International Relations
50th G7 Summit
- 17 Jun 2024
- 17 min read
For Prelims: G7 Summit, G7 Countries, Indo-Pacific region,
For Mains: Role of the G7 summit in addressing global challenges, the significance of the Quad in promoting regional cooperation, India's foreign policy, the relationship between climate change and global security
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister attended the annual G7 summit held in Italy from 13 to 15th June 2024. This summit marked the 50th anniversary of the group.
- This is his first foreign trip after assuming office for the third straight term.
What are the Key Highlights of the 50th G7 Summit in Italy?
- Promotion to G7 PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment):
- In the 50th G7 Summit, leaders decided to promote concrete G7 PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment) initiatives.
- This initiative was launched by the US and G7 allies at the 48th G 7 Summit in 2022 that aims to narrow the USD 40 trillion infrastructure gap in the developing world.
- It is a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low and middle-income countries.
- Under this, G7 will mobilise USD 600 billion by 2027 to deliver infrastructure projects to developing and middle-income countries.
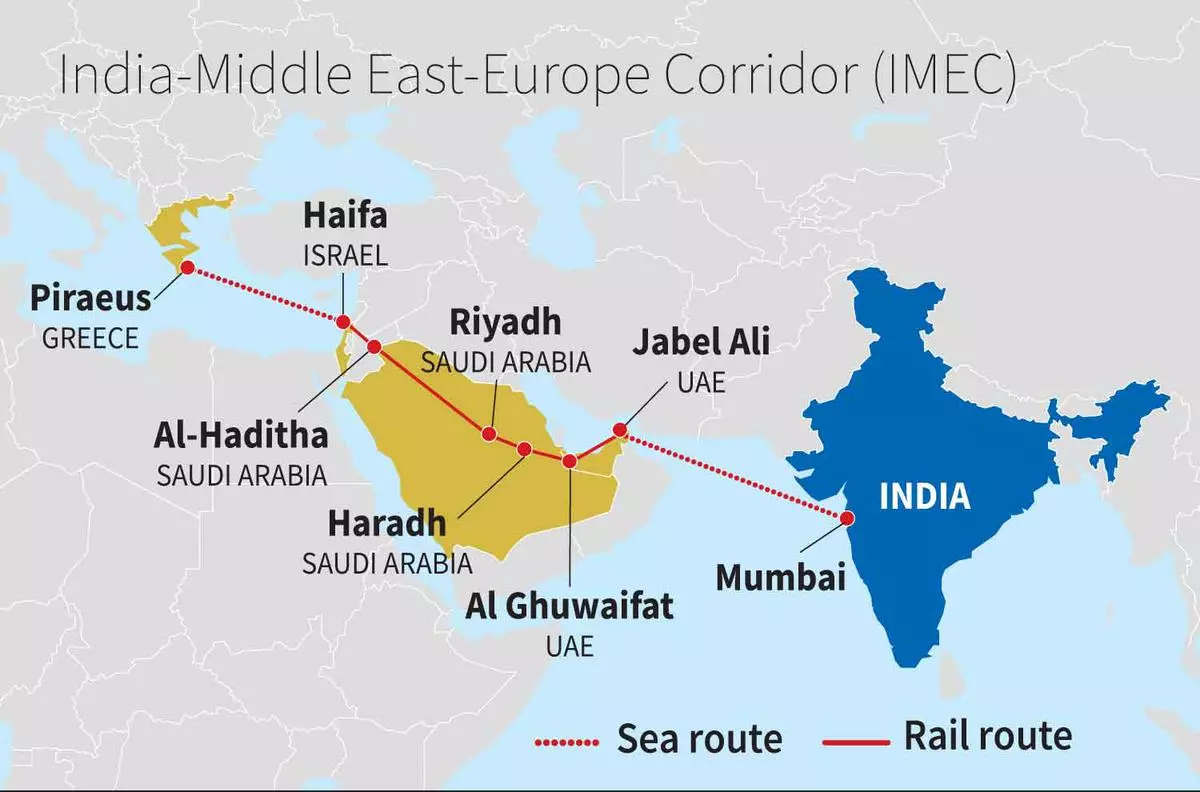
- Support and Promotion to India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- G-7 nations committed to promoting the IMEC.
- IMEC aims to create a comprehensive transportation network, comprising rail, road, and sea routes, connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- IMEC:
- It was signed at the G20 Summit in New Delhi, in September 2023.
- This project forms part of the PGII.
- The proposed IMEC will consist of Railroad, Ship-to-Rail networks and Road transport routes extending across 2 corridors:
- East Corridor: Connecting India to the Arabian Gulf
- Northern Corridor: Connecting the Gulf to Europe.
- It will also include an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline and a high-speed data cable.
- India, the US, Saudi Arabia, UAE, the European Union, Italy, France, and Germany are the signatories of IMEC.
- Support to Infrastructure Projects:
- G7 also extended support for the Lobito Corridor in Central Africa and Luzon Corridor and the Middle Corridor.
- Lobito Corridor: It extends from the port city of Lobito on the Atlantic coast of Angola through the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and into Zambia.
- Luzon Corridor: It is a strategic economic and infrastructure corridor located on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. Luzon is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines.
- Middle Corridor: It is also referred to as the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route (TITR), a vital logistics and transportation network connecting Europe and Asia.
- This route serves as an alternative to the traditional Northern and Southern corridors, enhancing trade and economic cooperation between the regions it traverses.
- The Great Green Wall Initiative: It is a project aimed at combating desertification and land degradation in the Sahel region of Africa.
- it aims to create a wall of trees stretching across Africa from west to east to help prevent the spread of the Sahara Desert, improve biodiversity, and provide economic opportunities for local communities.
- G7 also extended support for the Lobito Corridor in Central Africa and Luzon Corridor and the Middle Corridor.
- Enhancing Interoperability of AI Governance:
-
The G7 leaders commit to step up efforts to enhance interoperability amongst their AI governance approaches to promote greater certainty, transparency and accountability.
- It focuses on managing risks in a way that supports innovation and promotes healthy, inclusive, and long-lasting economic growth.
-
- Extraordinary Revenue Acceleration (ERA) Loans for Ukraine:
- The G7 agreed to provide financing of approximately USD 50 billion in additional funding to Ukraine by the end of 2024.
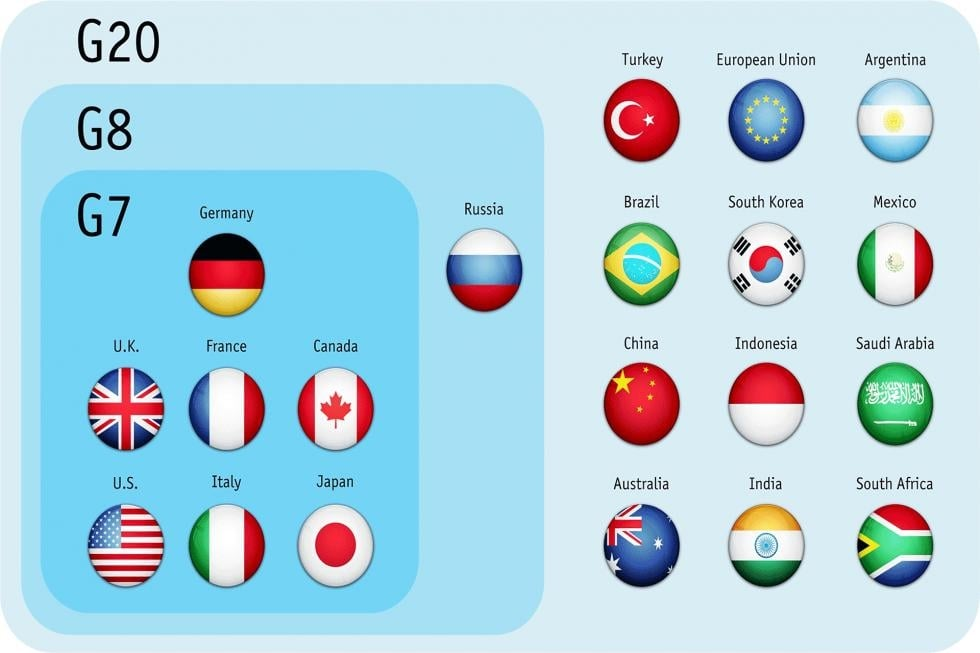
What is G7?
- About:
- G-7 is a group of the most developed and advanced economies of the world. i.e. France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and Canada.
- The leaders of important international organisations like the European Union (EU), IMF, World Bank and the United Nations are also invited.
- Summits are held annually and hosted on a rotation basis by the group's members.
- Origin:
- The G7 originated from the Oil crisis of 1973 and the resulting financial crisis, which forced the leaders of 6 major industrial nations to convene a meeting in 1975.
- The participating countries were the US, UK, France, West Germany, Japan, and Italy.
- Canada joined in 1976, leading to the formation of the G7.
- It was known as the ‘G8’ for several years after the original seven were joined by Russia in 1997, but it was renamed as G7 after Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following its annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine.
- Nature of Grouping:
- Informal Grouping: The G7 is an informal grouping that operates outside of formal treaties and lacks a permanent bureaucracy. Each member nation takes turns leading the discussions (presiding nation).
- Decision Through Consensus: Despite the absence of legal enforcement, the G7's power stems from its members' economic and political clout. When these major powers can agree on a course of action, it can significantly impact global issues.
- Limited Legislative Power: The G7 cannot enact laws directly. However, their pronouncements and coordinated efforts can influence international policies and shape global agendas.
- Purpose:
- Facilitate Dialogue: The G7 acts as a forum for member nations to have open and frank discussions on critical global issues. This allows them to understand different perspectives and build consensus.
- Forge Collective Action: It aims to develop coordinated political responses to global challenges. This could involve collaborative efforts on issues like trade agreements, security threats, or climate change initiatives.
- Set the Agenda: The G7's discussions and pronouncements can influence the direction of global conversations on pressing issues. This can help shape international policies and priorities.
- Significance:
- Wealth: Control 60% of global net wealth
- Growth: Drive 46% of global GDP
- Population: Represents 10% of the world's population.
Note
- India is not a member of the G7. However, India participated as a guest in the 2019, 2021, and 2022 G7 summits at the invitation of France, the UK, and Germany respectively.
Why is India's Role in the G7 Important?
- India's Economic Significance:
-
With a GDP of USD 3.57 trillion (nominal), India's economy is larger than 4 G7 member countries - France, Italy, the UK and Canada.
- According to the IMF, India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world.
- India's abundant young and skilled workforce, coupled with its market potential, low manufacturing costs, and favourable business climate, make it an attractive investment destination.
-
- India's Strategic Importance in the Indo-Pacific:
-
India has emerged as a major strategic partner for the West in containing China's expanding influence, particularly in the Indian Ocean.
-
India's strategic partnerships with the US, UK, France, Germany, and Japan, as well as its rapidly expanding ties with Italy, make it a crucial player in the Indo-Pacific.
-
-
India's Role in Addressing the European Energy Crisis:
- India's ability to secure discounted Russian oil and supply refined fuels to Europe has made it an important player in addressing the European energy crisis.
- The war in Ukraine has caused an energy crisis in Europe as they cut back on Russian energy imports. India has acted as a transit country for Russian oil. This oil is then refined in India and exported to Europe, helping to alleviate the pressure on their economies.
- India's ability to secure discounted Russian oil and supply refined fuels to Europe has made it an important player in addressing the European energy crisis.
- India's Potential for Mediating the Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
- India's long-standing relationships with both Russia and the West position it as a potential mediator in the Ukraine conflict. By leveraging its neutral stance, India could offer a way out for both sides, facilitating dialogue and diplomacy to bring an end to the war.
The Oil Crisis of 1973-74
- About:
- It refers to a period of sudden surge in oil prices, accompanied by a decrease in supply which has destabilised the global economy since oil is a major source of energy for many countries.
- Trigger:
- Yom Kippur War (October 1973): Egypt and Syria launched a surprise attack on Israel. The United States intervened by resupplying the Israeli military during the conflict.
- OPEC's Political Leverage: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), consisting of major oil-producing nations, decided to use oil as a political weapon in response.
- OPEC's Actions:
- Oil Embargo: OPEC, particularly its Arab members, imposed an oil embargo on countries that supported Israel, including the United States and some European nations.
- Production Cuts: OPEC also reduced overall oil production, further tightening the supply.
- Impact:
- Supply Shortage: The embargo and production cuts led to a global oil shortage. Long lines formed at gas stations in many countries, and rationing became necessary.
- Price Hike: With reduced oil availability, prices heavily increased (from USD 3 to USD 11).
- Economic Downturn: Higher oil prices had a cascading effect. Transportation costs increased, raising the prices of goods and services. This fueled inflation and economic stagnation in many countries.
What are the Challenges to India in Balancing Power Conflict Between West and China-Russia?
- Defence Dependence: India's reliance on Russia for over 60% of its military equipment creates a complex situation. A strained West-Russia relationship could disrupt supply chains and force India to diversify its defence partnerships.
- Economic Interdependence: Deepening economic ties with both the US and China expose India to potential decoupling pressures. Balancing trade relations with these competing entities will be crucial.
- Divergent Approaches: Disagreements within the West regarding how to confront Russia and China create uncertainty for India. Aligning with one bloc too closely could alienate the other.
- Domestic Political Turmoil: Internal political divisions in Western democracies could lead to policy inconsistencies, further complicating India's strategic calculations.
- Border Disputes: Unresolved territorial disputes with China, coupled with China's growing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific, will continue to pose a security threat to India.
- Geopolitical Rivalry: The intensifying competition between the US and China in the region could force India to take sides on issues that don't directly align with its national interests.
Conclusion
India's engagement with the G7 is crucial for the grouping to address the economic, geopolitical, and strategic challenges it faces. From its economic prowess and strategic significance in the Indo-Pacific to its role in the European energy crisis and potential for conflict mediation, India's participation in the G7 Summit holds immense value. As the global order continues to evolve, the G7's collaboration with India will be essential in shaping the future of international cooperation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyse the significance of India's engagement with the G7 group of nations. Discuss the key areas of cooperation and the challenges faced by India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The term ‘Intended Nationally Determined Contributions’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2016)
(a) pledges made by the European countries to rehabilitate refugees from the war-affected Middle East
(b) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to combat climate change
(c) capital contributed by the member countries in the establishment of Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
(d) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world regarding Sustainable Development Goals
Answer: (b)
Q. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
- The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2°C or even 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (b)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)
Q. Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)