Social Justice
Anaemia and Maternal Health
- 06 Jul 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Anemia and Maternal Health, Anemia, PPH, Anemia Mukta Bharat.
For Mains: Anemia and Maternal Health.
Why in News?
Recently, a study published in The Lancet Journal, titled- Maternal anaemia and the risk of postpartum haemorrhage: a cohort analysis of data from the WOMAN-2 trials, has found that there is a strong link between Anaemia and Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH).
- They used the data from the World Maternal Antifibrinolytic-2 (WOMAN-2) trial. This trial enrolled women with moderate or severe anaemia giving birth vaginally in hospitals in Pakistan, Nigeria, Tanzania, and Zambia.
What is Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)?
- PPH is severe vaginal bleeding after childbirth.
- WHO-defined postpartum haemorrhage (estimated blood loss of at least 500 mL); and calculated postpartum haemorrhage (blood loss of ≥1,000 mL).
- It's a serious condition that can lead to death. Other signs of postpartum hemorrhage are dizziness, feeling faint and blurred vision.
What are the Findings of the Study?
- Anaemia and PPH:
- Mean estimated blood loss was 301 mL for women with moderate anaemia and 340 mL for women with severe anaemia.
- Clinical postpartum haemorrhage occurred in 7.0% of women. The risk of clinical postpartum haemorrhage was 6.2% in women with moderate anaemia and 11.2% in women with severe anaemia.
- This data is based on the trial involving 10,620 women.
- Severe anaemia is associated with seven times higher odds of death or near miss compared to moderate anaemia.
- Anaemia and Pregnancy:
- Worldwide, over half a billion women of reproductive age are anemic.
- Approximately 70,000 postpartum deaths occur annually, mostly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Blood Loss and Shock:
- Lower haemoglobin values associated with increased blood loss and clinical PPH.
- Women with anaemia have reduced oxygen-carrying capacity and are more susceptible to shock.
- Clinical diagnosis of postpartum haemorrhage linked to worse maternal function.
What are the Recommendations of WHO to Reduce PPH?
- It is suggested to use some of the drugs such as oxytocin, oral misoprostol drug etc., to prevent PPH.
- Oxytocin is a commonly recommended medication to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
- Late cord clamping (performed after 1 to 3 minutes after birth) is recommended for all births while initiating simultaneous essential newborn care.
- Early cord clamping (<1 minute after birth) is not recommended unless the neonate is asphyxiated (baby's brain and other organs do not get enough oxygen and nutrients).
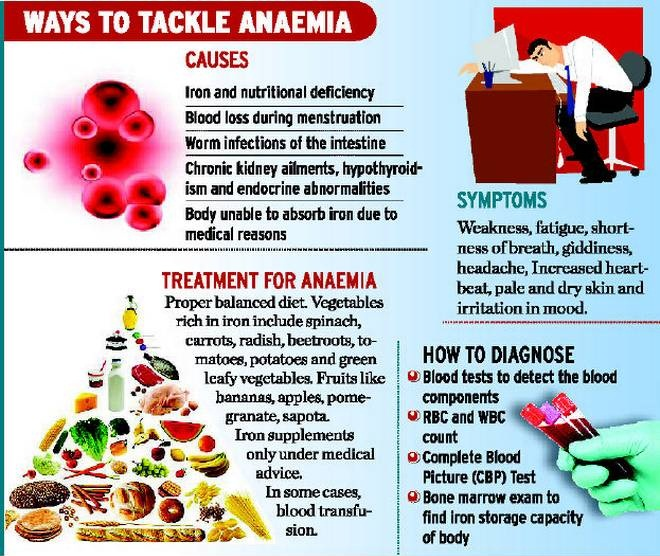
What is Anaemia?
- Anemic Condition:
- It is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or their oxygen-carrying capacity is insufficient to meet physiologic needs, which vary by age, sex, altitude, smoking, and pregnancy status.
- Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anaemia, although other conditions, such as folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin A deficiencies, chronic inflammation, parasitic infections, and inherited disorders can all cause anaemia.
- Status in India:
- The prevalence of anaemia among six groups as per the National Family Health Survey 5 (2019-21), is 25.0% in men (15-49 years) and 57.0% in women (15-49 years), 31.1% in adolescent boys (15-19 yrs), 59.1% in adolescent girls, 52.2% in pregnant women (15-49 years) and 67.1% in children (6-59 months).
What are Government Initiatives to Tackle Anemia?
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat(AMB): It was launched in 2018 as part of the Intensified National Iron Plus Initiative (NIPI) Program for accelerating the annual rate of decline of anaemia from one to three percentage points.
- The target groups for AMB are Children 6-59 months, 5-9 years, Adolescent Girls & Boys of 10-19 years, Women of Reproductive Age (15-49 years), Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers.
- Weekly Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation (WIFS):
- This Programme is being implemented to meet the challenge of high prevalence and incidence of anaemia amongst adolescent girls and boys.
- The intervention under WIFS includes supervised weekly ingestion of Iron Folic Acid (IFA) tablet.
- Operationalization of Blood Bank:
- In District Hospitals and Blood Storage Unit in subdistrict facilities such as Sub-Divisional Hospital/ Community Health Centers is being taken to tackle complications due to severe anaemia.
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA):
- It has been launched to focus on conducting special ANC check up on 9th of every month with the help of medical officers/ OBGYN to detect and treat cases of anaemia.
- Other Steps Taken:
- To control worm infestation biannual deworming with Albendazole is provided.
- Health management information system & Mother Child tracking system is being implemented for reporting and tracking the cases of anaemic and severely anaemic pregnant women.
- Universal screening of pregnant women for anaemia is a part of ante-natal care and all pregnant women are provided iron and folic acid tablets during their ante-natal visits through the existing network of sub-centres and primary health centres and other health facilities as well as through outreach activities at Village Health & Nutrition Days (VHNDs).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) Only three
d) All four Interventions of Anaemia Mukt Bharat:
Ans: (c)