Indian Economy
Perspective: Boosting Indian Economy
- 13 Feb 2025
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Union Budget 2025-26, GST, Indirect Tax, Capital Expenditure, Logistics Infrastructure, Blue Economy, PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, Six-year Pulses Mission, Kisan Credit Card, Makhana Board, Supply Chains, Make in India, Fund of Funds for Startups, BharatTradeNet, Atal Tinkering Labs, Industry 4.0, Fiscal deficit, PM Surya Ghar, Green Hydrogen, Direct Tax Reforms, Disinvestment, Sovereign Green Bonds, Circular Economy.
For Mains: Role of the Union Budget in Boosting Indian Economy.
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26 has announced several provisions aimed at boosting the Indian economy.
- It aims to make India a technologically advanced and inclusive economy by focusing on key areas such as infrastructure development, job creation, rural upliftment, and industrial growth.
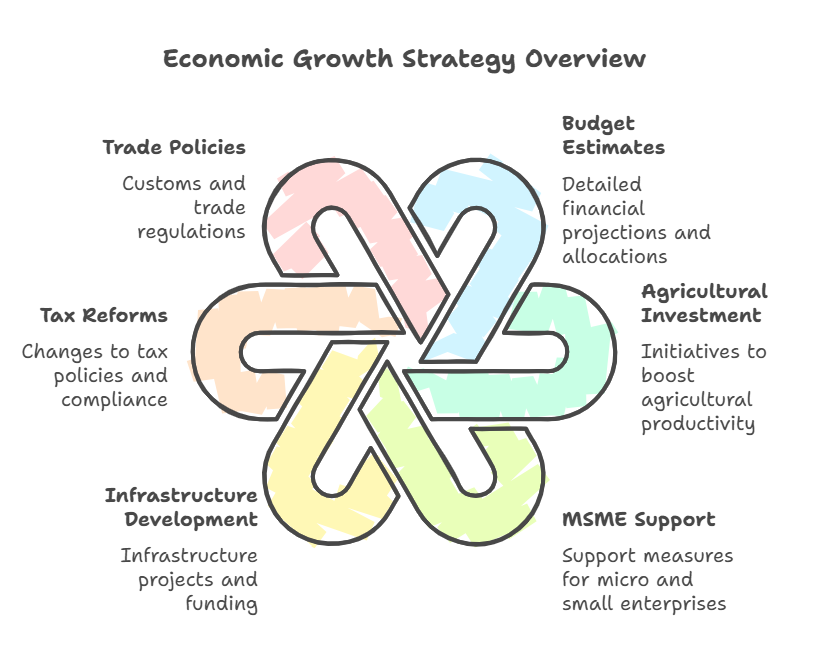
How Union Budget 2025-26 Provisions Will Spur Indian Economy?
- Tax Reforms for Higher Consumption: Income tax exemption raised to ₹12 lakh, reducing the direct tax burden on middle-class households.
- Revised highest tax slab to ₹24 lakh, ensuring more disposable income for higher-income groups.
- Increased consumption will boost demand, supporting sectors like Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), real estate, and retail.
- Higher private consumption will accelerate economic activity, contributing to higher GST and indirect tax revenue.
- Capital Expenditure for Growth: ₹11.21 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure, with 3.1% of GDP committed to capital formation.
- Public investment in transport, energy, and urban projects will create strong multiplier effects.
- Capital expenditure generates employment, increasing labor demand in construction and allied industries.
- Improved logistics infrastructure will enhance efficiency, lowering production costs for industries.
- Attracting Investment: The Deep Tech Fund of Funds will support next-generation startups, fostering innovation, technology development, and job creation.
- The FDI increase to 100% in the insurance sector will attract more foreign investments, strengthening financial stability and boosting domestic capital markets.
- The modified UDAN scheme will improve regional connectivity, promote tourism, enhance trade, and support economic development in remote and hilly areas, driving overall economic growth.
- Also, the budget proposes to rope in the private sector through Public-Private Partnership (PPP) models for investments.
- Boost to the Blue Economy: Government prioritizes marine fisheries and shipbuilding, enhancing coastal economic development.
- Maritime Development Fund with ₹25,000 crore corpus will strengthen port infrastructure and shipbuilding.
- Potential expansion of coastal tourism and aquaculture could create millions of jobs in related sectors.
- India can leverage the potential of the global Blue Economy which is estimated to be at $24 trillion.
- Agriculture Modernization: PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana aims to cover 100 low agricultural productivity districts, benefiting 1.7 crore farmers by enhancing irrigation, and post-harvest storage facilities.
- ₹5 lakh loan limit under the Kisan Credit Card ensures better financial support for farmers.
- Eventually, higher rural income will increase rural consumption, positively impacting small businesses and retail sectors.
- Also, Six-year Pulses Mission will reduce import dependency, increasing domestic agricultural self-sufficiency.
- Boosting Rural Economy: ₹5 lakh loan limit under the Kisan Credit Card ensures better financial support for farmers.
- Eventually, higher rural income will increase rural consumption (which comprises 60% of private consumption), positively impacting small businesses and retail sectors.
- Makhana Board in Bihar to be established to enhance production, processing, and value addition of Makhana, boosting rural employment and income.
- Comprehensive Program for Fruits and Vegetables to promote efficient supply chains and ensure better market prices for farmers, strengthening the rural economy.
- Support for MSMEs and Manufacturing: National Manufacturing Mission to boost Make in India, increasing the share of manufacturing in GDP.
- ₹10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups will improve innovation, job creation, and industrial diversification.
- Rs 5 lakh credit facility for 10 lakh micro enterprises will enhance access to finance.
- Investment in industrial corridors will integrate MSMEs into global supply chains, improving export potential.
- Urban Development Push: ₹1 lakh crore Urban Challenge Fund has been set up for 'Cities as Growth Hubs', 'Creative Redevelopment', and 'Water and Sanitation' to upgrade city infrastructure, ensuring sustainable urban expansion.
- Affordable housing and governance reforms will increase private sector participation in real estate.
- Transport and sanitation investments will improve urban productivity, supporting higher per capita output.
- Export Promotion and Global Trade Integration: Export Promotion Mission to coordinate policies, improving India's global trade competitiveness.
- The budget eliminates seven more tariff rates, following the removal of seven rates in the 2023-24 budget.
- BharatTradeNet to streamline trade documentation, reducing procedural bottlenecks in export processing.
- Investment in Human Capital: 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs to enhance digital and innovation skills in school students.
- Expansion of medical education by 10,000 additional seats to improve India's healthcare workforce.
- AI-driven skilling initiatives align workforce capabilities with Industry 4.0 requirements.
What are the Challenges for the Indian Economy?
- Global Supply Chain & Regulatory Uncertainties: Disruptions in raw material supply, rising costs, and logistical bottlenecks impact manufacturing and exports, slowing economic growth.
- Also, regulatory complexities, bureaucratic delays, and infrastructure gaps create hurdles for investments, entrepreneurship, and industrial expansion.
- Fiscal Deficit Management: With a Fiscal deficit projected at 4.4% of GDP, strict expenditure rationalization is needed. The government's ₹14.82 lakh crore market borrowings could push up interest rates, potentially crowding out private investment.
- Despite high public capital spending, private sector investment remains sluggish due to higher borrowing costs and external uncertainties.
- Employment and Skilling Issues: 170 million jobs created (2016-23), but Industry 4.0 demands AI, automation, and robotics expertise.
- Urban employment faces structural challenges, as urban share of GDP has remained stagnant between 52-55% from 2000-2020.
- Mismatch between labor supply and market demand requires urgent skilling and training reforms.
- Climate Change and Sustainability Gaps: Despite the growing risks of climate change, budgetary allocations for climate-resilient infrastructure remain insufficient
- Additionally, Carbon capture and sustainable agriculture projects lack policy incentives, slowing green transition efforts.
- MSME Competitiveness: MSMEs contribute 45% of exports but lack technology integration in global value chains.
- Government schemes focus on credit, but digital transformation and market linkages remain underdeveloped.
- Limited adoption of e-commerce and digital platforms restricts global expansion opportunities for MSMEs.
Way Forward
- High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms: This will streamline non-financial sector regulations, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and compliance costs.
- Simplifying certifications, licenses, and permissions will enhance ease of doing business, attract investments, and foster a more business-friendly environment, boosting economic growth.
- Fiscal Prudence with Growth: Revenue mobilization must improve through higher GST compliance and direct tax reforms.
- Disinvestment and asset monetization targets of ₹10 lakh crore in new investments (2025-30) should be met aggressively.
- Public-private partnerships in infrastructure will ease fiscal pressure and improve efficiency.
- Encouraging Private Investment: Government should provide targeted credit guarantees to revive private capital formation.
- Investment incentives should focus on high-growth sectors like electronics, renewables, and pharmaceuticals.
- By providing a conducive investment ecosystem India can attract foreign investors from countries like South Korea, Japan etc. in aforesaid sectors.
- Employment and Skilling Reforms: Linking education programs with industry requirements will improve employability across technology sectors.
- Urban employment programs must include rental housing reforms and transport subsidies for labor mobility.
- Incentivizing AI, automation, and sustainable energy jobs will future-proof India's workforce.
- Sustainable Growth and Climate Finance: Scaling up green finance through sovereign green bonds can fund climate adaptation projects.
- Carbon trading incentives and circular economy models should be integrated into national policy.
- Stronger state-level collaboration is necessary for effective climate resilience measures.
- Strengthening MSMEs for Global Trade: Digital transformation programs should focus on integrating MSMEs into e-commerce and export platforms.
- Investment in technology and logistics infrastructure will improve MSME participation in global supply chains.
- Better trade facilitation measures, including single-window clearance, will enhance export efficiency.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. A decrease in tax to GDP ratio of a country indicates which of the following? (2015)
- Slowing economic growth rate
- Less equitable distribution of national income
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- Tax revenue as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
- Fiscal deficit as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. One of the intended objectives of the Union Budget 2017-18 is to ‘transform, energise and clean India’. Analyse the measures proposed in the Budget 2017-18 to achieve the objective. (2017)