International Relations
Strategic Vision in the Evolving BRICS Landscape
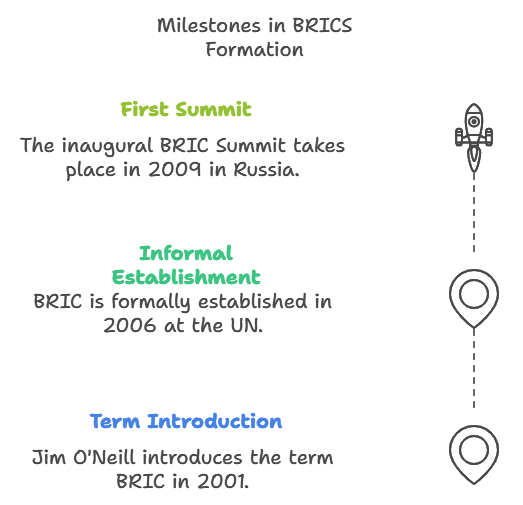
This editorial is based on “Why this is not just another BRICS in the wall” which was published in The Indian Express on 25/10/2024. The article discusses the Kazan Declaration from the 16th BRICS Summit emphasized multilateralism for equitable global development, outlining India’s vision for an expanded BRICS. Originally formed by Brazil, Russia, India, and China in 2006, BRICS now includes South Africa and new partners, focusing on economic cooperation and reforming global governance.
For Prelims: 16th BRICS Summit, Global South, BRICS group expanded, UN, WTO, World Bank, IMF, Contingency Reserve Arrangement (CRA), New Development Bank (NDB), Line of Actual Control (LAC), voice for the Global South, sustainable development, counter-terrorism, terror financing, Russia- Ukraine conflict, Global Financial Safety Net.
For Mains: Significance of International Groupings and Agreements for India’s Strategic Interests.
The 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan, Russia, focused on “Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security,” highlighting the bloc's commitment to tackling global challenges. India presented its vision for an expanded BRICS, marking a pivotal moment in the organization’s evolution. Founded in 2006, BRICS aimed to leverage Brazil, Russia, India, and China’s strengths while maintaining ties with developed nations. It now includes South Africa, Egypt, and UAE, reflecting its expanding influence.
BRICS leaders assert their non-alignment and commitment to partnership with all nations. The Kazan Declaration further emphasized intra-BRICS cooperation and innovative financial solutions, such as promoting local currency trade.
What is Genesis, Evolution and Significance of BRICS?
- Evolution:
- Membership Expansion: South Africa joined BRICS in 2010, enhancing the bloc's representation of emerging economies.
- In 2024, the BRICS group expanded further with the addition of Egypt, Ethiopia, the UAE, Iran, broadening its influence and development agenda.
- Significant Membership Changes: The inclusion of Egypt, Ethiopia, the UAE, and Iran, marks a pivotal moment for BRICS, enhancing its regional influence and cooperation.
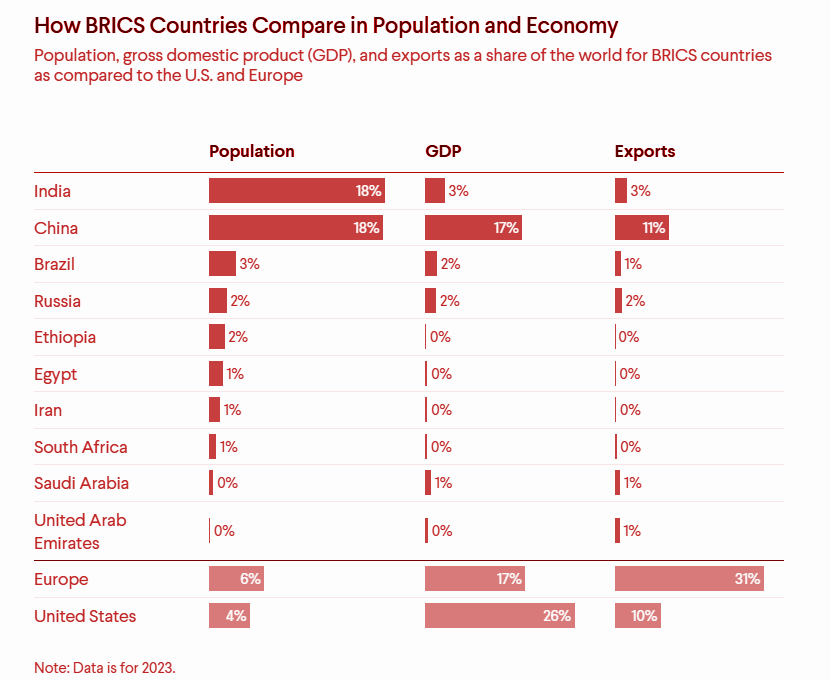
- The ten BRICS nations now represent over a quarter of the global economy and nearly half of the world's population.
- The membership of major oil-producing nations like the UAE enhances BRICS’ capacity to influence global energy markets.
- The diversity among new members emphasizes the importance of consensus-based decision-making, a foundational value for BRICS.
- Institutional Growth: BRICS has evolved to advocate for reforms in global governance structures, including the UN and WTO, and to promote changes within financial institutions like the World Bank and IMF.
- Key mechanisms such as the Contingency Reserve Arrangement (CRA) and the New Development Bank (NDB)(set up by the Fortaleza Declaration) have been established to support financial stability and development.
- Membership Expansion: South Africa joined BRICS in 2010, enhancing the bloc's representation of emerging economies.
- Significance:
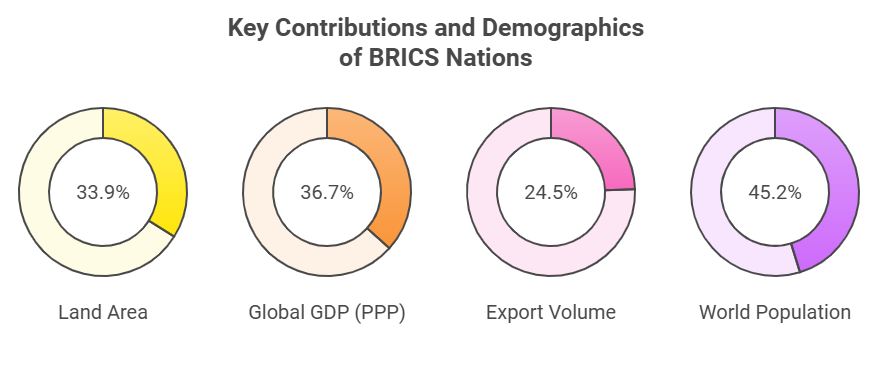
- Economic Growth Metrics: As of 2023, the BRICS bloc accounted for around 37% of global GDP.
- BRICS has surpassed the G7 in combined GDP (in PPP terms) and growth rates, demonstrating its rising importance in the global economy.
- Enhanced intra-BRICS cooperation supports this growth, yielding tangible benefits for member populations.
- Shaping Geopolitical Landscape: BRICS plays a vital role in influencing the geopolitical landscape and advocating for reforms in global governance structures.
- Its consensus-driven approach necessitates active participation and leadership from member states to navigate complex global issues.
- Women's Empowerment: BRICS highlights the importance of women's empowerment and decision-making participation, supported by the Ministerial Meeting on Women’s Affairs and the BRICS Women’s Forum.
- The BRICS Women’s Business Alliance fosters entrepreneurship through initiatives like a digital platform and regional offices to enhance support for women entrepreneurs.
- Affordable Housing and Urban Development: BRICS countries are advancing affordable housing and urban resilience through initiatives like the BRICS Urbanization Forum and Municipal Forum, in line with the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda.
What are the Significance and Challenges of BRICS for India?
- Significance of BRICS for India:
- Geopolitical Influence: BRICS provides India a key platform to balance the dominant Russia-China axis and assert its own multipolar vision in global politics.
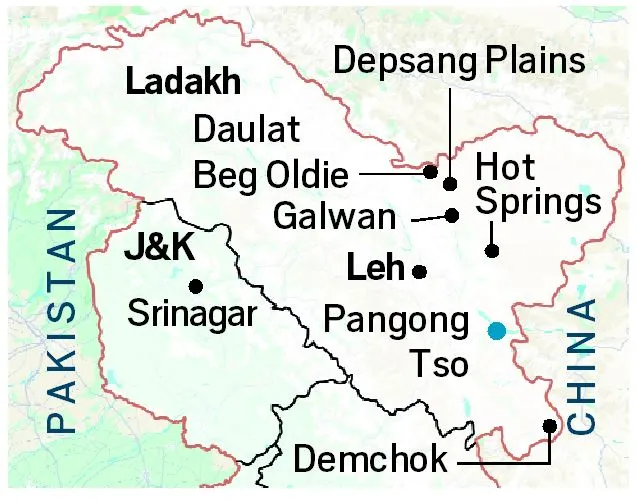
- For instance, by collaborating on the sidelines of 16th BRICS Summit, Indian and Chinese negotiators have reached an agreement on "patrolling arrangements" along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), enabling disengagement and resolving issues that surfaced in these areas in 2020.
- Also, BRICS allows India to advocate for reforms in the global financial system, seeking greater representation for developing economies in institutions like the IMF and World Bank.
- Developmental Financing: In the past five years, the NDB has approved 70 projects worth USD 25.07 billion across member countries, including 18 projects in India totaling USD 6.9 billion.
- It underscores India's strategic position within the BRICS framework, enhancing its infrastructure development and economic growth while fostering greater regional cooperation among member countries.
- Voice for Developing Nations: As a prominent member of BRICS, India can amplify its role as a voice for the Global South, especially on issues like fair trade, climate responsibility, and sustainable development.
- BRICS serves as a platform where India can advocate for the interests of developing nations, pushing back against policies from advanced economies that may hinder growth in emerging markets.
- Counterterrorism Collaboration: India has used BRICS to bring a strong focus on counter-terrorism, urging member countries to address specific aspects like terror financing and regional security challenges, which are critical for India’s national and regional security.
- Strategic Partnerships with New Members: The recent inclusion of countries like UAE, and Ethiopia further solidifies India’s partnerships, especially in vital areas like energy, trade, and infrastructure.
- For instance, UAE is significant trade and energy partners for India, while Ethiopia's strategic location and resource potential enhance India's presence in East Africa, thereby supporting its regional interests.
- Geopolitical Influence: BRICS provides India a key platform to balance the dominant Russia-China axis and assert its own multipolar vision in global politics.
- Challenges for India in BRICS:
- Diverse Member Interests: The BRICS grouping consists of countries with varying economic systems, political structures, and strategic interests, which poses coordination challenges for cohesive action.
- For India, aligning its priorities with those of all BRICS members, including countries with different regional goals like China, Brazil, and Russia, is often complex and requires careful diplomacy.
- China's Dominance: China’s substantial economic leverage within BRICS may overshadow India’s influence, especially with the group’s growing dependence on Chinese trade and investment.
- China's share in India's industrial goods imports jumped to 30% from 21% in the last 15 years.
- Further, China's strained relations with Russia complicate BRICS dynamics. Despite shared interests in countering Western influence, tensions like territorial disputes and competition for regional dominance may hinder unified decision-making.
- This dominance presents a challenge for India, as it has a significant trade deficit with China and must navigate this imbalance while trying to assert its own economic agenda within BRICS.
- Managing Regional Rivalries: BRICS includes countries with historical rivalries, whose tensions could impact group cohesion.
- India faces the challenge of balancing its relationships with these nations, as regional rivalries could complicate BRICS decision-making and create divisions that make it harder to achieve consensus on key issues.
- Global Governance Model: Amid global economic uncertainty, trade tensions, and protectionism, BRICS faces the challenge of developing an inclusive governance model that promotes stability.
- Diverse Member Interests: The BRICS grouping consists of countries with varying economic systems, political structures, and strategic interests, which poses coordination challenges for cohesive action.
What are the Highlights of the India-China Agreement at Kazan?
- Patrolling Agreement: Indian and Chinese negotiators have reached an agreement on “patrolling arrangements” along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), enabling disengagement from tensions that arose in 2020.
- This pact was discussed between India and China at the BRICS summit in Kazan.
- Restoration of Rights: The agreement allows Indian troops to patrol in Depsang Plains and Demchok, resuming pre-May 2020 activities.
- Troop Reduction: The deal aims to lower the presence of 50,000 to 60,000 troops on each side, with implementation expected in 10 days.
- Caution Ahead: Divergent statements suggest a need for trust-building, with India insisting that normalization hinges on resolving border issues. Future talks will involve Special Representatives.
What are the Major Highlights of the Kazan Declaration of the 16th BRICS Summit?
- Comprehensive Framework: The summit concluded with the adoption of the Kazan Declaration, a vital document outlining key areas of cooperation among BRICS nations.
- This declaration reinforces the bloc's commitment to mutual respect, sovereign equality, and a fairer international order.
- Strategic Importance: The declaration sets a foundation for enhanced collaboration across various sectors, aiming for sustainable development and peace, which are crucial for addressing the complex challenges facing the Global South.
- Diplomatic Resolutions of Conflict: BRICS leaders reaffirmed the importance of resolving the Russia- Ukraine conflict through diplomatic channels.
- The declaration voiced serious concern over the humanitarian crisis in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, particularly regarding the escalation of violence in Gaza and the West Bank.
- They expressed support for mediation efforts, highlighting adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter.
- This stance reflects BRICS's commitment to multilateralism and peaceful conflict resolution, positioning the bloc as a mediator in global conflicts.
- G20 and Multilateralism: The summit reiterated the significance of the G20 as a key platform for global decision-making, advocating for its continued and effective functioning based on consensus.
- BRICS nations expressed their commitment to maintaining a strong and effective IMF as part of the Global Financial Safety Net.
- The leaders called for reforms that better align the IMF's structure and operations with the interests of emerging economies, signaling a push for a more equitable global financial system.
- Trade & Dedollarization: A key outcome was the agreement to promote trade and financial transactions in local currencies among BRICS nations, which aims to reduce dependency on the U.S. dollar.
- BRICS is developing a digital currency to reduce reliance on Western currencies.The currency may be gold-backed for added security and appeal to nations seeking financial independence.
- This initiative aims to hedge against inflation and lessen U.S. dollar dependence amid global tensions.
- Also, BRICS Pay is an independent, decentralized payment messaging system designed to facilitate cross-border finance, operating without direct affiliation to the BRICS organization or its councils.
- BRICS Grain Exchange : Leaders discussed the establishment of a BRICS Grain Exchange and the exploration of a cross-border payment system.
- A grain exchange enables trading of grain commodities, improving market efficiency, price discovery, and food security among participating countries.
- Global Responsibilities: The summit emphasized the need for enhanced collaboration in health systems, supporting initiatives like the BRICS R&D Vaccine Center and the Integrated Early Warning System for infectious diseases.
- Also, this commitment underscores the importance of environmental stewardship, with BRICS nations.
- The leaders recognized India's initiative for an International Big Cats Alliance, committing to work together on conservation efforts for endangered species.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Strengthen Diplomatic Engagements: India should deepen diplomatic engagements within BRICS to bridge differing national interests.
- By fostering strong bilateral ties with new and existing members, India can facilitate greater consensus, particularly on issues like trade, climate action, and security.
- For India, it’s essential that BRICS doesn’t align as an anti-West bloc but instead advances a cooperative global framework that accommodates both developed and emerging economies.
- This requires India to advocate for balanced policies that avoid fragmenting the global economic order.
- Enhance Trade and Investment Ties: Expanding trade with BRICS nations, especially with new members like UAE,could help reduce India’s trade imbalance with China.
- Leveraging these economic partnerships can diversify India’s trade portfolio and strengthen its position within BRICS.
- Promote Multilateral Reforms: India should continue advocating for reforms in global institutions like the IMF and World Bank, emphasizing fairer representation for developing nations.
- A reformed multilateral system would align with BRICS’ shared vision and bolster India’s leadership role in promoting an equitable global order.
- Advance Counterterrorism Collaboration: India can work within BRICS to build more structured cooperation on counter-terrorism efforts, addressing issues like financing and radicalization.
- Strengthened security collaboration can enhance BRICS’ collective resilience to global security threats, benefiting India’s national security agenda.
- Leverage BRICS for Energy Security: As India’s energy needs grow, partnerships with energy-rich BRICS members like and Russia can secure long-term energy supplies.
- Collaborating on energy infrastructure and exploring renewable energy within BRICS can diversify India’s energy sources, promoting sustainable energy security.
- Support South-South Cooperation Initiatives: India should use BRICS as a platform to drive South-South cooperation, focusing on technology transfer, sustainable development, and infrastructure investments.
- Strengthening cooperation among developing nations within BRICS aligns with India’s vision of a multipolar world and enhances its influence in the Global South.
- Promote a Balanced BRICS Identity: To avoid BRICS becoming an anti-West bloc, India should champion a balanced identity for the group, emphasizing cooperation with both Eastern and Western economies.
- This will allow BRICS to emerge as an inclusive platform, promoting a global governance model that bridges East-West divides and accommodates India’s multi-alignment strategy.
Conclusion
BRICS serves as a vital platform for emerging economies to collaborate on economic growth and geopolitical stability. Its significance lies in advocating for developing nations. Strengthening diplomatic ties, enhancing trade relations, and advancing counterterrorism initiatives are essential for realizing BRICS's potential in sustainable development and global equity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the major economic and geopolitical challenges within BRICS, and how can India address them to enhance its cooperation in the group? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’, recently in the news, is related to the affairs of (2015)
(a) ASEAN
(b) BRICS
(c) OECD
(d) WTO
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. India has recently signed to become a founding member of New Development Bank (NDB) and also the Asian Infrastructure Bank (AIIB). How will the role of the two Banks be different? Discuss the strategic significance of these two Banks for India. (2014)