Important Facts For Prelims
Solar Radiation Management
- 05 Jul 2023
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Solar radiation management (SRM) has emerged as a potential tool to counter the effects of global warming by reflecting sunlight back into space.
- A recently released report by the US government highlights the need for comprehensive research and a governance framework to assess the risks and benefits associated with SRM.
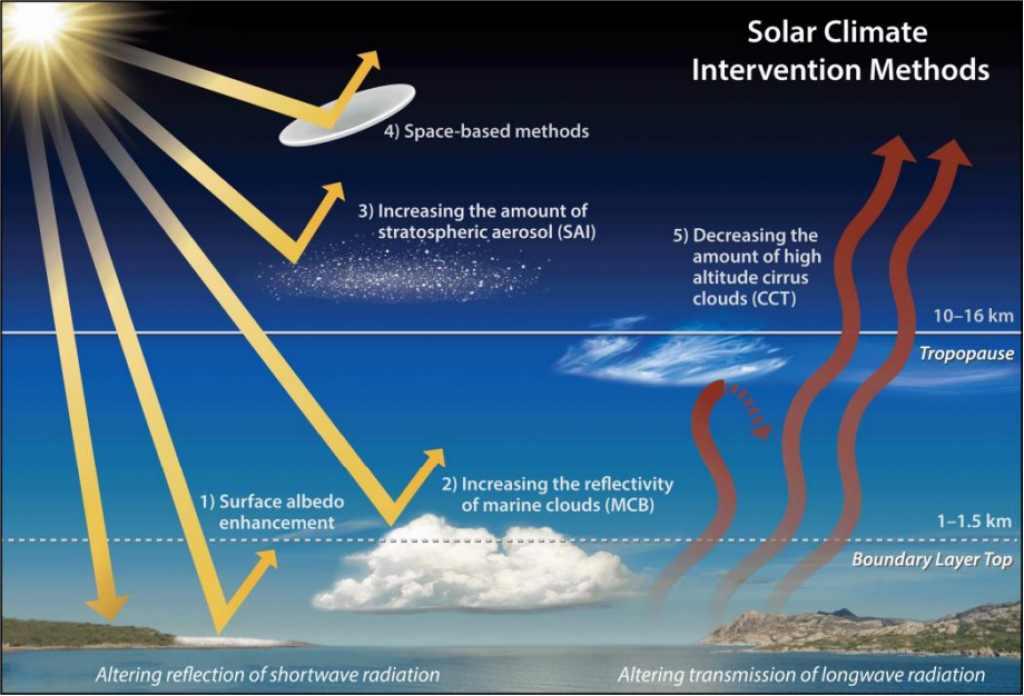
What is Solar Radiation Management?
- About:
- Solar radiation management is a form of climate engineering that aims to reduce global warming by reflecting some of the sun's energy back into space before it can heat up the Earth.
- SRM is an idea born of desperation, as the world faces an ongoing and accelerating climate crisis that threatens human well-being and planetary health.
- Some of Most Discussed Methods of SRM:
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI): This involves injecting reflective particles, such as sulfate aerosols, into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere), where they would scatter some of the incoming solar radiation back into space.
- This would mimic the cooling effect of volcanic eruptions, which also release aerosols into the stratosphere.
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB): This involves spraying fine droplets of seawater or other substances into low-level clouds (marine stratocumulus) over the oceans, where they would act as cloud condensation nuclei and increase the reflectivity and persistence of the clouds.
- This would enhance the cooling effect of clouds, which already reflect about 20% of the incoming solar radiation.
- MCB is considered to be more localized and reversible than SAI, but also more technically challenging and dependent on weather conditions.
- Space Sunshades: This involves placing large mirrors or screens in orbit around the Earth or at a stable point between the Earth and the sun (Lagrange point 1), where they would block or deflect some of the incoming solar radiation.
- This would reduce the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface.
- Space sunshades are considered to be more controllable and adjustable than SAI or MCB, but also more expensive and complex to deploy and maintain.
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI): This involves injecting reflective particles, such as sulfate aerosols, into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere), where they would scatter some of the incoming solar radiation back into space.
- Advantages:
- SRM could potentially provide a quick reduction in global temperatures, providing temporary relief from extreme climate events.
- It could be cost-effective compared to other options, depending on the method used and the scale required.
- SRM could be reversible on short timescales if stopped or adjusted.
- Disadvantages:
- SRM could not address all aspects of climate change, such as ocean acidification, biodiversity loss, or sea level rise due to thermal expansion.
- It could have negative or unintended side effects on regional or global climate systems, such as altering precipitation patterns, affecting monsoons, droughts, storms, or crop yields.
- SRM could pose ethical or geopolitical challenges, such as creating winners and losers among countries or regions, raising questions of justice, equity, consent, liability, or responsibility.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)