news? (2008)
(a) To study the possibility of life on Mars
(b) To study the satellites of Saturn
(c) To study the colourful display of high latitude skies
(d) To build a space laboratory to study the stellar explosions
Ans: (c)
Q. In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)


Facts for UPSC Mains
State of Global Climate Report 2024
Why in News?
According to the State of Global Climate report 2024 of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), global warming is nearing the 1.5°C Paris Agreement threshold.
What are the Key Findings of the Global Climate Report?
- Current Warming Levels: Global warming stands at 1.34–1.41°C above pre-industrial levels, with 19 of the last 20 months surpassing the 1.5°C threshold.
- The world could surpass the 1.5°C threshold by September 2029.
- Extreme Weather Events: In 2024, record displacements from cyclones, floods, and droughts worsened food crises, while heat waves hit East Asia, Southeast Europe, the Mediterranean, West Asia, and the southwestern US.
- Carbon Dioxide Levels: In 2023, atmospheric CO₂ reached 151% of pre-industrial levels, the highest in 800,000 years.
- Cryosphere Decline: Arctic sea ice hit record lows for 18 consecutive years, while Antarctic sea ice saw its 2nd-lowest extent in 2024.
- Irreversible Impacts:
- Ocean Warming: 2024 saw the highest ocean heat content in 65 years, with warming rates doubling since 1960.
- Sea Level Rise: Global mean sea level reached a record high, with rates doubling from 2.1 mm/year (1993–2002) to 4.7 mm/year (2015–2024).
- Glacier Melt: The period 2022–2024 recorded the most negative glacier mass balance, with significant losses in Norway, Sweden, Svalbard, and the tropical Andes.
- Ocean Acidification: pH levels are declining rapidly, particularly in the Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and equatorial Pacific, with irreversible effects over centuries.
What is the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)?Click Here to Read: World Meteorological Organization (WMO) What is the Paris Agreement?Click Here to Read: Paris Agreement |


Important Facts For Prelims
Micro-Lightning and Origin of Life
Why in News?
A Stanford University study suggests that micro-lightning i.e. tiny electrical discharges within water droplets could have played a crucial role in forming organic molecules necessary for life on earth, challenging the Miller-Urey hypothesis.
What are the Highlights of the Study About the Origin of Life on Earth?
- Key Findings:
- The study found that splashing/spraying water droplets generate electrical charges, and their interaction produces micro-lightning (tiny sparks), facilitating the formation of essential biomolecules.
- It also demonstrated the spontaneous synthesis of uracil (a key RNA and DNA component), glycine (a fundamental amino acid for protein synthesis), and hydrogen cyanide (a precursor to complex biochemical compounds).
- These findings suggest that microlighting in natural water bodies like oceans, waterfalls, and rainfall may have driven prebiotic chemistry, aiding the emergence of life on Earth.
- Implications:
- Challenges to the Miller-Urey Model: It suggests that frequent micro lightning in water bodies might have played a larger role than rare lightning strikes.
- Astrobiological Potential: Similar mechanisms could operate on icy moons like Europa and Enceladus, increasing the possibility of extraterrestrial life.
What is the Miller-Urey Hypothesis?
- The Miller-Urey hypothesis (1952) proposes that life on Earth originated through chemical reactions triggered by lightning (atmospheric electricity) in the early Earth's atmosphere.
- It demonstrated that amino acids (the building blocks of life) could form when electricity was applied to a mix of water, methane, ammonia, and hydrogen, suggesting that organic molecules necessary for life could form naturally under early Earth conditions.
- It provided a scientific explanation for abiogenesis (the origin of life from non-living matter).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (2008)
Theory/Law Associated Scientist
- Continental Drift : Edwin Hubble
- Expansion of Universe : Alfred Wegener
- Photoelectric Effect : Albert Einstein
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 only
Ans: (b)


Rapid Fire
Right to Development and Clean Environment
The Supreme Court (SC), in The Auroville Foundation vs. Navroz Kersasp Mody (2025), ruled that the right to development through industrialization is equally significant as the right to a clean environment, emphasizing a "golden balance" between the two under Articles 14, 19, and 21 of the Constitution.
- Case Background: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) halted Auroville’s development in Tamil Nadu in 2022, citing environmental concerns in the Darkali forest.
- The Auroville Foundation challenged the decision, asserting that Auroville’s Master Plan had statutory authority and required no additional environmental clearance.
- SC Ruling: SC overturned NGT’s 2022 order, upheld Auroville’s legally valid Master Plan, and ruled that "Darkali forest" is not classified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
- SC emphasized fundamental rights, stating that Article 14 (Right to Equality) ensures a fair balance between environmental protection and development, Article 19 (Right to Freedom) safeguards the right to trade and industrial activities with reasonable restrictions, while Article 21 (Right to Life) includes the right to a clean environment alongside sustainable economic progress.
| Read more: Balancing Development With Environment |


Place In News
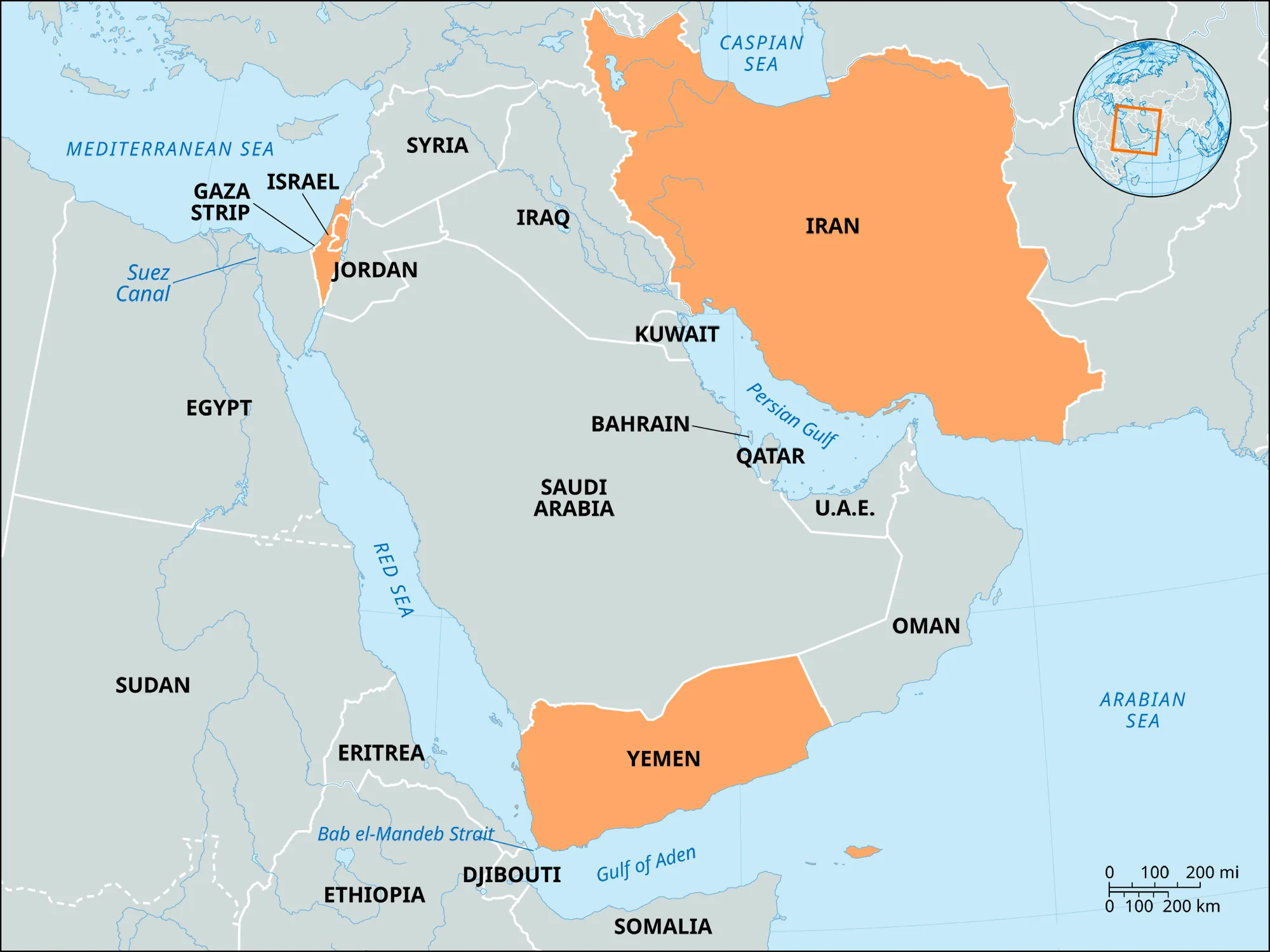
Yemen and Houthis
The US has intensified airstrikes on Houthi-controlled areas in Yemen to counter their missile and drone attacks in the Red Sea, citing threats to global shipping routes.
- Yemen: Located in the Middle East at the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula, borders Saudi Arabia (north) and Oman (east). It has a coastline along the Red Sea (west), Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, and Guardafui Channel (south).
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait, between Djibouti and Yemen, is a key maritime chokepoint connecting the Indian Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea via the Red Sea and Suez Canal, crucial for global trade.
- Houthis: A Zaidi Shia militant group from northwestern Yemen, the Houthis emerged in the 1990s as a rebellion against the Yemeni government. Backed by Iran, they are part of the Axis of Resistance (informal coalition of Iranian-supported militias) and target Israeli-linked ships in the Bab el-Mandeb Strait in response to the Gaza conflict.
| Read more: Escalating Threat in Red Sea |


Rapid Fire
23rd Exercise Varuna 2025
The Indian and French navies are set to commence the 23rd edition of the annual bilateral naval exercise, Varuna-2025, in the Arabian Sea.
- It will include aircraft carriers INS Vikrant (India) and Charles de Gaulle (France), along with fighter aircraft, destroyers, frigates, and an Indian Scorpene-class submarine.
- It was first held in 2001 and aims to enhance interoperability and operational synergy.
- Defence Cooperation: India and France strengthened military ties with a new defence industrial roadmap for co-design, co-development, and co-production of defense equipment.
- Upcoming Defence Deals: 26 Rafale-M fighter jets for INS Vikrant.
- 3 additional Scorpene-class submarines to be built at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) under Project 75.
- MDL has already built six Kalvari-class (Scorpene) submarines with French technology transfer.
| Read More: India-France Relations |


Rapid Fire
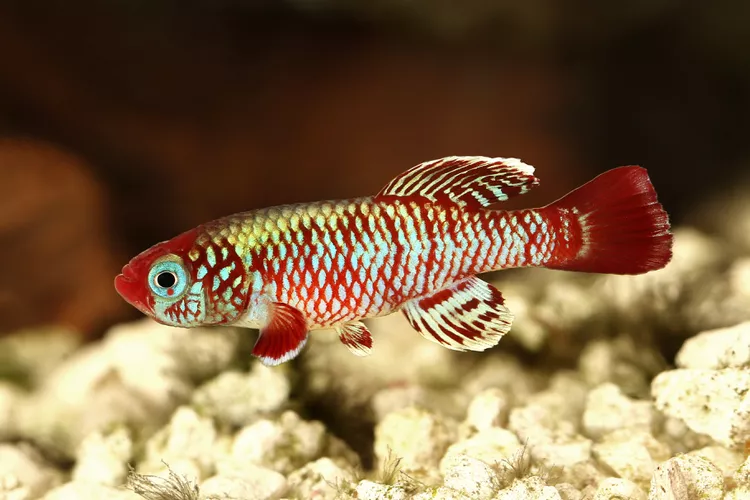
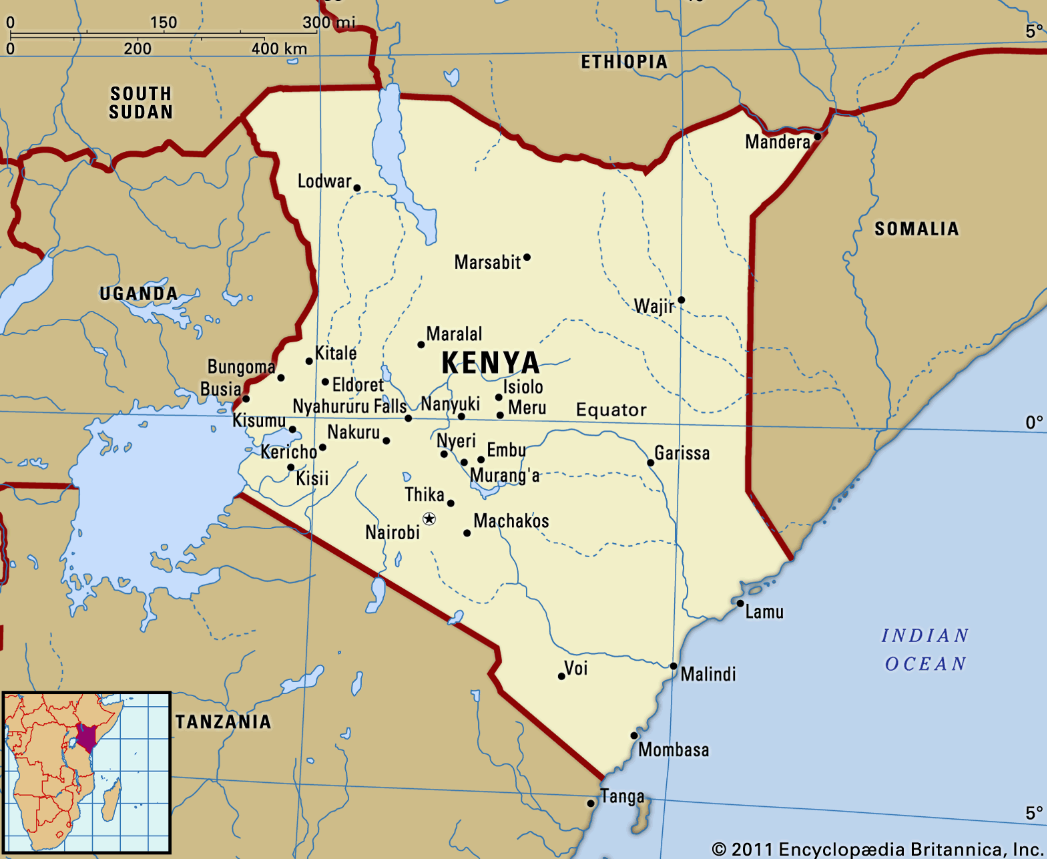
Killifish
A new species of killifish (Nothobranchius sylvaticus), has been discovered in Kenya’s Gongoni Forest (7.09 million years old). It is the first known endemic forest-dwelling killifish.
- It is endemic to Kenya and is classified as Critically Endangered (IUCN).
Killfish:
- About: Killifish are small, egg-laying (oviparous) fish belonging to the Cyprinodontiformes order, commonly known as toothcarps.
- Habitat: Killifish inhabit freshwater and brackish waters across the Americas, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia, with some species thriving in ephemeral (seasonal) water bodies like swamps and temporary pools.
- Adaptability: They adapt to extreme environments, tolerate high salinity and low oxygen, and serve as model organisms in aging and genetics research.
Kenya:
- Location: Kenya (an equatorial and East African nation), borders South Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia, Uganda, Tanzania, and the Indian Ocean.
- The Dadaab Refugee Complex is one of the largest camps, sheltering refugees from Somalia’s civil war.
- Major Lakes: Lake Turkana, Lake Victoria (shared by Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda), etc.
- India is sourcing 20 cheetahs from Kenya for Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh-Rajasthan) to aid population revival.
| Read More: New Fish Species Discovered |