FATF Mutual Evaluation Report on India
For Prelims: Financial Action Task Force, Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council, Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) initiative, Goods and Services Tax, National Investigation Agency, Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, Enforcement Directorate
For Mains: India’s Progress in Combating Illicit Finance, Money Laundering and Terror Financing
Why in News?
Recently, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) released its Mutual Evaluation Report on India, highlighting the country's significant progress in combating illicit finance.
Note: The FATF plenary held in Singapore in June 2024 adopted the Mutual Evaluation Report for India, stating that it had achieved "high level of technical compliance" with the requirements of the global money laundering watchdog.
- The FATF had placed India in the "regular follow-up" category, the highest rating category by FATF becoming the only major economy with a federal structure to achieve this status.
- UK, France and Italy are among the only G-20 countries which have been placed in this category apart from India.
What are the Key Highlights of the FATF Mutual Evaluation Report on India?
- Areas Requiring Improvement: India was found partially compliant in three areas.
- Non-Profit Organisations (NPOs): NPOs registered as charitable organizations and enjoying tax exemptions could be vulnerable to terror funding.
- The system requires better measures to address risks associated with these organisations.
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): Ambiguities exist regarding the source of wealth, source of funds, and beneficial ownership for domestic PEPs. The government needs to address these ambiguities.
- Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs): Gaps exist in the regulation and supervision of DNFBPs, especially regarding money laundering and terror financing.
- DNFBPs contribute significantly to India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP), with precious metals and stones accounting for 7% and real estate 5%.
- Non-Profit Organisations (NPOs): NPOs registered as charitable organizations and enjoying tax exemptions could be vulnerable to terror funding.
- Money Laundering Risks: Illegal activities within India are the primary sources of money laundering risks, including fraud, cyber fraud, corruption, and drug trafficking.
- PMS Vulnerable to Money Laundering: Precious metals and stones (PMS) can be used to move large amounts of funds without leaving an ownership trail.
- The size of India’s PMS market contributes to its vulnerability to money laundering and terrorist financing. The sector includes approximately 1,75,000 dealers, but only 9,500 are registered with the Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC).
- The FATF report noted that criminal networks operating cross-border in the PMS sector may be under-investigated by law enforcement.
- Given India’s global role as a major consumer and producer of refined diamonds and gems, fraud and smuggling techniques need to be continuously monitored to prevent money laundering activities.
- There is a need for better risk understanding and deeper qualitative and quantitative data on the ML/TF risks associated with gold and diamond smuggling.
- Terrorist Financing Threats: India faces significant terrorism threats, particularly from Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and Al-Qaeda-linked groups active in and around Jammu and Kashmir.
- Regional insurgencies in the Northeast and Left-Wing Extremist groups also pose terrorism risks.
- While the country emphasizes prevention and disruption of terrorist financing, more effort is required to conclude prosecutions and convict terrorist financiers.
- Financial Inclusion: India has significantly enhanced financial inclusion, with a sharp rise in bank account holders and the increased use of digital payment systems.
- Simplified due diligence for small accounts has supported financial transparency and contributed to AML/CFT efforts.
- Acknowledged the Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile (JAM) initiative for promoting digital payments.
- Appreciated the implementation of Goods and Services Tax (GST), e-invoices, and e-bills for increasing supply chain transparency.
- Action Against Terror Financing: Acknowledged effective action against terror financing by the National Investigation Agency (NIA) and the Enforcement Directorate.
- FATF’s Recommendations:
- Pending Trials: India needs to expedite the conclusion of pending money laundering trials and improve its handling of crimes like human trafficking and drug-related offences.
- Targeted financial sanctions: India must improve its framework to ensure the freezing of funds and assets without delay and streamline communication regarding sanctions.
- Domestic PEPs: India needs to define domestic PEPs under its anti-money laundering laws and implement risk-based enhanced measures for them.
What are the Implications of FATF’s Mutual Evaluation for India?
- International Collaboration and Asset Recovery: India’s recognition from FATF enhances its ability to cooperate with other nations in tracking and recovering illicit assets, including those related to fugitive offenders like Vijay Mallya and Nirav Modi.
- Improved collaboration with global financial watchdogs aids in counter-terror financing efforts.
- Improved Access to Global Financial Systems: FATF ratings improve India’s access to global financial markets, enabling easier borrowing and investments from international institutions.
- The recognition supports the global expansion of India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), making it a preferred choice for cross-border digital payments.
- Strengthening Investor Confidence: Positive evaluation enhances India’s credibility and boosts foreign investor confidence in financial markets, making India a more attractive destination for foreign direct investments (FDI).
Conclusion
The FATF Mutual Evaluation Report marks a significant milestone for India in its fight against illicit finance. The recognition as a leader in anti-money laundering and counter-terror financing sets a benchmark for other nations, while the need for continuous improvements in areas like NPOs and PEPs remains crucial. This evaluation positions India favourably for future economic growth and international collaboration.
Read more: FATF’s Mutual Evaluation Report on India
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the FATF Mutual Evaluation Report for India's financial integrity and its implications on India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)
Demand for Early Elections to Delhi Assembly
For Prelims: Special Provisions for Delhi under Article 239AA, NCT, Schedule VII, Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Act 2021.
For Mains: Special Provisions for Delhi under Article 239AA, Administration of UTs.
Why in News?
Recently, the Delhi Chief Minister has called for early assembly elections in Delhi, aligning this request with elections in Maharashtra, where a new assembly must be elected before 26th November 2024.
- The current term of the Delhi Assembly is set to conclude on 23th February 2025.
What are the Rules and Provisions for Holding Elections?
- Constitutional Framework:
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) holds the authority to oversee and conduct elections as per Article 324 of the Constitution.
- Article 324 grants the ECI the power of superintendence, direction, and control of the electoral process, ensuring elections are completed before the term of the existing Assembly ends.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) holds the authority to oversee and conduct elections as per Article 324 of the Constitution.
- Representation of the People Act (RPA Act), 1951:
- According to section 15(2) of The RPA, 1951, elections cannot be notified less than 6 months before the end of the Assembly's term unless the assembly is dissolved prematurely.
- This provision emphasizes the importance of adhering to the established timeline for electoral processes.
- Dissolution of the Assembly:
- Role of the Governor:
- Article 174(2)(b) of the Constitution allows the Governor to dissolve the Legislative Assembly "from time to time."
- The Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers can recommend the dissolution of the Assembly before its term expires.
- Once the Assembly is dissolved, the ECI is mandated to hold elections within six months.
- Special Case of Delhi
- In Delhi, the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991 governs the dissolution of the Assembly.
- Section 6(2)(b) states that the Lieutenant Governor (LG) may dissolve the Assembly, but the final decision lies with the Centre.
- Therefore, even if the Chief Minister recommends dissolution, it is ultimately contingent upon the approval of the LG and the Central Government.
- Role of the Governor:
What Factors Does the ECI Consider Before Deciding the Election Schedule?
- Term End Date: The new Assembly must be in place before the current Assembly's term concludes.
- Logistical Considerations: The ECI considers weather conditions, availability of security forces, and the need for training election officers.
- Administrative Inputs: The ECI conducts visits to gather inputs from local administrative and police machinery.
- Clubbing Elections: The ECI aims to combine elections in states where possible to streamline the electoral process.
What is the Governance Model of Delhi?
- Constitutional Provisions:
- The status of Delhi being a Union Territory under Schedule 1 of the Constitution but designated as the ‘National Capital Territory (NCT)’ under Article 239AA.
- Article 239 AA:
- Article 239 AA was inserted in the Constitution by the Constitution (69th Amendment) Act, 1991 to give Special Status to Delhi following the recommendations of the S Balakrishnan Committee that was set up to look into demands for statehood for Delhi.
- Provisions of Article 239 AA:
- It says that the NCT of Delhi will have an Administrator and a Legislative Assembly.
- Subject to the provisions of the Constitution, the Legislative Assembly “shall have power to make laws for the whole or any part of the NCT with respect to any of the matters in the State List or Concurrent List in so far as any such matter is applicable to Union territories” except on the subject of police, public order, and land.
- Further LG has to either act on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, or he is bound to implement the decision taken by the President on a reference being made by him.
- It also empowers the LG to refer a difference of opinion on ‘any matter’ with the Council of Ministers to the President.
- Thus, this dual control between LG and the elected government leads to a power tussle.
- Article 239AB (also added by Constitution (69th Amendment) Act, 1991) provides that the President may by order suspend the operation of any provision of Article 239AA or of all or any of the provisions of any law made in pursuance of that article.
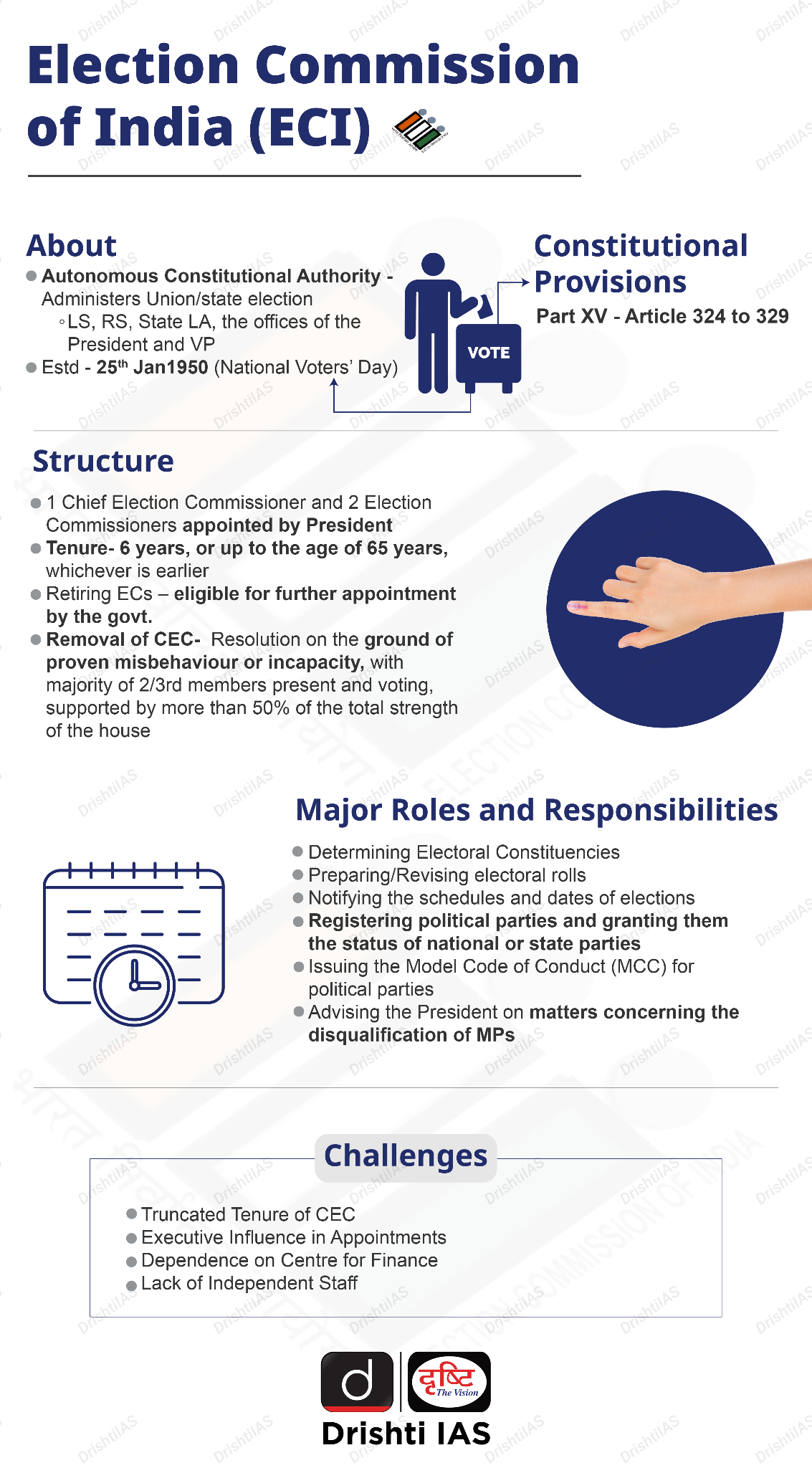
What is the Election Commission of India?
- About:
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India.
- It is not concerned with the elections to Panchayats and Municipalities in the states for which there is a separate State Election Commission.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Part XV (Article 324-329): It deals with elections and establishes a commission for these matters.
- Article 324: Superintendence, direction and control of elections to be vested in an Election Commission.
- Article 325: No person to be ineligible for inclusion in, or to claim to be included in a special, electoral roll-on grounds of religion, race, caste or sex.
- Article 326: Elections to the House of the People and to the Legislative Assemblies of States to be based on adult suffrage.
- Article 327: Power of Parliament to make provision with respect to elections to Legislatures.
- Article 328: Power of Legislature of a State to make provision with respect to elections to such Legislature.
- Article 329: Bar to interference by courts in electoral matters.
- Appointment & Tenure of Commissioners:
- The President appoints CEC and Election Commissioners as per the CEC and Other ECs (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023.
- They have a fixed tenure of 6 years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- The salary and conditions of service of the CEC and ECs will be equivalent to that of the Supreme Court Judge.
|
Drishti Mains Question Examine the role of the Election Commission of India in maintaining the integrity of the electoral process. What are the key challenges the ECI faces in dealing with electoral malpractices, and how can these be addressed? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections.
- Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognised political parties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in the light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)
US Federal Reserve's Rate Cut and Implications
For Prelims: Inflation, Russia-Ukraine Conflict, Unemployment, Recession, Carry trades, Foreign direct investment, Reserve Bank of India, Inflation target, Phillips Curve
For Mains: Impact of U.S. Federal Reserve Policies on Emerging Markets like India, Inflation vs. Employment, India's Monetary Policy Response to Global Economic Trends
Why in News?
Recently, the United States (US) Federal Reserve cut its benchmark interest rates by 50 basis points, marking its first significant reduction since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. This move signals a strategic approach to combat inflation while promoting economic growth.
Note
The US Federal Reserve conducts the nation's monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the US economy.
Why Did the US Federal Reserve Cut Interest Rates?
- Economic Recovery Post-Pandemic: Following the Covid-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve initially slashed interest rates to stimulate the economy. However, as inflation surged due to various factors, including global supply chain disruptions (due to Russia-Ukraine Conflict), the Federal Reserve raised rates to combat rising prices.
- Moderation of Inflation: By mid-2023, inflation had started to stabilise, moving closer to the Federal Reserve's target of 2%.
- Recent jobs data showed that high interest rates were negatively impacting employment, with U.S. unemployment rising to 4.2% in August 2024. This raised concerns about a potential recession, prompting the Federal Reserve to prioritize job creation alongside price stability.
- Dual Mandate: The Federal Reserve operates under a dual mandate of maintaining stable prices and achieving maximum employment. As the economic landscape evolved, it became clear that a rate cut would help balance these objectives.
- Implications for US:
- By cutting rates, the US hopes to balance inflationary pressures. Although inflation has moderated, the central bank is focused on maintaining its target rate of around 2%, seeking a “soft landing” for the economy.
- Lower interest rates typically make loans cheaper for both individuals and businesses. With unemployment rising, the Fed is prioritising job creation alongside price stability.
- The rate cut could help reduce borrowing costs for businesses, potentially leading to increased hiring and economic expansion.
- By cutting rates, the US hopes to balance inflationary pressures. Although inflation has moderated, the central bank is focused on maintaining its target rate of around 2%, seeking a “soft landing” for the economy.
How Inflation and Unemployment are Related?
- Inverse Correlation: Generally, inflation and unemployment are inversely related—when one rises, the other falls.
- During periods of low unemployment, wage inflation tends to rise as employers offer higher wages to attract workers, eventually pushing prices higher.
- Conversely, in times of high unemployment, wage growth remains stagnant, leading to lower inflation.
- During periods of low unemployment, wage inflation tends to rise as employers offer higher wages to attract workers, eventually pushing prices higher.
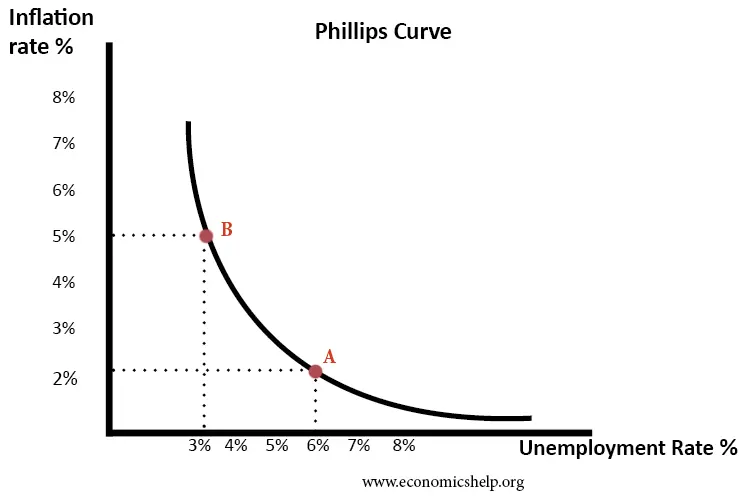
- Phillips Curve: The Phillips Curve is an economic theory that explains the inverse relationship between an economy's unemployment rate and inflation rate, as initially suggested by A.W. Phillips in the 1950s.
- The Phillips curve suggests that higher demand for labour during low unemployment periods leads to higher wages, which, in turn, drives inflation.
- This model has been widely used in monetary policy, particularly in balancing inflation and employment levels.
- The Phillips curve suggests that higher demand for labour during low unemployment periods leads to higher wages, which, in turn, drives inflation.
How will India be Affected by the Federal Reserve Rate Cut?
- Impact on Emerging Markets: The US plays a significant role in the global economy. A lower US interest rate makes investing in countries like India more appealing through carry trades.
- Carry trade is a strategy where investors(Foreign Institutional investors) borrow money in the US (where rates are low) and invest it where rates are higher, making a profit on the difference.
- Limited Impact: Chief Economic Adviser of India noted that while the rate cut could lower the dollar cost of capital and increase liquidity, it cannot be viewed as a standalone solution for boosting the global economy.
- Increased Foreign Investment: Lower US interest rates may incentivize global investors to borrow in the US and invest in India. This influx could take the form of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), or debt from the US, providing much-needed capital for the Indian economy.
- Stock Market Sentiment: The rate cut has attracted considerable investor interest in the Indian stock market, indicating a positive sentiment among investors despite global uncertainties.
- Crude Oil Prices: When the US dollar weakens, oil becomes cheaper for holders of other currencies, leading to increased demand and potentially higher prices.
- Increased oil prices may increase India's energy import costs and potentially reigniting inflation in India.
- Impact on Currency Exchange Rates: A weakening US dollar against other currencies, including the Indian rupee, could adversely affect Indian exporters while benefiting importers.
- RBI’s Response: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) faces pressure to cut interest rates, but it operates under different inflation targets and economic mandates compared to the Federal Reserve.
- The RBI is more focused on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth and is not as heavily influenced by US unemployment data.
Federal Tapering
- Federal tapering refers to the process by which the Federal Reserve gradually reduces its large-scale asset purchases, a monetary policy tool often employed during economic crises.
- This strategy, commonly associated with quantitative easing (QE), aims to stimulate the economy by lowering interest rates and increasing liquidity in financial markets.
- Tapering is intended to withdraw some of the economic stimulus provided during crises, transitioning towards a more normalised monetary policy.
India’s Repo Rate
- The RBI, at the 50th Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.50%.
- This decision reflects the committee's approach to managing inflation while supporting economic growth.
- The MPC's primary objective is to align inflation with the target rate of 4.0% with a tolerance band of +/- 2% points.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the implications of the US Federal Reserve’s interest rate cut on emerging economies like India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
- Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
- Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Pager, Walkie-Talkie Blasts in Lebanon
For Prelims: Pagers, Walkie-Talkie, Lebanon, Hizbullah, Middle East, Israel, Palestine, Middle-East, Arab World.
For Mains: Use of Electronic Devices and Modern Warfare Systems in Wars, Its Implications, Impact of Israel-Palestine Conflict on India and International geopolitical scenario.
Why in News?
Recently, several people were killed and hundreds injured in Lebanon following explosions of hand-held radios like walkie-talkies and pagers used by Hezbollah at multiple locations.
- These pagers, chosen by Hezbollah to evade detection through cell phones, were covertly modified with Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN).
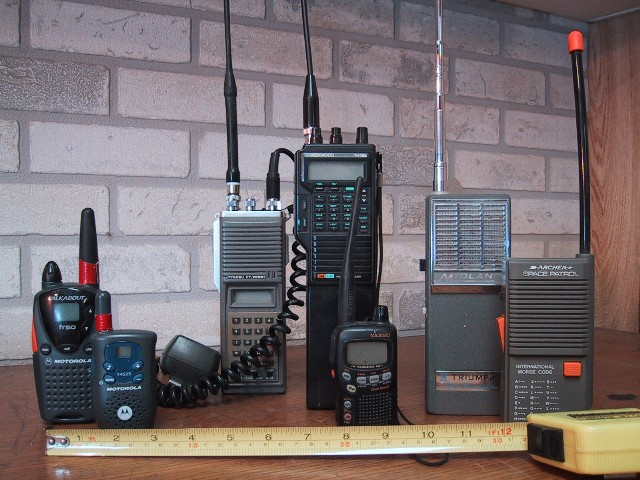
What are Walkie-Talkies?
- About:
- It is also known as a handheld two-way radio with a microphone and speaker.
- These are portable communication devices that utilize radio waves to transmit and receive messages on specific frequency bands.
- History and Invention:
- These were first used by the military in the 1930s and played an important role in wars of the 20th century.
- Its invention is attributed to Don Hings in 1937, initially created for pilots and known as wireless sets, pack sets, and two-way field radios.
- Components and Operation:
- It comprises a transmitter-receiver unit, an antenna, a loudspeaker-microphone combination, and a push-to-talk button.
- The device operates on a single frequency band, allowing it to transmit and receive signals.
- To communicate, users press the push-to-talk button, converting their voice into radio waves that are transmitted and received by other devices on the same channel.
- Applications:
- Walkie-talkies are extensively used in emergency services, security, military operations, and various industries like construction and hospitality.
- Their ability to function without a mobile network makes them invaluable in areas with poor signal reception.
- Modern-day walkie-talkies are much more advanced and now include features such as flashlights, hands-free technology, SOS signals, and weather alerts, in addition to basic communication.
- Limitations:
- Common issues with walkie-talkies include losing coverage due to battery depletion, excessive background noise, privacy concerns, and static during transmission.
Transmission Types:
- Simplex: Communication is unidirectional; only one party can transmit at a time. Example: Computer to printers, Pagers.
- Half Duplex: Communication is bidirectional but not simultaneous; only one party can talk at a time. Example: Walkie talkies.
- Full Duplex: Communication is bidirectional and simultaneous; both parties can talk and listen at the same time. Example: Telephones.
What are Pagers?
- About:
- Pagers, also known as beepers, are wireless devices that receive and display messages.
- They were widely used in the 1980s but are still relied upon by specific groups like healthcare and emergency services due to their reliability in low-signal areas.
- Working:
- Pagers operate using radio signals transmitted by towers that can penetrate areas where cellular signals may be weak.
- Types of Pager:
- One-way pagers: Receive messages from a central transmitter but cannot reply. They alert users through beeps or vibrations.
- Two-way pagers: Allow users to send and receive messages, though they are still less functional than smartphones.
- Pagers Application in Covert Operations:
- Low Susceptibility to Surveillance: Their lack of Global Positioning System(GPS) and internet connectivity reduces the risk of location tracking.
- Difficult to Intercept: The use of radio frequencies makes them harder to monitor than cellular or internet-based devices.
- Modifiable for Covert Use: Pagers can be modified to trigger signals for remote detonation or alerts without drawing attention.
- Remote detonators, including pagers and other consumer electronics, have been used in various conflicts.
- Armed groups have utilized Radio Controlled Improvised Explosive Devices (RCIEDs) to target police stations and government buildings, employing devices that emit weak signals to avoid detection.
- RCIED is explosive material integrated with a wireless radio or device that triggers upon receipt of a signal from a second wireless handheld device.
What is Hezbollah?
- Hezbollah, meaning "Party of God," is a Shia militia-cum-political party in Lebanon and one of the world's most heavily armed non-state actors, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS).
- It was formed during the Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990), largely in response to Israeli invasions of southern Lebanon in 1978 and 1982.
- Inspired by Iran’s 1979 Islamic revolution, it has received substantial support from Iran and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- It has been designated as a terrorist organisation by countries like the US and Israel.
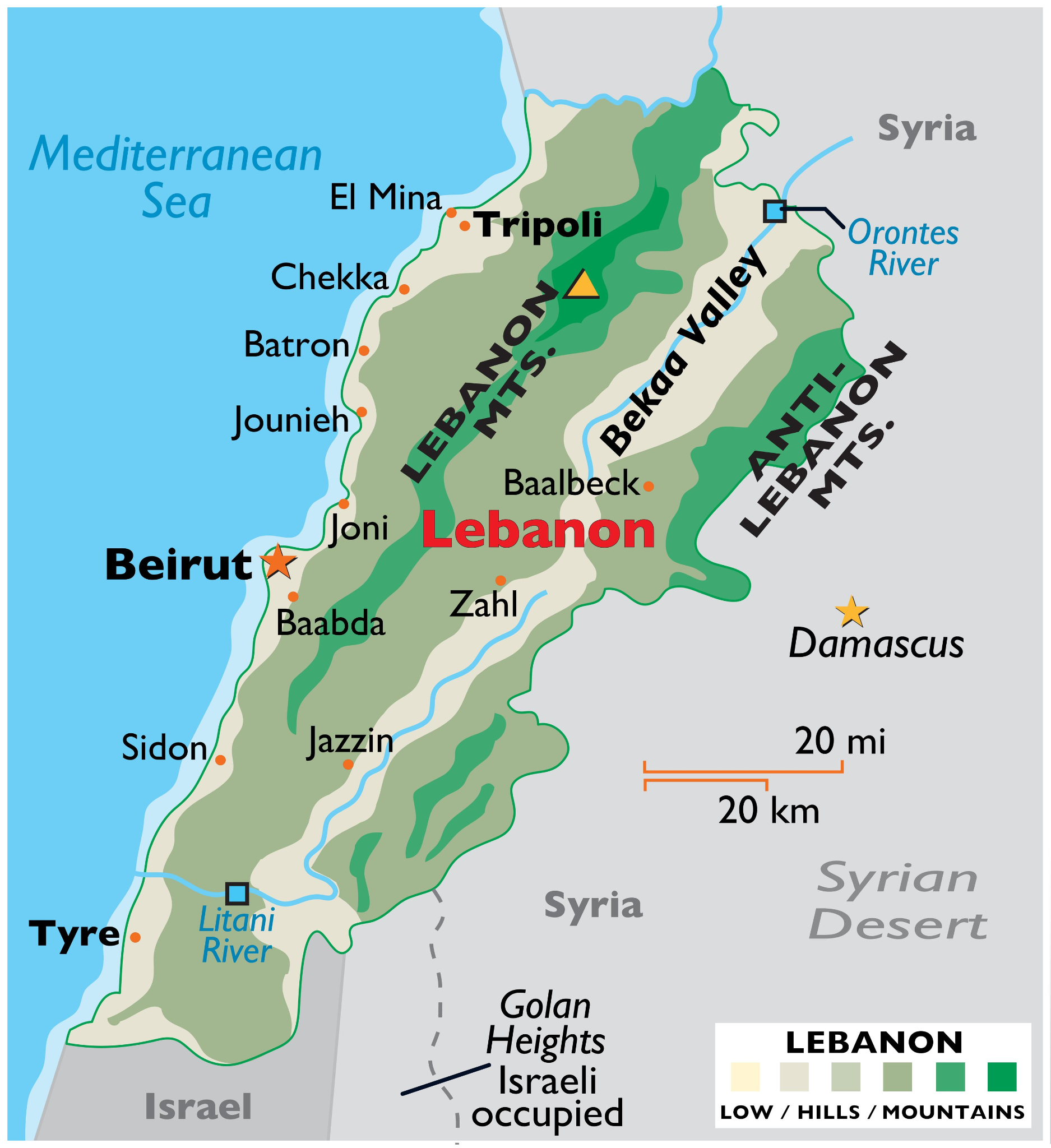
Lebanon
- Lebanon is a country in the Levant region (a region in the eastern Mediterranean Basin) of West Asia.
- Its capital and largest city is Beirut.
- It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, by Israel to the south, and by the Mediterranean Sea to the west.
- Cyprus island lies a short distance away from the country's coastline.
|
Drishti Mains Question Analyse how electronic devices, such as mobile phones and pagers, have been utilised in modern warfare. What are its implications and strategies to mitigate them? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to ‘LiFi’, recently in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It uses light as the medium for high speed data transmission.
- It is a wireless technology and is several times faster than ‘WiFi’.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q. What is the difference between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi devices? (2011)
(a) Bluetooth uses 2.4 GHz radio frequency band whereas Wi-Fi can use 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency band
(b) Bluetooth is used for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) only, whereas Wi-Fi is used for Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) only
(c) When information is transmitted between two devices using Bluetooth technology, the devices have to be in the line of sight of each other, but when Wi-Fi technology is used the devices need not be in the line of sight of each other
(d) The statements (a) and (b) given above are correct in this context
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following: (2010)
- Bluetooth device
- Cordless phone
- Microwave oven
- Wi-Fi device
Q. Which of the above can operate between 2.4 and 2.5 GHz range of radio frequency band?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Q. Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries? (2017)
- Jordan
- Iraq
- Lebanon
- Syria
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Q. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Q. The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)
NCERT Chapter on Veer Abdul Hameed
Why in News?
Recently, a chapter titled 'Veer Abdul Hameed’ and a poem titled 'National War Memorial' have been included in the NCERT curriculum of Class VI.
What are the Key Facts About Changes in the NCERT Textbook?
- Chapter on 'Veer Abdul Hameed': It honours Company Quarter Master Havildar (CQMH) Abdul Hameed. He is a war hero from the India-Pakistan war 1965 who was awarded the Param Veer Chakra posthumously.
- His story of bravery and supreme sacrifice is intended to inspire students with real-life examples of patriotism and devotion to duty.
- Poem on 'National War Memorial': It aims to cultivate a deep sense of respect for the soldiers who sacrificed their lives for the nation, and to promote a spirit of national pride and remembrance for their bravery.
- The National War Memorial stands testimony to the sacrifices made by our soldiers during various conflicts, United Nations Operations, Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response Operations since Independence.
- It was inaugurated on 25th Feb 2019 at the India Gate complex, New Delhi.
- The National War Memorial stands testimony to the sacrifices made by our soldiers during various conflicts, United Nations Operations, Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response Operations since Independence.
- Aligned with NEP 2020 and NCF 2023: The changes are aligned with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023.
- NEP 2020 and NCF 2023 emphasise holistic education that promotes ethical values, patriotism, and the development of responsible citizens.
What are the Key Facts About Veer Abdul Hameed?
- About Abdul Hamid: He served with the 4th Grenadiers Battalion of the Indian Army and was part of India’s defence force in the Battle of Asal Uttar during the India-Pakistan War in 1965.
- Battle of Asal Uttar: The Battle of Asal Uttar took place in early September 1965, near the India-Pakistan border in Punjab, close to the town of Khem Karan.
- Pakistan aimed to invade India, capture Khem Karan, and advance towards the Beas River bridge to isolate strategic areas like Amritsar.
- Utilizing a significant number of superior Patton tanks, Pakistan's offensive surprised Indian forces, initially forcing a retreat.
- This was one of the largest tank battles of the 1965 India-Pakistan War.
- Role of Abdul Hamid: Abdul Hameed was stationed near Chima village on the Amritsar-Khem Karan road, leading a detachment of Recoilless Guns to target enemy tanks.
- On 10th September 1965, he spotted four Pakistani Patton tanks, destroying three and damaging one. He was subsequently killed by fire from another tank.
- Recognition: The site of his death is now part of a war memorial.
- A captured Pakistani Patton tank stands guard at the entrance of the building, with its turret down, as a tribute to the Indian soldiers who fought and died in the battle.
GCF to Help Vulnerable Nations
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief of the Green Climate Fund (GCF) committed to ensuring that vulnerable nations receive the necessary financial support to address climate challenges.
What is the Green Climate Fund (GCF)?
- About:
- GCF is a fund for climate finance that was established within the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
- It was established in 2010, and headquartered in the Republic of Korea.
- Governed by:
- The Fund operates under the governance of the GCF Board and is accountable to the Conference of the Parties (COP), functioning in accordance with its guidance.
- It supports projects, programs, policies, and various activities in developing country Parties through designated thematic funding windows aimed at addressing specific priority areas.
- Functions:
- NDCs are climate action plans that outline how countries intend to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
- The Paris Agreement requires all countries to create, communicate, and update their NDCs every five years.
- GCF is mandated to support developing countries raise and realise their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) ambitions towards low-emissions, climate-resilient pathways.
- NDCs are climate action plans that outline how countries intend to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
Climate Finance
- About:
- It is the funding that supports actions to address climate change. It can come from public, private, and alternative sources.
- Importance:
- It is important for reducing emissions and adapting to the effects of climate change. It's also critical for enabling countries to transition to low-carbon economies and achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- Need in India:
- India needs climate finance to scale up renewable energy installations, modernise infrastructure, and improve energy efficiency.
- Financial mechanisms:
- UNFCCC has established several financial mechanisms to provide climate finance to developing countries, including the Adaptation Fund, Green Climate Fund, and the Global Environment Fund.
What are the Objectives and Ambitions of the GCF?
- It is a key mechanism for channelling climate finance to developing countries that, despite being least responsible for global carbon emissions, are disproportionately affected by climate change.
- The fund primarily supports nations in two key areas like reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to the worsening impacts of climate change, including storms, droughts, heatwaves, and rising sea levels.
- The GCF has recognized 19 climate-vulnerable countries that have received little to no financial assistance.
- This includes Algeria, the Central African Republic, Chad, Iraq, Lebanon, Mozambique, Papua New Guinea, and South Sudan.
- The GCF is now intentionally prioritizing these countries to provide targeted climate funding and support.
- The GCF emphasised the organization's commitment to becoming the "partner of choice" for vulnerable countries and ensuring funds are directed to where they are most urgently needed.
- Somalia, devastated by severe floods and its worst drought in decades, has been promised over USD 100 million in GCF investments for year 2025 to foster climate-related projects and attract further investments.
Government Initiatives Regarding Climate Finance
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following statements regarding ‘Green Climate Fund’ is/are correct? (2015)
- It is intended to assist the developing countries in adaptation and mitigation practices to counter climate change.
- It is founded under the aegis of UNEP, OECD, Asian Development Bank and World Bank.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Bio-RIDE Scheme
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio-RIDE) scheme.
- About Bio-RIDE:
- Its aim is to foster research, innovation, and entrepreneurship in biotechnology, positioning India as a global leader in this field.
- To make India a USD 300 billion bioeconomy by 2030 and achieve the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.
- The proposed budget for the scheme's implementation is ₹9,197 crore for the 15th Finance Commission period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Key Components:
- Biotechnology R&D: Supports innovation in synthetic biology, biopharmaceuticals, bioenergy, and more through grants and incentives.
- Industrial & Entrepreneurship Development: Nurtures startups with funding, incubation, and mentorship.
- Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry: Promotes sustainable practices in biomanufacturing.
- It supports a circular bioeconomy in line with the Lifestyle for the Environment (LiFE)’ initiative to develop eco-friendly solutions to tackle climate change, improve healthcare, boost agriculture, and scale bio-based products.
Read More: India's Biotech Revolution, National Biopharma Mission
Ammonium Nitrate Import Raises Concern
The sharp rise in ammonium nitrate (AN) imports from Russia has raised concerns for India's domestic fertiliser industry, which faces competition from cheaper imports.
- Indian fertiliser companies are investing over Rs 4,000 crore to boost AN capacity, vital for mining coal, iron ore, and limestone.
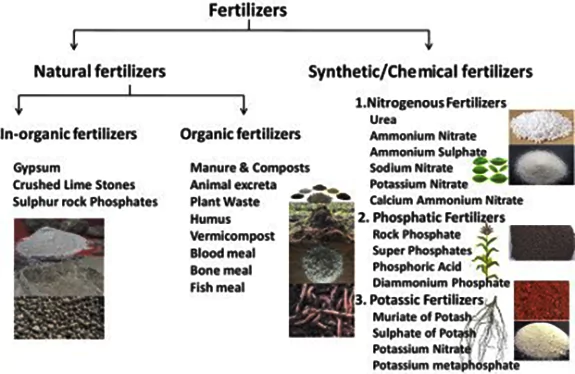
- Ammonium Nitrate (AN):
- Ammonium Nitrate (NH₄NO₃) is the nitrate salt of the ammonium ion, consisting of ammonia and nitric acid. It is a white crystalline solid highly soluble in water.
- Uses:
- Fertiliser: Its high nitrogen content makes it extensively used in agriculture.
- Explosives: Mixed with fuel oil to produce Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil (ANFO), commonly employed in mining and demolition.
- Cold Packs: These are found in instant cold packs and are useful for injury treatment.
- Matches: AN is used in safety matches.
- About the Fertilizer Industry in India:
- India is the world's second-largest consumer of urea, after China, and the second-largest producer of nitrogenous fertilisers
- The fertiliser Industry is one of the 8 core industries in India.
- It receives the second-largest subsidy, after food.
- India meets 100% of its potash requirement through imports from countries like Belarus, Russia, Israel, and Jordan.
Read More: Fertiliser Consumption in India
Upcoming Global Summits on Environment
The United Nations is going to host four major sessions to address key threats to the planet in the year 2024.
- Key threats to the planet include Global warming, disappearing plant and animal species, fertile land turning to desert, and plastic pollution in the oceans, in air and on land.
- Upcoming Four Major Sessions:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD COP16): CBD COP16 will be held in Cali, Colombia. The key objective is to assess how countries are advancing towards the 2022 Montreal commitment to protect 30% of the planet’s land and marine areas by 2030.
- UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC COP 29): UNFCCC COP 29 will be held in Baku, Azerbaijan. It aims to finalise agreements on climate finance and improve the quality and scope of financial support.
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD COP16): UNCCD COP16 will be held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Discussions will aim to restore 1.5 billion hectares of land by 2030 and manage ongoing droughts affecting various regions.
- Plastic Pollution Treaty Negotiations: It will be held in South Korea. The final session of negotiations will focus on creating a global treaty to address plastic pollution. This treaty aims to tackle plastic waste across environments, including oceans, rivers, and land.
Read More: UNFCCC
Neuralink's Blindsight Implant
Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration granted "breakthrough device" status to Elon Musk's Neuralink's Blindsight.
- This designation aims to speed up the development and review of innovative medical devices that address severe conditions.
- Blindsight is an experimental vision-restoring implant. It could help individuals who have lost both eyes and their optic nerve regain vision.
- It also offers a possibility of vision for those born blind, as long as their visual cortex remains intact.
- Initially, the visual experience will be low resolution, similar to early video game graphics. However, with future advancements, Blindsight could surpass natural vision.
- In addition to restoring sight, the device might enable users to perceive wavelengths outside the visible spectrum, such as infrared, ultraviolet, or radar, giving them superhuman-like vision abilities.
- In addition to Blindsight, the company is working on a device designed to help paralysed individuals control digital devices using only their thoughts.
- Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk in 2016, focuses on developing brain chip interfaces that could help restore vision, aid in movement, and facilitate communication for patients with disabilities.
Read more: First Human Neuralink Implant