Indian Economy
Union Budget 2025-26 Measures to Boost MSMEs
- 07 Feb 2025
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, Udyam portal, Stand-Up India, Make in India, Gross Value Added, Export Factoring, Self-Reliant India Fund
For Mains: Role of MSMEs in India’s economic growth, Challenges and opportunities for MSMEs, Make in India
Why in News?
The Union Budget for 2025-26 has introduced a series of significant measures to enhance the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector, recognising its vital role in driving India's economic growth.
What are the Key Budgetary Measures for MSMEs?
- Increased Investment and Turnover Limits: Investment limits raised by 2.5 times and turnover limits by 2 times to allow MSMEs to scale operations and adopt better technology.
- This will enable more businesses to qualify as MSMEs and avail government incentives.
- Enhanced Credit Availability: Credit guarantee cover increased from Rs 5 crore to Rs 10 crore for micro and small enterprises, unlocking Rs 1.5 lakh crore in additional credit over five years.
- Startups’ guarantee cover doubled from Rs 10 crore to Rs 20 crore, with a reduced fee of 1% for loans in 27 priority sectors.
- Exporter MSMEs eligible for Rs 20 crore term loans with enhanced guarantee cover, encouraging international trade.
- MSME Credit Cards: The 2025 budget introduces MSME credit cards to boost growth and streamline loan access, with experts urging reduced bureaucratic hurdles.
- Rs 5 lakh credit facility will be provided for micro-enterprises registered on the Udyam portal, with 10 lakh cards to be issued in the first year.
- Support for Startups: A new Fund of Funds with Rs 10,000 crore will be established to expand support for startups.
- Scheme for First-time Entrepreneurs: A new scheme aimed at empowering 5 lakh first-time entrepreneurs from women, Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- This initiative will offer term loans up to Rs 2 crore over the next five years.
- Drawing inspiration from the Stand-Up India scheme, the scheme will also include online capacity-building programs to enhance entrepreneurial and managerial skills.
- National Manufacturing Mission (NMM): The NMM, announced in Budget 2025-26, supports Make in India with a focus on clean tech manufacturing, including solar photovoltaic (PV) cells, Electric Vehicles batteries, wind turbines, and transmission equipment.
- It aims to boost domestic value addition and reduce reliance on Chinese imports.
- Labour-Intensive Sector Support:
- Focus Product Scheme: Supports design, component manufacturing, and non-leather footwear production, expected to create 22 lakh jobs and generate Rs 4 lakh crore turnover.
- Toy Sector: A new Scheme for the Toy Sector will promote cluster development and skill-building, aiming to position India as a global toy manufacturing hub.
- Food Processing: Establishment of a National Institute of Food Technology in Bihar to boost Eastern India’s food industries.
- Cross-Border Factoring: The government aims to scale cross-border factoring services to reach about 3% of India’s merchandise exports, aligning with the global average.
- This will help MSMEs access financing through export factoring, thereby improving cash flow and reducing financial strain.
- Export factoring is a financing method where exporters sell their receivables to a third party (factor) at a discount in exchange for immediate payment, reducing bank dependence and aiding growth.
- This will help MSMEs access financing through export factoring, thereby improving cash flow and reducing financial strain.
What is the Current Landscape of MSMEs in India?
- Employment: MSMEs employ over 25.18 crore individuals in India and play a pivotal role in economic growth and job creation.
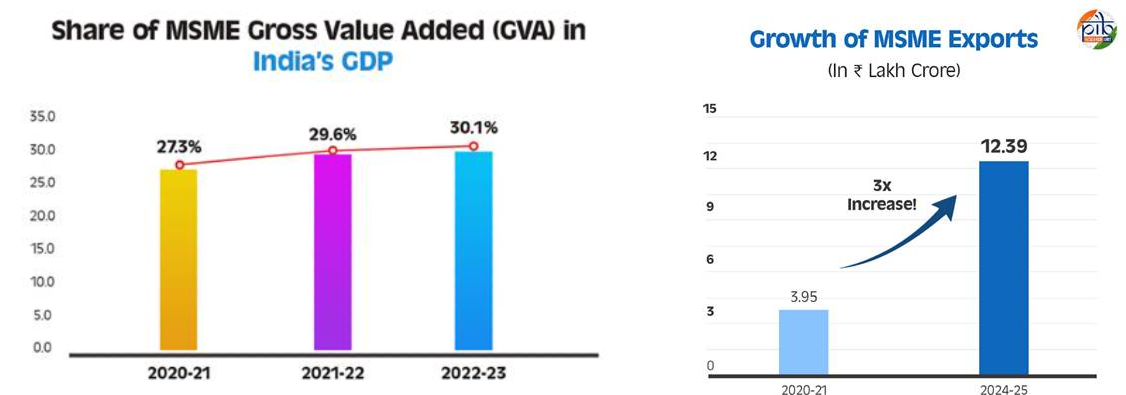
- Economic Contribution: The share of MSMEs in India’s Gross Value Added (GVA) has grown from 27.3% in 2020-21 to 30.1% in 2022-23, highlighting its growing importance in national economic output.
- Export Growth: Exports from MSMEs increased from Rs 3.95 lakh crore in 2020-21 to Rs 12.39 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- The number of exporting MSMEs surged from 52,849 in 2020-21 to 1,73,350 in 2024-25.
- The contribution of MSMEs to India's overall exports has steadily risen. MSMEs accounted for 43.59% of total exports in 2022-23, 45.73% in 2023-24, and 45.79% in 2024-25 (up to May 2024).
What are the Challenges Faced by MSMEs in India?
- Labour Issues: Labour-related issues, such as the absence of well-defined trial periods for new hires, an unskilled workforce, wage disparities across states, and inefficient training centres, hinder MSME growth and productivity.
- Lack of Clarity: There is a lack of awareness and confusion about various government schemes, coupled with poor coordination between the Centre and State, hindering MSMEs from fully benefiting from them.
- Export Issues: MSMEs struggle with inadequate export infrastructure and face challenges due to the lack of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reports, which negatively impacts their competitiveness in global markets.
- Formalisation and Inclusion Despite efforts like the Udyam Registration Portal, the formalisation of informal micro-enterprises is a significant challenge, as many do not have Permanent Account Number (PAN) or Goods and Services Tax (GST), limiting their access to government benefits.
- Regulatory Burden: MSMEs are burdened with complex licensing, inspection, and compliance requirements imposed by various government levels, making it particularly challenging for smaller businesses to meet regulations.
What are the Government Initiatives for MSMEs?
- PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- Udyam Assist Platform
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
- Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund
- MSME Samadhan
- CHAMPIONS Portal
- MSE-CDP (Cluster Development Programme)
- Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
- Government e-Marketplace
- Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS)
- Public Procurement Policy for MSEs: 25% of annual procurement by Central Ministries and CPSEs must be sourced from MSEs.
- 4% reserved for SC/ST-owned MSEs, 3% for women-owned MSEs.
- In 2023-24, Rs 74,717 crore worth of goods/services procured from MSEs, 43.71% of total procurement.
Way Forward
- Simplifying Regulations: A reduction in the regulatory burden (deregulation) is crucial for improving MSME productivity. Efforts should focus on creating a business-friendly environment that encourages innovation and scaling.
- Continued Support for Financing: Increasing access to funding through platforms like the SRI Fund and expanding the reach of MSME-focused initiatives will be key to unlocking the sector's potential.
- Technology and Skill Development: Ongoing efforts to upgrade technology and enhance skills will help MSMEs adapt to global standards and boost their competitiveness.
- Improving Market Access: Promote market awareness and standardization of products to increase market access of MSMEs. Also, work on reducing tariff and non-tariff barriers through trade agreements.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:(PYQ)
Prelims:
Q1. What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2. Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q3. Consider the following statements with reference to India : (2023)
- According to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between `15 crore and `25 crore.
- All bank loans to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)