International Relations
2nd India-CARICOM Summit
- 23 Nov 2024
- 12 min read
For Prelims: India-CARICOM, International Solar Alliance, Mission LiFE, Digital Public Infrastructure, Jan Aushadhi Kendras, Small Island Developing States (SIDS), Caribbean Sea, UN General Assembly (UNGA), India-UN Partnership Fund for South-South Cooperation, One World One Sun One Grid (OWOSOG), CoWin, National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
For Mains: Strengthening of India-CARICOM relations and its significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India chaired the 2nd India-CARICOM Summit in Georgetown, Guyana, alongside the Prime Minister of Grenada, the current CARICOM Chair.
- The first India-CARICOM Summit was held in 2019 in New York.
What are the Key Highlights of the 2nd India-CARICOM Summit?
- 7 Pillars of Cooperation: India’s Prime Minister proposed seven key pillars to strengthen ties between India and 'CARICOM'. These pillars are:
- C: Capacity Building: India announced an additional 1000 ITEC (Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation) slots for CARICOM countries over the next five years.
- A: Agriculture and Food Security: India shared its experience in agriculture, particularly in the use of technology such as drones, digital farming, and farm mechanisation.
- R: Renewable Energy and Climate Change: India called for greater collaboration on global initiatives like the International Solar Alliance and Mission LiFE.
- I: Innovation, Technology, and Trade: Prime Minister Modi offered India’s Digital Public Infrastructure and other technological models to improve public service delivery.
- C: Cricket and Culture: India proposed organising "Days of Indian Culture" in CARICOM countries and providing cricket training for young women cricketers from the region.
- O: Ocean Economy and Maritime Security: India expressed willingness to collaborate on maritime domain mapping and hydrography in the Caribbean Sea.
- M: Medicine and Healthcare: India offered its model for affordable healthcare, including the provision of generic medicines through Jan Aushadhi Kendras and the promotion of Yoga for well-being.
- Climate Justice: CARICOM leaders appreciated India’s leadership in championing climate justice for Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- SIDS are responsible for less than 1% of global greenhouse gas emissions but are among the most affected by climate change impacts.
- Climate justice means addressing the unequal and disproportionate impacts of climate change on different communities, particularly the poor, marginalised, and vulnerable groups.
Awards to PM Narendra Modi
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi received top awards from Guyana and Barbados during his visit.
- Guyana conferred the "Order of Excellence" and Barbados awarded the "Honorary Order of Freedom".
- Recently, Dominica also announced its highest national award, the "Dominica Award of Honour," for PM Modi.
- PM Modi's list of international awards now includes 19 prestigious recognitions.
- Notable awards include Russia's "Order of St. Andrew the Apostle" and the US's "Legion of Merit."
What is the Caribbean Community (CARICOM)?
- About: CARICOM is a grouping of 21 countries: 15 Member States and 6 Associate Members including both island states and mainland territories like Suriname and Guyana.
- CARICOM was founded in 1973 with the signing of the Treaty of Chaguaramas by four founding members of Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- 15 member states are Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Belize, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Lucia, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- The 6 associate members are Anguilla, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Curaçao, and Turks and Caicos Islands
- Diversity: The community is made up of people from African, Indian, European, Chinese, Portuguese, and Indigenous backgrounds.
- Population: Approximately 16 million, with a young demographic, 60% under the age of 30.
- Languages: The region is multilingual, with English as the primary language, alongside French, Dutch, and various African and Asian languages.
- Geographical Spread: The member states stretch from The Bahamas in the north to Suriname and Guyana in the south, making it a vast and diverse region with varying levels of economic and social development.
- They are primarily located in the Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean).
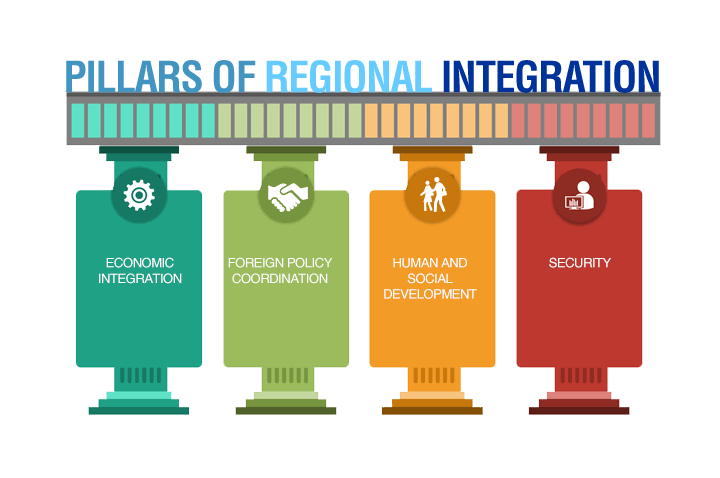
- Pillars of CARICOM's Integration: CARICOM's integration is built on four main pillars, which guide the objectives of the Community:
- Economic Integration: Enhance development and competitiveness through trade and productivity.
- Foreign Policy Coordination: Present a unified voice in international diplomacy.
- Human and Social Development: Focus on health, education, and poverty alleviation.
- Security: Strengthen regional security, disaster response, and crime prevention.
India-CARICOM Relations
- In November 2003, a CARICOM delegation visited India, leading to the establishment of a Standing Joint Commission.
- India's High Commissioner in Georgetown (Capital of Guyana) is also accredited as Ambassador to CARICOM, highlighting its commitment to regional cooperation.
- First Meeting of India-CARICOM Foreign Ministers (2005) laid the groundwork for closer collaboration, particularly in areas like trade and development projects through the Caribbean Development Bank.
- First India-CARICOM Joint Commission (2015) held in Georgetown which led to promotion of business partnerships between India and CARICOM countries.
- India-CARICOM Ministerial Meetings are held regularly, with notable events occurring on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly (UNGA).
- Humanitarian Assistance: In 2017, after hurricanes in the Caribbean sea, India provided USD 200,000 in emergency aid and additional support through the India-UN Partnership Fund for South-South Cooperation.
- India-CARICOM Summit (2019) took place in New York on the sidelines of the UNGA, saw India offering substantial support to CARICOM countries.
- USD 14 million Grant: For community development projects.
- USD 150 million Line of Credit: Specifically for solar energy and climate change projects.
- Special Training Programs: In response to the needs of CARICOM nations, India offered tailored capacity-building programs.
- India-CARICOM Task Force: It was established to reinvigorate cooperation by streamlining and enhancing ongoing initiatives and establishing clearer strategies for the future.
Why is India and CARICOM Important for Each Other?
- Strategic Expansion: The Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) region is diversifying its geopolitical ties, seeking new partnerships in Asia, which aligns with India’s ambition to expand its presence in the region.
- Shared Climate Concerns: India and CARICOM face climate change impacts, including rising sea levels and extreme weather.
- India’s COP-26 efforts align with CARICOM’s call for climate finance for mitigation and adaptation.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): The ISA, co-founded by India, offers a platform for CARICOM nations to enhance solar energy deployment.
- Additionally, the One World One Sun One Grid (OWOSOG) initiative is an innovative approach to creating a global grid that could transmit solar energy across continents.
- Digital Health Collaboration: India’s digital health advancements, like CoWin and National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), offer a model for improving healthcare systems in CARICOM, especially for climate-induced health threats.
- Biofuel and Energy Cooperation: India’s collaboration with Brazil in biofuel research could be extended to CARICOM nations, creating a platform for joint energy solutions and biofuel production.
- Strengthened Partnerships: India’s Prime Minister’s visit and India’s ongoing development assistance programs, such as the USD 1 million contribution to the CARICOM Development Fund, lay a strong foundation for future collaborations.
Conclusion
The 2nd India-CARICOM Summit marked a significant step in deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on areas such as renewable energy, climate change, healthcare, and economic development. This collaboration offers vast opportunities to address shared challenges, particularly climate change and sustainable growth, enhancing India’s role in the Caribbean region.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the current state of India-CARICOM relations and the potential for enhancing bilateral cooperation in trade, climate change, and people-to-people connections? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched? (2013)
Geographical Feature - Region
(a) Abyssinian Plateau - Arabia
(b) Atlas Mountains - North-Western Africa
(c) Guiana Highlands - South-Western Africa
(d) Okavango Basin - Patagonia
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Why indentured labour was taken by the British from India to other colonies? Have they been able to preserve their cultural identity over there? (2018)
Q. Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South East Asian countries’ economy and society. Appraise the role of Indian Diaspora in South-East Asia in this context. (2017)