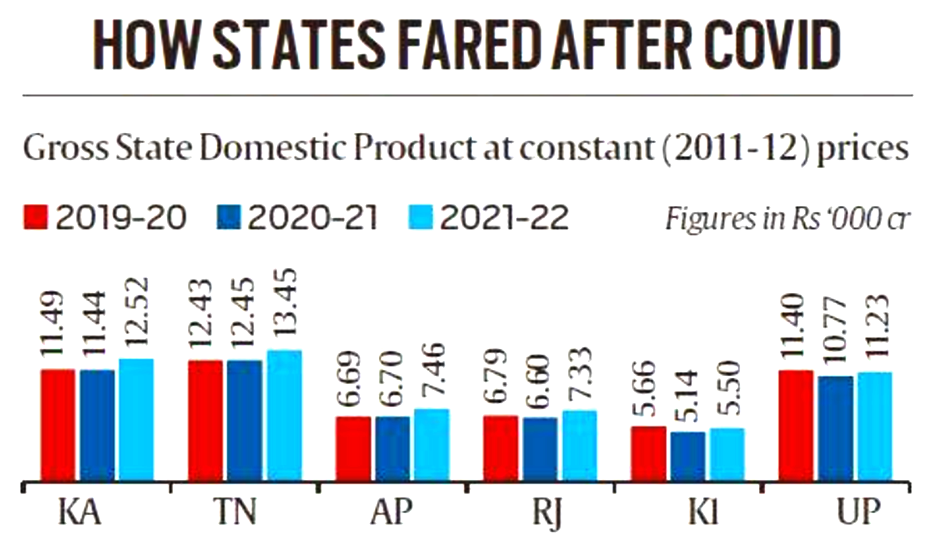
Gross State Domestic Product
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has released figures for the Gross State Domestic Products.
- The economies of 19 states and Union Territories exceeded their pre-Covid levels, with 7 recording double-digit growth rates during 2021-22.
- The growth rates of 11 states including Gujarat and Maharashtra were not available for 2021-22.
What are the Key Findings?
- Size of the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of the 19 states and UTs had contracted or recorded a negligible growth during 2020-21 — the year when the government had imposed a nationwide lockdown in view of the Covid-19 outbreak.
- These 19 states and UTs are Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, Telangana, Delhi, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Tripura, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Jharkhand, Tamil Nadu, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Uttarakhand and Puducherry.
- Their economies (GSDP) bounced back in 2021-22 and exceeded their pre-Covid (2019-20) levels.
- Kerala and Uttar Pradesh are the only exceptions in 2021-22 which recorded GSDP below the pre-Covid levels.
- Andhra recorded the highest growth of 11.43%, Puducherry recorded the lowest at 3.31%.
- Besides Andhra Pradesh, five other states and one UT recorded double digit growth in 2021-22:
- Rajasthan: 11.04%
- Bihar: 10.98%
- Telangana: 10.88%
- Odisha: 10.19%
- Madhya Pradesh: 10.12%
- Delhi: 10.23%
- Sharp jump in the GSDP of some states is due to the base effect, the general trend mirrors the post-pandemic economic recovery.
- In 2021-22, India’s GDP expanded at 8.7% against a 6.6% contraction in 2020-21.
What is Gross State Domestic Product?
- About:
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is a measure in monetary terms, the sum total volume of all finished goods and services produced during a given period of time, usually a year, within the geographical boundaries of the State, accounted without duplication.
- Significance:
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) or State Income is the most important indicator for measuring the economic growth of a State.
- These estimates of the economy, over a period of time, reveal the extent and direction of the changes in the levels of economic development.
- The State Domestic Product is classified under three broad sectors such as Primary sector, Secondary sector and Tertiary sector and is compiled economic activity wise as per the methodology prescribed by the National Accounts Division, National Statistical Office, Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation, Govt. of India.
- In 2015, NSO introduced the new series of national accounts statistics with base year 2011-12, replacing the previous series with base year 2004-05.
- Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) or State Income is the most important indicator for measuring the economic growth of a State.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2015)
- The rate of growth of Real Gross Domestic Product has steadily increased in the last decade.
- The Gross Domestic Product at market prices (in rupees) has steadily increased in the last decade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the monetary value of all the final goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period, generally 1 year. It is a broad measurement of a nation’s overall economic activity.
- Real Gross Domestic Product is an inflation-adjusted measure that reflects the value of all goods and services produced by an economy in a given year, expressed in base-year prices.
- The rate of growth of real GDP has not steadily increased in the last decade. It has fluctuated due to various international and domestic economic pressures. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The GDP at market prices of India has steadily increased in the last decade from around 900 billion USD in 2005 to 2.1 trillion USD in 2015. As of 2020 India’s GDP is 2.63 trillion USD. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.