India’s Energy Strategy
For Prelims: Liquefied Natural Gas, International Energy Agency, Ethanol Blended Petrol, Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, Global Biofuel Alliance
For Mains: Energy Security & Diversification, Opportunities and challenges in India’s Energy Security.
Why in News?
India has committed to increasing its oil and natural gas imports from the US, with energy trade expected to rise from USD 15 billion to USD 25 billion in the near future. This move is part of a broader goal to double bilateral trade to USD 500 billion.
- The decision enhances India’s energy security while strengthening economic ties amid global geopolitical shifts.
Why is India Expanding Energy Trade with the US?
- Energy Security: India, the world's 3rd-largest oil importer and consumer, relies on imports for over 85% of its crude needs. With primary energy demand set to nearly double to 1,123 million tonnes of oil equivalent by 2040 driven by a projected Gross Domestic Product (GDP) rise to USD 8.6 trillion, making supply stability crucial.
- Expanding energy trade with the US reduces dependency on West Asia and Russia, while diversifying sources mitigates risks from geopolitical disruptions.
- Bilateral Trade Growth: Expanding energy imports helps balance India’s USD 45.7 billion trade surplus with the US in 2024, while advancing the ‘Mission 500’ initiative to double bilateral trade to USD 500 billion by 2030.
- Infrastructure Boost: Competitively priced US crude and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) aim to make the US a leading supplier to India, supporting industrial growth, refining expansion, and petrochemical investments.
- Geopolitical Benefits: Stronger US energy ties support India’s bid for full membership in the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Strengthened US-India ties in energy can counterbalance China’s influence in global energy markets.
What is the State of India’s Energy Consumption?
- Crude Oil:
- Total Imports (2023-24): 234.26 million tonnes of crude oil.
- Import Dependence: India's crude oil import dependence increased to 87.8% in 2023–24, with domestic production meeting less than 13% of the total demand.
- Future Projection: Crude oil consumption is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.59% to 500 million tonnes by FY40.
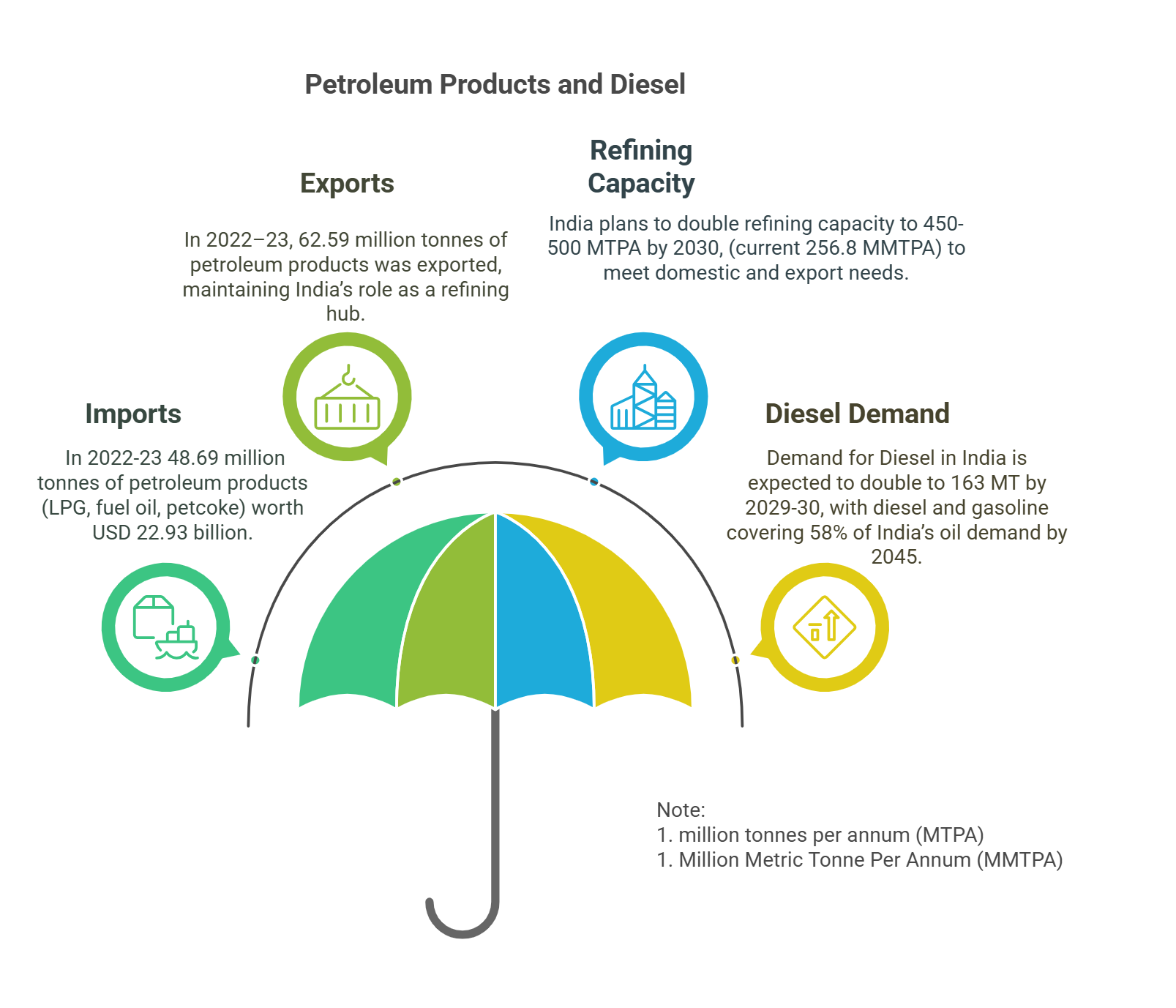
- Petroleum Products and Diesel:
- Natural Gas and Cleaner Fuels: India aims to increase natural gas’s share in the energy mix to 15% by 2030 (from the current ~6%).
- Total LNG Imports (2023-24): 31.80 billion cubic meters (bcm) worth USD 13.405 billion.
- Ethanol Blending Target: Advanced to 20% by 2025-26 to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, with ethanol production capacity reaching around 1,600 crore litres as of September 2024.
- The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme has reduced CO₂ emissions by 544 lakh metric tons and substituted 181 lakh metric tons of crude oil.
What is India Doing to Meet the Energy Needs?
- Increasing Domestic Production: India aims to double its oil & gas exploration area from 0.5 million sq. km by 2025 to 1 million sq. km by 2030.
- New projects in the Krishna-Godavari (KG) Basin and offshore exploration efforts are expected to boost output.
- Global Energy Partnerships: India’s diversified import strategy from sources like US, Russia, Brazil, Canada, and Africa helps ensure supply security amid geopolitical disturbances, though it may not fully shield against long-term price volatility.
- Russia now supplies 40% of India's crude imports (largest supplier of crude oil to India) (less than 1% before 2022).
- India is strengthening ties with IEA, Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)+ for long-term contracts.
- The Global Biofuel Alliance, an initiative by India which intends to expedite the global uptake of biofuels.
- LNG & Gas Pipeline Expansion: The Unified Pipeline Tariff aims for "One Nation, One Grid, One Tariff," benefiting remote consumers and boosting gas market growth.
- India is expanding city gas distribution networks, and import terminals to support growing demand.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR): SPR Program acts as a buffer against supply disruptions and price volatility in global markets.
- India aims to commercialize 50% of its SPR to raise funds and build additional storage tanks to offset high oil prices.
- Clean & Renewable Energy: India targets 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 with expansion of solar, wind, and hydro projects to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- The government promotes ethanol blending, biodiesel, and compressed biogas (CBG) while announcing a USD 67 billion investment in hydrogen energy projects in 2024.
- Policy Reforms: The government allows 100% FDI under the automatic route for oil & gas PSUs and upstream and private sector refining projects, boosting investment and energy sector growth.
- The Hydrocarbon Exploration and Licensing Policy aims to increase domestic oil and gas production.
- Subsidies are provided for electric vehicles (EVs), green hydrogen, and biofuels to reduce dependence on crude oil.
Conclusion
India's oil and gas needs are driven by economic growth, rising demand, and high import dependence. To ensure energy security, the country is expanding refining capacity, investing in natural gas, and diversifying imports while transitioning to cleaner energy.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does India's strategy of diversifying its oil and gas imports impact its energy security? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to furnace oil, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a product of oil refineries.
- Some industries use it to generate power.
- Its use causes sulphur emissions into environment.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 The term ‘West Texas Intermediate’, sometimes found in news, refers to a grade of (2020)
(a) Crude oil
(b) Bullion
(c) Rare earth elements
(d) Uranium
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)
India’s AI Revolution
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, IndiaAI Mission, DeepSeek, BharatGen, Digital India BHASHINI, Semicon India
For Mains: India’s AI Mission and Global Competitiveness, AI and Economic Growth in India
Why in News?
India is undergoing a holistic transformation in Artificial Intelligence (AI), led by proactive government policies under the IndiaAI Mission.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047, positioning India as a global AI powerhouse.
How is India Transforming into a Global AI Powerhouse?
- Strengthening AI Infrastructure: The government is setting up a high-end computing center with 18,693 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), nearly 9 times more than DeepSeek and two-thirds of ChatGPT’s capacity.
- Open GPU Marketplace allows startups, researchers, and students to access affordable high-performance computing.
- India aims to develop its own GPUs within 3-5 years, reducing dependency on foreign technology such as Quantum chips.
- IndiaAI Dataset Platform provides high-quality, anonymized datasets for AI research and development.
- India has established AI Centres of Excellence(CoEs) in Healthcare, Agriculture, and Sustainable Cities in New Delhi. Union Budget 2025 allocated Rs 500 crore for a new AI CoE in Education.
- AI Skilling: Five National AI Skilling Centres will train youth for AI industries, aligning with Make for India, Make for the World vision.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 integrates AI education at all levels.
- India ranks 1st in Global AI Skill Penetration (Stanford AI Index 2024), with 263% AI talent growth since 2016 and a 14 times rise in AI-skilled workforce (2016-2023).
- India has around 520 tech incubators and accelerators, making India 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- Indigenous AI Models: BharatGen world’s first government-funded multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) initiative for AI-driven public services.
- Sarvam-1, a 2-billion-parameter model supporting 10 Indian languages for translation and content generation.
- AI Kosha is a government-backed platform designed to provide non-personal datasets to help businesses, researchers, and startups develop AI solutions.
- Digital India BHASHINI is an AI-powered language translation platform for digital accessibility.
- Chitralekha is an open-source video transcreation tool for Indic languages.
- AI with Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): AI integrated with Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), DigiLocker to improve efficiency.
- AI-driven crowd monitoring optimized railway passenger movement, and MuleHunter.AI developed by Reserve Bank of India to detect mule bank accounts used for fraud and money laundering.
- AI-Driven Economic Growth: 80% of Indian companies prioritize AI as a core strategic goal. 69% plan to increase AI investments in 2025.
- Indian Generative AI (GenAI) startup funding surged 6 times, reaching USD 51 million in FY2025 (NASSCOM Report).
- India holds 16% of the world’s AI talent, driving AI-powered automation, fintech, and healthcare.
- 78% of Small & Medium Businesses (SMBs) using AI reported revenue growth.
- India’s AI market is projected to grow at 25-35% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). AI talent demand is expected to reach 1 million by 2026.
- AI Regulation: India's AI regulation framework includes the Information Technology Act of 2000, Principles for Responsible AI (2021) and National Artificial Intelligence Strategy (2018) to ensure safety, transparency, and accountability.
- India is avoiding overregulation while addressing risks like deep fakes, privacy, and cybersecurity threats.
- Global AI Governance Leadership: India is actively shaping international AI regulatory frameworks by hosting the Global INDIAai Summit 2024 and showcasing its AI initiatives at G20, Paris AI Summit 2025 and Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit.
What is IndiaAI Mission?Click here to Read: IndiaAI Mission |
What are the Concerns in India’s AI Transformation?
- Limited AI Hardware Capabilities: India is still dependent on foreign-made GPUs and semiconductor technologies.
- Many AI startups depend on cloud computing services from global tech giants (AWS, Google, Microsoft).
- Limited Indian AI chip manufacturing means startups must rely on foreign-made AI chips.
- Skilling Challenges: While India leads in AI skill penetration, there is a shortage of highly specialized AI researchers. Most AI professionals are engaged in service-based roles rather than deep-tech innovation.
- Automation could displace up to 60 million workers in India's manufacturing sector by 2030. Uneven AI adoption in rural and Tier-2/Tier-3 cities is widening the digital divide.
- Ethical Concerns: Risks of bias in AI models due to insufficiently diverse datasets.
- No dedicated AI law to regulate data usage, facial recognition, and deepfake risks.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: India lacks a dedicated AI regulatory framework, current policies are fragmented across different ministries.
- Comprehensive AI ethics guidelines are absent, leaving bias, accountability, and transparency unaddressed.
- Environmental Impact: AI hardware and data centers contribute 1% of global GHG emissions, expected to double by 2026. India lacks regulations on AI data centers' water usage and carbon footprint.
What Steps Can India Take to Address AI Transformation Challenges?
- Strengthening AI Hardware: Boost domestic AI chip manufacturing under Semicon India Programme. Incentivize fabless chip design startups and AI hardware R&D.
- Support development of quantum AI processors through the National Quantum Mission.
- AI Workforce: Expand FutureSkills Prime to train young individuals in AI and digital technologies, reinforcing India’s position as a Digital Talent Nation.
- AI Regulatory Framework: Enact a dedicated AI & Quantum Act to regulate AI development and its environmental impact, drawing inspiration from the EU AI Act (2024) and the US Artificial Intelligence Environmental Impacts Act (2024).
- Ensuring Inclusive AI Growth: Under RAISE 2020, promote AI as a tool for social transformation, inclusion, and empowerment through responsible development.
- Sustainable AI Development: Design AI algorithms and infrastructures that consume less energy and integrate AI into smart grids to optimize power use.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss India’s transformative shift in Artificial Intelligence (AI), what steps should India take to ensure sustainable AI development? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to the privacy of the individual in the use of AI in healthcare? (2023)
India 2nd largest Arms Importer: SIPRI
Why in News?
India's share of global arms imports fell to 8.3% in 2020–24, making it the 2nd-largest arms importer, after Ukraine, as per the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) report.
What are the Key Findings of the Report on Arms Trade?
- India: India's arms imports declined by 9.3% compared to 2015-19. Russia remained India's top supplier, but its share dropped from 72% (2010-14) to 36% (2020-24).
- France emerged as India’s second-largest supplier (28% of its total exports went to India).
- India’s Neighbors: Pakistan's Arms Imports Grew by 61%. China supplied 81% of Pakistan’s total arms imports.
- For the first time since 1990-94, China dropped out of the top 10 arms importers as its arms imports declined by 64%, reflecting a stronger domestic defense industry.
- Asia and Oceania: India, Pakistan, Japan, and Australia ranked among the 10 largest arms importers globally in 2020-24.
- US: Retains position as the largest arms exporter, supplying weapons to Ukraine, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) allies, and Asia-Pacific nations.
- Europe: European arms imports surged by 155%, as countries increased defense spending in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- France overtakes Russia as the 2nd-largest arms exporter, with India (28%) as the top buyer, followed by Qatar.
- India procured Rafale jets and Scorpene submarines from France.
- Ukraine saw a 100-fold increase in arms imports due to the war with Russia. It received 8.8% of global arms imports, with the US, Germany, and Poland as top suppliers.
- France overtakes Russia as the 2nd-largest arms exporter, with India (28%) as the top buyer, followed by Qatar.
- Russia: Russia’s global arms exports dropped by 64%, falling to 7.8% of global exports (third place) due to Western sanctions and production constraints.
- However, India (38%), China (17%), and Kazakhstan (11%) remained its top buyers.
- Middle East: Arms imports fell by 20%, but the region remains a major importer, with Qatar becoming the 3rd-largest arms importer globally.
- Global Arms Transfers: Global arms transfers remained stable compared to 2015–19 and 2010–14, but were 18% higher than 2005–09, with rising imports in Europe and the Americas offset by decreases in other regions like China.
What are India’s Initiatives to Reduce Arms Imports?
- Budget: Rs 6.21 lakh crore allocated for defence in Budget 2024-25, with 75% of capital procurement reserved for domestic manufacturers.
- Self-Reliant Initiatives through Joint Action (SRIJAN) portal launched to facilitate procurement from Indian vendors.
- Production: India’s defence production reached a record value of Rs 1. 27 lakh crore in 2023-24, a 174% rise from 2014-15.
- The top three destinations for India's defence exports in 2023-24 were the US, France, and Armenia.
- Positive Indigenization Lists: Five ‘Positive Indigenization Lists’ comprising defence items have been released. These lists place an embargo on the import of these items, ensuring they are produced within India.
- Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020: Prioritizes domestic procurement over foreign purchases.
- Defence Industrial Corridors (DICs): Two corridors established in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu to boost defence manufacturing.
- Private Sector & FDI Participation: 74% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) via the Automatic Route and 100% via the Government Route in defence manufacturing.
- 21% of India's total defence production now comes from the private sector.
- Defence Public Sector Units (DPSUs): India has 16 DPSUs, including Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL), and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders.
- Major indigenization projects led by DPSUs include INS Vikrant (India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier), LCA Tejas (advanced fighter jet developed by HAL).
- R&D & Innovation: iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) initiative promotes startups and MSMEs in developing cutting-edge military technology.
- Future Goals: India is aiming for Rs 1.75 lakh crore worth of defence production in 2025, with a target of Rs 3 lakh crore by 2029.
|
Drishti Mains Question: India’s defence production has seen significant growth in recent years. Critically examine the government’s initiatives to boost domestic defence manufacturing. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the defence sector is now set to be liberalized: What influence this is expected to have on Indian defence and economy in the short and long run? (2014)
Poshan Abhiyan
Why in News?
Poshan Abhiyaan aims to improve nutritional outcomes through technology, cross-sectoral convergence, and community involvement.
What is Poshan Abhiyan?
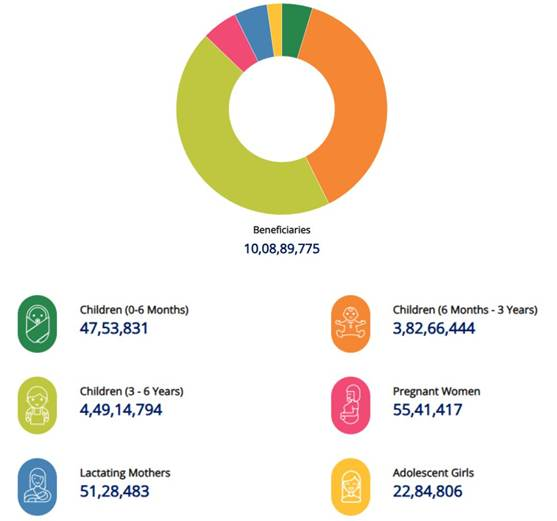
- About: It is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, launched on 8th March 2018 in Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan. The program aims to address the nutrition needs of adolescent girls, pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children (0-6 years) through a targeted and convergent approach.
- Objectives: It aims to reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and reduce low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively
- Strategic Pillars: It operates through four strategic pillars:
- Quality Services: Strengthens health services via ICDS, NHM, and PMMVY, focusing on a child’s first 1,000 days.

- Cross-Sectoral Convergence: Integrates ministries like Water & Sanitation for holistic nutrition.
- The National Council on India’s Nutrition Challenges, led by NITI Aayog, guides policy and reviews nutrition convergence quarterly.
- Technology: Uses the Poshan Tracker for real-time data and monitoring and ICDS-Common Application Software to strengthen delivery of Anganwadi Services.
- Jan Andolan: Promotes community-led nutrition awareness and behavioral change.
- Quality Services: Strengthens health services via ICDS, NHM, and PMMVY, focusing on a child’s first 1,000 days.
- Nutritional Improvement: As per the NFHS-5 (2019-21) for children under 5 years.
|
Indicator |
NFHS-4 (2015-16) |
NFHS-5 (2019-21) |
|
Wasting (Low weight-for-height) |
21% |
19.30% |
|
Undernutrition (Low weight-for-age) |
35.70% |
32.10% |
|
Stunting (Low height-for-age) |
38.40% |
35.50% |
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0: It is also known as Mission Poshan 2.0, that fosters health, wellness, and immunity and infrastructure upgrades for Anganwadi Centre (AWCs) e.g., dedicated buildings, functional toilets, with drinking water access.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
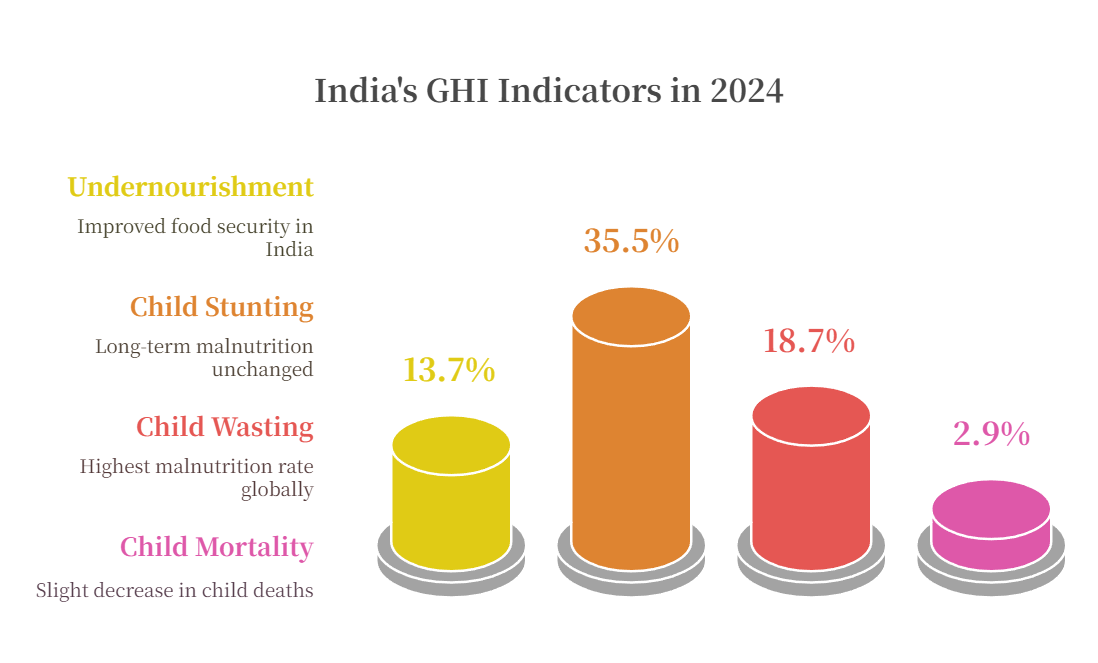
Q. Which of the following is/are the indicator/indicators used by IFPRI to compute the Global Hunger Index Report? (2016)
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child mortality
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (c)
Namami Gange Programme
Why in News?
The Namami Gange Programme (NGP) has marked significant progress in its mission to rejuvenate the sacred River Ganga.
- It was launched in 2014 with a Rs 20,000 crore budget until 2021, and now extended to March 2026 with Rs 22,500 crore (total: Rs 42,500 crore).
What is the Namami Gange Programme?
- About: It is a flagship programme for the rejuvenation of the Ganga River and its tributaries by reducing pollution, improving water quality, and restoring the river’s ecosystem.
- Implementation: Five-Tier Structure for Ganga Rejuvenation.
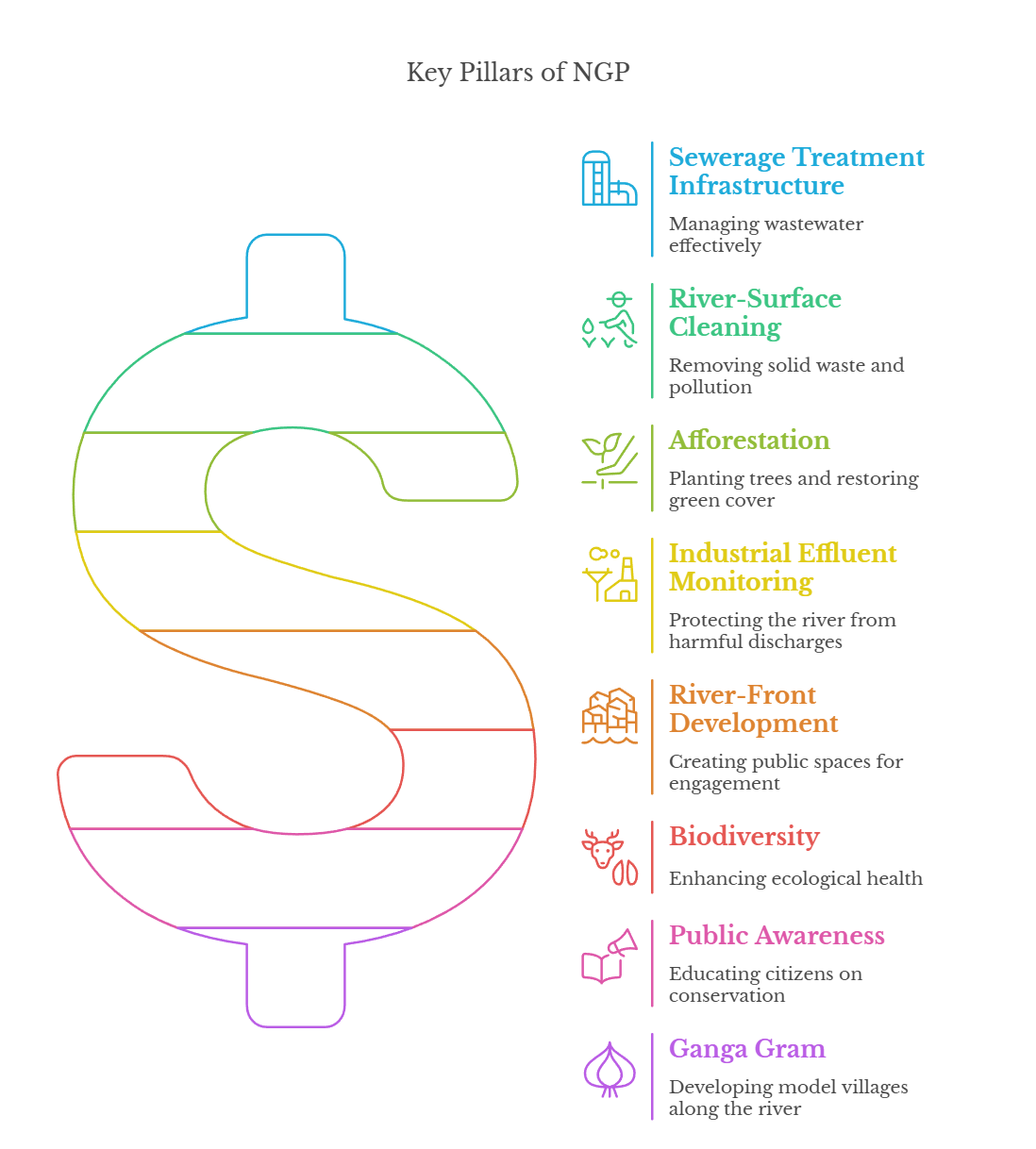
- 8 Pillars of NGP:
- Key Interventions:
- Pollution Abatement (Nirmal Ganga): Setting up sewage treatment plants (STPs), reducing industrial and domestic waste discharge.
- Improving Ecology and Flow (Aviral Ganga): Restoring natural flow and biodiversity, implementing water conservation measures.
- Strengthening People-River Connect (Jan Ganga): Promoting community participation and awareness, involving local stakeholders in conservation efforts.
- Facilitating Research and Policy (Gyan Ganga): Supporting scientific research and studies, formulating evidence-based policies.
- Implementation: Under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM), an Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) by the winning bidder handles STP development, operation, and maintenance.
- 40% of costs are paid post-construction, 60% over the project’s lifespan.
- Key Achievements:
- Pollution Abatement: Sewage treatment capacity surpassed the pre-2014 capacity by over 30 times.
- Improvement in Water Quality: Water quality improved in Uttar Pradesh from BOD 10-20 mg/l (2015) to 3-6 mg/l (2022), in Bihar from 20-30 mg/l (2015) to 6-10 mg/l (2022), and in West Bengal from 10-20 mg/l (2018) to 6-10 mg/l (2022).
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) measures oxygen needed by microorganisms to break down organic matter in water. Higher BOD indicates more pollution; lower BOD means cleaner water.
- Impact on Biodiversity: The Gangetic river dolphin population increased from 3,330 in 2018 to 3,936 in 2024, with sightings in new stretches like Bithura to Rasula Ghat (Prayagraj), Babai, and Bagmati Rivers.
- Global Recognition: In December 2022, the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration acknowledged NGP as one of the Top 10 World Restoration Flagship Initiatives.
- The International Water Association awarded NGP the title of Climate Smart Utility.
| Click Here to Read: What are the Challenges in the Namami Gange Programme? |
Importance of River Ganga
- Lifeline of India: Supports 47% of India’s population across 11 states.
- Agriculture & Economy: 65.57% of the basin is used for agriculture.
- Cultural & Religious Significance: Sacred to million people across different religions.
- Water Scarcity: The Ganga River Basin is the second most water-stressed in India, receiving only 39% of the average per capita annual rainwater input.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the key features of ‘National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA)’? (2016)
- River basin is the unit of planning and management.
- It spearheads the river conservation efforts at the national level.
- One of the Chief Ministers of the States through which the Ganga flows becomes the Chairman of NGRBA on rotation basis.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Q. Consider the following statements: (2014)
- Animal Welfare Board of India was established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body.
- The National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Govind Ballabh Pant
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister paid tribute to Govind Ballabh (G.B.) Pant (1887-1961), a revered freedom fighter and the 1st chief minister (CM) of the Uttar Pradesh (UP) on his death anniversary (7th March)
- GB Pant Early Life: Born in Almora, Uttarakhand, Pant was inspired by Gopal Krishna Gokhale and Madan Mohan Malaviya.
- Role in the Freedom Movement: Active participant in the Salt March(1930) and Civil Disobedience Movement(1930) and Quit India Movement (1942).
- Political Journey: Became a member of the Constituent Assembly, contributing to the framing of the Indian Constitution.
- GB Pant as CM of UP worked towards Zamindari abolition and emphasized modernization.
- GB Pant was appointed as Union Home Minister by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1955, he was instrumental in establishing Hindi as one of the official languages of India.
- Honour and Legacy: In 1957, he was conferred with the Bharat Ratna. His political legacy includes mentoring UP leaders like Chaudhary Charan Singh.
| Read more: Pandit Govind Ballabh Pant |
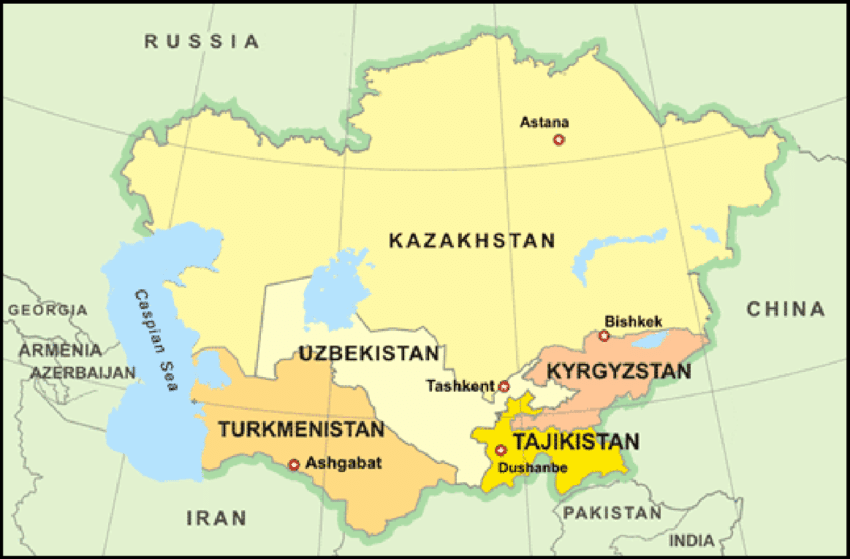
Exercise KHANJAR-XII
The 12th edition of the India-Kyrgyzstan Joint Special Forces Exercise KHANJAR-XII is being held in Kyrgyzstan.
- Initiated in 2011, it is an annual exercise conducted alternately in both countries.
- The Indian Army’s Parachute Regiment (Special Forces) and Kyrgyzstan’s Scorpion Brigade are participating.
- The exercise aims to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism and special operations in urban and high-altitude terrain.
- Key areas of focus include sniping, building intervention, and mountain warfare. Additionally, cultural exchanges, including Kyrgyz festival Nowruz celebrations, will strengthen bilateral ties.
- This exercise reinforces India-Kyrgyzstan defence cooperation, addressing regional security challenges like terrorism and extremism, while promoting peace and stability in the region.
- Kyrgyzstan, located in Central Asia, shares the Fergana Valley with Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. The region is rich in hydrocarbons, making it crucial for India’s energy security.
| Read More: India-Kyrgyzstan |
55th Anniversary of NPT
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) marks 55 years on 5th March, 2025.
- It was approved by the UN General Assembly on 12th June, 1968 and came into force on 5th March, 1970.
- About NPT: It is the only multilateral binding treaty for Nuclear-Weapon States (NWS) to disarmament while promoting peaceful nuclear energy use.
- Key Provisions: It defines NWS as countries possessing nuclear weapons before 1st January , 1967 (USA, UK, France, China, and USSR/Russia).
- Non-nuclear states agree not to develop nuclear weapons, while nuclear states pledge not to transfer them.
- It allows peaceful use of nuclear energy and provides a withdrawal option if national security is threatened.
- Membership: 191 members with 5 NWS (US, Russia, UK, France & China).
- India is not a member.
- Monitoring: International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) monitors compliance.
- India and NPT: India opposes the NPT, calling it discriminatory, as it legitimizes nuclear weapons for five countries while denying the same right to others.
- India follows a "No First Use" (NFU) policy and is committed to global nuclear disarmament.
Read More: Nuclear Disarmament
KVIC’s Honey Mission
The Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) has distributed bee boxes, honey colonies, and toolkits to beekeepers under the ‘Honey Mission’ to spread the Sweet Revolution.
- Honey Mission (2017): It is an initiative of KVIC that promotes beekeeping and honey production (apiculture), and integrates bee farming with agriculture for additional income.
- Apiculture products include honey, royal jelly, beeswax, pollens that are widely used in pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, beauty, and other industries.
- KVIC: It is a statutory body established under the Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act, 1956 and functions under the Ministry of MSME.
- It plans, promotes, and implements programs for Khadi and village industries, coordinating with rural development agencies.
Note: Like KVIC’s Honey Mission, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare implements the National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM), a Central Sector Scheme aimed at promoting scientific beekeeping to promote the Sweet Revolution in India.
- Sweet revolution promotes apiculture (beekeeping) to boost the production of high-quality honey and other bee-derived products.
| Read More: Honey Mission and Sweet Revolution |
Smooth-coated Otters
Two smooth-coated otters (Lutrogale perspicillata) were brought to the Delhi zoo after two decades.
- About Smooth-coated Otters: They are a species of otter found in freshwater habitats across South and Southeast Asia.
- Physical Traits: They have smooth, velvety fur, a round head with a prominent naked nose, a flattened tail, and webbed feet.
- Behavior: They are social animals and hunt fishes in groups.
- Protected Areas: Corbett and Dudhwa Tiger Reserves, Katerniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary, Kaziranga National Park, Periyar Tiger Reserve and the Nagarhole National Park.
- Conservation Status:
Read More: Eurasian Otters in Kashmir Valley
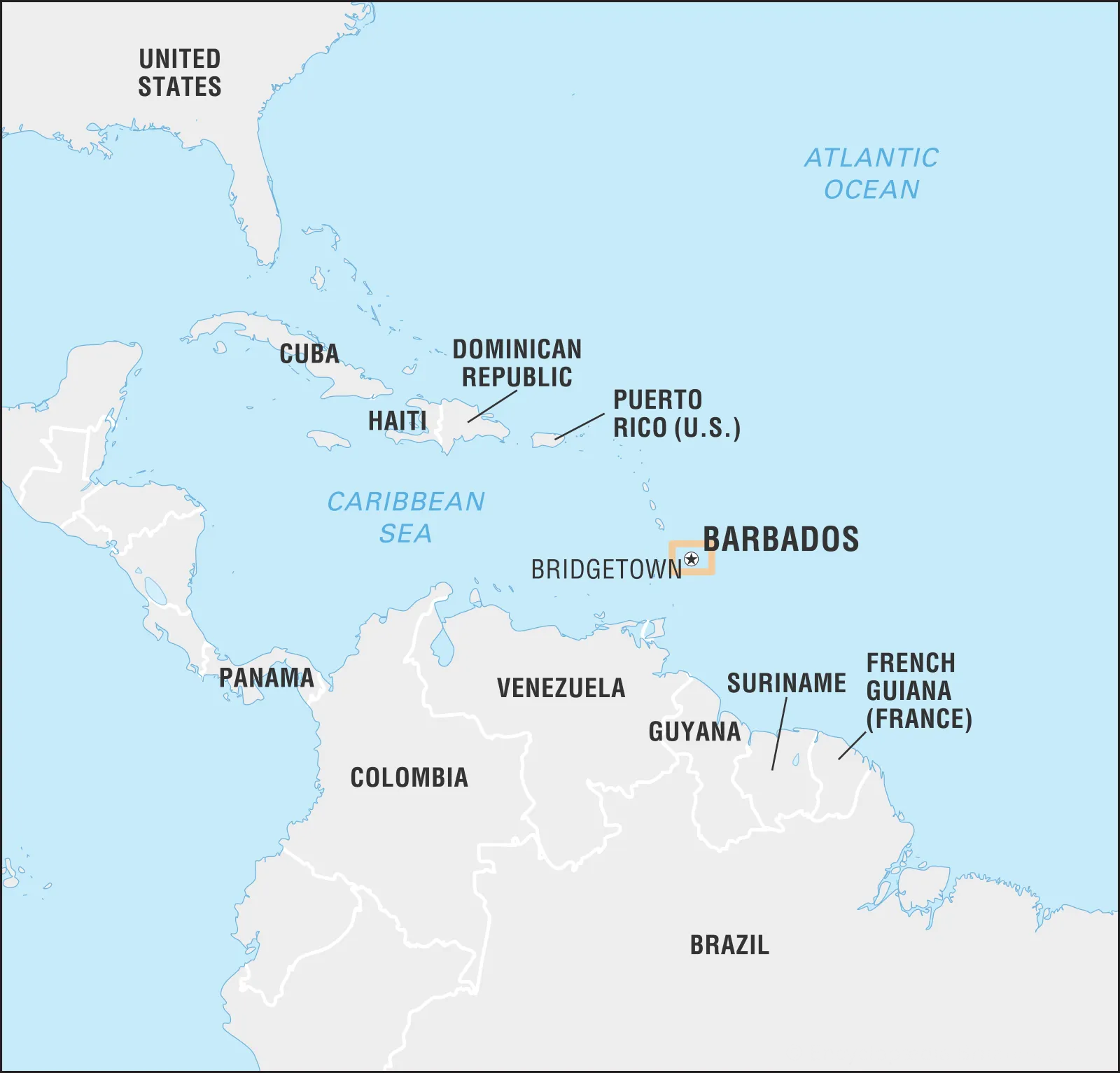
Order of Freedom of Barbados
India’s Prime Minister has been conferred the 'Honorary Order of Freedom of Barbados' in recognition of his strategic leadership and support during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- It was announced during a meeting with India’s PM in November, 2024, in Guyana during the India-CARICOM Summit.
- India and Barbados established diplomatic ties in 1966.
- In 2021, Barbados officially removed Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state and became the world's newest republic with Dame Sandra as the first head of state (President) of the Republic of Barbados.
- Barbados got independence from Britain on 30th November, 1966.
- Barbados is a Caribbean island in the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela.
- PM Modi's list of international awards now includes 19 prestigious recognitions. Notable awards include Russia's "Order of St. Andrew the Apostle" and the US's "Legion of Merit."
| Read More: Barbados: World’s Newest Republic |