Infographics
Social Justice
MGNREGS Scheme
For Prelims: Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), Covid-19, Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS).
For Mains: MGNREGS Scheme, Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Relating to Development.
Why in News?
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) has witnessed a significant surge in women's participation, marking a historic high in the current financial year of 2023-24.
What are the Women Participation Trends in MGNREGA?
- Women Participation Trends:
- There has been a gradual increase in women's participation over the last decade, with percentages rising from 53.19% during the Covid-19 outbreak in 2020-21 to the current 59.25%.
- Southern states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and Goa showcase notably high rates of women's involvement, surpassing 70%, while northern states like Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh lag behind at around 40% or below.
- Despite historical disparities, some states like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Lakshadweep show recent improvements in women's participation rates in the ongoing financial year, attributed to incremental percentages.
- Rural Labor Force Trends:
- Beyond MGNREGS, the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation demonstrates a substantial surge in female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in rural areas.
- Notable figures show an increase from 18.2% in 2017-18 to 30.5% in 2022-23 in rural female LFPR, along with a decline in female unemployment rates from 3.8% to 1.8% during the same period.
What is MGNREGA Scheme?
- About:
- MGNREGA is one of the largest work guarantee programmes in the world launched in 2005 by the Ministry of Rural development.
- It provides a legal guarantee for one hundred days of employment in every financial year to adult members of any rural household willing to do public work-related unskilled manual work at the statutory minimum wage.
- Active workers: 14.32 Crore (2023-24)
- Major Features:
- The cornerstone of MGNREGA's design is its legal guarantee, ensuring that any rural adult can request work and must receive it within 15 days.
- If this commitment is not met, an "unemployment allowance" must be provided.
- It requires that priority shall be given to women in such a way that at least one-third of the beneficiaries shall be women who have registered and requested for work.
- Section 17 of the MGNREGA has mandated Social audit of all Works executed under the MGNREGA.
- The cornerstone of MGNREGA's design is its legal guarantee, ensuring that any rural adult can request work and must receive it within 15 days.
- Implementation Agency:
- The Ministry of Rural Development (MRD), Govt of India is monitoring the entire implementation of this scheme in association with state governments.
- Objective:
- This act was introduced with an aim of improving the Purchasing Power of the rural people, primarily semi or unskilled work to people living below poverty line in rural India.
- It attempts to bridge the gap between the rich and poor in the country.
- Achievements of 2022-23:
- 11.37 crore households availed employment.
- 289.24 crore person-days employment has been generated out of which:
- 56.19% were for women
- 19.75% were for Scheduled Castes (SCs)
- 17.47% were for Scheduled Tribes (STs).
What are the Challenges with the Implementation of the Scheme?
- Delay and Insufficiency in Funds Dispersal:
- Most states have failed to disburse wages within 15 days as mandated by MGNREGA. In addition, workers are not compensated for a delay in payment of wages.
- This has turned the scheme into a supply-based programme and subsequently, workers had begun to lose interest in working under it.
- There is ample evidence by now, including an admission by the Ministry of Finance, that delays in wage payments are a consequence of insufficient funds.
- Most states have failed to disburse wages within 15 days as mandated by MGNREGA. In addition, workers are not compensated for a delay in payment of wages.
- Caste Based Segregation:
- There were significant variations in delays by caste. While 46% of payments to SC (Scheduled Caste) workers and 37% for ST (Scheduled Tribes) workers were completed in the mandated seven-day period, it was a dismal 26% for non-SC/ST workers.
- The negative impact of caste-based segregation was felt acutely in poorer States such as Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal.
- Ineffective Role of PRI:
- With very little autonomy, Panchayati Raj Institution (PRI) are not able to implement this act in an effective and efficient manner.
- Large Number of Incomplete works:
- There has been a delay in the completion of works under MGNREGA and inspection of projects has been irregular. Also, there is an issue of quality of work and asset creation under MGNREGA.
- Fabrication of Job cards:
- There are several issues related to the existence of fake job cards, the inclusion of fictitious names, missing entries and delays in making entries in job cards.
What are the Initiatives under MGNREGS?
- Amrit Sarovar: Construction/renovation of at least 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district of the country; they will help in increasing the availability of water, both on surface and under-ground.
- Jaldoot App: It was launched in Sept 2022 for measuring the water level in a Gram Panchayat through 2-3 selected open wells twice a year.
- Ombudsperson for MGNREGS: Ombudsperson App was launched in Feb 2022 for smooth reporting and categorization of grievances received from various sources related to the implementation of the MGNREGS.
Way Forward
- There is a need to ensure consistent fund flow to states and implementing agencies while leveraging digital tools for transparent, timely wage payments.
- Focus on exclusion errors, identifying pockets where marginalized SC and ST families are missing out on MGNREGA benefits.
- Empower State and Central Employment Guarantee Councils for informed decisions, incorporating public participation via assemblies, civil society, and worker unions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Among the following who are eligible to benefit from the “Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act”? (2011)
(a) Adult members of only the scheduled caste and scheduled tribe households
(b) Adult members of below poverty line (BPL) households
(c) Adult members of households of all backward communities
(d) Adult members of any household
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee (MGNREGA), which is the largest work guarantee programme in the world, was enacted in 2005 with the primary objective of guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment per year to every household whose adult members volunteer to do unskilled manual work.
- It aims at addressing the causes of chronic poverty through the ‘works’ (projects) that are undertaken, and thus ensuring sustainable development. There is also an emphasis on strengthening the process of decentralisation by giving a significant role to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in planning and implementing these works.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.


Science & Technology
Dark Energy
For Prelims: Dark Energy, Dark Matter, Radiation
For Mains: Role of Dark Energy in Expansion of Universe.
Why In News?
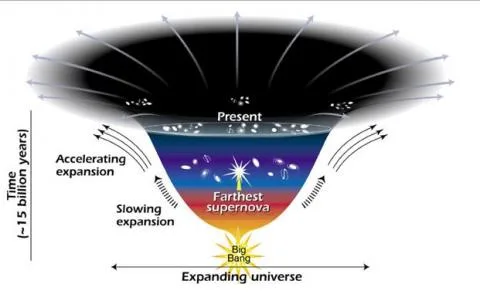
The universe's energy makeup involves a delicate balance between different forms of matter and radiation.
- Dark energy, constituting a significant 68%, plays a dominant role in dictating the universe's expansion.
What is Dark Energy in the Universe?
- About:
- Dark energy is a mysterious and elusive form of energy that makes up a significant portion of the total energy content of the universe.
- It is thought to be responsible for the observed accelerated expansion of the cosmos.
- Roughly 68% of the universe is dark energy and dark matter makes up about 27%.
- The rest of everything on Earth, everything ever observed with all of our instruments, all normal matter adds up to less than 5% of the universe.
- Key points to understand about dark energy:
- Invisible Force Steering Expansion:
- Dark energy is an unseen influence responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe. Unlike gravity, which tends to pull objects together, dark energy acts as a repulsive force, pushing galaxies away from each other.
- Characteristics of Space:
- Contrary to the notion of space being a void, dark energy introduces a new perspective. Space is not just an empty expanse; it's a dynamic, stretchable medium that responds to the presence of energy.
- Expansion Dictated by Energy Forms:
- Balancing Act:
- Dark energy dominates the universe's energy budget, and its presence dictates the overall rate at which space expands. Striking a delicate balance with other forms of energy is crucial for the stability of the cosmos.
- Implications:
- The amount of dark energy has significant implications for the observable universe.
- Adding too much positive energy could result in galaxies moving away from us faster than light, making only nearby regions visible.
- Conversely, excessive negative energy might lead to the universe collapsing to a tiny point.
- The amount of dark energy has significant implications for the observable universe.
- Diluteness of Dark Energy:
- Despite its dominance, dark energy is incredibly dilute across the vastness of the universe. In a cubic kilometer, it's as sparse as a single sugar crystal. This diluteness raises questions about the nature and distribution of this enigmatic force.
- Invisible Force Steering Expansion:
What are the Possible Explanations of Dark Energy?
- Property of Space:
- Albert Einstein was the first person to realize that empty space is not nothing.
- One version of Einstein's gravity theory, the version that contains a cosmological constant, implies that "empty space" can possess its own energy.
- Because this energy is a property of space itself, it would not be diluted as space expands. As more space comes into existence, more of this energy-of-space would appear. As a result, this form of energy would cause the universe to expand faster and faster.
- Quantum Theory of Matter:
- Another explanation for how space acquires energy comes from the quantum theory of matter.
- In this theory, "empty space" is actually full of temporary ("virtual") particles that continually form and then disappear.
- Fifth Fundamental Force:
- There are four fundamental forces in the universe, and speculative theories have proposed a fifth force, something that can’t be explained by the four forces.
- To hide or screen this fifth force, many models for dark energy use special mechanisms.
- Some theorists have named this "quintessence," after the fifth element of the Greek philosophers.
- However, none of the theories have been proved. Due to this, Dark energy has been noted as “the most profound mystery in all of science”.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidence for the continued expansion of the universe? (2012)
- Detection of microwaves in space
- Observation of redshift phenomenon in space
- Movement of asteroids in space
- Occurrence of supernova explosions in space
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above can be cited as evidence
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson in 1963 found mysterious microwaves coming equally from all directions. The radiation called the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation was the radiation predicted years earlier by Gamow, Herman, and Alpher. This convinced most astronomers that the Big Bang theory was correct and provided an evidential base for continued expansion of the universe. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Edwin Hubble in 1929 measured the redshifts of a number of distant galaxies. On ploting redshift against relative distance, the redshift of distant galaxies increased as a linear function of their distance. Astronomers measure the movement of objects relative to us using Doppler shift. Light from distant objects in the universe is redshifted (shift in the frequency of light towards red colour), which tells us that the objects are all receding away from us. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Movement of an asteroid in space may provide information regarding the type of material in early universe, but as such no evidence regarding expanding universe is provided. Hence, 3 is not correct.
- The supernova explosion occurs when there is a change in the core, or centre, of a star. It happens in either binary star system or at the end of a single star’s lifetime. It helps in studying the distribution of elements throughout the universe. These elements travel on to form new stars, planets and everything else in the universe. However, it does not provide evidence for expanding universe. Hence, 4 is not correct.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Internal Security
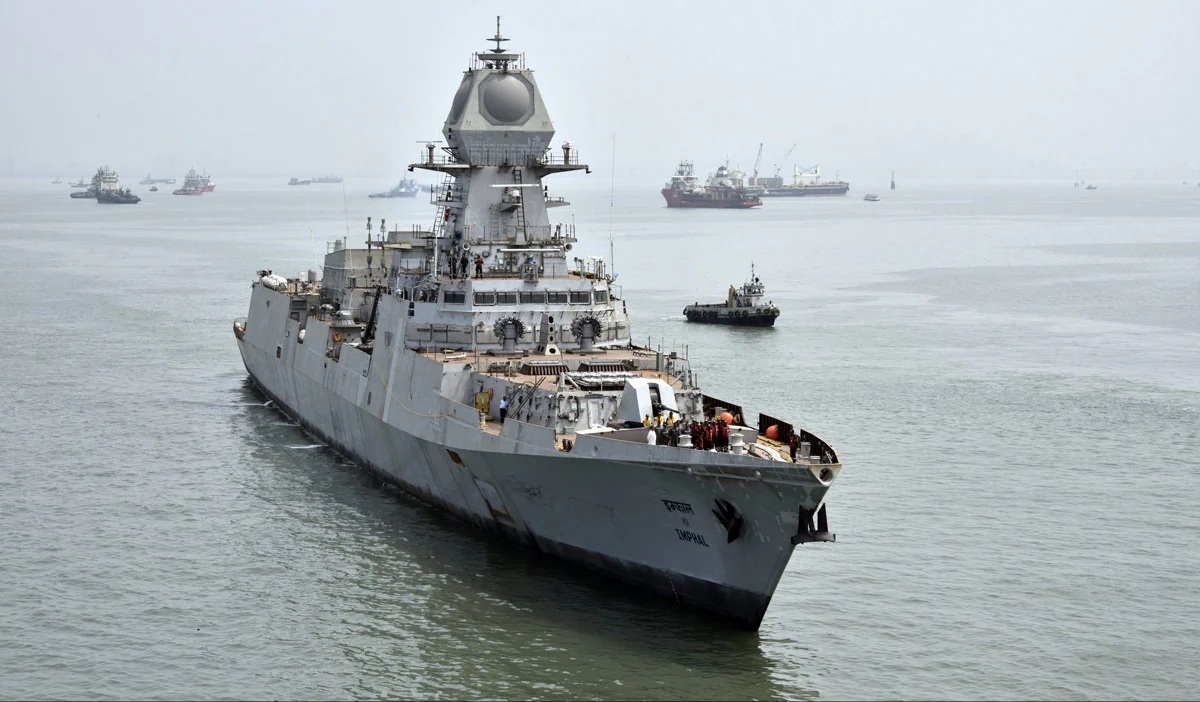
INS Imphal
For Prelims: INS Imphal, Indian Navy, INS Surat, BrahMos cruise missile, Project 15B.
For Mains: Defence technologies, Maritime security
Why in News?
Recently, INS (Indian Naval Ship) Imphal (Pennant D68) has been commissioned into the Indian Navy.
What is INS Imphal?
- About:
- INS Imphal is the third of the four 'Project 15 Bravo Vishakhapatnam class' guided missile destroyers.
- The fourth will be named INS Surat.
- INS Imphal is among "the most technologically advanced guided missile destroyers in the world.
- It was launched and "christened" as 'Imphal" on 20th April, 2019.
- INS Imphal is the third of the four 'Project 15 Bravo Vishakhapatnam class' guided missile destroyers.
- Features:
- The ship measures 163m in length, and 17m in breadth with a displacement of 7,400 tonnes and is amongst the most potent warships built in India.
- It is propelled by four powerful Gas Turbines, in a Combined Gas and Gas configuration, and is capable of speeds in excess of 30 knots.
- It is capable of launching the BrahMos cruise missile, the world's fastest supersonic cruise missile.
- The ship is also equipped to fight under Nuclear, Biological and Chemical warfare conditions.
- It is armed with sophisticated state-of-the-art weapons and sensors, including Surface-to-Surface Missiles, Surface-to-Air Missiles, Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) rocket launchers and Torpedo launchers, ASW helicopters, radars, sonar and Electronic Warfare systems.
- Significance:
- The ship reinforces the principle of "Jalmev Yasya, Balmev Tasya," signifying that controlling the seas grants immense power. In the Indo-Pacific region, where multiple powers vie for influence, INS Imphal contributes to India's efforts to establish itself as a significant maritime player.
- India heavily relies on sea routes for international trade due to geographical barriers like the Himalayas and challenges from neighboring countries.
- INS Imphal aids in securing these crucial sea lanes, ensuring safe passage for trade vessels and thereby safeguarding India's economic interests.
What is Project 15B?
- India’s indigenous Destroyer construction programme commenced in the late 1990s with the three Delhi class (P-15 class) warships and this was followed by three Kolkata class (P-15A) destroyers commissioned a decade later.
- Presently, under the P-15B (Visakhapatnam Class), a total of four warships are planned (Visakhapatnam, Mormugao, Imphal, Surat), following the success and technological advancements achieved in Project 15A.
- Project 15B aimed to build the advanced variants of Kolkata class destroyers as Visakhapatnam class destroyers.
- The class is identified by the name of its lead ship, hence known as the Visakhapatnam class.
- Under Project 15B, a contract was signed in January 2011 with the objective to build on the capabilities of the earlier ships while incorporating technological advancements and improvements in weaponry, electronics, and other systems.
- The lead ship of Project 15B is INS Visakhapatnam (Pennant No D66), which was commissioned in November 2021.
- INS Mormugao (D67) is the second ship commissioned in December 2022, and INS Surat (to be designated D69 upon commissioning) was launched in May 2023.
- These ships are designed by the Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau and constructed by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDSL) in Mumbai.


Science & Technology
PwC's 2023 Global Risk Survey
For Prelims: Cyber risks, Cybersecurity, Generative Artificial Intelligence, Ransomware Attacks.
For Mains: Challenges Related to Cyber Risk in India, Provisions for Cyber-Security in India.
Why in News?
According to the Global Risk Survey 2023 by PwC, a global consultancy firm, Cyber risks are the biggest threat faced by Indian organizations.
What are the Key Highlights of the Global Risk Survey 2023?
- Cyber Risks:
- Cyber risks are cited as the biggest threat faced by Indian organizations, with 38% of respondents feeling highly or extremely exposed to it.
- Climate change (37%) and inflation (36%) rank second and third among the top threats to Indian organizations.
- Digital and technology risks rank fourth, with 35% of Indian business leaders concerned about these risks.
- Cyber risks are cited as the biggest threat faced by Indian organizations, with 38% of respondents feeling highly or extremely exposed to it.
- Risk Management:
- Indian organizations are proactively investing in cybersecurity, with over half planning investments in cybersecurity tools (55%) and AI-related technologies (55%) in the next 1–3 years, aligning with global trends (51% and 49%, respectively).
- To reinforce these investments, 71% of Indian organizations are actively leveraging cybersecurity and IT data for risk management and opportunity identification, surpassing the global average of 61%.
- The survey also revealed how organizations are using emerging technologies such as Generative Artificial Intelligence for risk management, with 48% of Indian enterprises having deployed AI and machine learning for automated risk assessment and response to a large extent. This is slightly lower than the global response of 50%.
- This strategic approach signifies a commitment to fortify cybersecurity defences and embrace evolving technologies for resilience.
- Legacy Technologies:
- 42% of Indian organizations grapple with heightened security vulnerabilities attributed to legacy technologies (Outdated technology systems and infrastructure), surpassing the global average of 36%.
- Moreover, 46% of Indian companies face increased maintenance costs due to legacy tech, limiting budgets for innovative risk solutions, exceeding the global figure of 39%.
- Resilience Investments:
- 88% of Indian organizations have actively invested in resilience building over the past year, surpassing the global average of 77%.
- Resilience Investments include a resilience team, comprising members from functions such as business continuity, cyber, crisis management and risk management to swiftly respond to risk events as they occur.
- 88% of Indian organizations have actively invested in resilience building over the past year, surpassing the global average of 77%.
Why are Cyber Risks a Primary Threat to Indian Organizations?
- Cyber risks, encompassing malware, trojans, and spyware, have prominently emerged as the foremost threat for Indian organizations, notably highlighted by a substantial increase in ransomware attacks.
- Despite containment, such risks significantly impact market perception, influencing stock prices and eroding trust.
- Companies paying the ransom witnessed a doubling of the cost of data recovery compared to those relying on backups, emphasizing the financial toll of succumbing to ransomware demands.
- IT organizations store a diverse range of critical data, encompassing personally identifiable information, intellectual property, access credentials, and financial data.
- This multi-dimensional data provides threat actors with leverage to execute and perpetuate a range of malicious activities.
- Leaked data, especially intellectual property, can lead to devaluation and replication of software, posing a severe threat to revenue streams.
- The data's intrinsic value and potential impact on the organization's stakeholders increase the likelihood of successful ransom collection.
Laws Addressing Cyber Risks for Indian Organizations:
- The Information Technology (IT) Act, of 2000:
- It is the primary legislation dealing with cybersecurity, data protection and cybercrime. Identifying activities such as hacking, denial-of-service attacks, phishing, malware attacks, identity fraud and electronic theft as punishable offences.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023:
- The DPDP Act, 2023 is legislation acknowledging individuals' right to protect their digital personal data while emphasizing the lawful processing of such data for legitimate purposes
- It imposes accountability and responsibilities on data processors. The DPDP Act, 2023 addresses concerns about the use of personal data by employees and customers, fostering a higher standard of data privacy.
- The DPDP Act, 2023 is legislation acknowledging individuals' right to protect their digital personal data while emphasizing the lawful processing of such data for legitimate purposes
- National Cyber Security Policy 2013:
- It is designed to safeguard information and infrastructure in cyberspace by building capabilities for threat prevention and response, reducing vulnerabilities, and strengthening national security digitally.
- It focuses on ensuring a secure computing environment, fostering trust in electronic transactions, and guiding stakeholders' actions for cyberspace protection.
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020:
- Aims to improve cyber awareness and cybersecurity through more stringent audits. Empanelled cyber auditors will look more carefully at the security features of organizations than are legally necessary now.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)


Important Facts For Prelims
Field Pansy's Evolution
Why in News?
Recently, scientists have uncovered evidence of rapid evolution in a flowering plant found in Paris, France. The plant, identified as Field Pansy (Viola arvensis) is showing signs of self-pollination, a behaviour contradicting the conventional reliance on external pollinators.
What are the Key Facts about Field Pansy?
- The Field Pansy (Viola arvensis), is a common wildflower that can be found in many parts of Europe, Asia, and North America.
- It belongs to the group of plants called angiosperms, which produce seeds inside a protective structure called a fruit.
- Angiosperms rely on insects and other animals to pollinate them and help them reproduce.
Pollination
- Pollination is the process by which pollen grains, which contain the male reproductive cells of plants, are transferred from one flower to another, usually by insects that visit the flowers for nectar.
- Nectar is a sugary liquid that plants produce to attract pollinators.
- Pollination is essential for the genetic diversity and survival of many plant species, and it has evolved over 100 million years of coevolution between plants and animals.
- Pollination is carried through pollinators(vectors that move pollen within the flower and from flower to flower).
- However, some plants can also pollinate themselves, without the help of any external agent. This is called self-pollination, and it is a way for plants to ensure their reproduction in case there are no suitable pollinators around.
- Self-pollination can also save energy and resources for plants, as they do not need to produce as much nectar and flowers to attract pollinators.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Rapid Evolution:
- The study marks the first evidence of rapid evolution in plants, with the field pansy, showing significant changes in nectar production and flower size over a relatively short period.
- The study found that flowers of the wild pansy variety produced 20% less nectar and were 10% smaller.
- The study marks the first evidence of rapid evolution in plants, with the field pansy, showing significant changes in nectar production and flower size over a relatively short period.
- Self-Pollination:
- The field pansy has evolved to self-pollinate, reducing its reliance on pollinators due to a decreasing availability of insects.
- This behaviour is contrary to the conventional reliance on insects for pollination in angiosperms, marking a significant departure from established plant reproductive strategies.
- The field pansy has evolved to self-pollinate, reducing its reliance on pollinators due to a decreasing availability of insects.
- Convergent Evolution:
- The study reveals convergent evolution across populations, with a reduction in rewarding traits and attractiveness to pollinators.
- This convergence suggests a consistent evolutionary response to environmental pressures across different plant populations.
- The study reveals convergent evolution across populations, with a reduction in rewarding traits and attractiveness to pollinators.
- Resurrection Ecology Method:
- The researchers used the "resurrection ecology" method, planting seeds from the 1990s and 2000s against their contemporary descendants from 2021 to observe changes over time.
- This method allowed them to track and compare changes in plant traits and behaviour across different periods.
- The researchers used the "resurrection ecology" method, planting seeds from the 1990s and 2000s against their contemporary descendants from 2021 to observe changes over time.
- Environmental Impact:
- The move towards selfing may benefit plants in the short term but poses a threat to their long-term survival, especially in the face of climate change and other environmental changes.
- Self-pollination reduces the genetic diversity and adaptability of the plant, making it more susceptible to diseases and environmental stresses.
- The move towards selfing may benefit plants in the short term but poses a threat to their long-term survival, especially in the face of climate change and other environmental changes.
- Pollinator Decline:
- The study warns of a potential feedback loop that could lead to further declines in pollinators as a result of plant trait evolution, impacting the plant-pollinator network.
- Urgent Analysis:
- The study emphasizes the need to analyze whether these results are symptomatic of broader behavioral changes in the relationship between angiosperms and their pollinators.
- Researchers call for a thorough understanding of the possibility of reversing the process and breaking the eco-evolutionary-positive feedback loop to preserve plant-pollinator networks.
- The study emphasizes the need to analyze whether these results are symptomatic of broader behavioral changes in the relationship between angiosperms and their pollinators.


Important Facts For Prelims
Pantoea Tagorei
Why in News?
Researchers at Visva-Bharati University have discovered a new species of bacteria that could transform agricultural practices. They named it Pantoea Tagorei after the famous Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore.
What are the Key Facts About Pantoea Tagorei?
- Pantoea Tagorei bacteria belong to the genus Pantoea, which is part of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- Pantoea bacteria can be isolated from various environments including Water, Soil, Humans, Animals, and Plants.
- It is described as a plant growth-promoting bacteria, Pantoea Tagorei has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in boosting the cultivation of crops like paddy, pea, and chilli.
- The bacteria efficiently extracts potassium from the soil, enhancing plant growth. Additionally, it facilitates the solubilization of both potassium and phosphorus, nitrogen fixation, and enhances overall nutrient availability for plants.
- Positive effects on plant growth suggest a potential boost in crop yield. It can aid in addressing critical issues related to food security.
- Pantoea Tagorei enhances soil nutrient availability, reducing the need for commercial fertilizers.
- Minimizing reliance on fertilizers, the bacteria offers a cost-effective approach to sustainable agriculture and it can be a potential Biofertilizer.
Biofertilizer
- Biofertilizer can be defined as biological products containing living microorganisms that, when applied to seed, plant surfaces, or soil, promote growth by several mechanisms such as increasing the supply of nutrients, increasing root biomass or root area and increasing nutrient uptake capacity of the plant
- They are made up of living organisms like bacteria, blue-green algae, and mycorrhizal fungi.
- Example:
- Bacterial Biofertilizers: e.g. Rhizobium, Azospirilium, Azotobacter, Phosphobacteria.
- Fungal Biofertilizers: e.g. Mycorhiza.
- Algal Biofertilizers: e.g. Blue Green Algae (BGA) and Azolla.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Prelims
Q. With reference to Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct?(2021)
(a) Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolour Indian National Flag here.
(b) Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of Andhra region from here.
(c) Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here.
(d) Madame Blavatsky and Colonel Olcott set up headquarters of Theosophical Society first here.
Ans: (c)
- The original song ‘Jana Gana Mana’ (National Anthem) was written in Bengali, but in a Sanskritized dialect known as Sadhu Bhasha.
- The idea of translating the song from Bengali to English came to Rabindranath Tagore while he was visiting the Besant Theosophical College on the invitation of Irish poet James H. Cousins. He penned down the English translation during his stay at Madanapalle, a small town in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh.
- Jana Gana Mana was officially proclaimed as India’s National Anthem by the Constituent Assembly of India on 24th January 24, 1950.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. Which feature of some species of blue-green algae helps promote them as bio-fertilizers? (2010)
(a) They convert atmospheric methane into ammonia which the crop plants can absorb readily
(b) They induce the crop plants to produce the enzymes which help convert atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates
(c) They have the mechanism to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that the crop plants can absorb readily
(d) They induce the roots of the crop plants to absorb the soil nitrates in larger quantities
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae is an example of a bio-fertilizer, a type of organic fertilizer which contains living organisms and harnesses naturally occurring inputs like solar energy, nitrogen, and water to ensure soil fertility and plant growth
- Blue green algae is photoautotrophic microbes. They have specialised cells whcih utilises solar energy to reduce atmospheric N2 into Ammonia. Ammonia is used by plants for growth and increased production.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Sensor for Formalin Detection in Fish
Why in News?
A team of researchers from Guwahati University, Assam, has developed a new sensor made of a metal oxide-reduced graphene oxide(metal oxide- rGO) composite that can detect formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature in a non-invasive way.
Note
- Food adulteration is the practice of adding illegal or harmful substances to food to make it appear more appealing or to increase its shelf life.
- Formaldehyde is a colourless, pungent gas that is used in a variety of industrial processes, including as a preservative in some foods, commonly in fish in developing countries.
- However, the use of formaldehyde in food is illegal in many countries, as it is a known carcinogen.
What are the Key Facts of the Metal oxide- rGO Sensor?
- About:
- The sensor used Graphene(material that is extracted from graphite) oxide (GO) and tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2) to detect formalin in adulterated fishes.
- The sensor is low-cost, non-invasive, and selective, and can be used to prevent food adulteration and protect consumers.
- Need:
- Traditional formalin sensors for fish are either expensive electrochemical-based or less costly but invasive colorimetric-based methods.
- Both face issues of low-level and selective detection.
- Traditional formalin sensors for fish are either expensive electrochemical-based or less costly but invasive colorimetric-based methods.
- Working Procedure:
- GO, the oxidized form of graphene, initially poses a challenge due to low electrical conductivity.
- To overcome GO's limitations, scientists developed a composite called tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) with enhanced properties.
- The reduced graphene oxide provides high solution processability and ease of chemical modification with other materials, while the tin oxide offers high stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
- The sensor, crafted from tin oxide (SnO2) decorated Reduced graphene oxide (rGO), demonstrates effective sensing of formaldehyde vapour at room temperature.
- rGO is known for detecting toxic gasses, while SnO2 excels in formaldehyde detection. The combination maximizes their strengths.
- The designing of the prototype is in process in the lab which may be regarded as a breakthrough in the field of food adulteration.
- GO, the oxidized form of graphene, initially poses a challenge due to low electrical conductivity.


Rapid Fire
Palna Scheme
The Union Women and Child Development Ministry plans to set up 17,000 creches within Anganwadi centers across India under the 'Palna' scheme.
- This initiative aims to provide safe day-care facilities, enhancing the cognitive, nutritional, and health development of children.
- With an increased participation rate of women in the workforce, reaching 37% in 2022, this expansion of creches signifies a concerted effort to support women while nurturing the development of future generations.
- In July 2022, the Ministry of Women and Child Development revamped the National Creche Scheme into the Palna Scheme under 'Mission Shakti.'
- This transformation brought about Anganwadi cum Creches and reclassified existing creches from the old scheme as Stand Alone Creches.
Read more: Mission Shakti, Anganwadi Services


Rapid Fire
JAXA's SLIM Lunar Mission Analysis
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) recently achieved a significant milestone as its "Smart Lander for Investigating Moon" (SLIM) successfully entered lunar orbit, aiming to join the elite group of countries capable of soft-landing probes on the Moon.
- This mission marks Japan's second attempt at a soft Moon landing after the Hakuto-R mission, a private commercial venture, met with failure earlier in 2023.
- SLIM, having a dry weight of around 190 kilograms, stands as an example of precision technology, aiming to touch down within 100 meters of its target site, the Shinoli crater in the equatorial region.
Read more: Hakuto-R mission


Rapid Fire
P-Note Surge in Indian Markets
In November 2023, there was an increase in participatory note investments, reaching a total of ₹1.31 lakh crore.
- Participatory Notes (P-Notes) are financial instruments used by foreign investors who wish to invest in Indian markets without directly registering with the market regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- They are issued by registered foreign institutional investors (FIIs) or their sub-accounts against underlying Indian securities.
- While P-Notes offer flexibility and ease of investment, they have been a subject of regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about their potential use in money laundering, round-tripping, and lack of transparency.
Read more: Participatory Notes


Rapid Fire
Pong Dam Wildlife Sanctuary
The Union Ministry of Environment and Forests has recently issued a draft notification declaring an area of one kilometre from the boundaries of Pong Dam Wildlife Sanctuary in Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh as an eco-sensitive zone.
- The Pong Dam Wildlife Sanctuary is located around the Pong Dam Lake(also known as Maharana Pratap Sagar), a manmade reservoir formed due to the construction of the Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- The Pong Dam is the highest earth-fill dam in India and was constructed in 1975. In 1983, the entire reservoir was declared a Wildlife Sanctuary by the Himachal Pradesh government.
- In 1994, the Government of India declared it a "wetland of national importance". Pong Dam Lake was declared as a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- The sanctuary area is covered with tropical and subtropical forests.
Read more: Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary

, 2023.jpg)