Economy
3O Years of TRIPS
- 14 May 2024
- 7 min read
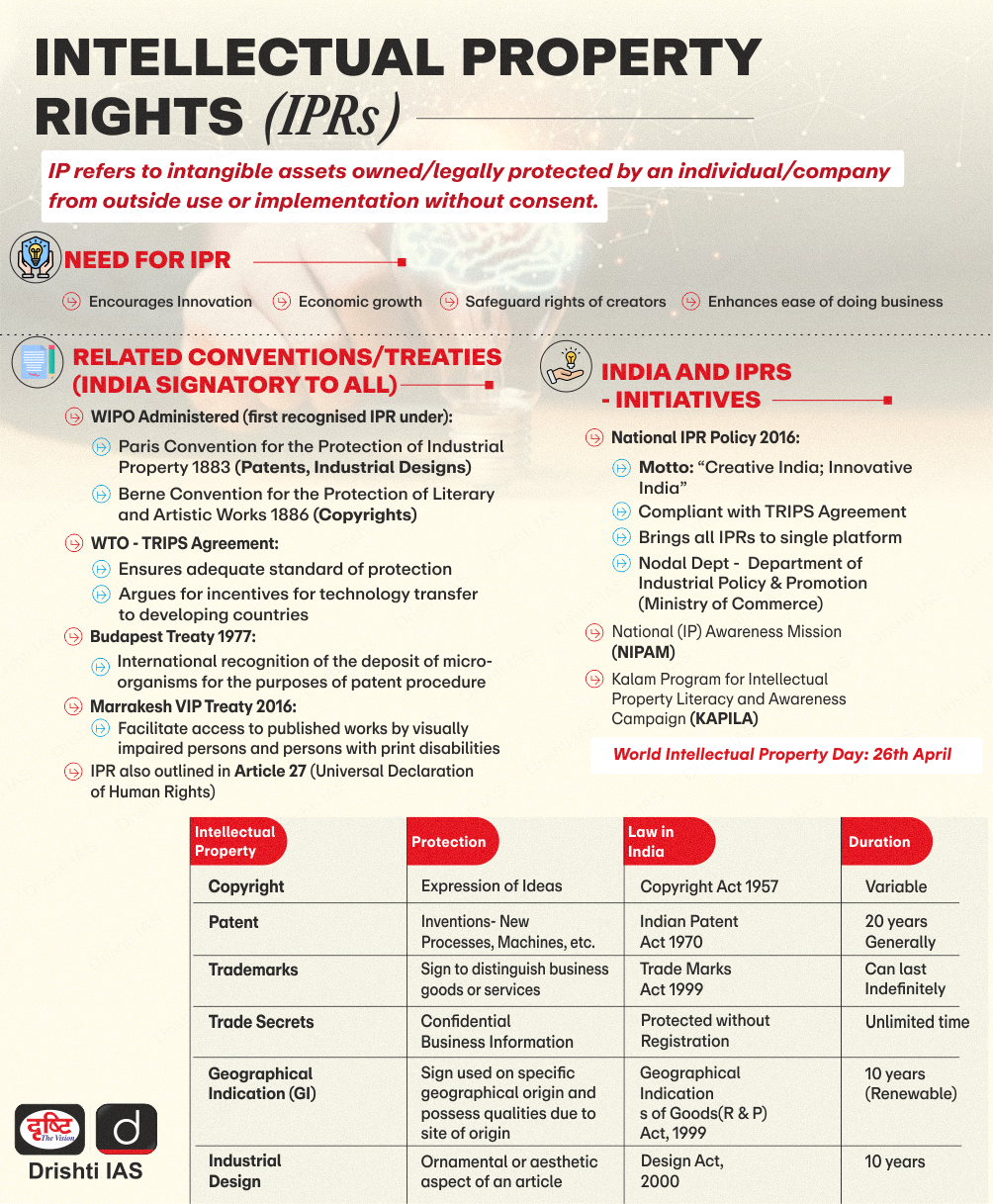
For Prelims: World Intellectual Property Organization’s (WIPO), Patent Criteria in India, National IPR Policy, TRIPS
For Mains: Issues relating to Intellectual Property Rights, Role and Importance of a Strong IPR Ecosystem, India’s Current Scenario, Significance of TRIPS
Why in News?
Recently, World Trade Organisation (WTO) members commemorated the 30th anniversary of the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- In Marrakesh, an important agreement was made that helped create the WTO in 1995. This agreement, called TRIPS, has had a long-lasting effect.
How does the TRIPS Agreement Evolved?
- The Venetian Patent Statute (1474): It was the first codified patent system in Europe that granted inventors a temporary monopoly on "new and ingenious devices".
- The Industrial Revolution and the Need for International Standards (19th Century): Rapid technological advancements created a need for the harmonisation of patent laws.
- The Paris Convention (1883) was the first step taken to protect intellectual work in other countries.
- The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) addressed intellectual property in a limited way.
- The Uruguay Round, spanning from 1987 to 1994, led to the Marrakesh Agreement establishing the WTO, including the TRIPS Agreement.
- The WTO Agreement on TRIPS is the most comprehensive multilateral agreement on intellectual property (IP).
What has been the TRIPS Agreement's Role in International Collaboration?
- Harmonisation of IP Laws: TRIPS set minimum standards for IP protection across member countries.
- This created a more predictable legal environment for international trade and collaboration in research and development (R&D).
- Increased Transparency: TRIPS obligated members to disclose their Intellectual Property (IP) laws and regulations, fostering greater transparency in the global IP system.
- Knowledge Sharing: TRIPS provisions on technology transfer encourage collaboration between developed and developing countries.
- Developed countries are obligated to provide mechanisms for transferring technology to developing countries under certain conditions.
- Promotion of Social and Economic Welfare: WTO highlighted TRIPS' role in balancing rights with obligations to promote social and economic welfare, aligning with the SDGs' objectives.
- During the late 1990s crisis, TRIPS' flexibilities were crucial for access to antiretroviral treatments, illustrating its significance in public health emergencies.
What are the Challenges Related to TRIPS?
- Balance Between Rights and Access: TRIPS' focus on strong IP rights can limit access to essential medicines, educational materials, and agricultural technologies in developing countries.
- Biopiracy and Traditional Knowledge: Concerns exist regarding the patenting of genetic resources and traditional knowledge from developing countries without fair compensation.
- TRIPS' provisions on disclosure of the origin of genetic resources and traditional knowledge are seen as inadequate.
- Enforcement Issues: Enforcing IP rights, particularly in areas like copyright infringement and counterfeiting, remains a challenge for many developing countries.
- Lack of resources and robust legal systems can hinder effective IP protection.
- Data Privacy: International discussions are needed to address data ownership, privacy, the issue of e-commerce, and the patentability of data-driven inventions in the context of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and big data.
- Global Health Equity: Amidst ongoing debate on flexibilities within the TRIPS agreement, like compulsory licensing, access to affordable medicines still remains a challenge, especially in the global south.
Way Forward
- Standardisation and Capacity Building: Developing common standards and best practices for IP enforcement across countries, along with capacity-building initiatives for developing nations, can create a fairer global IP landscape.
- Open Innovation and Knowledge Sharing: Exploring models like open-source collaboration and Creative Commons licenses can promote innovation while ensuring knowledge accessibility.
- Addressing Emerging Technologies: Establishing clear guidelines for IP ownership and rights related to artificial intelligence (AI) and other emerging technologies will be crucial for fostering responsible innovation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the evolution and impact of the TRIPS Agreement on global intellectual property rights, trade, and development. How has TRIPS influenced access to medicines, technology transfer, and economic growth, especially in developing economies? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. With reference to the ‘National Intellectual Property Rights Policy’, consider the following statements: (2017)
- It reiterates India’s commitment to the Doha Development Agenda and the TRIPS Agreement.
- Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion is the nodal agency for regulating intellectual property rights in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- According to the Indian Patents Act, a biological process to create a seed can be patented in India.
- In India, there is no Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
- Plant varieties are not eligible to be patented in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. In a globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms—Copyrights, Patents and Trade Secrets. (2014)