Governance
New Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
- 01 Oct 2022
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Chief of Defence Staff, Kargil Review Committee (1999) report, Naresh Chandra Committee.
For Mains: Significance of Chief of Defence Staff.
Why in News?
Recently, the central government appointed the former head of eastern command Lt General Anil Chauhan (retired) as the new Chief of Defence Staff (CDS).
What is Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)?
- Background: Its creation was recommended in 2001 by a Group of Ministers (GoM) that was tasked with studying the Kargil Review Committee (1999) report.
- After the GoM recommendations, in preparation for the post of CDS, the government created the Integrated Defence Staff in 2002, which was to eventually serve as the CDS’s Secretariat.
- In 2012, the Naresh Chandra Committee recommended the appointment of a Permanent Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee as a midway to eliminate apprehensions over the CDS.
- Finally, the post of CDS was created in 2019 on the recommendations of a committee of defence experts headed by Lt General DB Shekatkar.
- Roles and Responsibilities: His core function will be to foster greater operational synergy between the three service branches of the Indian military and keep inter-service frictions to a minimum.
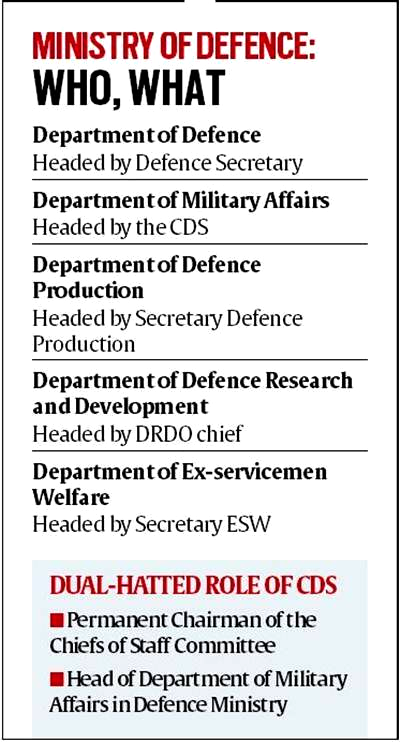
- He also heads the newly created Department of Military Affairs (DMA) in the Ministry of Defence.
- The CDS will be the single-point military adviser to the Defence Minister on matters involving all three services and the service chiefs will be obliged to confine their counsel to issues pertaining to their respective services.
- As the head of DMA, CDS is vested with the authority in prioritising inter-service procurement decisions as Permanent Chairman-Chiefs of Staff Committee.
- The CDS is also vested with the authority to provide directives to the three chiefs. However, he does not enjoy any command authority over any of the forces.
- CDS is first among equals, he enjoys the rank of Secretary within the DoD (Department of Defence) and his powers will be confined to only the revenue budget.
- He will also perform an advisory role in the Nuclear Command Authority (NCA).
- Significance:
- Synergy between Armed forces and Government: CDS’ role is not simply about tri-service (Army, Navy and Indian Air Force) cooperation, it is equally about fostering better cooperation between the Ministry of Defense bureaucracy and the Armed services.
- Since 1947, there have been three Service Headquarters (SHQ) designated as “Attached Offices” of the Department of Defense (DoD). Due to this, communication between SHQ and DoD takes place largely through the medium of files.
- With the creation of CDS as Principal Military Adviser (PMA) to Defense Minister, the process of decision-making will be accelerated.
- Jointness in operations: The Chiefs of Staff Committee-COSC (predecessor of CDS), has been dysfunctional because its chairmanship is held by one of the three chiefs on a part-time rotational basis.
- Historically, the chairman COSC lacked the authority as well as capacity and inclination to tackle tri-service issues of substance.
- With the CDS now being designated as “permanent chairman of COSC”, he will be able to devote undivided attention to the administration of tri-service organisations.
- Operationalisation of Theatre Command: Creation of DMA will facilitate the operationalisation of joint/theatre command.
- Although a successful template for joint operations was created in the Andaman & Nicobar Command, the lack of political direction and indifference of the COSC has led to inactivity of this joint command.
- Theatre commands would need staff with the knowledge and experience to deploy land, maritime and air forces. Given the disruptive impact of each of these measures, they would best be implemented by the CDS.
- CDS as a key functionary in the nuclear command chain will also administer the Strategic Forces Command.
- This measure will go a long way in enhancing the credibility of India's nuclear deterrent.
- The CDS would also initiate an early review of India's Nuclear Doctrine.
- In the approaching era of dwindling defence budgets, a crucial function of CDS will be “prioritising” the capital acquisition proposals of individual services.
- Synergy between Armed forces and Government: CDS’ role is not simply about tri-service (Army, Navy and Indian Air Force) cooperation, it is equally about fostering better cooperation between the Ministry of Defense bureaucracy and the Armed services.