Indian Economy
Repo Rate Cut and its Implications
- 08 Feb 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), Inflation, Personal Income Tax, Repo Rate, Interest Rate, Wholesale Price Index (WPI), M3 Money Supply.
For Mains: Repo rate and its impact on the economy.
Why in News?
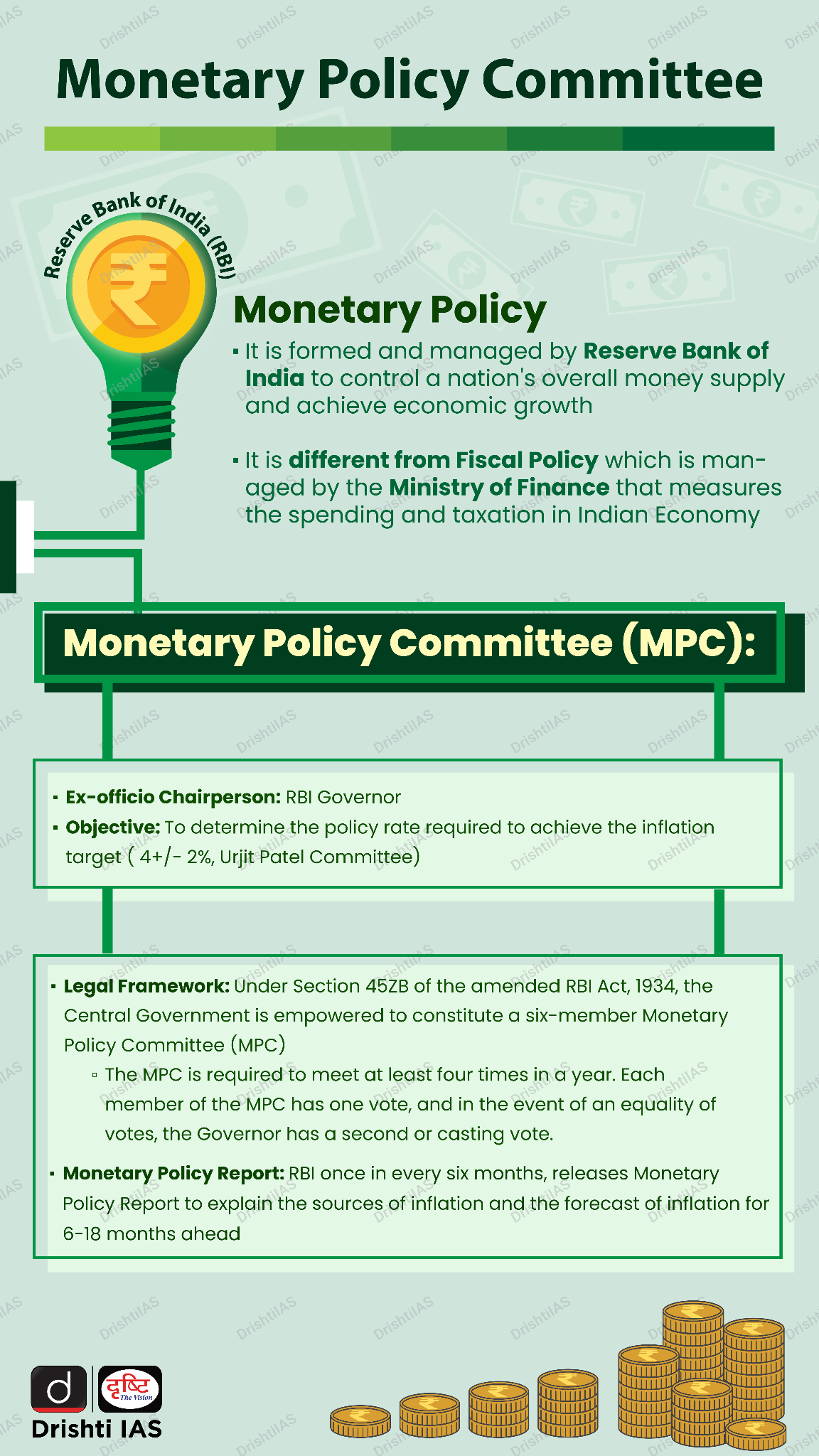
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of Reserve Bank of India cut the repo rate to 6.25% from 6.5% (25 basis points (bps)) for the first time in 5 years (since 2020).
- After the Union Budget 2025-26 reduced personal income tax to spur consumption, this step aims to revive economic growth amid a slowdown.
What Factors Led to RBI's Decision to Cut the Repo Rate?
- Growth-Stimulating Budget: The Union Budget 2025-26 introduced a personal income tax cut and revised TDS limits, increasing disposable income.
- The RBI’s repo rate cut supports the government’s tax reductions by lowering borrowing costs and sustaining demand.
- Declining Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) eased to 5.22% in December 2024, a four-month low, down from 5.48% in November that provides room for monetary easing.
- Market Liquidity Enhancement: The RBI recently introduced measures to improve liquidity in the banking system by injecting Rs 1.5 trillion.
- Liquidity injection eased tight credit markets, while the repo rate cut ensured liquidity and lower rates to boost growth.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: The recent US tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China sparked trade war fears, weakening the rupee to 87.29 per dollar and raising inflation risks.
- A repo rate cut could help cushion the impact of external shocks and support domestic growth.
What is Repo Rate?
- About: Repo rate (Repurchase Agreement Rate) is the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the central bank.
- Purpose & Functioning: It helps banks meet short-term liquidity needs by borrowing funds.
- Banks provide securities as collateral and agree to repurchase them later at a higher price (including interest).
- Impact on Borrowing Costs:
- Higher repo rate → Costlier loans for banks → Higher interest rates for consumers & businesses → Slower borrowing & spending.
- Lower repo rate → Cheaper loans for banks → Lower interest rates for borrowers → Increased borrowing & spending.
- Role in Monetary Policy: It is used by the central bank to control money supply, inflation, and economic growth.
What are the Implications of the Repo Rate Cut?
- Economic Growth: Lower borrowing costs make it easier for businesses to expand and invest, leading to higher production and job creation.
- A repo rate cut reduces interest rates, making loans cheaper, lowering EMIs, and boosting borrowing and spending.
- Strengthening Financial Markets: Banks may reduce interest rates on savings accounts and fixed deposits, making savings less attractive that may drive consumers toward stocks, mutual funds, or real estate.
- Export Competitiveness: A lower repo rate may cut investment returns, leading to capital outflows. This may weaken the currency, raising import costs but enhancing export competitiveness.
- Inflation: Increased spending due to rate cuts may push up prices and inflation over time, breaching the RBI inflation target (4% within a band of +/- 2%)
Background of the 4% Inflation Target
- Chakravarty Committee (1982-85): It was set up by the then RBI Governor Manmohan Singh under Sukhamoy Chakravarty to review monetary policy. Its recommendations included:
- Emphasized price stability as a core objective of monetary policy.
- Proposed 4% average annual inflation in the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to balance economic priorities.
- Recommended market-driven government borrowing and an active government securities market to reduce reliance on RBI funding.
- Advocated monetary targeting (M3 money supply control) to manage inflation.
- M3 = M1 (Currency held by the public+Demand Deposits held by commercial banks)+Net time deposits of commercial banks
- Urjit Patel Committee (2014): It formalized inflation targeting, setting the 4% target (±2% band), a target first proposed by the Chakravarty Committee 40 years ago.
- India's inflation targeting framework, adopted in 2016, aligns India’s monetary policy with global best practices.
Click Here to Read: What is the Consumer Price Index?
Conclusion
The RBI’s repo rate cut aims to boost economic growth by lowering borrowing costs. However, it may lead to inflationary pressures, challenging the 4% target set by RBI MPC. Balancing growth and price stability remains crucial, especially amid global uncertainties.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the impact of repo rate cuts on economic growth and inflation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- The Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do?(2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Define potential GDP and explain its determinants. What are the factors that have been inhibiting India from realizing its potential GDP? (2020)
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments (2019)