Science & Technology
Impact of Space Missions on Indian Economy
For Prelims: Indian Space Policy 2023, NewSpace India Limited, IN-SPACe, Department of Space, ISRO
For Mains: Indian Space Policy 2023, Significance of Private Sector, Gaps in the Policy, Key Amendments in FDI Policy Related to the Space Sector
Why in News?
A recent study, commissioned by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in collaboration with the European space consultancy, Novaspace, has revealed that ISRO's space missions have resulted in employment opportunities for lakhs of people besides developing support systems for fishermen, agriculture, crop forecasting, natural resource planning, and disaster avoidance.
How ISRO’s Space Programmes and Investments in the Space Sector have Benefited Society?
- Employment Generation: ISRO has created numerous jobs, directly employing scientists, engineers, and technicians, and indirectly generating opportunities in related industries, such as satellite manufacturing and data analysis.
- Other Economic Benefits: As per the ISRO estimates, investing in the space missions have yielded a return of approximately 2.54 times the amount spent.
- A report by Novaspace reveals that between 2014 and 2024, the Indian space sector has generated USD 60 billion for the national economy, created 4.7 million jobs, and contributed USD 24 billion in tax revenues.
- ISRO’s satellites enhance communication, weather forecasting, and navigation, benefiting various sectors and boosting economic productivity.
- Agricultural Development: ISRO's Earth Observation Satellites, like Resourcesat and Cartosat, enhance agricultural development by monitoring crop health, soil moisture, and land use, helping farmers make informed decisions and improve productivity.
- Disaster Management and Resource Planning: Satellites provide critical data for disaster management, enabling timely response to natural calamities. They also assist in monitoring natural resources, supporting sustainable management and agricultural planning.
- ISRO has helped around 8 lakh fisher folk daily and 1.4 billion Indians get the benefit of satellite-based weather forecasts.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: High-resolution satellite imagery aids in urban mapping, traffic management, and infrastructure monitoring. This data allows cities to optimise land use and improve public services, contributing to sustainable urban development.
- Inspiring Youth and Education: ISRO’s achievements, like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan, inspire students and promote careers in STEM fields. Educational initiatives related to space technology further stimulate interest in science and technology.
- Lunar Exploration and Scientific Advancement: The Chandrayaan missions have advanced lunar exploration and demonstrated India’s capabilities in space science, fostering national pride and contributing to global space exploration efforts.
- International Collaboration and Soft Power: ISRO's success in launching over 300 foreign satellites has established it as a global space technology leader, boosting India's international reputation and soft power while fostering global collaborations.
- ISRO’s low-cost approach to space missions, such as Mangalyaan, makes India an attractive partner for international collaborations.
- The growth of space-related startups fosters innovation and contributes to economic development.
What is India's Current Position in the Space Sector?
- As of 2024, the Indian space economy is valued at around Rs 6,700 crore (USD 8.4 billion), contributing 2%-3% of the global space economy which is expected to reach USD 13 Bn by 2025 at Compound annual growth (CAGR) of 6%.
- As per the new estimates by ISRO, the gross value added by the Indian space sector between 2014 and 2023 was USD 60 billion, and in the next 10 years it can go up to USD 89 billion to USD 131 billion.
- India aims to capture a 10% share of the global economy by the next decade.
- ISRO is the sixth largest space agency in the world and has a high success rate of launch missions.
- US’ NASA, China National Space Administration (CNSA), European Space Agency (ESA), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) are among the other five major space agencies.
- India has over 400 private space companies. The number of startups in India's space sector has surged from 54 in 2020, coinciding with the establishment of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe), to over 200 currently.
Amended FDI Policy for the Space Sector
- About:
- Recently, the government has made amendments in the FDI policy pertaining to the space industry.
- It aims to align with the Indian Space Policy 2023, which seeks to unlock the nation's potential in the space domain through enhanced private participation.
- Amendments in FDI Policy for Space Sector:
- 100% FDI Allowed: After the recent amendment, 100% FDI is permitted in the space sector, aiming to attract potential investors to Indian space companies.
- Liberalised Entry Routes: The entry routes for various space activities are as follows:
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Satellites-Manufacturing & Operation, Satellite Data Products, Ground Segment & User Segment.
- Beyond 74%, the government route applies.
- Up to 49% under Automatic Route: Launch Vehicles, associated systems or subsystems, Creation of Spaceports.
- Beyond 49%, the government route applies.
- Up to 100% under Automatic Route: Manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems for satellites, ground segment, and user segment.
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Satellites-Manufacturing & Operation, Satellite Data Products, Ground Segment & User Segment.
What is the Indian Space Policy 2023?
- Transition of ISRO's Role: The Indian Space Policy 2023 divides the responsibilities of space activities (traditionally managed by ISRO) among the following entities:
- ISRO: ISRO is directed to shift its focus from routine tasks to research and innovation, developing advanced space technologies to maintain India's leadership in space infrastructure, transportation, applications, capacity building, and human spaceflight.
- ISRO has announced its vision to increase India's share in the global space economy from approximately 2% to 10% by 2034.
- InSPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre): Acts as the single-window agency for authorising space activities and promoting industry-academia collaboration.
- New Space India Limited (NSIL): It has been tasked with commercialising space technologies and platforms, manufacturing, leasing, or procuring space components, and servicing space-based needs on commercial principles.
- Department of Space: Implements the policy, ensures safe space operations, and coordinates international cooperation.
- ISRO: ISRO is directed to shift its focus from routine tasks to research and innovation, developing advanced space technologies to maintain India's leadership in space infrastructure, transportation, applications, capacity building, and human spaceflight.
- Private Participation Encouragement: Private companies, termed non-governmental entities were allowed to engage in end-to-end space activities, including launching and operating satellites, developing rockets, building spaceports, and offering services like communication, remote sensing, and navigation both domestically and internationally.
Major Developments in the Space Sector in India
How can India Increase the Share of the Space Sector in the Economy?
- Skill Development: Investing in space-related education and training programs is essential to build a highly skilled workforce capable of driving innovative space projects.
- Establishing Space Technology Incubation Centres can help nurturing talent and fostering advanced research.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading space launch facilities and research centres will provide the necessary infrastructure to support more ambitious and large-scale space missions.
- The development of the Virtual Launch Control Center (VLCC) at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre is a step in the right direction, enhancing operational capabilities.
- Government-Industry Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships between government agencies and private enterprises can leverage the strengths of both sectors. Collaborative efforts can accelerate advancements in space exploration and technology, driving innovation and expanding capabilities.
- Promotion of Indigenous Technologies: Encouraging the development of homegrown technologies will foster self-reliance and reduce dependence on external sources for space hardware. Investing in indigenous research and manufacturing will enhance India's capacity to design and produce advanced space technologies.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the Private Sector in Space Economy as a major driver of growth in the Indian space sector. How can India leverage its strengths to become a global leader in this field? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Biodiversity & Environment
National Glacial Lake Outburst Floods Risk Mitigation Programme
For Prelims: Tawang, Dibang Valley, National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOFs), South Lhonak Lake, Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Indian Meteorological Department, Landslides, Yarlung Zangbo River, Lake Lowering, Ground Truthing, Thyanbo Glacial Lake, Flash Floods, International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), Hindu Kush Himalayas.
For Mains: Impact of Climate Change on Glacial Lakes and their Consequences.
Why in News?
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has taken up expeditions to glaciers at an altitude of 4500m and above to map their vulnerability to Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF).
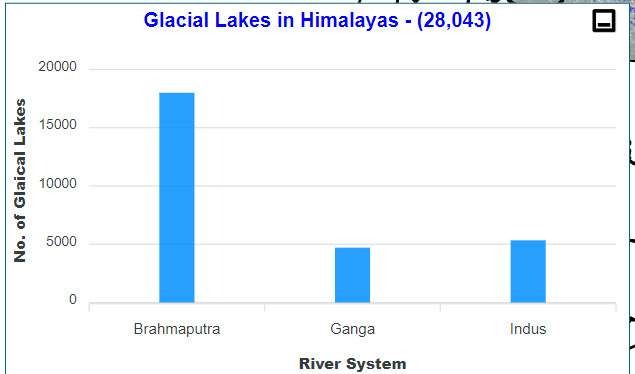
- Of the nearly 7,500 glacial lakes in the Indian Himalayas, NDMA has finalised 189 high-risk lakes that require mitigation measures.
What is the National Glacial Lake Outburst Floods Risk Mitigation Programme (NGRMP)?
- About: It is an initiative launched by the Government of India to address the risks posed by GLOFs.
- 16 teams went out for expedition out of which 15 teams completed their expedition. Another seven expeditions are underway.
- Of the 15 expeditions completed, 6 were in Sikkim, 6 in Ladakh, 1 in Himachal Pradesh, and 2 in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Teams on expeditions assess the structural stability and potential breach points of glacial lakes, gathering relevant hydrological and geological samples and data, measuring water quality and flow rates, identifying risk zones and making downstream communities aware.
- 16 teams went out for expedition out of which 15 teams completed their expedition. Another seven expeditions are underway.
- Objective:
- To assess hazards, install automated monitoring and early warning systems, and implement lake-lowering measures to mitigate glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) risks.
- Lake-lowering measures are techniques used to reduce the volume of water in a glacial lake to mitigate the risk of a GLOF.
- NDMA is focussing on ground-truthing of selected 189 “high-risk” glacial lakes.
- Ground-truthing is the process of validating and verifying data collected through remote sensing or other indirect methods by comparing it with direct observations made on-site.
- To assess hazards, install automated monitoring and early warning systems, and implement lake-lowering measures to mitigate glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) risks.
- Methodology to Prevent GLOF: Three activities are planned to be executed simultaneously.
- Placement of automated weather and water level monitoring stations and early warning systems
- Digital elevation modelling and bathymetry.
- Assessing best means to reduce the risk of that lake including by lake-lowering.
- Need of the Study:
- ICIMOD Findings: As per the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), Hindu Kush Himalayas are experiencing rapid, irreversible changes due to climate change, increasing the risk of floods and landslides.
- Climate Change: Due to climate change, India faces hazards like extreme altered FDI (frequency, duration and intensity) of precipitation and extreme heat. It may lead to an increased number of flash floods.
- Previous Incidents of GLOFs:
- Nepal Incident: Recently, flash floods struck Thame, a village in the Khumbu region of Nepal which was due to an outburst flood from Thyanbo glacial lake.
- Sikkim Flash Flood: A catastrophic GLOF occured in South Lhonak Lake, Sikkim, in October 2023.
- Uttarakhand Flash Floods: A glacier breach-induced flood in February 2021 in Rishi Ganga valley resulted in over 200 deaths and significant damage to hydropower plants and Raini village.
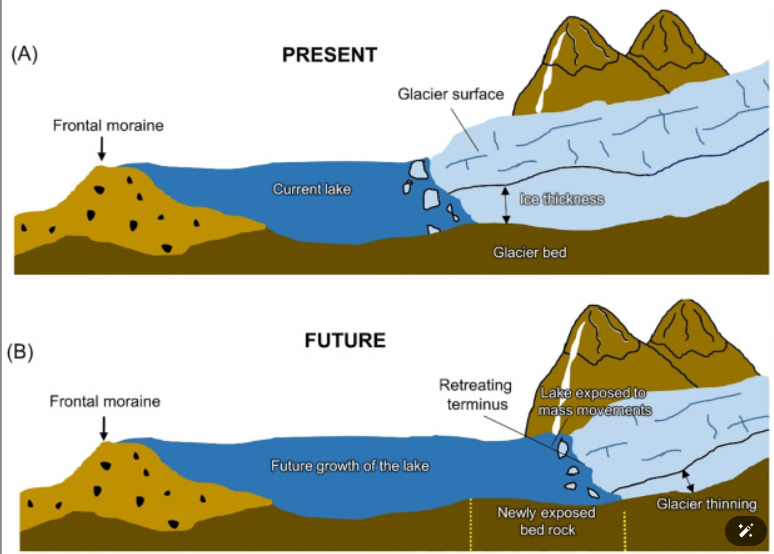
GLOF
- A GLOF is a type of flood occurring when water dammed by a glacier or a moraine is released suddenly.
- When glaciers melt, the water in these glacial lakes accumulates behind loose naturally formed 'glacial/moraine dams' made of ice, sand, pebbles and ice residue.
- Unlike earthen dams, the weak structure of the moraine dam leads to the abrupt failure of the moraine dam on top of the glacial lake, which holds a large volume of water.
- A catastrophic failure of the dam can release the water over periods of minutes to days causing extreme downstream flooding.
What are the Recent Developments in NGRMP?
- About: The Arunachal Pradesh State Disaster Management Authority (APSDMA) to carry out a survey of high-risk glacial lakes in the Tawang and Dibang Valley districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is part of the larger National Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) Mission of the NDMA to map all glacial lakes in the country.
- High-Risk Glacial Lakes Identified in Arunachal Pradesh:
- Total High-Risk Lakes: 27 high-risk glacial lakes have been identified across five districts in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The lakes are located in Tawang (6 lakes), Kurung Kumey (1), Shi Yomi (1), Dibang Valley (16), and Anjaw (3).
- The current expedition teams will focus on three high-risk lakes in each of the Tawang and Dibang Valley districts.
- Total High-Risk Lakes: 27 high-risk glacial lakes have been identified across five districts in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Study Objectives: The team will study the accessibility, location, size, elevation, nearby habitations, and land use of the lakes at risk of GLOF.
- This will help the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and the Indian Meteorological Department install an Automatic Early Warning System and an Automatic Weather Station.
- Significance of the Study:
-
Strategic Location: Both Tawang and Dibang Valley districts share borders with China. It will be closely watched given its strategic location.
-
Fragile Himalayan Ecosystem: Landslides on the Chinese side, caused by China's interference with Himalayan geology and river systems, could also occur on the Indian side of the border.
-
Threat of Floods: In 2018, the Arunachal and Assam governments issued flood alerts after China reported a landslide blockage at the Yarlung Zangbo River.
- Heavy Infrastructure: The mega dam being built by China on the Yarlung Tsangpo river in Medog near the international border has been a constant worry over fear of adverse impact right from Arunachal to Assam.
-
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. How Himalayas and glacial lakes are increasingly becoming vulnerable to climate change? What steps are being taken to mitigate risks like Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following pairs (2019)
Glacier - River
- Bandarpunch : Yamuna
- Bara Shigri : Chenab
- Milam : Mandakini
- Siachen : Nubra
- Zemu : Manas
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 2 and 5
(d) 3 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2010)
- On the planet Earth, the fresh water available for use amounts to about less than 1% of the total water found.
- Of the total fresh water found on the planet Earth 95% is bound up in polar ice caps and glaciers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With reference to National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines, discuss the measures to be adopted to mitigate the impact of the recent incidents of cloudburst in many places of Uttarakhand. (2016)
Indian Economy
CBDT to Overhaul Income Tax Act 1961
For Prelims: Direct tax, Central Board of Direct Taxes, Income Tax Act, 1961, Vivad Se Vishwas, Angel tax, Capital gains
For Mains: Reforms, Issues in the Taxation system in India, Indian Economy and issues relating to Policies, Changes in the Tax Regime
Why in News?
The Income Tax Department is undertaking a significant overhaul of the Income Tax Act, 1961, through a newly formed internal committee.
- This move, announced by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) chairman, is part of a central government-mandated initiative aimed at simplifying and modernizing India's direct tax laws.
Why is the Income Tax Act Being Reviewed?
- Historical Complexity: The Income Tax Act, 1961, has been criticized for its complexity and outdated provisions.
- Previous efforts to simplify the Act, including the 1958 Law Commission’s work on the Income Tax Act 1922, highlighted that true simplification requires overhauling the tax structure itself.
- Need for Modernization: The Act’s complexity has led to disputes and confusion among taxpayers. The review aims to update the law to reflect current economic realities and global best practices, making it more transparent and easier to navigate.
- Improvement of Compliance: Simplifying the tax law is expected to enhance taxpayer compliance by reducing ambiguities and making the filing process more straightforward.
- The review is part of a broader effort to make the tax system more efficient and in line with global standards.
- Dispute Resolution: The Vivad Se Vishwas scheme has been implemented to settle long-standing disputes.
- The review will also consider shortening the reassessment period and setting higher monetary thresholds to reduce confrontations between taxpayers and the tax department.
What are the Key Aspects of the Income Tax Act, 1961?
- About: The Income Tax Act of 1961 is a foundational statute governing income taxation in India. As a comprehensive framework, it dictates how income tax is levied, administered, and collected from individuals and corporations.
- It contains 298 sections, 23 chapters and several important provisions which contain all the aspects of taxation in India.
- Income tax is a direct tax that individuals are required to bear, without the option to transfer it.
- Objectives:
- Economic Stability: The Act aims to maintain economic stability by regulating private spending and ensuring progressive taxation.
- Progressive Taxation: It seeks to ensure that individuals contribute to taxes according to their income levels, promoting fairness and equity in the tax system.
- Revenue Collection: By outlining clear rules for taxing income from various sources, the Act helps in efficient revenue collection and management.
- Key Provisions:
- Tax Slabs: Defines income brackets and the corresponding tax rates applicable to individuals and businesses.
- Deductions: Allows for deductions under sections such as 80C (investments), 80D (medical insurance premiums), and 80G (donations), subject to annual limits.
- Assessment: Details the procedures for assessing taxable income, filing returns, and conducting audits.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): Requires tax to be deducted at the source for certain payments, simplifying the tax collection process.
- Capital Gains: Regulates taxation on profits from the sale of assets, including provisions for short-term and long-term gains.
- Penalties and Appeals: Outlines penalties for non-compliance and the procedures for resolving disputes through appeals.
- Key Recent Reforms:
-
Corporate Tax Rates: Recent reforms have included reducing corporate tax rates and phasing out certain incentives.
-
The effective tax rate for corporate taxpayers decreased from 29.49% in 2017-18 to 23.26% in 2021-22. The corporate tax rate for foreign companies has also been reduced to 35%, and the angel tax has been abolished.
-
-
Personal Income Tax Slabs: Fewer income-tax slabs and reduced rates for lower-income groups are expected to benefit a large number of individual taxpayers.
- Simplification of Tax Slabs has led to an increase in the number of taxpayers, from 89.8 million to 93.7 million between 2019-20 and 2022-23.
-
What are the Expected Benefits of the Overhaul of Income Tax Act, 1961?
- Conciseness and Clarity: The revised Act will be more concise, making it easier to understand and navigate.
- By eliminating redundant and outdated clauses, the Act will become less cumbersome, reducing the administrative burden on taxpayers and tax authorities.
- Enhanced Taxpayer Experience: A more straightforward tax law will reduce ambiguity and make it easier for taxpayers to navigate the system, fostering trust and compliance.
- Capital Gains Tax Reform: The government plans to reform the capital gains regime, aligning with global trends.
- This includes increasing taxes on equity capital gains and raising the securities transactions tax on futures and options. The reform aims to balance the tax burden between different asset classes and income groups.
- Broader Tax Base: Simplified compliance procedures and clearer regulations may lead to higher tax compliance and broaden the tax base.
- With better enforcement and reduced loopholes, the government expects to boost revenue collection despite potential reductions in tax rates or exemptions.
- Improved Business Environment: A more transparent and predictable tax regime will make India a more attractive destination for foreign and domestic investors.
- Adjustments to corporate and capital gains tax rates can be designed to foster investment and economic growth.
- Long-Term Economic Benefits: A modernized tax system will support economic growth and stability, contributing to India’s goal of achieving developed country status by 2047.
- Streamlined processes and clearer regulations will enhance the overall efficiency of the tax administration and reduce the cost of compliance.
What are the Key Facts About the Central Board of Direct Taxes?
- Historical Background: The origins of the CBDT trace back to the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1924, which initially established the Central Board of Revenue responsible for both direct and indirect taxes.
-
The administrative burden of managing both direct and indirect taxes led to the bifurcation of the Board in 1964.
-
This split created two distinct bodies: the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) for direct taxes and the Central Board of Excise and Customs for indirect taxes.
-
This restructuring was formalised under the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963.
-
- It is a part of the Department of Revenue within the Ministry of Finance, the CBDT plays a crucial role in managing direct taxes in India.
-
- Structure: The CBDT is headed by a Chairman, who coordinates the functions of the Board.
-
The Board comprises six members, each holding the rank of ex-officio Special Secretary to the Government of India.
-
-
Selection: The Chairman and Members are selected from the Indian Revenue Service (IRS), ensuring that the leadership is well-versed in tax administration and policy.
-
Functions: The CBDT is responsible for formulating policies related to direct taxes, including income tax and corporation tax.
- The Board oversees the functioning of the entire Income Tax Department, ensuring efficient administration and enforcement of tax laws.
- The CBDT proposes changes in direct tax laws and rates in alignment with government policies. It also suggests legislative amendments to enhance the tax system.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Analyze the complexity of the Income Tax Act of 1961 and the need for modernization to align with current economic realities and global practices. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following effects of creation of black money in India has been the main cause of worry to the Government of India? (2021)
(a) Diversion of resources to the purchase of real estate and investment in luxury housing.
(b) Investment in unproductive activities and purchase of precious stones, jewellery, gold, etc.
(c) Large donations to political parties and growth of regionalism.
(d) Loss of revenue to the State Exchequer due to tax evasion.
Ans: (d)
Mains:
What is the meaning of the term ‘tax expenditure’? Taking the housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences the budgetary policies of the government. (2013)
Science & Technology
Dual Use Defence Technology
For Prelims: Dual-Use Technology, SCOMET Items, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), European Union (EU), Global Positioning Satellites, Wassenaar Arrangement (WA), Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), National Export Control List, Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC)
For Mains: India’s Position Related to Trade and Export of Dual-Use Goods and Technologies and Balancing it with National Interests.
Why in News?
Recently, United States (US) government officials are sensitising Indian companies and exporters to deter them from supplying dual-use technology to Russia.
- Exporting chemicals, aeronautic parts, and components that can be used in defence equipment can attract Western sanctions.
What are Dual Use Goods/Technologies?
- About Dual Use Goods:
- Dual-use goods are items that can be used both for civilian and military applications.
- Examples of dual-use goods and technology include global positioning satellites, missiles, nuclear technology, chemical and biological tools, night vision technology, thermal imaging, drones etc.
- Examples of Dual-Use Technologies:
- Hypersonics: Hypersonic systems fly at or above 5 times the speed of sound. They could be used for low-cost satellite launches and as a backup if satellites fail.
- Integrated Network Systems-of-Systems: It allows governments to better integrate many diverse mission systems and provide fully networked command, control, and communication that is capable, resilient, and secure.
- Microelectronics: Every military and commercial system relies on microelectronics for creation of personal computers, cell phones and defence equipment.
- Export Controls Provisions Related to Dual Use Goods/Technologies: Their trade and export are regulated by multilateral dual-use export control regimes.
- Wassenaar Arrangement (WA): It aims to contribute to regional and international security and stability, by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies.
- India was inducted to the Wassenaar Arrangement in 2017 as the 42nd member.
- Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG): NSG is a group of nuclear fuel/technologies supplier countries that seeks to contribute to the non-proliferation of nuclear weapons.
- India is not a member of the NSG as India's non-signatory status to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
- Although India is not a member of the NSG, it voluntarily practices non-proliferation of nuclear technologies
- India is not a member of the NSG as India's non-signatory status to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
- Australia Group: It is an informal forum of countries which, through the harmonisation of export controls, seeks to ensure that exports do not contribute to the development of chemical or biological weapons.
- India joined the Australia Group in 2018.
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR): MTCR is an informal and voluntary partnership among 35 countries to prevent the proliferation of missile and unmanned aerial vehicle technology capable of carrying greater than 500 kg payload for more than 300 km.
- India was inducted into the Missile Technology Control Regime in 2016.
- CWC and BWC: India is a signatory to international conventions on disarmament and non-proliferation, viz. the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) and Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC).
- UN Security Council Resolution 1540: The United Nations requires member countries to control the export of goods that could cause harm to humanity and the pursuit of global peace.
- Wassenaar Arrangement (WA): It aims to contribute to regional and international security and stability, by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies.
What are Key Developments in Dual-Use Defence Technology in Relation to Russia?
- Fear of Sanctions: Indian companies are at a risk of facing sanctions from the US under the Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
- Limiting Financial Access: U.S. Treasury officials have advised Indian banks and financial institutions that doing business with Russia's military-industrial base could risk their access to the U.S. financial system.
- India’s Position on Dual-Use Exports: The items identified by the US are not Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET) items, which require licensing for trade.
- Dual-use goods are categorised under the SCOMET list in India.
- India’s Role and US Concerns: The US believes certain SCOMET items are entering the Russian defence manufacturing system.
- India’s exports to Russia increased by 40% in 2023, surpassing USD 4 billion. Engineering goods played a major role, with exports nearly doubling from USD 680 million in 2022 to USD 1.32 billion in 2023.
- China’s Role and US Concerns: The US said that China is the top supplier of machine tools, microelectronics, and nitrocellulose, which are critical for manufacturing munitions and rocket propellants.
- The US has blacklisted over 300 companies, citing China as the top supplier of critical dual-use items to Russia.
- Iran has supplied Russia with munitions, artillery shells, and drones.
Note:
- Russia’s Increased Defense Spending: Russia’s military spending grew by 24% in 2023 to an estimated USD 109 billion, as per the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
- As per the World Bank, economic activity in Russia was influenced by a significant increase in military-related activity in 2023.
What is India’s Strategic Trade Control System?
- About: Strategic Trade Controls are laws and regulations on managing the flow of dual-use goods, services and technologies across national borders.
- Important Legislations Include
- These laws and regulations primarily focus on controlling the export of such items to balance the country’s commercial and security considerations.
- SCOMET List: India regulates the exports of dual-use items, nuclear-related items, and military items, including software and technology under the SCOMET list.
- The SCOMET list is our National Export Control List of dual-use items, munitions and nuclear-related items, including software and technology
Conclusion
Balancing the export control of dual-use goods with national interests is crucial for India. While it's essential to comply with international regulations and avoid sanctions, especially in sensitive geopolitical contexts like those involving Russia, India must also protect its economic interests and maintain strategic autonomy. Strengthening oversight and industry awareness ensures that export policies align with international standards, fostering both innovation and national security.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. What are dual-use goods and technologies? Discuss India’s national and international commitment in non-proliferation of dual-use goods and technologies. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Recently, the USA decided to support India’s membership in multilateral export control regimes called the “Australia Group” and the “Wassenaar Arrangement”. What is the difference between them? (2011)
- The Australia Group is an informal arrangement which aims to allow exporting countries to minimize the risk of assisting chemical and biological weapons proliferation, whereas the Wassenaar Arrangement is a formal group under the OECD holding identical objectives.
- The Australia Group comprises predominantly Asian, African and North American countries whereas the member countries of Wassenaar Arrangement are predominantly from the European Union and American Continents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2008)
- The Nuclear Suppliers Group has 24 countries as its members.
- India is a member of the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. What is/are the consequence/consequences of a country becoming the member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme?
Q. Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)
Ethics
Passive Euthanasia
For Prelims: Passive euthanasia, National Health Digital Record, Article 21, Living Will.
For Mains: Major Changes in Guidelines of Passive Euthanasia, Euthanasia in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court of India denied a petition from an elderly couple seeking "passive euthanasia" for their comatose (deeply unconscious) son, who has been bedridden for 11 years following a fall.
- This ruling has reignited discussions on the legal and ethical dimensions of euthanasia in India.
What is the Background of the Case?
- The Supreme Court ruled against the patient’s parents' plea, stating that the case did not qualify as passive euthanasia since the patient was not on any life support systems and was receiving nutrition through a feeding tube.
- The court said that allowing him to die would not constitute passive euthanasia but rather active euthanasia, which remains illegal in India.
What is Passive Euthanasia?
- About:
- Euthanasia is the practice of ending the life of a patient to limit the patient's suffering.
- Types of Euthanasia:
- Active Euthanasia:
- Active euthanasia occurs when the medical professionals, or another person, deliberately do something that causes the patient to die, such as administering a lethal injection.
- Passive Euthanasia:
- Passive euthanasia is the act of withholding or withdrawing medical treatment, such as withholding or withdrawing life support, with the intention of allowing a person to die.
- Active Euthanasia:
- Euthanasia in India:
- The Supreme Court of India in a landmark judgement in Common Cause vs Union of India (2018) recognised a person’s right to die with dignity, saying that a terminally ill person can opt for passive euthanasia and execute a living will to refuse medical treatment.
- It also laid down guidelines for ‘living will’ made by terminally ill patients who beforehand know about their chances of slipping into a permanent vegetative state.
- Previously in 2011, the SC recognised passive euthanasia in the Aruna Shanbaug case for the first time.
- The court specifically stated that “Dignity in the process of dying is as much a part of the right to life under Article 21. To deprive an individual of dignity towards the end of life is to deprive the individual of a meaningful existence.”
- The Supreme Court of India in a landmark judgement in Common Cause vs Union of India (2018) recognised a person’s right to die with dignity, saying that a terminally ill person can opt for passive euthanasia and execute a living will to refuse medical treatment.
- Different Countries with Euthanasia:
- Netherland, Luxembourg, Belgium allows both types of euthanasia and assisted suicide for anyone who faces “unbearable suffering” that has no chance of improvement.
- Switzerland bans euthanasia but allows assisted dying in the presence of a doctor or physician.
- Since 1942, Switzerland has allowed assisted suicide, focusing on personal choice and control over the dying process. The law requires individuals to be of sound mind and their decision must not be driven by selfish motives.
- Australia has also legalised both types of euthanasia, and applies to adults with full decision-making capacity who have a terminal illness with a prognosis of death within six or twelve months.
- The Netherlands has a well-established legal framework for euthanasia, regulated by the “Termination of Life on Request and Assisted Suicide (Review Procedures) Act” of 2001.
What were the Recent Changes in Guidelines made by the Supreme Court on Passive Euthanasia?
- The Supreme Court in 2023 modified the 2018 Euthanasia Guidelines to ease the process of granting passive euthanasia to terminally ill patients.
- In 2018 the Supreme Court recognised the Right to die with dignity as a fundamental right and prescribed guidelines for terminally ill patients to enforce the right.
- Modifications in SC Guidelines:
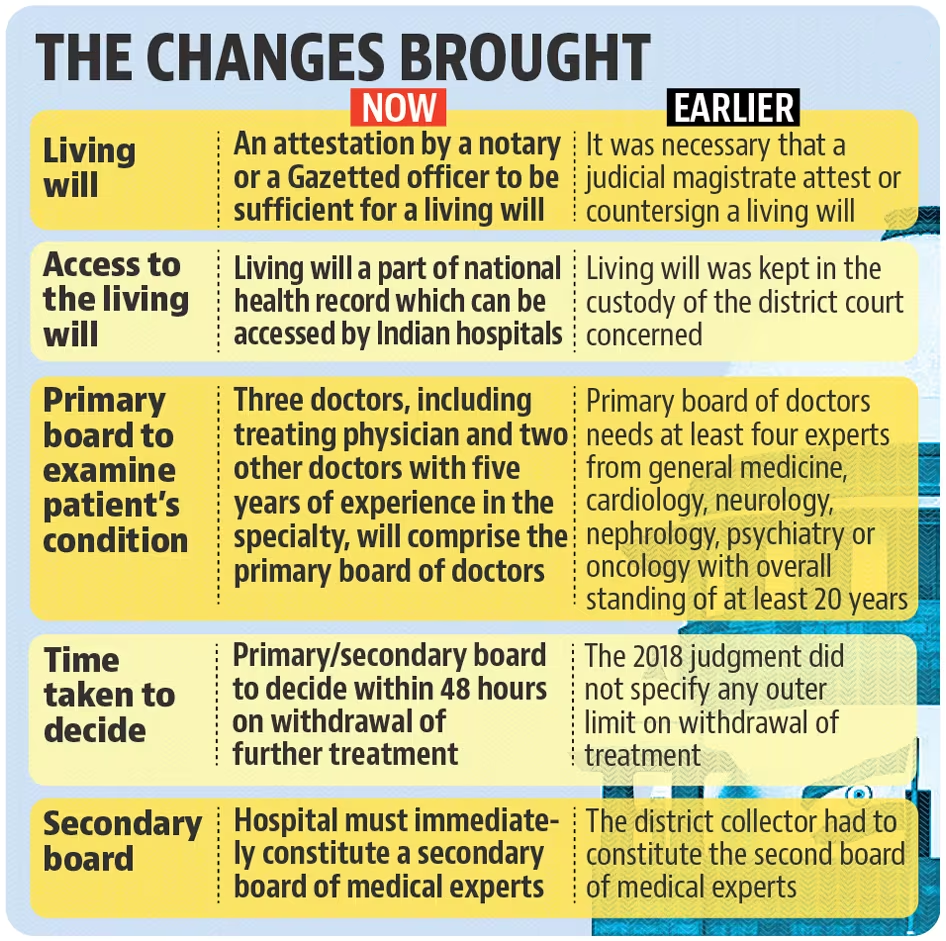
- Attestation of Living Will: The Court removed the requirement for a judicial magistrate's attestation on a living will. Now, attestation by a notary or a gazetted officer suffices, simplifying the procedure for individuals to express their end-of-life choices.
- Integration with National Health Digital Record: Previously, living wills were held by the district court. The revised guidelines mandate that these documents be part of the National Health Digital Record. This ensures easier access for hospitals and doctors nationwide, facilitating timely decision-making.
- Appeal Process for Denial of Euthanasia: If a hospital’s medical board denies permission to withdraw life support, the patient's family can appeal to the relevant High Court. The Court will then form a new medical board to reassess the case, ensuring a thorough and just review.
What are the Ethical Considerations of Euthanasia?
- Autonomy and Informed Consent: Euthanasia involves respecting individual autonomy, meaning people should have the right to decide about their own lives, especially to end suffering if they are mentally competent.
- It also requires informed consent, where the person must fully understand their condition, the euthanasia process, and its consequences to ensure they are not coerced or manipulated.
- Quality of Life vs. Sanctity of Life: Euthanasia debates often centre on quality of life, which argues that ending suffering and preserving dignity in severe illness can be ethical, versus sanctity of life, which holds that life is intrinsically valuable and should not be ended prematurely, often reflecting religious or philosophical beliefs.
- Legal and Social Implications: Euthanasia's legal framework varies by jurisdiction, reflecting different cultural attitudes and ethical debates on end-of-life issues.
- The social impact involves questions about medical professionals' roles, societal responsibilities, and the need for equitable access to palliative care and psychological support to address the underlying reasons for seeking euthanasia.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is Active Euthanasia? What are the ethical and moral implications for this practice? |
Rapid Fire
Vaccine-Derived Polio Detected
Recently, a child from Meghalaya was diagnosed with vaccine-derived polio (VDP).
- VDP occurs when the weakened (attenuated) strain of poliovirus used in the oral polio vaccine (OPV) mutates and regains the ability to cause paralysis.
- VDP typically occurs in areas with low immunisation coverage, poor sanitation, or among immunocompromised individuals.
- More than 90% of VDP outbreaks are due to the Wild poliovirus type 2 (WPV2) present in OPV.
- The Indian government does not count vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP) as polio since these cases are sporadic and pose little or no threat to others.
- The WHO declared India polio-free in 2014. This case does not jeopardise India’s polio-free status.
- Types of Poliovirus: WPV1, WPV2, and WPV3 are three types of wild polioviruses (naturally occurring), with identical symptoms but different genetic structures.
- WPV2 and WPV3 were eradicated in 2015 and 2019 respectively with ongoing global efforts to eradicate WPV1.
- Currently, wild poliovirus is endemic in Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) was developed by Jonas Salk using an inactivated virus while Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) was developed by Albert Sabin, containing a live, attenuated virus.
Read More: Polio Eradication
Rapid Fire
JUICE Probe’s Double Slingshot Manoeuvre
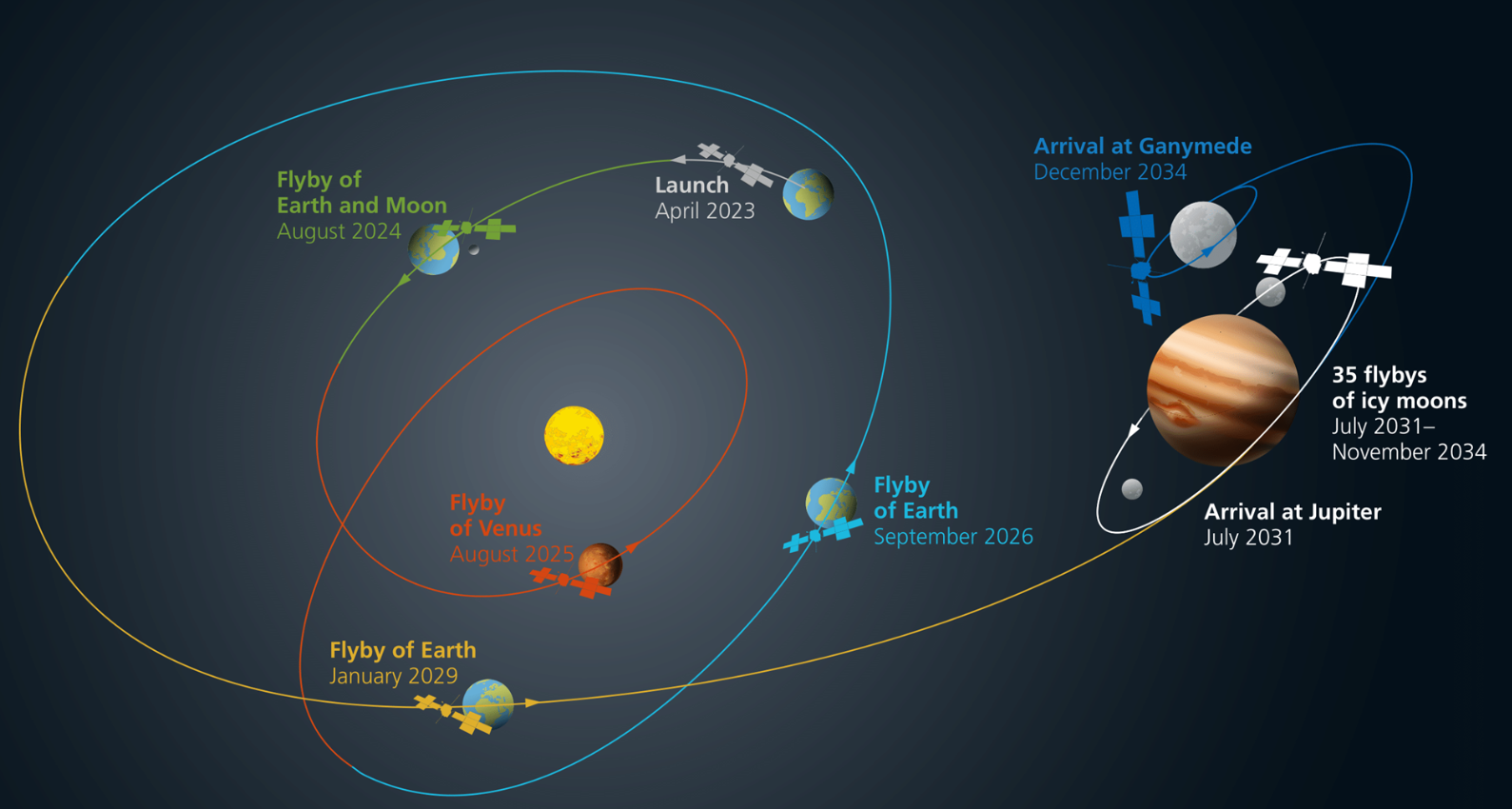
Recently, the European Space Agency's (ESA) Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) Probe performed a double slingshot manoeuvre, using the gravitational forces of both the Moon and Earth in quick succession.
- JUICE first flew 434 miles from the Moon's surface, then 4,229 miles from Earth's surface. The Moon's gravity slightly altered JUICE's path, allowing a significant gravity assist from Earth.
- This is called the "gravity assist" method which saves propellant by using the gravitational pull of celestial bodies to alter the spacecraft's speed and trajectory.
- Successful execution of the slingshot put JUICE on course to reach Jupiter by 2031 with the help of three further single gravity assists: Venus in 2025, and then the earth again in 2026 and 2029.
- JUICE Probe:
- It was launched in April 2023 and aims to explore Jupiter and its three large icy moons viz. Callisto, Europa, and Ganymede.
- It will perform fly-bys of its three large icy moons and finally orbit Ganymede to study the potential to support life.
- Following up on NASA’s 1990s Galileo mission to Jupiter, the ESA-led JUICE mission will orbit Jupiter.
- Other important missions to study Jupiter are Juno Mission (NASA), Cassini-Huygens (NASA and ESA) and Galileo (NASA).
Rapid Fire
ADB Aid for Improving Healthcare in Maharashtra
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) committed a loan package of USD 500 million to improve access to quality and affordable tertiary health care and medical education in Maharashtra.
- It will help establish four medical colleges incorporating climate and disaster-resilient, gender-responsive, and socially inclusive features in under-served districts.
- It will reduce out-of-pocket expenses, and create policy actions for recruiting and retaining quality medical staff.
- It envisages hiring at least 500 new doctors for four new governmental medical colleges.
- It will help establish India's first state led health care and medical education centres of excellence (CoE).
- About ABD:
- The ADB is a multilateral development bank focused on reducing poverty and improving quality of life in its developing member countries.
- It was established in 1966, with 31 members.
- Currently, ADB has 68 members of which 49 are from within Asia and the Pacific and 19 outside.
- It is headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- India is a founding member of ADB and its fourth largest shareholder after the US, China and Japan.
Read More: ADB's Commitment to India's Development
Rapid Fire
Enhancing Support for Students with Learning Disabilities
The Ministry of Education has launched the second cycle of its Capacity Building Program on Specific Learning Disabilities (SLD) under the Malaviya Mission Teacher Training Programme (MMTTP), aimed at empowering Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) to better support students with learning disabilities.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 recognizes learning disabilities, advocating for HEIs to be aware and sensitised to address these challenges, ensuring equitable and inclusive education for all.
- The MMTTP, launched in 2023, aims to improve the quality of higher education in India by providing teachers with specialised training and knowledge in various areas.
- It has been restructured from existing mechanisms, such as University Grants Commission (UGC)-Human Resource Development Centres (HRDCs) and Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya National Mission on Teachers and Teaching Centres (PMMMNMTT), to better support teacher training.
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, mandates the government to ensure that PWDs enjoy the right to equality, life with dignity, and respect for their integrity, while also providing for their education, employment, social security, healthcare, and accessibility rights.
- Other Initiatives Related to Education of PWDs:
Read More: National Workshop on Empowering PwD in Education