Governance
Scheme of Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment
- 01 Jan 2024
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Scheme of Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment, Covid-19 Pandemic, 15th Finance Commission, Urban Planning, Make in India.
For Mains: Scheme of Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment.
Why in News?
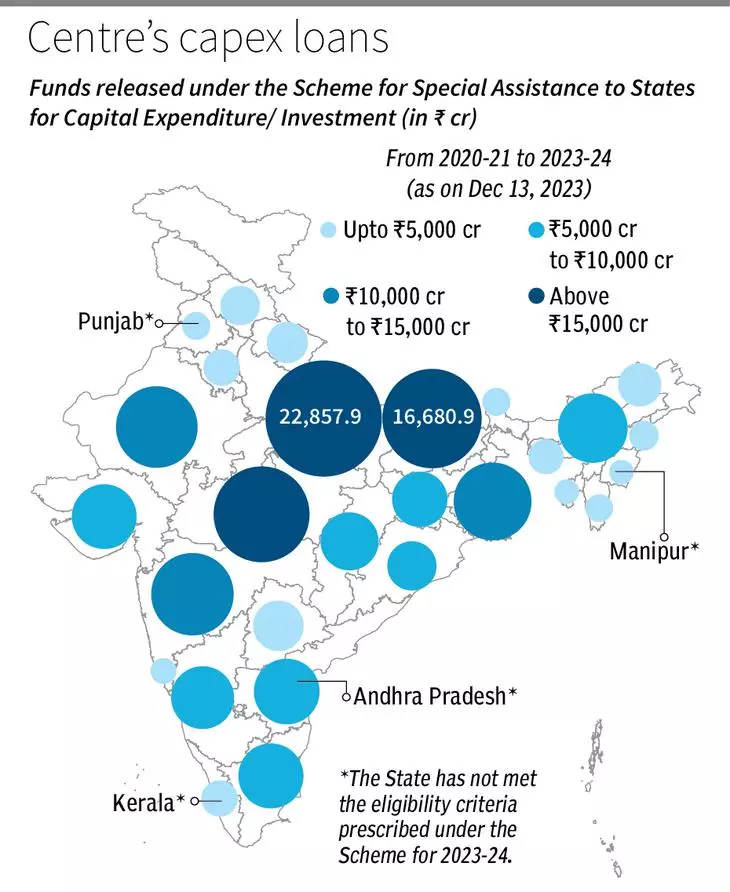
Out of the Rs 1,67,518.6-crore special assistance (loan) allocated by the Centre under the Scheme for Special Assistance to States for capital expenditure/investment, Uttar Pradesh (UP) has been the highest recipient over the last four years.
- The substantial financial support underscores the government’s commitment to bolstering development initiatives in UP.
What are the Trends in Capital expenditure as per the Ministry of Finance?
- UP and Bihar are the top two States which have fulfilled the criteria related to Capital Expenditure and received maximum allocation under the Scheme in the last four years.
- Uttarakhand, Haryana, Kerala and Punjab are among the States which have received about 1-2% of the total released amount under the Scheme.
- Andrha Pradesh, Kerala, Manipur and Punjab have not received any allocation in 2023-24 and as per the Ministry of Finance, these States have not met the eligibility criteria prescribed under the Scheme.
What is the Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment Scheme?
- About:
- The Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Expenditure was launched in FY 2020-21 in the wake of Covid-19 Pandemic.
- The scheme has been expanded and continued as ‘Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’ with allocation of Rs 1.3-lakh crore.
- Parts:
- The scheme has eight parts, Part-I being the largest with allocation of Rs. 1 lakh crore. This amount has been allocated amongst states in proportion to their share of central taxes and duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission.
- Other parts of the scheme are either linked to reforms or are for sector-specific projects.
- Part-II provides incentives to states for scrapping of old vehicles and setting up of automated vehicle testing facilities;
- Part-III and IV provide incentives to states for reforms in urban planning and urban finance;
- Part-V provides funds for increasing the housing stock for police personnel and their families within the police stations in urban areas.
- Part-VI of the scheme supports the vision of national integration, Make in India and One District One Product by promoting cultural diversity and local products through Unity Mall projects.
- Under Part-VII, Rs. 5,000 crore is provided as financial assistance to states for establishing libraries with digital infrastructure at the Panchayat and Ward level, primarily benefiting children and adolescents.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- The scheme is expected to have a higher multiplier effect on the economy by stimulating demand and creating jobs.
- The scheme also aims to enhance the pace of projects in key sectors such as Jal Jeevan Mission and Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana by providing funds for meeting the state share.
- The scheme also seeks to encourage states to undertake reforms in urban planning and urban finance to improve the quality of life and governance in cities.
What is Capital Expenditure in India?
- Capital Expenditure (Capex):
- It refers to the funds allocated by the government for the acquisition, construction, or improvement of physical assets such as infrastructure, buildings, machinery, and equipment.
- It is considered to be productive and growth enhancing as it adds to the productive capacity of the economy and generates income and employment in the future.
- The Indian government allocates capital expenditure through its annual budget, which is presented by the finance minister.
- The capital investment outlay has experienced a consecutive three-year increase, reaching Rs 10 lakh crore, which accounts for 3.3% of the GDP, marking a significant growth of 33% ( Union Budget 2023-24).
- Effective Capital Expenditure:
- The capital expenditure presented in the budget does not include the spending by the government on creating capital assets through grants-in-aid to states and other agencies.
- These grants are classified as revenue expenditure in the budget, but they also contribute to the creation of fixed assets such as roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, etc.
- Therefore, to capture the true extent of public investment by the central government, a concept of ‘effective capital expenditure’ has been introduced.
- Effective capital expenditure is defined as the sum of capital expenditure and grants for creation of capital assets.
- It is budgeted at Rs 13.7 lakh crore or 4.5% of GDP (Union Budget 2023-24).
- The capital expenditure presented in the budget does not include the spending by the government on creating capital assets through grants-in-aid to states and other agencies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is/are included in the capital budget of the Government of India? (2016)
- Expenditure on acquisition of assets like roads, buildings, machinery, etc.
- Loans received from foreign governments
- Loans and advances granted to the States and Union Territories
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)