Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Solar Water Desalination
Why in News?
Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT)- Bombay scientists have developed a new material to enable water desalination and address global freshwater scarcity. 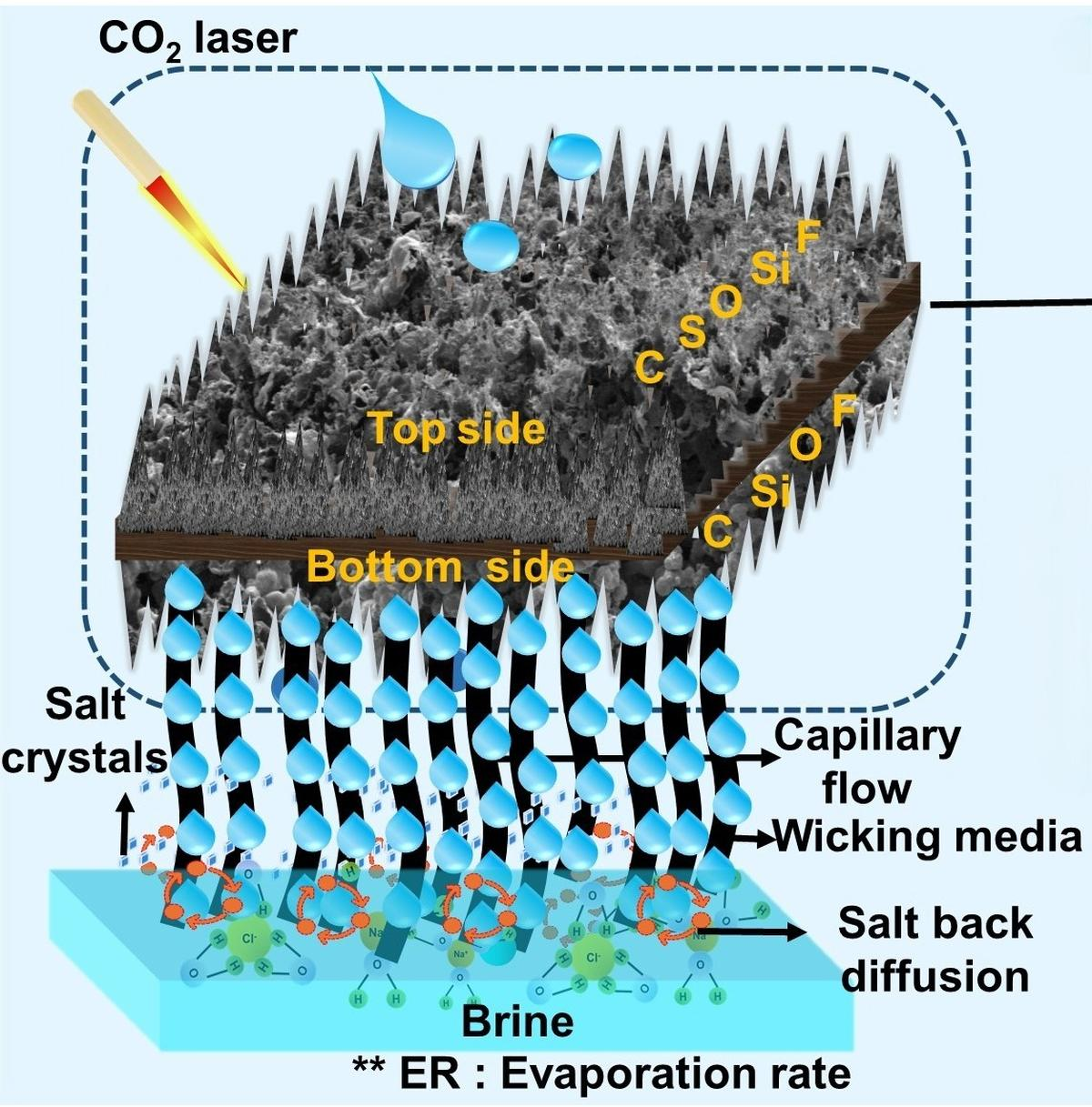
Key Points
- About the Innovation:
- Researchers have developed a Dual-Sided Superhydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene (DSLIG) evaporator.
- The DSLIG addresses limitations of traditional evaporators and shows promise for large-scale desalination and wastewater treatment.
- The Freshwater Challenge:
- Only 3% of Earth’s water is freshwater, and less than 0.05% is easily accessible.
- Desalination of seawater and brackish water is a key solution to this scarcity.
- However, desalination produces brine, a concentrated salt byproduct, which poses disposal challenges, especially in landlocked areas.
- Industries now aim for zero liquid discharge systems to avoid environmental harm.
- Solar Desalination:
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Yet, sunlight variability and poor light absorption reduce efficiency.
- Interfacial evaporation systems help by heating a thin surface layer of water instead of the whole volume, enhancing efficiency.
- Challenges in Interfacial Evaporation:
- Cloud cover and fluctuating solar intensity hamper consistent performance.
- Evaporation peaks around 2 pm, when solar radiation is highest.
- Salt deposition on the evaporator surface blocks water contact, reducing long-term efficiency.
- DSLIG Overcomes the Challenges:
- DSLIG allows dual heating—solar and Joule heating (electric)—ensuring performance even in low sunlight.
- Superhydrophobic properties (lotus effect) prevent salt from sticking to the evaporator surface.
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Fabrication of DSLIG:
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
- PDVF are polymers that can generate electric charges on the surface under pressure/strain thus converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- PES is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and biocompatibility.
- They used laser engraving to inscribe graphene onto the PVDF layer.
- PES ensures mechanical strength, while PVDF contributes to dual-sided water repellency.
- The result is a durable, superhydrophobic surface effective in both electric and solar modes.
- Applications:
- It is suitable for treating industrial wastewater and brine from desalination plants.
- Researchers observed improved performance by stacking multiple evaporators.
- DSLIG is low-cost, non-toxic, and sustainable, making it ideal for large-scale applications.
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
Desalination
- A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink.
- Desalination is the process of removing salts from water to produce water that meets the quality (salinity) requirements of different human uses.
- The most commonly used technology for the process is reverse osmosis.
- An external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
- The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side.
- These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
ATM on Wheels
Why in News?
Indian Railways installed an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) onboard the Manmad-CST Panchvati Express as part of a pilot initiative in Maharashtra.
Key Points
- About the Initiative:
- The initiative aligns with the Railway Board's push to boost non-fare revenue through innovative, out-of-the-box solutions.
- It aims to provide banking access to passengers, especially in regions with limited financial infrastructure.
- This setup could particularly benefit commuters on long-distance routes with fewer banking facilities en route.
- Indian Railways’ Modernisation Drive:
- The ATM initiative is a part of the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision, focusing on passenger convenience and tech-led upgrades.
- Indian Railways is already transforming travel with high-tech trains like Vande Bharat, modern stations, and advanced safety systems.
- Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:
- Under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme, Indian Railways has selected 1,337 stations for redevelopment, aiming to enhance infrastructure and passenger experience.
- The Scheme was launched in February 2023 by the Ministry of Railways.
Indian Railways
- 169 Years of Heritage:
- The Indian Railways was established on 16th April 1853. The inaugural passenger train covered a 34-kilometer route between Mumbai's Bori Bandar and Thane.
- Unique Mascot:
- The Indian Railways boasts its own mascot, a 'Shubhankar named 'Bholu,' created by the National Institute of Design in 2002. Bholu is an elephant dressed as a railway guard, introduced on the railways' 150th anniversary.
- World's 4th Largest Rail Network:
- The Indian Railways ranks as the world's fourth-largest railway network, encompassing a track length of 67,368 km. Only the US, China, and Russia have larger networks. It's also the world's second-largest network managed under a single administration, spanning 115,000 km.
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites:
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites.
- Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus in Mumbai, Nilgiri Mountain Railway, and Kalka Shimla Railway.
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Rishikesh-Karnaprayag Rail Link Project
Why in News?
On 16 April 2025, the Union Railway Minister and Chief Minister of Uttarakhand witnessed the breakthrough program of India’s longest rail tunnel at Janasu, Uttarakhand.
Key Points
- Part of Rishikesh–Karnaprayag Rail Project:
- The 14.57-km-long Tunnel 8 lies between Devprayag and Janasu and forms a key part of the 125-km Rishikesh–Karnaprayag Broad Gauge Rail Line.
- This project aims to enhance connectivity across five Himalayan districts—Devprayag, Srinagar, Rudraprayag, Gauchar, and Karnaprayag.
- The project uses Tunnel Boring Machine (TBM) technology for the first time in mountainous regions of India.
- Technical and Logistical Challenges Overcome:
- TBM components weighing 165 MT were transported from Mundra Port across narrow Himalayan roads and old bridges.
- The tunnel passes through Seismic Zone IV, demanding advanced design and geological probing due to tectonic activity.
- Impact and Broader Significance:
- Over 83% of the 125-km alignment runs through tunnels, involving a total of 213 km of tunnelling across main and escape routes.
- Once completed, the project will reduce travel time, ensure all-weather access, and boost tourism and regional economy in Uttarakhand.
- It also represents a major leap toward realising the Char Dham Rail Connectivity Initiative under the government's Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
Vision India@2047
- The Project:
- Vision India@2047 is a project initiated by the NITI Aayog, the apex policy think tank of India, to create a blueprint for India’s development in the next 25 years.
- The project aims to make India a global leader in innovation and technology, a model of human development and social welfare, and a champion of environmental sustainability.
- Objectives:
- Achieving a USD 30 trillion economy with a per-capita income of USD 18,000-20,000 and strong public finances and a robust financial sector.
- Building world-class infrastructure and facilities in both rural and urban areas.
- Eliminating unnecessary interference by the government in the lives of citizens and promoting digital economy and governance.
- Developing 3-4 global champions in every sector by merger or restructuring and boosting indigenous industry and innovation.
- Becoming self-reliant in defence and space sectors and enhancing India’s role in the world.
- Fostering green growth and climate action by increasing renewable energy capacity and reducing carbon emissions.
- Empowering the youth with skills and education and creating more employment opportunities.
- Partnering with foreign R&D organizations to build top 10 labs in the country and bringing at least 10 Indian institutions among the top 100 globally.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Drive Against Illegal Residents in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
On 17 April 2025, Uttarakhand Chief Minister directed the police to launch a drive to identify and take action against people living illegally in the state using fake identification papers.
Key Points
- About the Drive:
- The CM also directed to intensify action against the drug mafia and all individuals disrupting law and order.
- Taking note of delays in registering First Information Report (FIR) related to cybercrime, the CM demanded a status report on actions taken in these cases.
- He urged the police to strengthen response mechanisms for cybercrime complaints.
- He also called for improving work culture across all levels of the police department to enhance public trust and efficiency.
First Information Report (FIR)
- It is a written document prepared by the police when they receive information about the commission of a cognizable offence.
- It is a report of information that reaches the police first at that point of time and that is why it is called the First Information Report.
- It is generally a complaint lodged with the police by the victim of a cognizable offence or by someone on his/her behalf. Anyone can report the commission of a cognizable offence either orally or in writing.
- There are three important elements of an FIR:
- The information must relate to the commission of a cognizable offence,
- It should be given in writing or orally to the head of the police station,
- It must be written down and signed by the informant, and its key points should be recorded in a daily diary.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
On 16 April, 2025, a seven-year-old boy died in a tiger attack near the Trinetra Ganesh temple in Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan .
Key Points
- About Ranthambore Tiger Reserve :
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve is located at the confluence of the Aravalli and Vindhya mountain ranges in Karauli and Sawai Madhopur districts in the eastern part of the state of Rajasthan.
- It includes Ranthambore National Park as well as Sawai Mansingh and Kailadevi sanctuaries.
- The Ranthambore Fort, after which the forest is named, is said to have a history of over 1000 years. It is strategically located on a 700 feet high hill within the park.
- It was constructed by a Chauhan ruler in 944 AD.
- This isolated tiger-infested area represents the northwestern limit of the distribution range of the Bengal tiger and is an outstanding example of Project Tiger's conservation efforts in the country.
- Features:
- The reserve consists of highly fragmented forest areas, ravines, river channels and agricultural lands.
- It is connected to the Kuno-Palpur landscape of Madhya Pradesh through parts of the Kailadevi Wildlife Sanctuary, the ravine habitats of the Chambal and the forest areas of Sheopur .
- The tributaries of the Chambal River provide an easy route for the tigers to move towards Kuno National Park.
- Flora and Wildlife:
- Vegetation includes grasslands on the plateaus and dense forests along the seasonal rivers.
- The forest is predominantly tropical dry deciduous , with the most common tree species being 'Dhak' (Butea monosperma) , which is able to withstand long periods of drought.
- This tree is also called 'forest fire' and is one of the many flowering plants that add colour to the dry summers here.
- The park is rich in wildlife , with tigers being at the top of the food chain among mammals.
- Other animals found here include leopard , striped hyena, common or Hanuman langur, rhesus macaque , jackal, jungle cats, caracal, blackbuck, blacknaped hare and chinkara etc.
- Vegetation includes grasslands on the plateaus and dense forests along the seasonal rivers.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
McGregor Memorial Medal
Why in News?
On 16 April 2025, Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan awarded the McGregor Memorial Medal for the year 2023 and 2024 to five military personnel .
Key Points
- About the Winners:
- They has been given this honour for their outstanding contribution in military reconnaissance, exploration and adventure activities .
- The awardees for the year 2023 included Wing Commander D. Panda of the Air Force and Electrical Artificer (Radio) Rahul Kumar Pandey of the Navy.
- For the year 2024, Chief Electrical Aircraft Artificer (Radio) of the Navy, Ram Ratan Jat and Sergeant Jhumar Ram Poonia of the Air Force were awarded the medal.
- Apart from this, Colonel Ranveer Singh Jamwal, Director of National Mountaineering and Adventure Sports Institute in Arunachal Pradesh was also honored.
- They has been given this honour for their outstanding contribution in military reconnaissance, exploration and adventure activities .
- McGregor Memorial Medal
- The MacGregor Memorial Medal is awarded in memory of Major General Sir Charles Metcalfe MacGregor, the founder of the United Service Institution of India (USI).
- This award was established on July 3, 1888.
- The main objective of this award was to honour reconnaissance and exploratory journeys undertaken by the armed forces, but in the year 1986 the scope of the award was extended to include military operations and adventure activities as well.
- The award is now open to all serving and retired ranks of the Indian Armed Forces , Territorial Army, Reserve Forces, National Rifles and Assam Rifles.
- A total of 127 MacGregor Medals have been awarded so far, of which 103 medals date back to before independence .
- The MacGregor Memorial Medal is awarded in memory of Major General Sir Charles Metcalfe MacGregor, the founder of the United Service Institution of India (USI).
Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
- The CDS serves as the permanent chairman of the 'Chiefs of Staff Committee' which will also have the three service chiefs as members.
- Its main function is to promote greater operational synergy among the tri-services of the Indian Army and to minimise inter-service conflicts.
- He also heads the newly created Department of Military Affairs (DMA) in the Ministry of Defence.
- He will function as the principal military adviser to the Defence Minister on matters relating to the three services, but the three service chiefs will continue to advise the Defence Minister on matters relating to their respective services.
- As head of the DMA, the CDS is empowered to prioritise inter-service procurement decisions as the permanent chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee.
- CDS has also been given the authority to give instructions to the three chiefs.
- However, he does not have the authority to command any army.
- The CDS is the first among equals and has the rank of Secretary within the DoD (Department of Defence) and his powers will be limited to the revenue budget only.
- He also plays an advisory role in the Nuclear Command Authority (NCA) .


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh First in GI Tagging
Why in News?
The Prime Minister presented Geographical Indicator (GI) tag certificates to 21 traditional products of Uttar Pradesh during his Varanasi visit .
Key Points
- GI Certified Products:
- Varanasi: Banarasi Tabla , Banarasi Stuffed Chilli, Shehnai , Metal Casting Craft, Mural Painting, Red Peda, Thandai, Tricolor Barfi, and Karonda of Chirgaon.
- Bareilly: Bareilly furniture, Zari Zardosi, Terracotta.
- Mathura : Mathura's Sanjhi Craft.
- Products from other districts:
- Kathia wheat of Bundelkhand,
- Flute of Pilibhit,
- Wood Craft of Chitrakoot,
- Stone inlay work of Agra
- Imarti of Jaunpur.
- Uttar Pradesh has now become the top state in India with 77 GI tags .
- The Kashi region alone has 32 GI tagged products , making it one of the GI hubs of the world .
- Importance:
- Getting legal protection will stop counterfeit products and increase the credibility of original producers in the market .
- From an economic point of view, GI tag will increase the brand value of products and boost exports .
- New employment opportunities will be created at the local level.
Geographical Indication (GI) Tag
- A Geographical Indication (GI) tag is a name or mark used on special products that belong to a specific geographical location or origin.
- The GI tag ensures that only authorised users or people residing in the geographical region are allowed to use the name of a popular product.
- It also protects the product from being copied or imitated by others.
- A registered GI tag is valid for 10 years.
- GI registration is overseen by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Legal Framework:
- It is regulated and guided by the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Farmers Welfare Mission
Why in News?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh approved the launch of the ‘Krishi Kalyan Mission (KKM)’.
Key Points
- About the Mission:
- The objective of this mission is to increase farmers' income , make agriculture climate-resilient , adopt sustainable agricultural practices , conserve biodiversity and traditional agricultural knowledge .
- This mission will also work towards nutrition and food security , as well as providing fair prices to the farmers for their produce .
- Under this mission, schemes prevalent in the departments of Farmer Welfare and Agricultural Development , Horticulture and Food Processing , Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairy , Cooperation, Food, Civil Supplies and Consumer Protection will be integrated .
- Key Goals:
- 1.5 times increase in agricultural mechanization .
- 75% increase in capital investment in the agriculture sector .
- Taking organic/natural farming to 10% of the area .
- Increasing crop insurance coverage to 50% .
- Micro irrigation area up to 20%.
- Solar energy pumps to farmers under Urjadata scheme .
- 50% increase in livestock productivity
- Administrative structure:
- The Chief Minister will be the chairman of the general body of the mission , while the Chief Secretary will head the executive committee.
- At the district level, the mission will be operated under the chairmanship of the District Magistrate.
Agriculture sector in Madhya Pradesh
- According to government data, Madhya Pradesh has made remarkable progress in the agricultural sector . While agricultural productivity was 1,195 kg per hectare in the year 2002-03 , it increased to 2,393 kg per hectare in the year 2024 , which shows an increase of 200 percent .
- Similarly, crop production has also registered a significant increase - it was 224 lakh metric tonnes in the year 2002-03 , which increased to 723 lakh metric tonnes in the year 2024 i.e. an increase of 323 percent .
- The agricultural growth rate of the state has also been remarkable. While it was 3 percent in the year 2002-03 , it has increased to 9.8 percent in the year 2024 .
- Additionally, the agriculture budget has also increased substantially— from Rs. 600 crore in 2002-03 , it has increased to Rs. 27,050 crore in 2024 .
- Currently, the agriculture sector contributes 39 per cent to the state's gross domestic product (GDP) .






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan



