Indian Economy
RBI's 50th Monetary Policy Committee Meeting
- 09 Aug 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India, Monetary Policy Committee, Flexible inflation targeting, Repo rate, Artificial intelligence, Index of Industrial Production, Digital lending apps, Unified Payments Interface
For Mains: Monetary Policy Committee Decisions, Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in News?
- The Reserve Bank of India's 50th Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting has brought notable updates on interest rates and economic policies.
- This meeting highlights eight years of the flexible inflation targeting (FIT) framework and introduces measures to manage inflation and boost economic efficiency.
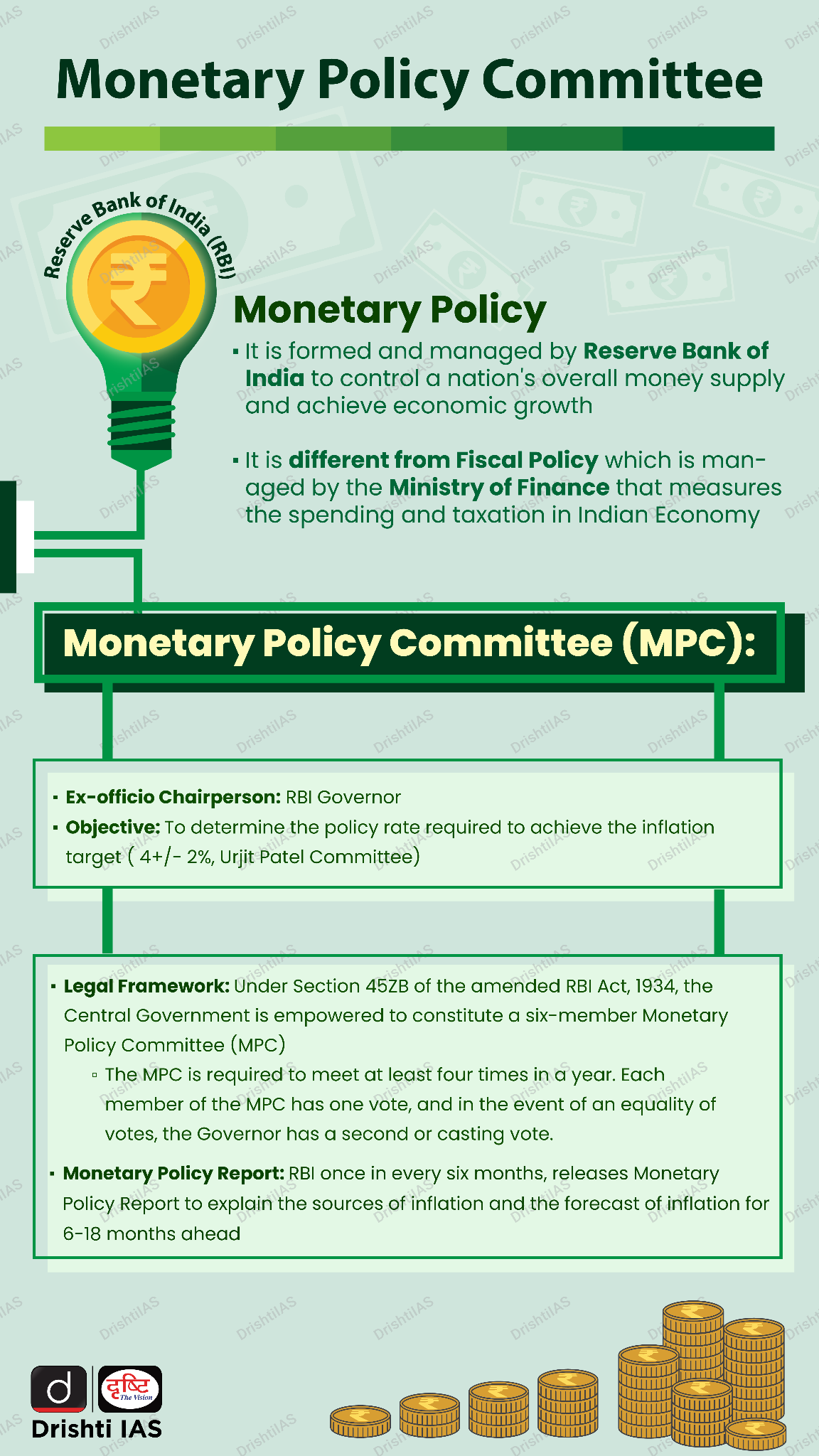
What are the Key Highlights of the 50th MPC Meeting?
- Rate Decisions of the MPC:
- The MPC decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.50%. This decision reflects the committee's current approach to managing inflation and supporting economic growth.
- Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) Rate remains at 6.25%, aligning with the unchanged repo rate.
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate and Bank Rate both rates are set at 6.75%. These rates are used to manage liquidity and borrowing costs within the economy.
- The MPC's primary objective is to withdraw accommodation to gradually align inflation with the target of 4.0%. Despite the strong economic growth, the committee emphasizes the need to control inflation to ensure price stability while supporting economic expansion.
- Assessment of Growth:
- Global Economic Conditions: MPC stated that the global economy is showing steady but uneven growth. Manufacturing sectors are experiencing a slowdown, while service industries continue to perform well.
- Major economies are witnessing a gradual reduction in inflation rates, although services prices remain sticky.
- Different countries are adopting varied monetary policies, with some central banks cutting rates while others tighten their policies.
- Challenges: Key global challenges include demographic shifts, climate change, geopolitical tensions, rising public debt, and advancements in technology such as artificial intelligence. These factors contribute to uncertainties in the medium-term global growth outlook.
- Domestic Economic Conditions: MPC highlighted India’s economic activity remains resilient with a positive outlook driven by steady monsoon progress, higher kharif sowing, and improved reservoir levels.
- Manufacturing and services sectors are robust, with the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) showing accelerated growth.
- Household consumption is supported by rising rural demand and steady urban discretionary spending.
- Global Economic Conditions: MPC stated that the global economy is showing steady but uneven growth. Manufacturing sectors are experiencing a slowdown, while service industries continue to perform well.
- Inflation Trends and Implications:
- Headline Inflation increased to 5.1% in June 2024, largely due to higher food prices. Core inflation (excludes food and fuel price) moderated, with fuel prices in deflation.
- Food prices have a significant impact on overall inflation, given their substantial weight (around 46%) in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) basket. High food prices, particularly for vegetables, have driven up headline inflation.
- Future Outlook: While food inflation is expected to remain high in the short term, there may be some relief due to favourable base effects and improved monsoon conditions.
- Headline Inflation increased to 5.1% in June 2024, largely due to higher food prices. Core inflation (excludes food and fuel price) moderated, with fuel prices in deflation.
- Financial Market Conditions
- MPC noted that the global financial markets have experienced volatility due to concerns about economic slowdowns, geopolitical tensions, and changes in carry trade dynamics.
- Despite this, India’s financial markets are stable, supported by strong macroeconomic fundamentals.
- MPC noted that the global financial markets have experienced volatility due to concerns about economic slowdowns, geopolitical tensions, and changes in carry trade dynamics.
- Additional Measures Announced:
- Digital Lending Apps Repository:
- The RBI will establish a public repository of digital lending apps (DLAs) used by regulated entities (REs) like banks. This measure aims to help consumers identify unauthorised lending apps and ensure more transparency in the digital lending ecosystem.
- This development follows the RBI's September 2022 guidelines on digital lending, prompted by a report from an RBI Working Group revealing that approximately 600 of 1,100 lending apps available to Indian Android users are illegal.
- Unregulated digital lending has led to exploitation of consumers through predatory practices, highlighting the urgent need for stringent regulations and consumer protections in this rapidly evolving sector.
- The RBI asked REs to ensure Lending Service Providers (LSPs) and DLAs comply with guidelines. They must disclose interest rates upfront, inform borrowers of product details, and capture borrowers' economic profiles to promote responsible lending.
- The RBI will establish a public repository of digital lending apps (DLAs) used by regulated entities (REs) like banks. This measure aims to help consumers identify unauthorised lending apps and ensure more transparency in the digital lending ecosystem.
- UPI Transaction Limit:
- The transaction limit for tax payments through Unified Payments Interface (UPI) will be raised from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 5 lakh. This adjustment is designed to facilitate easier and more efficient tax payments for consumers.
- This change addresses the high value and frequency of direct and indirect tax payments, aiming to streamline and facilitate these transactions.
- The RBI also plans to introduce ‘Delegated Payments’ via UPI, allowing a secondary user (such as a spouse) to make payments using the primary user's bank account.
- Primary UPI users will be able to set specific payment limits for secondary users on their accounts.
- This feature is expected to expand the reach of digital payments and cater to UPI’s growing user base of 424 million individuals.
- Continuous Cheque Clearing:
- RBI has proposed continuous clearing of cheques with 'on-realisation-settlement' Cheque Truncation System, instead of the current clearing cycle of two working days to speed up payments and enhance efficiency.
- This system aims to clear cheques within hours on the day of presentation, improving efficiency, reducing settlement risk, and enhancing customer experience.
- RBI has proposed continuous clearing of cheques with 'on-realisation-settlement' Cheque Truncation System, instead of the current clearing cycle of two working days to speed up payments and enhance efficiency.
- Digital Lending Apps Repository:
Flexible Inflation Targeting Framework
- Introduced in February 2015, FIT aims to control inflation with a target of 4% (±2%) while allowing temporary deviations to support economic growth.
- This framework, established through an agreement between the RBI and the Finance Ministry (GoI), aims to manage inflation while accommodating growth. The framework builds on recommendations from the Urjit Patel Committee Report (UPCR).
- FIT aims to stabilise inflation expectations, which can enhance macroeconomic stability and foster growth.
- The RBI Act, 1934 was amended in 2016 to provide statutory basis for a monetary policy framework, the amendment provides for the inflation target to be set by the Government, in consultation with the RBI, once every five years.
- The framework is designed to make monetary policy more transparent and predictable, which can strengthen coordination between the RBI and the government.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the impact of the recent monetary policy decisions on India's financial stability and economic efficiency. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)