Indian Economy
Repo Rate Cut and its Implications
For Prelims: Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), Inflation, Personal Income Tax, Repo Rate, Interest Rate, Wholesale Price Index (WPI), M3 Money Supply.
For Mains: Repo rate and its impact on the economy.
Why in News?
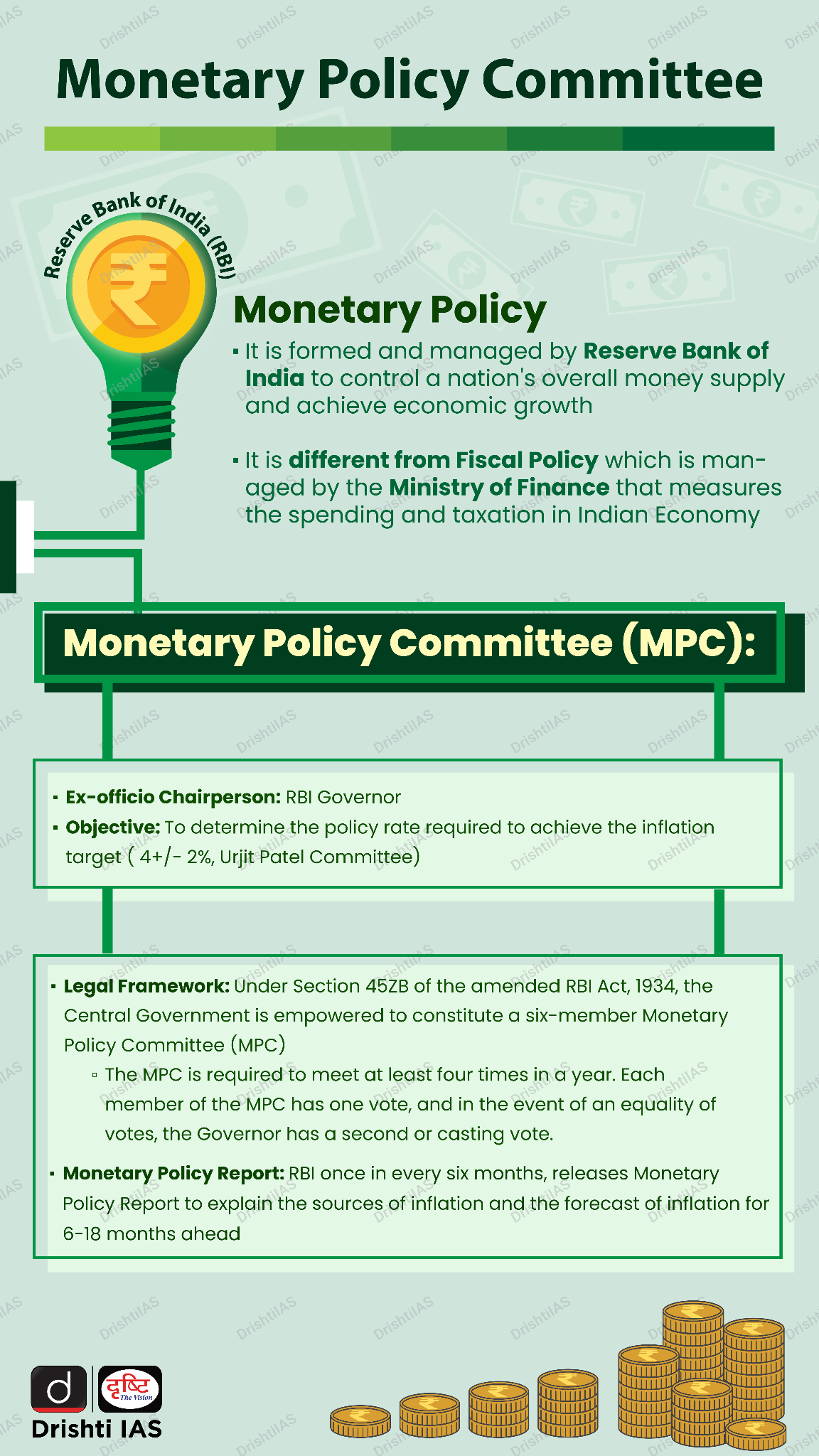
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of Reserve Bank of India cut the repo rate to 6.25% from 6.5% (25 basis points (bps)) for the first time in 5 years (since 2020).
- After the Union Budget 2025-26 reduced personal income tax to spur consumption, this step aims to revive economic growth amid a slowdown.
What Factors Led to RBI's Decision to Cut the Repo Rate?
- Growth-Stimulating Budget: The Union Budget 2025-26 introduced a personal income tax cut and revised TDS limits, increasing disposable income.
- The RBI’s repo rate cut supports the government’s tax reductions by lowering borrowing costs and sustaining demand.
- Declining Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) eased to 5.22% in December 2024, a four-month low, down from 5.48% in November that provides room for monetary easing.
- Market Liquidity Enhancement: The RBI recently introduced measures to improve liquidity in the banking system by injecting Rs 1.5 trillion.
- Liquidity injection eased tight credit markets, while the repo rate cut ensured liquidity and lower rates to boost growth.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: The recent US tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China sparked trade war fears, weakening the rupee to 87.29 per dollar and raising inflation risks.
- A repo rate cut could help cushion the impact of external shocks and support domestic growth.
What is Repo Rate?
- About: Repo rate (Repurchase Agreement Rate) is the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the central bank.
- Purpose & Functioning: It helps banks meet short-term liquidity needs by borrowing funds.
- Banks provide securities as collateral and agree to repurchase them later at a higher price (including interest).
- Impact on Borrowing Costs:
- Higher repo rate → Costlier loans for banks → Higher interest rates for consumers & businesses → Slower borrowing & spending.
- Lower repo rate → Cheaper loans for banks → Lower interest rates for borrowers → Increased borrowing & spending.
- Role in Monetary Policy: It is used by the central bank to control money supply, inflation, and economic growth.
What are the Implications of the Repo Rate Cut?
- Economic Growth: Lower borrowing costs make it easier for businesses to expand and invest, leading to higher production and job creation.
- A repo rate cut reduces interest rates, making loans cheaper, lowering EMIs, and boosting borrowing and spending.
- Strengthening Financial Markets: Banks may reduce interest rates on savings accounts and fixed deposits, making savings less attractive that may drive consumers toward stocks, mutual funds, or real estate.
- Export Competitiveness: A lower repo rate may cut investment returns, leading to capital outflows. This may weaken the currency, raising import costs but enhancing export competitiveness.
- Inflation: Increased spending due to rate cuts may push up prices and inflation over time, breaching the RBI inflation target (4% within a band of +/- 2%)
Background of the 4% Inflation Target
- Chakravarty Committee (1982-85): It was set up by the then RBI Governor Manmohan Singh under Sukhamoy Chakravarty to review monetary policy. Its recommendations included:
- Emphasized price stability as a core objective of monetary policy.
- Proposed 4% average annual inflation in the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to balance economic priorities.
- Recommended market-driven government borrowing and an active government securities market to reduce reliance on RBI funding.
- Advocated monetary targeting (M3 money supply control) to manage inflation.
- M3 = M1 (Currency held by the public+Demand Deposits held by commercial banks)+Net time deposits of commercial banks
- Urjit Patel Committee (2014): It formalized inflation targeting, setting the 4% target (±2% band), a target first proposed by the Chakravarty Committee 40 years ago.
- India's inflation targeting framework, adopted in 2016, aligns India’s monetary policy with global best practices.
Click Here to Read: What is the Consumer Price Index?
Conclusion
The RBI’s repo rate cut aims to boost economic growth by lowering borrowing costs. However, it may lead to inflationary pressures, challenging the 4% target set by RBI MPC. Balancing growth and price stability remains crucial, especially amid global uncertainties.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the impact of repo rate cuts on economic growth and inflation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- The Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do?(2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Define potential GDP and explain its determinants. What are the factors that have been inhibiting India from realizing its potential GDP? (2020)
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments (2019)


Biodiversity & Environment
India’s Shift from Mitigation to Adaptation in Climate Action
For Prelims: Adaptation, Mitigation, Conference of the Parties 29, Nationally Determined Contributions, Paris Agreement, Small Modular Nuclear Reactors
For Mains: India’s Climate Strategy and NDC Commitments, Adaptation vs. Mitigation, Energy Transition
Why in News?
India has signaled a shift in its climate stance by prioritizing adaptation over emission cuts (Mitigation).
- This reflects concerns over global inaction and weak financial commitments at United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties 29 (COP29), further underscored by its likely delay in submitting the 2035 Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Why is India Prioritizing Adaptation Over Mitigation?
- Reevaluation of Global Climate Commitments: The world is not on track to meet its emissions reduction targets for 2030 or 2035 (nations must cut greenhouse gas emissions by 42% by 2030 and 57% by 2035).
- Developed nations have failed to meet their climate finance obligations, with COP29 securing only USD 300 billion per year (starting 2035) instead of the USD 1 trillion demanded by developing nations.
- The withdrawal of the US from the Paris Agreement in 2025 has further weakened global climate action momentum.
- India aims for low-carbon growth at its own pace, with energy transition driven by domestic priorities.
- Immediate and Local Benefits: India argues that global climate targets overlook developing nations' immediate needs.
- Unlike mitigation, which requires global cooperation, adaptation like building climate-resilient infrastructure offers direct, immediate benefits, and local benefits.
- Economic development enhances resilience, making prosperity a key factor in tackling climate change.
- Economic Growth: The Economic Survey 2024-25 suggests that achieving “developed country” status by 2047 should take precedence, allowing for a more robust and sustainable transition to clean energy thereafter.
- India argues that rapid industrialization and economic growth, as seen in China, provide the resources necessary for future decarbonization.
- Flexibility: India is seeking greater autonomy in determining its energy transition pace, rather than adhering to externally imposed targets.
- While decarbonization remains a long-term goal, India is unwilling to compromise economic growth through immediate restrictions on fossil fuel use.
- A bottom-up approach through ground-level initiatives is seen as more effective than top-down mandates.
Adaptation, Mitigation and Resilience
|
Term |
Definition |
Examples of Actions |
|
Mitigation |
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting climate change impacts. |
|
|
Adaptation |
Adjusting to climate change effects to minimize harm or take advantage of benefits. |
|
|
Enhancing the ability to anticipate, prepare for, and respond to climate-related impacts. |
|
How is India Balancing Growth and Clean Energy Transition?
- Low-Carbon Development: Despite resisting strict coal phase-down commitments, India is expanding its renewable energy sector.
- India is on track to meet its 2030 NDC targets: India targets 50% installed electricity capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030, reaching 46.8% as of November 2024.
- India aims to create an additional 2.5-3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) sink through forest expansion by 2030, based on 2005 levels.
- The Forest Survey of India (2024) estimates a carbon sink of 30.43 billion tonnes in 2023, up from 28.14 billion tonnes in 2005, an addition of 2.29 billion tonnes.
- Projections indicate 31.71 billion tonnes by 2030, surpassing the NDC target.
- India targets a 45% reduction in GDP emissions intensity by 2030. As of 2019, it has already achieved a 33% reduction from 2005 levels.
- Solar and wind energy investments remain a priority, with ambitious targets for hydrogen energy development.
- The installed renewable electricity generation capacity is as follows: Solar (20.6%), Wind (10.5%), Hydro (10.3%), and Nuclear (1.8%).
- Domestic Clean Energy: India aims to reduce its dependence on foreign supply chains for clean energy technologies like solar panels, electric batteries, through a new National Manufacturing Mission (announced in Union Budget 2025-26).
- Policies are being designed to support indigenous production of solar cells, wind turbines, and battery storage solutions.
- Developing SMRs: Recognizing its slow progress in nuclear energy, India is now pushing for indigenous Small Modular Nuclear Reactors (SMRs) to enhance energy security.
- Delay in Submitting 2035 NDCs: India has postponed its 2035 climate commitments to later in 2025, likely to negotiate better financial terms at COP30 in Brazil.
- Holding back allows India to adjust its targets based on domestic priorities and global climate finance developments.
Note: NDCs are country-specific climate action plans to cut emissions and adapt to climate change under the Paris Agreement, updated every five years.
- The existing NDCs, submitted in 2020, pertain to the 2030 period, with 2035 submissions by 10th February 2025. The 2035 NDC must build on the 2030 targets, but countries set their own progression based on resources.
How has India’s Role in Global Climate Governance Evolved?
Click Here to Read: India’s Role in Global Climate Governance
What are India’s Key Climate Adaptation Initiatives?
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP): Developed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Focuses on climate resilience across sectors, including agriculture, water management, and urban planning.
- Adaptation in Agriculture: Heat and water stress threaten food security, adaptation measures include:
- Climate-resilient seeds and improved soil health practices.
- Groundwater conservation and modified cropping techniques.
- Urban Climate Resilience: The National Mission on Sustainable Habitat (NMSH) promotes waste and water management and green buildings.
- Coastal Adaptation Measures: Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI) aims to restore 540 sq. km of mangroves across nine coastal states.
- Expected to sequester 4.5 million tons of carbon and create 22.8 million jobs.
- Seawalls, artificial reefs, and dune planting to combat coastal erosion and rising sea levels.
- Water Resource Management: Jal Shakti Abhiyan focuses on rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and afforestation.
- Mission LiFE: Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) is an India-led global initiative, it promotes sustainable living and individual responsibility in climate action, shifting from a "use-and-dispose" mindset to a circular economy.
Way Forward
- Economic Growth with Sustainability: Prioritize industrial growth and job creation while ensuring low-carbon development. Implement sectoral decarbonization plans in steel, cement, and heavy industries.
- Encourage green urban planning for sustainable cities through Smart Cities Mission and smart mobility solutions.
- Develop climate-resilient infrastructure, strengthen disaster preparedness, and expand afforestation for natural carbon sinks.
- Clean Energy Expansion: Expand solar, wind, and green hydrogen investments, enhance battery storage and grid infrastructure, and promote waste-to-energy and biofuels for a diversified clean energy mix.
- Just and Inclusive Transition: Support Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) and fossil fuel workers in transitioning to green jobs while ensuring affordable clean energy access for rural and underprivileged communities.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically examine the impact of India’s shift towards adaptation and economic growth on its development and global climate commitments. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.3 With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)
Q.2 ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How will India be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
PM-JAY’s Impact on Cancer Treatment
Why in News?
A study published in The Lancet highlights a substantial decrease in delays for initiating cancer treatment across India, with a notable 90% improvement among beneficiaries of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY).
What are the Key Findings of the Study on Cancer?
- Improved Timely Initiation of Treatment: 36% overall improvement in timely cancer treatment, with a 90% rise among AB PM-JAY beneficiaries post-2018.
- Treatment delays reduced significantly, especially for reproductive, genitourinary, breast, and blood cancers.
- Demographic Insights: Younger patients (<30 years: 77%) and those with higher education (70.2%) had better access to timely treatment.
- Insurance coverage (69%) improved accessibility, while higher-income groups faced fewer delays.
- Challenges:
- Delayed Diagnosis and Treatment: Study revealed that treatment delays, especially in radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery, reduce survival rates.
- Limited Healthcare Infrastructure: India has only 779 radiotherapy machines, far below the WHO-recommended 1,350–5,000.Shortage of oncologists and diagnostic centers.
- High Financial Burden: High out-of-pocket (OOP) expenses persist as AB-PMJAY excludes diagnostics and follow-ups. Public health spending below 2% of GDP worsens affordability.
Cancer
- About: Cancer refers to a group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled proliferation and spread of abnormal cells in the body, which can infiltrate and harm healthy tissues and organs.
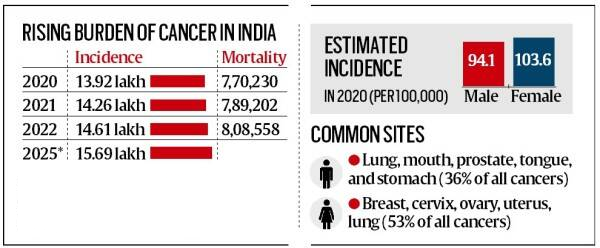
- State of Cancer Burden in India: The cancer cases in the country are projected to increase from 14.6 lakh in 2022 to 15.7 lakh in 2025, as per the Indian Council of Medical Research.
- Breast cancer was the most prevalent, representing 13.6% of all cases and over 26% among women.
- Globally, in 2022, there were an estimated 20 million new cancer cases and 9.7 million deaths.
Click Here to Read: Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) Immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) Construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to the treatment of cancerous tumours, a tool called cyberknife has been making the news. In this context, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2010)
(a) It is a robotic image guided system
(b) It delivers an extremely precise dose of radiation
(c) It has the capability of achieving sub-millimetre accuracy
(d) It can map the spread of tumour in the body
Ans: (d)
Q. ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why? (2019)
- It is used in developing gene-silencing therapies.
- It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer.
- It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies.
- It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1 and 4 only
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Asteroid 2024 YR4
Why in News?
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has identified a near-Earth Asteroid 2024 YR4, which has a slightly over 1% chance of impacting Earth in 2032.
What are the Key Facts About Asteroid 2024 YR4?
- About: The asteroid, detected in December 2024, passed 800,000 km from Earth (twice the Moon’s distance) and remained observable until April 2025, set to reappear in 2028.
- Potential Risk: NASA has classified it as Level 3 on the Torino Scale, indicating a potential for localized destruction if it impacts Earth.
- The Torino Scale, adopted by the IAU (International Astronomical Union) in 1999, categorizes asteroid impact risks on a 0 to 10 scale based on likelihood and severity.
- It can release 8-10 megatons in case of impact, higher than the 2013 Chelyabinsk, Russia meteor (released 500 kilotons of energy— about 30 times more than the Hiroshima atomic bomb).
What are Asteroids?
- About: Asteroids are rocky, airless remnants from the solar system's formation (4.6 billion years ago).
- They primarily orbit the Sun in the Asteroid Belt, though some follow Earth-crossing paths.
- Their sizes vary from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers.
- Categorisation:
- Main Asteroid Belt: Located between Mars and Jupiter, this region contains the majority of known asteroids.
- Trojans: These asteroids share an orbit with a larger planet and remain near Lagrangian points (L4 and L5), where gravitational forces of the Sun and the planet balance, preventing collisions.
- Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs): These asteroids have orbits that bring them close to Earth. Those that intersect Earth's orbit are specifically termed Earth-crossers.
- Asteroid Collision Frequency: Small asteroids frequently burn up in the atmosphere.
- Larger asteroids occasionally reach the surface but rarely cause significant damage. Global-scale impacts, like the Chicxulub event in Mexico that led to the extinction of dinosaurs and 75% of Earth's species, occur approximately once every 260 million years.
- Planetary Defense Against Asteroids: NASA and other space agencies are developing planetary defense mechanisms to prevent asteroid collisions.
- NASA’s DART mission (2022) successfully altered the trajectory of asteroid Dimorphous, showcasing the potential for deflection strategies to mitigate future threats.
Initiatives Related to Monitoring of Near-Earth Objects:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. What is the difference between asteroids and comets? (2011)
- Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are formed of frozen gases held together by rocky and metallic material.
- Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and Mercury.
- Comets show a perceptible glowing tail, while asteroids do not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Rapid Fire
Sahitya Akademi Award 2024
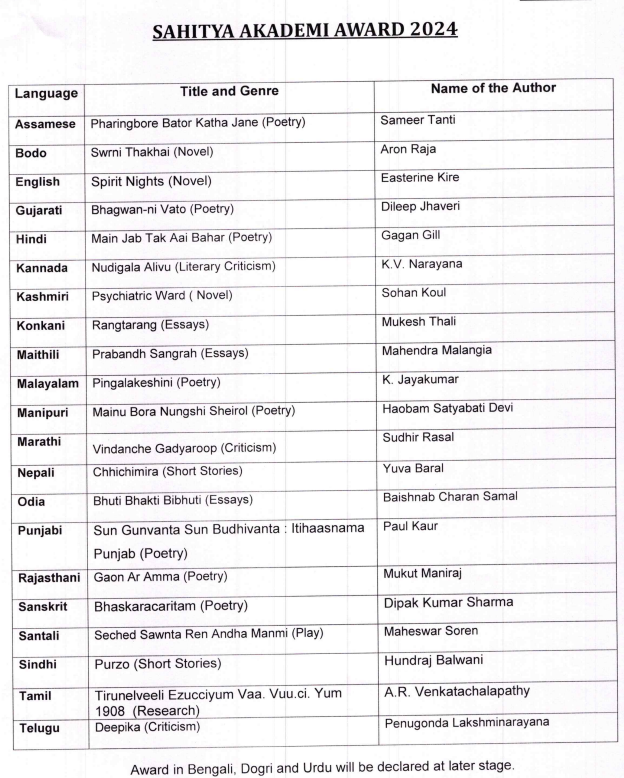
The Sahitya Akademi Awards 2024 have announced 22 winners, with Bengali and Urdu awards pending, bringing the total to 24.
- About: The Sahitya Akademi Awards honor exceptional literary contributions in categories like novels, poetry, essays, and plays.
- It is the 2nd-highest literary honor in India, after the Jnanpith Award.
- It was established in 1954 as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Culture.
- Eligibility: Award categories include works in 22 languages of the Eighth Schedule, along with English and Rajasthani (total: 24 languages), and translations of Indian literary works.
- The author must be an Indian citizen.
- Recipients:
- Other Sahitya Akademi Awards: Bal Sahitya Puraskar for children’s literature and Yuva Puraskar for works by authors under the age of 35.
- Other Initiatives: The Akademi also runs programs like Gramalok (for remote writers) and Dalit Chetna (for Dalit writers).
Read More: Sahitya Akademi Awards 2023


Rapid Fire
Beggar-thy-Neighbour Policy
The US imposed tariffs on imports from China, Canada and Mexico as part of Beggar-thy-neighbour policy.
- About Beggar-thy-Neighbour Policy: It is a protectionist strategy that involves measures like trade barriers, currency devaluation, and subsidies, to improve its own economic situation at the expense of other nations.
- Origins: Adam Smith coined the term in The Wealth of Nations (1776), criticizing mercantilism that impoverishes others and advocating free trade for all nations' benefit.
- Supporters’ Arguments: Help boost the domestic economy by protecting important industries and jobs.
- Currency devaluation can reduce export costs and increase import prices, possibly resulting in a trade surplus.
- Critics’ Arguments: Countries imposing such policies often face retaliatory tariffs, leading to a decline in global trade and investment. E.g., the Great Depression (1929-39).
- Benefit domestic producers but harm consumers due to higher prices from reduced foreign competition.
- Alternative View: Countries should refrain from retaliating and instead adopt unilateral free trade.
Read More: Trade War


Rapid Fire
SARAT Version 2
The Ministry of Earth Sciences launched SARAT (Search and Rescue Aid Tool) Version 2 to enhance search-and-rescue efficiency in the Indian Ocean.
- Key Enhancements: More accurate search areas, enhanced data visualization, and future upgrades (e.g., surface current and wind prediction accuracy).
- About SARAT: It is a satellite-based distress alert system aiding vessels, aircraft, and individuals in remote or high-risk areas at sea.
- Developed by: ESSO-INCOIS under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) as part of the Make in India initiative.
- Key Features:
- Customizable Tracking: Tracks 60 object types, including people, rafts, boats, and aircraft.
- Accurate Predictions: Forecasts search areas up to 10 days using wind, currents, and drifting buoys.
- User-Friendly Interface: Interactive maps, SMS/email alerts, and local language support for fishermen.
- INCOIS, a top tsunami service provider recognized by UNESCO, specializes in ocean disaster management and early warnings.
- INCOIS won the Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar 2025 (Institutional Category) for excellence in disaster management.
Read More: SC Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar 2025 to INCOIS


Rapid Fire
Polar Bear Sebum Sustainable Alternative to Forever Chemicals
A study published in Science Advances, reveals that polar bear fur contains an oily substance called sebum with anti-icing properties, which could provide a natural alternative to harmful ‘forever chemicals’ like Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
- Study Focus: Researchers tested the resistance of polar bear fur and human hair to ice, finding that sebum in the fur has unique properties, lacking squalene (organic compound) found in human sebum.
- Sebum Properties: Polar bear fur sebum helps keep them dry and enables them to slide on ice and dive into water, which is similar to fluorinated ski skins used for ice resistance, but without the harmful PFAs.
- PFAS: Group of forever chemicals that are resistant to water, oil, grease, and heat.
- Health Concerns: PFAS, widely used in cookware, food packaging, and food processing, do not degrade in the environment and pose serious health risks.
- Potential Applications: The study suggests that the properties of sebum could be used to create naturally sourced coatings, reducing reliance on PFAs and offering a more environmentally friendly solution.
Read more: Forever Chemicals