International Relations
16th BRICS Summit & India-China Border Agreement
- 25 Oct 2024
- 10 min read
For Prelims: 16th BRICS Summit, India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Line of Actual Control (LAC), Depsang Plains and Charding Nullah, New Development Bank (NDB)
For Mains: BRICS: Challenges & Way Forward, India-China Border Agreement
Why in News?
Recently, the 16th BRICS Summit was held in Kazan, Russia.
- On the sidelines of the Summit, the PM welcomed the recent agreement with China for "complete disengagement and resolution" of 2020 border issues, marking their first bilateral meeting since 2020.
Note:
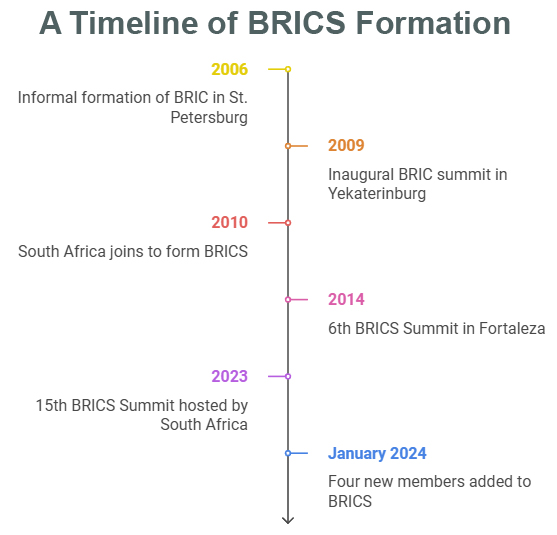
- In January, 2024, the alliance added four new members – Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran and the UAE.
- Saudi Arabia is yet to formalise its BRICS membership, however its foreign minister attended the summit.
What are the Key Highlights of the Summit?
- New Members Participation:
- The summit showcased the participation of new member countries, underscoring the increasing influence and diversity within the BRICS+ alliance.
- Focus on Multilateralism:
- Leaders engaged in discussions about strengthening multilateralism, countering terrorism, fostering economic growth, pursuing sustainable development, and addressing the concerns of the Global South.
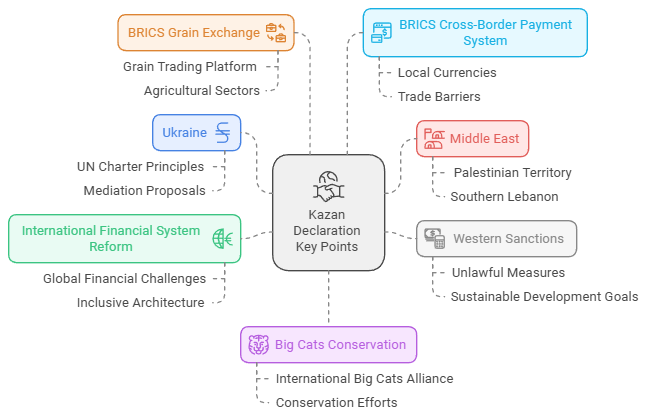
- Kazan Declaration:
- Stand on Geopolitical Conflicts:
- On Ukraine: Emphasised mediating a peaceful resolution through dialogue and diplomacy.
- On West Asia Crisis: Expressed deep concern over the escalating humanitarian crisis in Gaza Strip and West Bank.
- Condemned the loss of civilian lives and infrastructure damage from Israeli attacks in Southern Lebanon.
- On Western Sanctions: Emphasised the disruptive effects of unlawful unilateral coercive measures, including illegal sanctions, on the global economy, international trade, and the achievement of SDGs.
- On BRICS Grain Exchange: Explored the establishment of a grain trading platform within BRICS, known as the BRICS Grain Exchange, with plans for future development that may include other agricultural sectors.
- Financial Integration Support: The summit emphasised the need for greater financial integration among member countries. Key Aspects Highlighted:
- Importance of trade in local currencies.
- Facilitating smooth cross-border payments
- India’s UPI was highlighted as a successful model.
- BRICS-led payment system to rival SWIFT
- On Big Cats: Supported the efforts of member countries to preserve rare species, particularly big cats, and notes India's initiative to create an International Big Cats Alliance.
- BRICS countries are encouraged to collaborate further on conservation efforts for these vulnerable species.
- Stand on Geopolitical Conflicts:
What are the Key Highlights of India-China Bilateral Meeting?
- About:
- The meeting followed significant incidents in 2020 which deteriorated relations between the two countries and aimed to revive bilateral relations.
- India-China Border Agreement:
- The importance of the agreement is highlighted by China's previous unwillingness to discuss the Depsang Plains and Charding Nullah while negotiating disengagement at other points.
- Both nations have consented to allow troops to patrol up to the old Patrolling Points (PPs) along the LAC in the Depsang Plains and Demchok.
What is BRICS?
- About: First informally formed during a meeting of the leaders of Brazil, Russia, India, and China (BRIC) on the sidelines of the G8 (now G7) Outreach Summit in 2006, BRICS represents the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies.
- In 2010, South Africa joined the grouping to form what is known as BRICS.
- It now includes 9 countries - Brazil, China, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Iran, Russian Federation, South Africa and UAE.
- The inaugural BRIC summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia, in 2009.
- During the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014) the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB).
- In 2010, South Africa joined the grouping to form what is known as BRICS.
- Significance:
- As of August 2023, the BRICS contributes 40% of the world's population which controls 26% of the global GDP.
Why BRICS Matters?
- Engagement of Non-Western Countries with Russia: The Kazan Summit highlighted that non-Western nations acknowledge Russia's strategic significance and its role as a key supplier of weapons and energy.
- BRICS as a Cohesive Institution: Despite diverse membership, BRICS has demonstrated effective management as a cohesive institution. Critics argue that economic disparities hinder unity, with some economies vastly larger than others.
- However, BRICS has maintained collaboration through annual Summits and the establishment of institutions like the NDB, which has funded projects worth USD 30 billion since 2015. The Summit schedule has remained intact despite geopolitical tensions.
- Emergence as an Influential Bloc: BRICS has become an important group in global politics, causing concern in the West about its ability to compete with the G7 and influence the G20.
- Although it focuses mainly on economic issues, BRICS also addresses political matters, emphasising discrimination and inequality in international institutions. Its members believe they are underrepresented in major organisations like the UNSC, IMF, and World Bank, especially as Western influence decreases.
- The Kazan Declaration reflected BRICS's collective ambition to reform existing international frameworks, aiming for enhanced representation and influence on the global stage.
What are the Challenges Related to the BRICS?
- Countering the Dollar: Despite ambitions to dethrone the dollar and foster a multipolar financial system, BRICS faces significant hurdles. The NDB, established as an alternative to the World Bank, has made limited progress, with its lending far overshadowed by the World Bank's figures.
- Efforts to promote non-dollar currencies in international transactions have also been sluggish.
- Geopolitical Contradictions: The diversity of new members introduces complexities. The UAE and Egypt maintain alliances with the US, while Iran stands as a direct adversary. These contradictions could challenge BRICS in maintaining a unified agenda.
- Decision-Making Difficulties: The expansion of BRICS could complicate decision-making, as the group operates on a consensus basis. With more members, achieving consensus may become increasingly challenging, potentially leading to a situation similar to that of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and the Group of 77 (G77), which, although still in existence, hold limited influence.
- Additionally, the organisation may reflect broader geopolitical rivalries among its members, particularly concerns that tensions in West Asia could hinder its functionality.
Way Forward
- Establish clear, shared objectives among member countries, focusing on cooperation in trade, technology, and security.
- Actively engage in initiatives that strengthen collaboration in supply chains, energy, food security, and financial resilience.
- Promote universal security by ensuring respect for all nations' security and fostering dialogue over confrontation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How do the developments from the recent BRICS summit, particularly the India-China bilateral meeting, impact regional stability and international relations? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- New Development Bank has been set up by APEC.
- The headquarters of the New Development Bank is in Shanghai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’, recently in the news, is related to the affairs of (2015)
(a) ASEAN
(b) BRICS
(c) OECD
(d) WTO
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements: (2014)
- The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009.
- South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (2016)