Important Facts For Prelims
Blue Economy 2.0
- 08 Feb 2024
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The recent presentation of the Interim Budget included a significant emphasis on advancing Blue Economy 2.0 through the introduction of a novel scheme focused on restoration, adaptation measures, coastal aquaculture, and mariculture, employing an integrated and multi-sectoral strategy.
What is the Blue Economy?
- About:
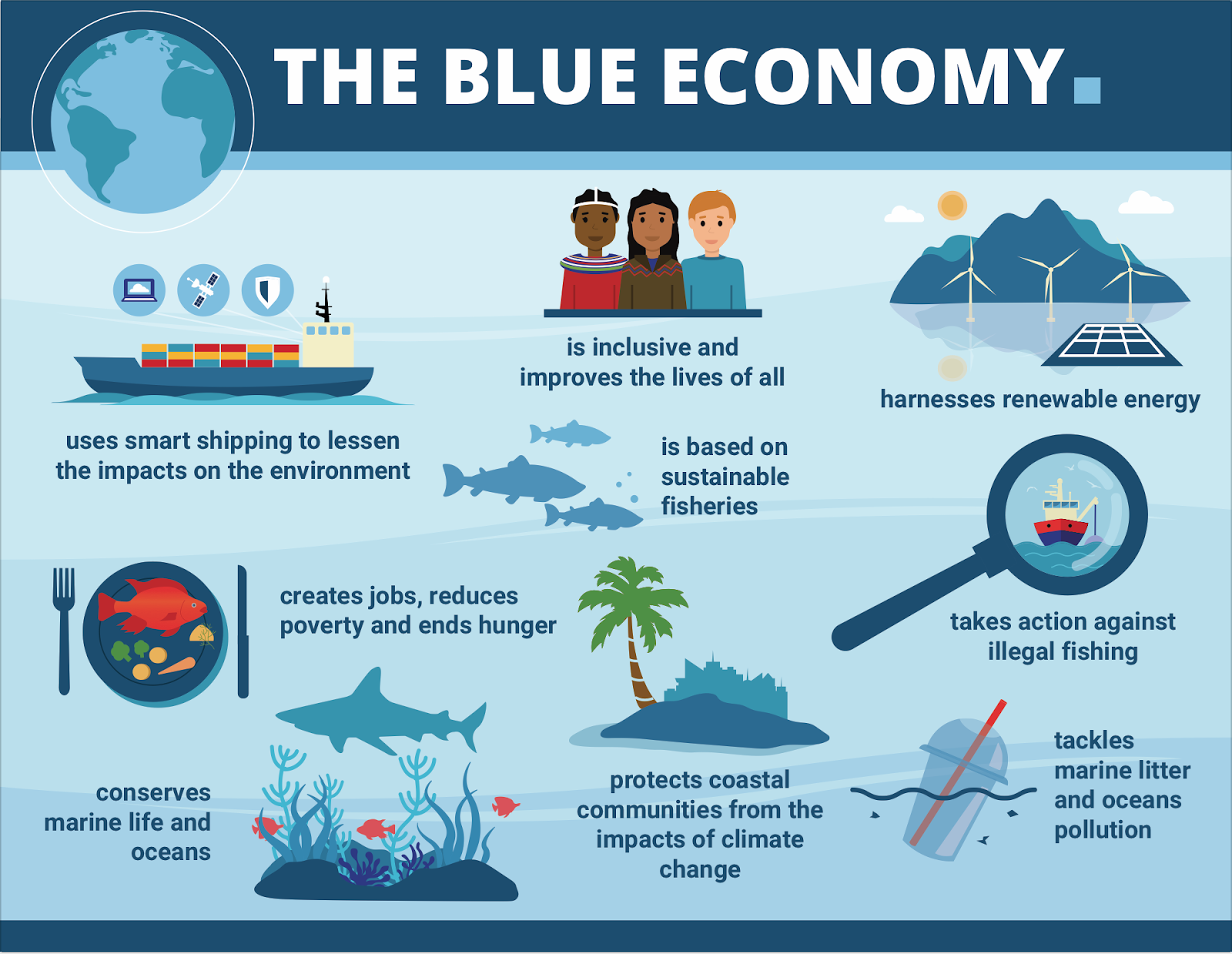
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
- This is reflected in the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 14), which calls to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development.
- Necessity for Blue Economy:
- India has a vast coastline of 7500 km, and its exclusive economic zones (EEZ) extend over 2.2 million square km. Also, India is home to 12 major ports, over 200 other ports, 30 shipyards and a comprehensive hub of diverse maritime service providers.
- It advocates the greening of ocean development strategies for higher productivity and conservation of the ocean's health.
- Oceans cover three-quarters of the Earth’s surface, contain 97% of the Earth’s water, and represent 99% of the living area on the planet.
- Growth Prospects:
- The global ocean economy is currently valued at approximately USD 1.5 trillion annually, ranking it as the world's seventh-largest economy. Projections indicate that it will double by 2030, reaching USD 3 trillion.
- The total value of ocean assets, also known as natural capital, has been estimated at USD 24 trillion.
- The global ocean economy is currently valued at approximately USD 1.5 trillion annually, ranking it as the world's seventh-largest economy. Projections indicate that it will double by 2030, reaching USD 3 trillion.
What is Blue Economy 2.0?
- About:
- This is aimed at promoting climate-resilient activities and sustainable development in coastal areas.
- With marine ecosystems facing unprecedented threats from climate change, pollution, and overexploitation, there is an urgent need for coordinated action to safeguard the health and resilience of ocean resources.
- Components:
- Restoration and Adaptation:
- Central to the scheme are measures aimed at restoration and adaptation, which will involve restoring degraded coastal ecosystems and implementing adaptation strategies to mitigate the effects of rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
- These efforts are crucial for preserving biodiversity, protecting coastal communities, and maintaining the ecosystem services provided by marine habitats.
- Expansion of Coastal Aquaculture and Mariculture:
- Blue Economy 2.0 scheme will focus on the expansion of coastal aquaculture and mariculture, which play a vital role in meeting the growing demand for seafood while reducing pressure on wild fish stocks.
- By promoting sustainable aquaculture practices and integrating them with other sectors such as tourism and renewable energy, the scheme aims to create economic opportunities for coastal communities while ensuring the long-term viability of marine resources.
- Integrated and Multi-Sectoral Approach:
- The integrated and multi-sectoral approach adopted by the Blue Economy 2.0 scheme recognises the interconnectedness of various sectors and the need for coordinated action across government departments, industries, and civil society.
- By fostering collaboration and partnership, the scheme seeks to harness the collective efforts of stakeholders to achieve sustainable development goals in coastal areas.
- Restoration and Adaptation:
What are the Key Government Initiatives Related to the Blue Economy?
- Deep Ocean Mission
- Sagarmala project
- O-SMART
- Integrated Coastal Zone Management
- NavIC
- India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development
- National Fisheries Policy
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. What is blue carbon?
(a) Carbon captured by oceans and coastal ecosystems
(b) Carton sequestered in forest biomass and agricultural soils
(c) Carbon contained in petroleum and natural gas
(d) Carbon present in atmosphere
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)