Important Facts For Prelims
Increasing Real Effective Exchange Rate in India
- 27 Dec 2024
- 5 min read
Why in News?
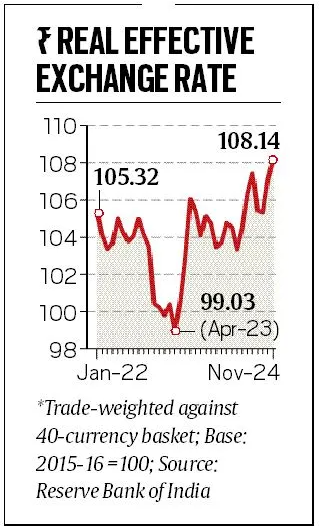
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reported that the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached 108.14 in November 2024 from 107.20 in October 2024, marking its highest level this year.
What are RBI’s Findings Related to REER?
- Record High REER Values: The rupee’s REER of 108.14 indicates overvaluation since 2015-16, undermining export competitiveness, despite nominal depreciation against the USD, revealing contrasting Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) and REER indices.
- A REER above 100 signifies overvaluation relative to its base year (2015-16), reducing export competitiveness, while a value below 100 suggests undervaluation.
- Volatility Trends: The rupee experienced the lowest volatility (it has appreciated against other currencies) among major global currencies, even as emerging market currencies faced outflows due to rising US bond yields and a strong dollar index.
- Trade Balance Implications: Overvaluation of the rupee, as indicated by REER, makes Indian exports costlier, undermining competitiveness in global markets.
- At the same time, it reduces import costs, potentially widening the trade deficit.
- Capital Outflows: The strengthening US dollar, fueled by higher bond yields and global demand for safe-haven assets, has caused capital outflows from India, pressuring the rupee.
What is NEER and REER, and their Significance?
- Definition:
- NEER: The Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) is a weighted average of a currency’s bilateral exchange rates relative to multiple trading partner currencies.
- It reflects nominal currency strength without accounting for inflation or price level differences between countries.
- A rise in NEER indicates nominal appreciation, while a fall signals depreciation.
- REER: The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) improves upon NEER by adjusting for relative price levels (inflation) between the domestic economy and its trading partners.
- REER is calculated as the NEER multiplied by the ratio of domestic price indices to foreign price indices, making it a purchasing power parity (PPP)-adjusted measure.
- Indices of NEER/REER: The NEER/REER indices for India includes six currencies: the US Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Chinese Yuan (CNY), and Singapore Dollar (SGD).
- The NEER/REER indices have been revised to include a broader basket of 36 currencies.
- Influencing Factors: NEER and REER trends are influenced by productivity differences (affecting competitiveness), trade terms (affecting export/import balance), inflation (eroding currency value), and fiscal spending (impacting economic stability and demand).
- NEER: The Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) is a weighted average of a currency’s bilateral exchange rates relative to multiple trading partner currencies.
- Significance of NEER:
- Trade-weighted Index: NEER gauges a currency's nominal performance against multiple trading partners, reflecting broad external currency trends.
- Limited Insight: Since it ignores inflation differences, NEER may not accurately reflect actual trade competitiveness or purchasing power.
- Macroeconomic Use: Policymakers use NEER to understand trends in currency strength and plan nominal interventions when needed.
- Significance of REER:
- Indicator of Competitiveness: REER measures a country's external competitiveness by accounting for inflation, with a higher value indicating reduced export competitiveness and cheaper imports.
- Policy Guide: REER is critical for determining whether a currency is overvalued or undervalued, guiding monetary policy and exchange rate adjustments.
- Trade Balance Impact: Depreciation of REER improves the trade balance more in the short term by enhancing export competitiveness.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate(REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India? (2018)