Science & Technology
India's Chandrayaan-3 and Russia's Luna 25 Mission
- 17 Aug 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Chandrayaan-3, Luna 25, GLONASS navigation system, Aryabhata Mission, Gaganyaan, Soyuz rocket, USSR’s Interkosmos program.
For Mains: Difference in Luna 25 and Chandryaan 3 Mission.
Why in News?
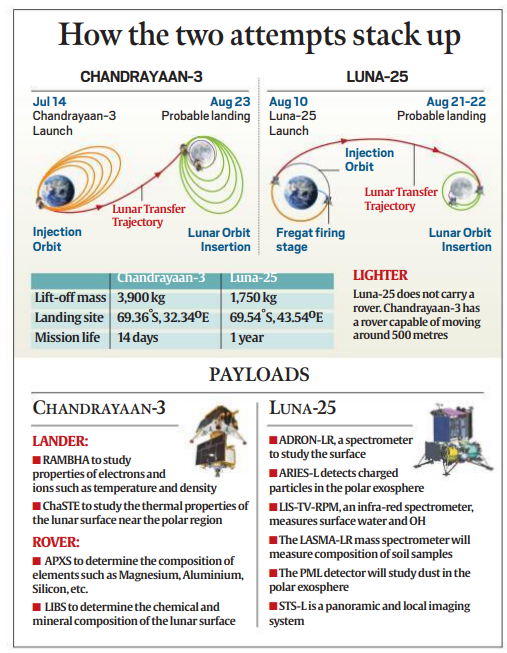
The race for lunar exploration has taken an intriguing turn as Russia's Luna 25 mission, launched aboard its Soyuz rocket on August 10, 2023, seeks to soft-land close to the lunar South Pole, just days before India's Chandrayaan-3.
- Russia's space agency, Roscosmos asserts that Luna 25's landing would not impact Chandrayaan-3, as their landing regions are distinct.
Why is Luna 25 Reaching the Moon Earlier than Chandrayaan-3?
- Direct Trajectory Advantage: Despite being launched almost a month later than Chandrayaan-3, Luna 25 is set to reach the moon earlier due to its more direct trajectory.
- Payload and Fuel Storage: Luna 25's lift-off mass of 1,750 kg is significantly lighter than Chandrayaan-3's 3,900 kg, facilitating a quicker journey.
- Circuitous Route for Chandrayaan-3: Chandrayaan-3 took a longer route to compensate for its lower fuel reserve, involving maneuvers to gain velocity and slingshotting towards the moon.
- This elongated its journey to the lunar orbit by 22 days.
- Lunar Dawn Timing: Luna 25 benefits from an earlier lunar dawn at its landing site, ensuring full solar panel power for its payloads during the lunar day (equal to 14 Earth days).
Note: Only three countries have managed to complete a soft landing on the Moon in history: the United States, the Soviet Union, and China.
What are the Other Differences between Luna 25 and Chandrayaan 3?
- About: Luna 25 marks Russia's return to lunar exploration after 47 years, aiming to reclaim its reputation in space exploration.
- Chandrayaan-3 is India's third lunar mission and second attempt at achieving a soft landing on the moon's surface
- Payload Difference: Luna 25 is lighter and lacks a rover, focusing on studying soil composition, dust particles, and detecting surface water.
- Chandrayaan-3 carries a rover capable of moving 500 meters, aims to study lunar soil, and has instruments to detect water-ice in shadowed craters near the lunar South Pole.
- Lifespan: Luna 25 is designed for a year-long mission, equipped with heating mechanisms and a non-solar power source.
- In contrast, Chandrayaan-3 is built for a single lunar day due to lack of heating during lunar nights.
- Objective of the Mission: The Russian lander has eight payloads mainly to study the soil composition, dust particles in the polar exosphere, and most importantly, detect surface water.
- The Indian mission also has scientific instruments to study the lunar soil as well as water-ice. The location near the southern pole was chosen because of the presence of craters that remain in permanent shadow, increasing the likelihood of finding water-ice.
- The lander will carry four experiments on-board (RAMBHA, ChaSTE, ILSA, LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA)) .
- There are two scientific experiments on the rover.
- The LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS).
- The Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS).
- The Indian mission also has scientific instruments to study the lunar soil as well as water-ice. The location near the southern pole was chosen because of the presence of craters that remain in permanent shadow, increasing the likelihood of finding water-ice.
What is the Status of India Russia Space Collaboration?
- India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1975.
- Only one Indian citizen has ever flown to space- Rakesh Sharma flew to the Salyut 7 space station on a Soyuz rocket in 1984 as part of the USSR’s Interkosmos program.
- In 2004, the two countries signed a protocol to boost cooperation in space. This included the development of the GLONASS navigation system and the launching of Russian GLONASS satellites by Indian rockets.
- Chandrayaan-2 was initially supposed to be a collaboration between India and Russia.
- However, Russia withdrew from designing the lander-rover for Chandrayaan-2, leading India to develop it independently.
- Also, four astronauts who will be part of India’s first crewed space mission: Gaganyaan have been trained in Russian facilities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)