3 Years of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
For Prelims: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DPDP Act, 2023, Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), National Medical Commission, National Dental Register (NDR).
For Mains: Key Features of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and Related Challenges.
Why in News?
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) completed its three-year journey on 27th September, aiming to revolutionize the nation's digital healthcare ecosystem by enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and transparency in healthcare.
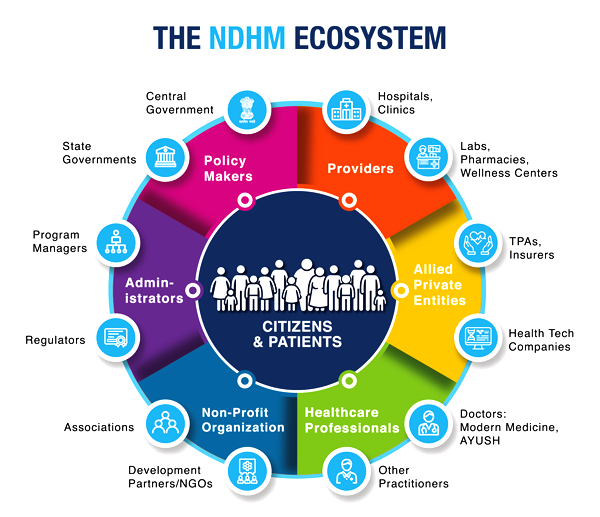
What is Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- About:
- It was launched in 2021 with the aim to provide digital health IDs for all Indian citizens to help hospitals, insurance firms, and citizens access health records electronically when required.
- The National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the implementing Agency of ABDM.
- Key Features of ABDM:
- Unique Health Identifier for Citizens: A unique Health ABHA ID for each individual to securely store and manage health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A comprehensive repository of healthcare professionals across modern and traditional systems, enabling connection to India’s digital health ecosystem.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): A comprehensive repository of public and private health facilities across all systems of medicine, including hospitals, clinics, labs, and pharmacies.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services, thereby streamlining healthcare interactions and improving service accessibility.
- Data Privacy and Security: In alignment with the DPDP Act, 2023, the ABDM ensures the security, confidentiality, and secure sharing of patient related health information.
- Transparency: It offers individuals access to public and private health services, ensures guideline compliance, and promotes transparency in pricing and accountability.
- Key Initiatives:
- Scan and Share: A QR-code-based OPD registration service allows patients to scan facility QR codes and share their demographic details, minimising queues and reducing data inaccuracies.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): The DHIS encourages hospitals, diagnostic labs, and digital health solution providers to adopt transformative digitization practices through various incentives.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: It is aimed at addressing various challenges in ABDM adoption, especially for private sector providers, has successfully operationalised 106 microsites, surpassing the initial target of 100.
- End to End ABDM Adoption Pilot: The pilot aims to digitise public and private facilities nationwide through comprehensive ABDM adoption, establishing model facilities as benchmarks for future efforts.
- New Portals: The NHA has also developed portals like the National Medical Register (NMC) for the National Medical Commission and the National Dental Register (NDR) for the National Dental Council.
Note:
- National Health Authority (NHA) is the apex body responsible for implementing India’s flagship public health insurance/assurance scheme.
- It was established on 2nd January 2019 under the Society Registration Act, 1860.
What are the Achievements of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- ABHA ID: By September 2024, over 67 crore ABHA IDs have been created, providing citizens with unique digital health IDs for secure access to and sharing of their health records.
- More than 42 crore health records have been linked to ABHA, allowing seamless access to medical histories and improving healthcare delivery.
- Integration: Over 236 private entities, including labs, pharmacies, and digital solution companies, have integrated with the ABDM ecosystem to support interoperability.
- Public institutions like AIIMS Delhi and AIIMS Bhopal are top performers in generating Scan and Share OPD registrations.
- Leading private healthcare chains have also played a major role in the success of the ABDM.
- National Healthcare Providers Registry (NHPR): The launch of the NHPR has resulted in the registration of 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals.
- NHPR is a comprehensive repository of registered healthcare professionals and health facilities.
What are the Major Concerns Related to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- Limited Digital Infrastructure:
- Many rural and remote areas suffer from unreliable internet connectivity and low digital literacy, hindering effective engagement with and access to the ABDM.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns:
- The digitization of health records raises concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and consent management, highlighting challenges in protecting sensitive health information.
- Cost and Resource Allocation:
- High implementation costs and inadequate government funding for infrastructure, training, and capacity building make it challenging for smaller healthcare facilities and practitioners to adopt the ABDM.
- Regulatory and Legal Framework:
- The evolving regulatory framework for digital health, including unclear data protection laws and patient consent guidelines, creates ambiguity in accountability and responsibility regarding health data ownership and management.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Digital Infrastructure: Investment in enhancing internet connectivity and digital literacy programs in rural and remote areas can be done to ensure equitable access to the ABDM. Collaboration with telecom providers can facilitate the establishment of robust digital networks.
- Enhancing Data Privacy and Security Measures: Developing comprehensive data protection regulations and cybersecurity protocols to address privacy concerns. Implementing strict consent management frameworks will help safeguard sensitive health information and build trust among users.
- Increased Funding and Resource Allocation: Allocating sufficient government resources to support the implementation of ABDM, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities. This includes providing financial assistance for infrastructure development, training programs, and capacity building initiatives.
- Establishing a Clear Regulatory Framework: Creating a coherent and comprehensive regulatory framework that defines data protection laws, patient consent guidelines, and accountability measures. This will clarify responsibilities regarding health data ownership and management, fostering a secure and trustworthy digital health ecosystem.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key components of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and analyse its potential impact on the Indian healthcare system? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements:
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Resurgence of the Cholera Pandemic
For Prelims: Cholera, World Health Organization (WHO), Vibrio cholerae, Oral Cholera Vaccines (OCV)
For Mains: Causes of Cholera and Related Intiatives, Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services Relating to Health.
Why in News?
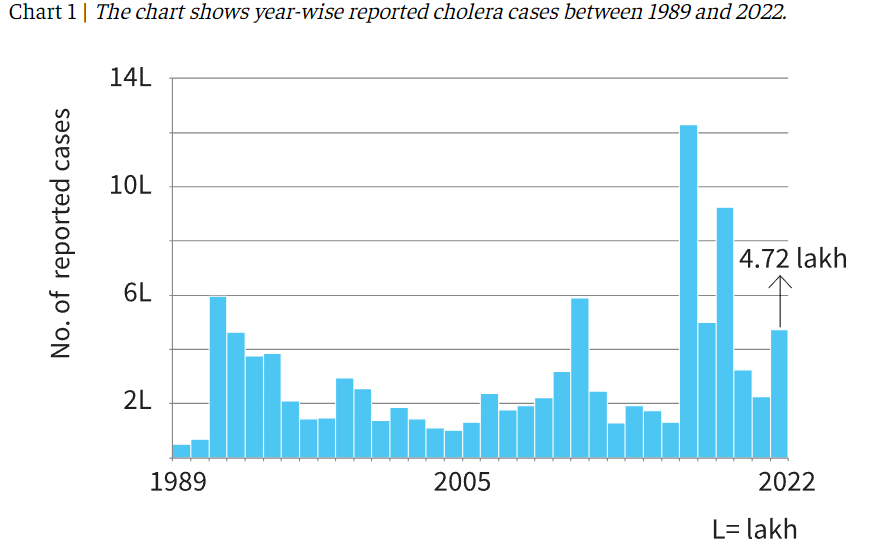
Recently, Cholera, a preventable and treatable disease, has experienced a resurgence, leading to approximately 4,000 deaths in 2023, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
What is Cholera?
- About:
- Cholera, a water-borne disease primarily caused by the bacteria Vibrio cholerae.
- It is an acute diarrheal illness caused by infection of the intestine.
- The infection is often mild or without symptoms, but sometimes can be severe.
- Symptoms:
- It includes severe watery diarrhoea, vomiting, leg cramps, and weakness, and can lead to death through dehydration if untreated.
- Transmission:
- A person may get cholera by drinking water or eating food contaminated with the cholera bacterium.
- The disease can spread rapidly in areas with inadequate treatment of sewage and drinking water.
- Vulnerable populations, particularly malnourished children and individuals living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) are at a higher risk of mortality.
- Vaccine:
- Currently there are 3 WHO pre-qualified Oral Cholera Vaccines (OCV)- Dukoral, Shanchol, and Euvichol-Plus. All three vaccines require two doses for full protection.
What is the Global Distribution and Burden of Cholera?
- Global Burden:
- The global cholera burden worsened between 2022 and 2024, with the WHO reporting significant increases in both cases and deaths across various regions.
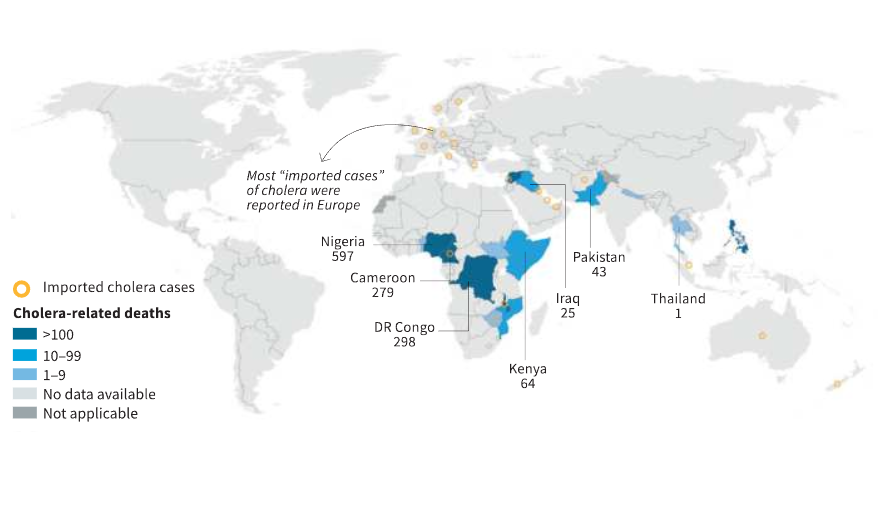
- 22 countries reported active outbreaks and 2,400 deaths had been recorded globally by August 2024.
- Global Cholera Distribution:
- Cholera primarily affects countries in Africa and Asia, with occasional "imported cases" in Europe.
- WHO reported that in 2023, global cholera cases increased by 13%, and deaths rose by 17% compared to 2022, resulting in 4,000 fatalities.
- By 2024, 22 countries were experiencing ongoing cholera outbreaks.
- In 2022, cholera cases were more evenly spread across Africa compared to 2021.
- The geographic distribution of cholera has shifted, with Asia showing a decline but cases in Africa doubling, largely due to inequities in healthcare access.
- Asia also experienced a rise in cholera cases in 2022.
- As of August 2024, India reported 3,805 cases of cholera in a multi-country outbreak that also impacted Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Nepal.
What are the Key Factors Contributing to Cholera Resurgence?
- Climate Change: It has a profound effect on water quality and availability. Extreme weather events, such as floods and intense monsoonal rains, can lead to the overflow of sewage into water sources, while droughts and heatwaves concentrate cholera bacteria in diminishing water supplies. These changes significantly exacerbate the spread of cholera.
- Lack of Access to Clean Water and Sanitation: According to United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), in the year 2019, approximately 2 billion people lack access to safely managed drinking water, and around 3.6 billion lack adequate sanitation facilities.
- This leads to cholera outbreaks, as contaminated water and poor sanitation create fertile conditions for the disease to thrive.
- Vibrio Pathogens and Microplastics: Research from the University of Florida in June 2023 reveals that Vibrio pathogens can adhere to microplastics, allowing them to potentially adapt to this environment in the open ocean.
- Conflict and Displacement: Regions affected by conflict face major disruptions in health services and sanitation, increasing vulnerability to cholera.
- Displaced individuals are especially at risk due to overcrowded living conditions and inadequate access to clean water.
- Vaccine Shortage and Inadequate Health Infrastructure: In 2023, only 36 million cholera vaccine doses were produced, half the demand from 14 countries. Due to the shortage, a single-dose regimen replaced the standard two doses.
- Currently, there is only one manufacturer supplying OCVs worldwide and a shortage of around 40 million doses annually.
- Also, the limited health infrastructure in affected areas exacerbates the crisis, hindering effective response and control measures.
Initiatives to Control Cholera
- Global Task Force for Cholera Control (GTFCC): GTFCC was launched by the WHO, and has created a Global Roadmap for Ending Cholera by 2030.
- This roadmap emphasises crucial initiatives such as monitoring disease transmission, engaging communities in hygiene and sanitation education, improving access to sanitation facilities in high-risk areas, and implementing OCV campaigns in cholera hotspots.
- Collaborative Efforts with Health Partners: In May 2023, seven countries and ten health partners, including International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) and UNICEF, convened during the World Health Assembly (WHA) to reaffirm their commitment to combating cholera.
- They called for immediate action and sustainable funding to enhance Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) services, strengthen disease surveillance in high-risk areas, and boost local production of oral cholera vaccines.
Way Forward
- Increased Investment: Governments and international organisations must prioritise funding for WASH initiatives to address the root causes of cholera outbreaks.
- For Example, Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) has been instrumental in improving sanitation infrastructure and reducing open defecation, contributing to cholera prevention
- Strengthening Health Systems: Enhancing health infrastructure, particularly in vulnerable regions, is essential for effective disease monitoring and response.
- The WHOs efforts in cholera-endemic countries like Haiti and Yemen have been crucial in containing outbreaks by improving healthcare infrastructure and response capabilities.
- Community Engagement: Local communities must be engaged in hygiene education and sanitation efforts to foster ownership and sustainable practices.
- Addressing Climate Change: Governments should recognise the impact of climate change on health and implement measures to mitigate its effects.
- For Example, India took several measures such as National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), National Solar Mission, Renewable Energy Initiatives etc.
|
Drishti Mains Question Water-borne diseases continue to pose significant public health challenges in India. Analyze the factors contributing to their prevalence and suggest effective measures to mitigate their impact. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: (a)
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Functionality and Essentially Test for ITC
For Prelims: Supreme Court, Input Tax Credit (ITC), Goods and Services Tax (GST), Cascading Effect of Taxes, Excise Duty, VAT.
For Mains: Functioning of Input Tax Credit (ITC) mechanism under the GST system and its implications.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court laid down functionality and essentially test for Input Tax Credit (ITC) eligibility under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
- The verdict was delivered in the Chief Commissioner of Central Goods and Service Tax & Ors. Vs Safari Retreats Case, 2024.
What are the Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Ruling on ITC?
- ITC for Real Estate Sector: The Supreme Court (SC) ruled that the real estate sector can claim ITC on construction costs for commercial buildings used for renting or leasing purposes under the functionality and essentially test.
- Earlier ITC was not allowed on such immovable property construction.
- Clarification on 'Plant and Machinery' Category: The court clarified that if the construction of a building is essential for providing services like leasing or renting, the building may fall under the category of 'plant and machinery.'
- This is based on Section 17(5)(d) of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017 which permits ITC claims on plant and machinery used in the business of supplying services.
- The court read down the scope of Sections 17(5)(c) and (d) of the CGST Act, 2017 which prohibit ITC claims for construction materials used for immovable property, except for plant or machinery.
- Case-Specific Determination: The SC emphasised that determining whether a building like a mall or warehouse qualifies as ‘plant’ under Section 17(5)(d) should be assessed on a case-by-case basis.
- The business nature and the role of the building in the registered person’s business are key factors in this determination.
What are Functionality and Essentially Tests?
- Functionality Test: It will evaluate whether the building plays a role in the supply of services, akin to the function of plant and machinery in a factory.
- Essentially Test: The SC held that procurement of goods or services must be directly essential to business operations.
- It means that only those goods and services that are directly needed for constructing or developing property can be claimed for tax benefits or input tax credit (ITC). E.g., cement, steel etc.
What is Goods and Services Tax?
- About GST: GST is a value-added tax system (ad valorem tax) that is levied on the supply of goods and services in India.
- It is a comprehensive indirect tax implemented in India on 1st July 2017, via the 101st Constitution Amendment Act, 2016, with the vision of ‘One Nation, One Tax.’
- Tax Slabs: The primary GST slabs for regular taxpayers are currently 0% (nil-rated), 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
- GST Council: The GST Council is a constitutional body that recommends matters concerning GST implementation in India. According to Article 279A(1) of the Constitution, the President established the GST Council.
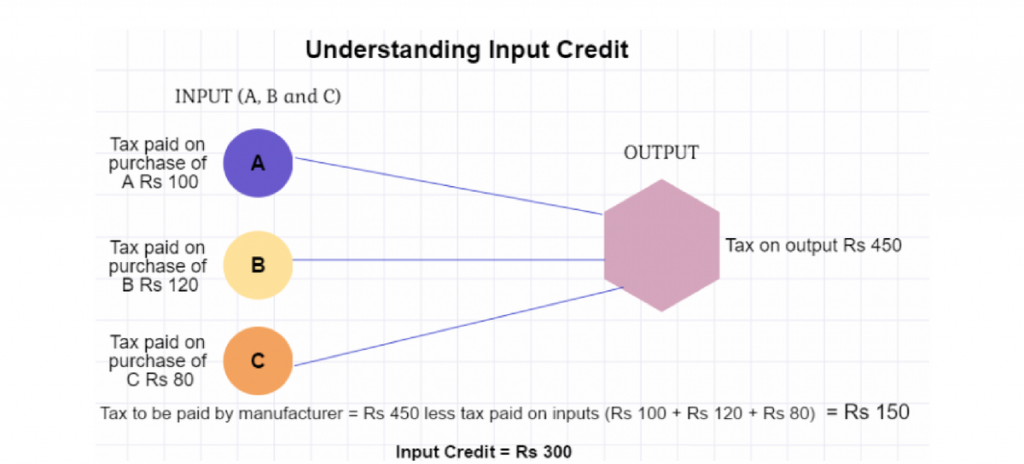
What is Input Tax Credit Under GST?
- About ITC: ITC is one of the foundational elements of the GST system that allows businesses to claim credit for taxes paid on inputs used in their business.
- It implies at the time of paying tax on output, one can reduce the tax he has already paid on inputs and pay the balance amount.
- It enables an uninterrupted and seamless credit flow across the supply chain.
- It eliminates the cascading effect of taxes by imposing tax only on the value addition to the input.
- ITC Working Mechanism: When someone buys a product/service, he pays taxes on the purchase and on selling, he collects the tax.
- He adjusts the taxes paid at the time of purchase with the amount of output tax (tax on sales) and balance liability of tax (tax on sales minus tax on purchase) has to be paid to the government.
- Avoiding Cascading of Taxes using ITC: Cascading of taxes occurs when a tax is levied on a product, and subsequent taxes are imposed on the taxed value of that product, thus leading to multiple layers of taxation.
- In the pre-GST tax system, taxes levied by the Central Government (like central excise duty) could not be used to offset taxes levied by the State Governments (like VAT). VAT was levied not just on the value of the product but also on the tax (excise duty) included in the price.
- Since GST subsumes most central and state indirect taxes into a single levy, the tax paid at one stage can be used to offset the tax payable at subsequent stages. This ensures that tax is only paid on the value added at each stage, not on the entire cost, including previous taxes.
- Impact of ITC: The introduction of ITC under GST has led to greater transparency and efficiency in the supply chain.
- Since the tax paid at each stage can be claimed as a credit, businesses are incentivised to ensure proper documentation and compliance.
- The ITC mechanism reduces the overall tax burden on businesses, making goods and services more competitively priced in the market.
What is Reversal of Input Tax Credit?
- About Reversal of ITC: Reversal of ITC means that the input tax credit one had claimed earlier is cancelled, and the amount is added to his tax liability.
- Conditions for ITC Reversal:
- Non-payment Of invoices within 180 days: ITC will be reversed for invoices that remain unpaid beyond 180 days from the date of issue.
- Credit note issued to ISD by seller: If a seller issues a credit note to the Input Service Distributor (ISD), it means that the amount of input tax credit (ITC) previously claimed will be reduced.
- Partially used business inputs: In cases where inputs are used for both business and non-business (personal) purposes, the portion of ITC used for personal purposes must be reversed proportionately.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court's ruling on ITC introduces the functionality and essentiality tests, offering clarity for businesses in the real estate sector on claiming ITC for construction used in renting and leasing. This decision promotes transparency and efficiency, while reducing the overall tax burden, fostering investment and growth in commercial real estate.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does the Input Tax Credit (ITC) mechanism under the GST system mitigate the cascading effect of taxes? Illustrate with examples to support your explanation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q.What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of the economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Q. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (2019)
Q. Explain the salient features of the Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016. Do you think it is efficacious enough “to remove cascading effect of taxes and provide for the common national market for goods and services”? (2017)
Q. Discuss the rationale for introducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Bring out critically the reasons for the delay in rollout for its regime. (2013)
5 New Classical Languages and Change in Criteria
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the recognition of five more languages as "classical," expanding the nation's list of culturally significant tongues.
- Other than 6 languages, Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali have been included in the prestigious category.
What is a Classical Language?
- About:
- In 2004, the Indian government began designating languages as "Classical Languages" to acknowledge and preserve their ancient legacy.
- The 11 classical languages of India serve as custodians of the nation's rich cultural heritage, representing key historical and cultural milestones for their communities.
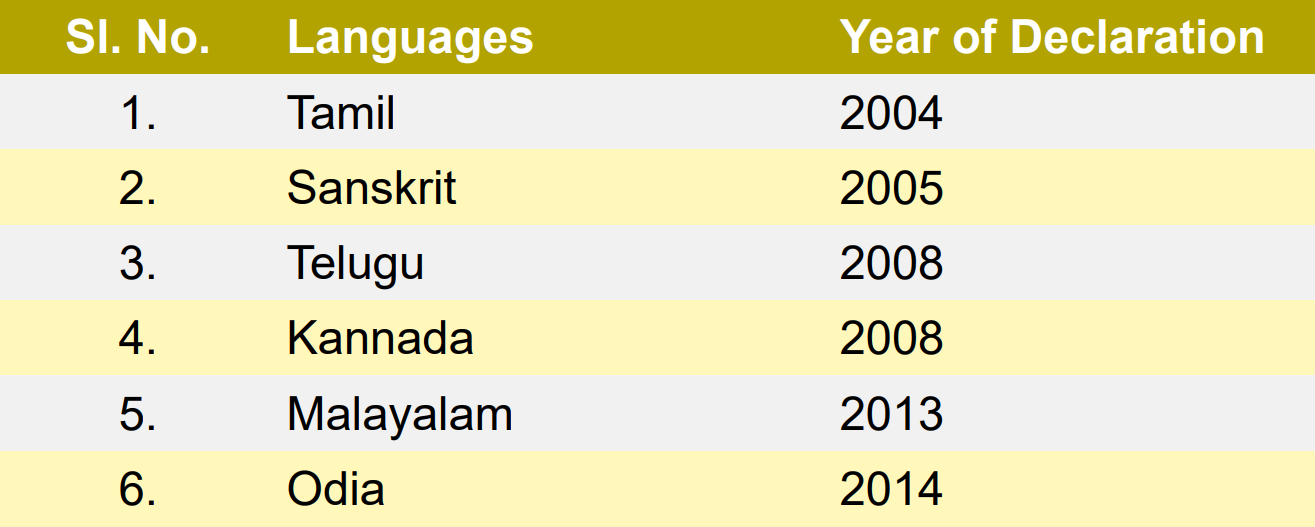
- Indian classical languages (Shastriya Bhasha) are languages with a rich historical legacy, profound literary traditions, and distinctive cultural heritage.
- Significance:
- These languages have played a key role in the intellectual and cultural evolution of the region.
- Their texts provide valuable insights into diverse fields such as literature, philosophy, and religion.
- Criteria: It was revised in 2005 and 2024 on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi.
-
Revised criteria in 2005 are as follows:
- High Antiquity: Early texts and recorded history spanning 1,500–2,000 years.
- Ancient Literature: Possession of a body of ancient literature/texts considered valuable heritage by generations.
- Knowledge Texts: Presence of an original literary tradition not borrowed from another speech community.
- Distinct Evolution: The classical language and literature are distinct from modern, there can also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or its offshoots.
- In 2024, criteria for declaring a language as classical were revised.
- Under which “Knowledge Texts: Presence of an original literary tradition not borrowed from another speech community” was replaced by “Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence”.
-
- Benefits:
- Languages designated as 'classical' receive various government benefits aimed at promoting their study and preservation.
- Two international awards are given annually to scholars who have made notable contributions to the research, teaching, or promotion of classical Indian languages.
- These are the Presidential Award of Certificate of Honour and the Maharshi Badrayan Samman Award.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) supports the creation of Professional Chairs in central universities and research institutions to focus on classical Indian languages.
- To safeguard and promote these linguistic treasures, government established the Center of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages at the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL) in Mysore.
What are the Other Provisions to Promote Language?
- Eighth Schedule: To promote the progressive use, enrichment and promotion of the language. Consists of 22 languages:
- Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Bodo, Santhali, Maithili and Dogri.
- Article 344(1) provides for the constitution of a Commission by the President on the expiration of five years from the commencement of the Constitution for the progressive use of Hindi .
- Article 351 provides that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language
- Other Efforts to Promote Languages:
- Project ASMITA: The project ASMITA aims to produce 22,000 books in Indian languages within five years.
- New Education Policy (NEP): The NEP policy aims to turn Sanskrit universities into multi-disciplinary institutions.
- Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL): This institute works to promote four classical languages: Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia.
- Central Sanskrit Universities Bill, 2019: It granted Central status to three deemed Sanskrit universities: the Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan and Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Delhi, and the Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Tirupati.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following languages: (2014)
- Gujarati
- Kannada
- Telugu
Which of the above has/have been declared as ‘Classical Language/Languages’ by the Government?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
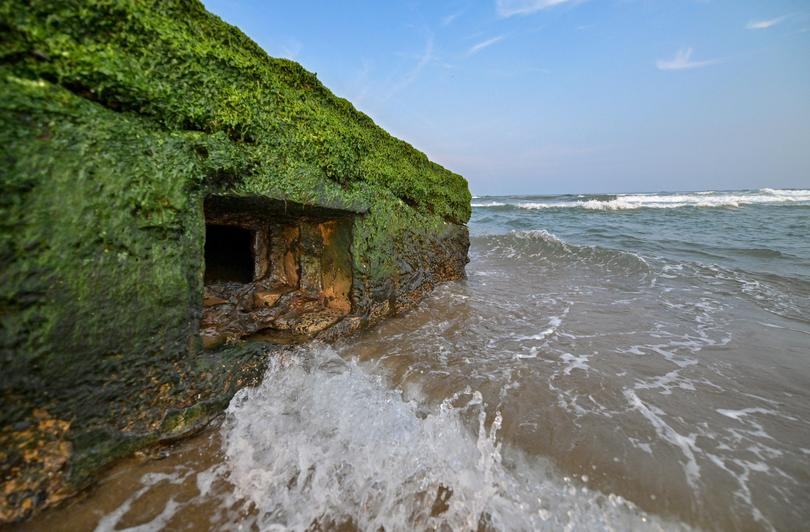
Visakhapatnam’s Pillboxes
Why in News?
Due to the monsoon, Visakhapatnam's beaches have shifted, revealing World War II pillboxes that were buried in the sand, offering a look into the city's forgotten maritime history.
What are Pillboxes?
- About:
- The pillboxes, constructed during the height of World War II, were part of a strategic defense network to safeguard Visakhapatnam's shores from potential enemy invasions.
- The name "pillbox" comes from their resemblance to medicine containers used in the early 20th century for storing pills.
- Visakhapatnam's Pillboxes:
- The most visible pillbox is located at R.K. Beach, revealed by beach erosion, while a second one at Jalaripeta fishing colony is buried under sand, garbage, and neglect.
- Visakhapatnam was a significant target during the war, as it is one of India's key naval bases with a deep natural harbor.
- The most visible pillbox is located at R.K. Beach, revealed by beach erosion, while a second one at Jalaripeta fishing colony is buried under sand, garbage, and neglect.
- Strategic Importance:
- The pillboxes were designed to blend into the landscape, making them difficult for enemies to detect.
- They functioned as tactical posts, allowing soldiers to defend the coastline while providing secure cover for firing at enemies.
World War I and II
- World War I (1914-1918) was fought between the Allied Powers (France, Russia, Britain, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), with the Allied Powers emerging victorious.
- World War II (1939-1945) was fought between the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy, and Japan) and the Allied Powers (France, Great Britain, the United States, the Soviet Union, and China), with the Allied Powers winning the war.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The plan of Sir Stafford Cripps envisaged that after the Second World War (2016)
(a) India should be granted complete independence
(b) India should be partitioned into two before granting independence
(c) India should be made a republic with the condition that she will join the Commonwealth
(d) India should be given Dominion status
Ans: (d)
International Day of Older Persons 2024
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment observed International Day of Older Persons 2024 on 1st October 2024.
- Theme for 2024: Ageing with Dignity: The Importance of Strengthening Care and Support Systems for Older Persons Worldwide
- About International Day of Older Persons:
- This day is celebrated to recognise the contributions made by older people and promote the need for inclusive and age-friendly societies.
- Designated by the UN General Assembly on 14th October, 1990, it is based on the Vienna International Plan of Action on Ageing (1982) and the UN Principles for Older Persons.
- Commitments & Global Framework:
- The UN Decade of Healthy Ageing (2021-2030) aligns with SDG-3 on Good Health and Well-Being.
- India formulated the National Policy on Older Persons (NPOP) in 1999 and is a signatory to the Madrid International Plan of Action on Ageing (2002).
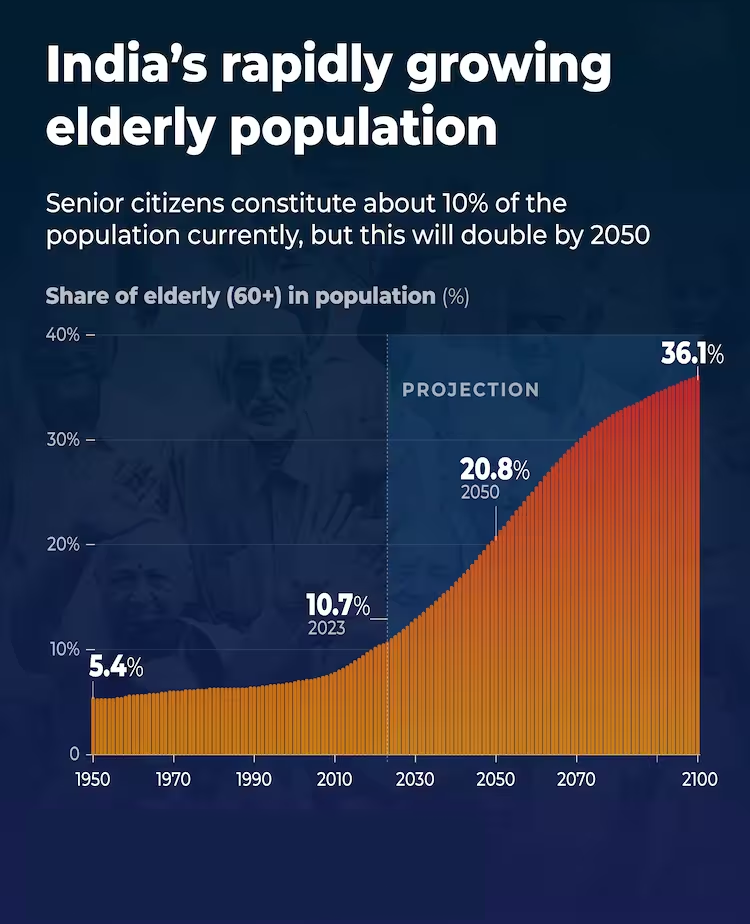
- As of December 2023, India has 153 million elderly individuals (60+), projected to rise to 347 million by 2050, making up 20.8% of the total population.
- Globally, the elderly population rose from about 260 million in 1980 to 761 million in 2021, with projections indicating it will increase from under 10% in 2021 to around 17% by 2050.
Read More: Empowering India's Elderly.
BharatGen
Recently, the Ministry of Science & Technology launched BharatGen, a generative AI initiative designed to enhance public service delivery.
- It aims to create foundational models in language, speech, and computer vision to address India's socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- It is the world’s first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) project for Indian languages.
- LLMs are AI systems capable of understanding and generating human language by processing vast amounts of text data.
- It is led by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS), and involves collaboration with academic institutions like IITs and IIM Indore.
- It emphasises developing processes to curate India-centric data, enhancing the country’s control over its digital resources.
- It has four key features:
- Multilingual and multimodal models,
- Bhartiya dataset-based training,
- Open-source platform,
- Generative AI research ecosystem in India.
- Generative AI can produce various types of content, including text, imagery, and audio.
Read More: Large Language Models (LLMs)
Dadasaheb Phalke Award to Mithun Chakraborty
Recently, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting has announced that the Dadasaheb Phalke Award for 2022 will be awarded to the actor and former Rajya Sabha Member of Parliament (MP) Mithun Chakraborty.
- It will be presented during the 70th National Film Awards ceremony, for his significant contribution to Indian cinema.
- He will be the 54th recipient of the DadaSaheb Phalke Award.
- About Dadasaheb Phalke Award:
- It is the country’s highest film honour introduced in 1969, conferred for “Outstanding contribution for the growth and development of Indian cinema”.
- It was awarded for the first time to Devika Rani, “the first lady of Indian cinema”.
- This award includes a 'Swarna Kamal,' a cash prize of INR 10 lakh, a certificate, a silk roll, and a shawl.
- It is presented by the President of India.
- About Dhundiraj Govind Phalke:
- He was an Indian producer, director, and screenwriter, who directed India's first feature film Raja Harischandra (1913).
- He is known as the “Father of Indian Cinema”.
Read More: National Film Awards
Exercise KAZIND 2024
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024, commenced in Uttarakhand and is being held from 30th September to 13th October 2024.
- The Exercise between India and Kazakhstan was initiated as ‘Exercise PRABAL DOSTYK’ in 2016.
- After the second edition, it was upgraded to a company-level exercise and renamed ‘Exercise KAZIND’.
- The exercise aims to enhance joint military capabilities for counter-terrorism operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrain, focusing on physical fitness, tactical drills, and sharing of best practices under Chapter VII of the UN Charter.
- Chapter VII includes action with respect to threats to the Peace, Breaches of the Peace, and Acts of Aggression.
Read More: Exercise Kazind-2023