Internal Security
Drug Trafficking and Threat to Security
- 20 Apr 2023
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Methamphetamine, Fentanyl, NDPS Act, NCB, Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle, National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse, National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction
For Mains: Drug Menance: Threats, Challenges, Initiatives taken, challenges
Why in News?
The global drug trade is a major problem that has put security and law enforcement agencies on high alert worldwide, including in India.
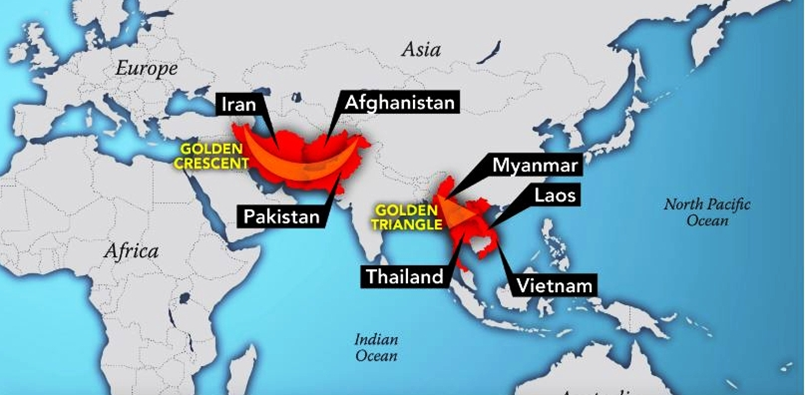
- Traditionally India has been seen as sandwiched between the Death (Golden) Crescent and Death (Golden) Triangle and is being flooded with drugs, especially heroin and methamphetamine, from these two regions by drug lords indirectly supported by intelligence setups.
Why is Drug Trafficking Dangerous?
- It is a social problem that harms youth and families and the money it generates is diverted for disruptive activities that have bearings on national security.
- Criminal networks traffic a range of drugs including cannabis, cocaine, heroin and methamphetamine.
- Methamphetamine (meth) is an addictive drug and can cause considerable health adversities that can sometimes result in death.
- Recently, USA has witnessed a new zombie drug (fentanyl) gripping its population.
- This drug can cause raw wounds on the user’s skin that can spread rapidly with repeated exposure.
- It starts with ulcers, hardens to dead skin called eschar, and if left untreated can result in amputation.
- Drug trafficking is often associated with other forms of crime, such as terrorism, money laundering or corruption.
- Trafficking routes can also be used by criminal networks to transport other illicit products.
What is the Status of Drug Addiction in India?
- In 2018, The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has conducted a “National Survey on Extent and Pattern of Substance Use in India” in collaboration with AIIMS, New Delhi. The survey’s findings are as follows:
| Name of the substance | Prevalence of use (Age Group 10-75 years) |
| Alcohol | 14.6% |
| Cannabis | 2.83% |
| Opiates/ Opioids | 2.1% |
- According to World Drug Report 2022, India has the fourth largest quantity of opium seized in 2020 at 5.2 tons and the third-highest amount of morphine was also seized in the same year at 0.7 tons.
From where the Illegal Drugs are trafficked in India?
- Threats from Death (Golden) Crescent: Comprises Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan.
- Parts of Pakistan adjoining Afghanistan are also used by Pakistani drug traffickers to convert Afghan opium to heroin and then sent to India.
- Threats from Death (Golden) Triangle: Consists of Vietnam, Thailand, Laos and Myanmar.
- The Shan and Kachin provinces of Myanmar bordering China also pose challenges.
- China Factor: These heroin and methamphetamine-producing areas have porous borders and are, reportedly, under the control of rebel groups, indirectly supported by the Chinese.
- Illicit arms are manufactured here and supplied to underground groups active in India.
- According to the latest annual report by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), drug trafficking through sea routes in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, estimated to account for around 70% of the total illegal drugs smuggled into India.
What are the Initiatives taken by India to curb the Drug Menace?
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, (NDPS) 1985: It prohibits a person from producing, possessing, selling, purchasing, transporting, storing, and/or consuming any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has prepared a plan for Drug Demand Reduction for the period of 2018-25. This plan focuses on:
- Preventive education
- Awareness generation
- Identification, counselling, treatment and rehabilitation of drug dependent persons
- Training and capacity building of service providers through collaborative efforts of government and NGOs.
- National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse: It was created in accordance with a provision of the NDPS, 1985 for meeting the expenditure incurred in measures taken for:
- Combating illicit trafficking
- Controlling abuse of drugs and substances
- Identifying, treating and rehabilitating addicts
- Preventing drug abuse
- Educating public against drug abuse
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Campaign: Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA) was launched in 2020 to tackle the issue of Substance Abuse and a vision to make India Drug Free. It is a three-pronged attack combining:
- The supply curb by Narcotics Control Bureau
- Outreach and Awareness and Demand Reduction effort by Social Justice and Empowerment
- Treatment through Health Department.
- Initiatives of Indian Coast Guards: The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) has developed a good synergy with the security agencies and with the coast guards of Sri Lanka, Maldives and Bangladesh for seizure of such drugs.
- It seized 2,160 kgs of meth in two different instances recently near the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- International Treaties and Conventions to Combat Drug Menace: India is signatory of the following international treaties and conventions:
- United Nations (UN) Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961)
- UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971).
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988)
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) 2000
What are the Challenges in tackling Drug Trafficking in India?
- Dark Net: Darknet markets are difficult to trace because of their anonymity and low risks. They have taken over the traditional drug markets. Studies reveal that 62% of the darknet is being used for illicit drug trafficking.
- The success rate in catching traffickers using the darknet has been very low the world over.
- Transactions in Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrency payments and doorstep deliveries, through courier services, have made darknet transactions attractive.
- Traffickers have become Creative and Tech Savvy: The traffickers have adopted to new age technologies such as supplying drug and guns through drones in Punjab which have posed new challenges before the security forces.
- Using more Safe and Anonymous methods: The drug traffickers have started relying more upon courier/parcel/post after the restrictions imposed on vehicular/ship/airline movement during Covid-19 pandemic.
- In 2022, a person was arrested for doing the drugs business through making an e-commerce dummy website.
- In one more instance, few persons were arrested for selling drugs through e-commerce websites like amazon by listing fake products on the website.
- Nexus between Drugs Lords and NRIs: Recent investigations have revealed the connection of the drug cartels with NRIs based in Canada, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong and several European countries along with local drug lords and gangsters in India, who have links with Khalistani terrorists and the ISI in Pakistan.
- Trafficking through Local Gangs: A new trend has emerged wherein organised gangs, which primarily used to carry out extortion activities in their local areas are being used for drug trafficking as they are ready-made logistics to carry out such activities.
Way Forward
- To stop drugs from entering the country, measures must be taken such as controlling cross-border trafficking and improving drug enforcement. However, to fully address the problem, India must also work on reducing the demand for drugs through measures such as imposing harsher punishments under NDPS Act, 1985.
- Awareness must be spread among the people to lower down the drug addiction through campaigns and NGOs. The stigma associated with drug taking needs to be reduced. Society needs to understand that drug-addicts are victims and not criminals.
- Certain crop drugs which have more than 50% alcohol and opioids need to be contained. Strict action is required from police officers and the excise and narcotics department to curb the problem of drug menace in the country.
- Education curriculum should include chapters on drug addiction, its impact and also on de-addiction. Proper Counselling is another alternative.
- Concerted and coordinated efforts of all the agencies will be required to tackle this growing threat.
- Creating more employment opportunities would solve the problem to some extent as Quick, and more, money attracts unemployed youth towards such activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In one of the districts of a frontier state, narcotics menace has been rampant. This has resulted in money laundering, mushrooming of poppy farming, arms smuggling and near stalling of education. The system is on the verge of collapse. The situation has been further worsened by unconfirmed reports that local politicians as well assume senior police officers are providing surreptitious patronage to the drug mafia. At that point of time a woman police officer, known for her skills in handling such situations is appointed as Superintendent of Police to bring the situation to normalcy.
If you are the same police officer, identify the various dimensions of the crisis. Based on your understanding, suggest measures to deal with the crisis. (2019)