Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Exchange of Fire on Line of Control (LoC)
Why in News?
Recently, an exchange of fire erupted on the Line of Control (LoC) in the Pir Panjal Valley’s Poonch. Authorities reported no casualties in the incident.
Key Points
- Ceasefire Violations and Militant Infiltrations:
- Despite the ceasefire renewal in 2020, the Jammu region has witnessed frequent firing incidents, including close to the LoC. Several incidents involved infiltrating militants.
- In February 2025, an IED explosion killed two Army personnel. In a separate cross-border firing incident, two soldiers sustained injuries in a ceasefire violation.
- Indian troops retaliated effectively, inflicting "heavy casualties" on the Pakistani side.
- Status of Ceasefire Agreement:
- Ceasefire violations along the J&K borders have significantly reduced since India and Pakistan reaffirmed the ceasefire agreement on 25th February 2021.
Line of Control
- The Line of Control (LoC) emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the United Nations (UN) after the Kashmir War.
- It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Shimla Agreement between the two countries.
- LoC is demarcated up to the Siachen Glacier (Point NJ9842)- the world's highest battlefield.
- LoC is delineated on a map signed by the Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement.
Pir Panjal
- About:
- The Pir Panjal Range is a mountain range in the northern Indian subcontinent.
- It begins in Ramban and extends westward, lying south of Jammu and Kashmir’s Vale of Kashmir, reaching Muzaffarabad District.
- The range rises sharply to an average elevation of over 13,000 feet (4,000 meters).
- It separates the Jammu Hills in the south from the Vale of Kashmir, beyond which lie the Great Himalayas.
- The range separates from the Himalayas near the banks of the Sutlej River.
- It forms a natural divide between the Beas and Ravi rivers on one side and the Chenab River on the other.
- Major Passes:
- The range has six historical passes, Hajipir Pass, Gulabgarh Pass, Ratanpir Pass, Pir Panjal Pass, Banihal Pass, Bairam Gala Pass.
- Important Peaks:
- Deo Tibba (6,001 m) and Indrasan (6,221 m) are two significant peaks at the eastern end of the range
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Winter Games in Gulmarg Postponed
Why in News?
Authorities have postponed the 5th edition of the Khelo India Winter Games, originally set for 22-25th February in Gulmarg, due to inadequate snowfall caused by the prolonged dry spell.
Key Points
- Severe Precipitation Deficit in Kashmir:
- According to the Meteorological Department in Srinagar, precipitation has been “negligible” over the past few months.
- The cause of the deficit is the dry spell in the absence of western disturbances, which usually bring rain and snow to the region.
- Water Shortage:
- Several water bodies have witnessed significant depletion, highlighting the impact of the dry weather.
- The natural spring at Achabal Mughal Garden in South Kashmir, built by Mughal Empress Noor Jahan, has nearly dried up.
- The Irrigation and Flood Control Department warned that continued dry conditions could severely impact both drinking water supply and irrigation in the coming months.
- Impact:
- Authorities have deferred the national winter games in Gulmarg, with the J&K Sports Council stating that a reassessment will take place once snow conditions improve.
- Multiple forest fires have been reported, including in Tral, Pulwama district.
- Environmental Concerns and Future Risks:
- Environmentalists fear long-term consequences due to the lack of winter precipitation.
- Experts urge authorities to implement mitigation strategies to address the worsening crisis.
Khelo India Winter Games (KIWG)
- The KIWG is a multidisciplinary, national-level winter sports competition that promotes winter sports and encourages more athletes to take up skiing and skating.
- It includes events such as skiing, alpine skiing, nordic skiing, snow rugby, ice stock sport, snow baseball, mountaineering, snowshoe running, ice hockey, figure skating, and speed skating.
- It is organized by the Sports Authority of India and the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- The 2025 KIWG will be held in the Union Territory of Ladakh from 23 to 27 January for ice events, and in the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir from 22 to 25 February for snow events.
India Meteorological Department
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It works as an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Stubble Burning
Why in News?
A study published in January 2025, based on field measurements, airmass trajectories, and chemical transport models, found no linear correlation between stubble-burning events in Punjab and Haryana and PM2.5 concentration in Delhi-NCR.
Key Points
- Limited Impact of Stubble Burning:
- Researchers found that crop residue burning in Punjab and Haryana contributes only about 14% of PM2.5 in Delhi-NCR, making it an insignificant primary source of pollution.
- Despite a 50% decline in stubble-burning incidents from 2015 to 2023, PM2.5 concentration in Delhi-NCR remained fairly constant, indicating other major pollution sources.
- Scientific Observations on Air Pollution:
- Researchers from the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN), Kyoto, confirmed that PM2.5 variations in Delhi-NCR do not directly correlate with fire counts in Punjab and Haryana.
- Stubble burning largely stops after November, yet Delhi-NCR’s air quality index has remained in the "very poor" to "severe" category every winter since 2016 due to stagnant winds, lower mixing heights, and inversion conditions.
- Key Findings on Pollution Sources:
- In 2023, CO concentration at night was 67% higher than during the day in Delhi-NCR, compared to 48% in 2022, while Punjab and Haryana showed clear day-night variations only during peak stubble-burning periods.
- Even during the peak crop residue burning season (October-November), local industrial and anthropogenic sources contribute more to PM2.5 than stubble burning.
- During the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) Stage III and IV periods, strict controls on transport and construction significantly reduced PM2.5 levels, but once restrictions were lifted, pollution levels surged again.
- Major Contributors to PM2.5 in Delhi-NCR:
- Transport Sector – 30%
- Local Biomass Burning – 23%
- Construction and Road Dust – 10%
- Cooking and Industry – 5-7%
- Unaccounted Sources – 10%
- Stubble Burning – 13% (only in October-November)
The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- About:
- The GRAP consists of emergency measures designed to prevent the deterioration of air quality after reaching specific thresholds in the Delhi-NCR region.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC) notified the GRAP in 2017.
- Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR & Adjoining Areas (CAQM) implements the GRAP.
- Implementation: It is implemented under four stages:
- GRAP is incremental in nature and thus, when the air quality dips from ‘poor’ to ‘very poor,’ measures listed under both sections have to be followed.
Particulate Matter (PM)
- Particulate matter, or PM, refers to a complex mixture of extremely small particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. These particles come in a wide range of sizes and can be made up of hundreds of different compounds.
- PM10 (coarse particles) - Particles with a diameter of 10 micrometres or less.
- PM2.5 (fine particles) - Particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or less.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Pending Cases at Haryana State Information Commission
Why in News?
According to a Right to Information (RTI) reply, the Haryana State Information Commission is handling a backlog of over 7,000 appeal cases. Authorities have yet to recover Rs 2.84 crore, as the penalty imposed on State Public Information Officers (SPIOs) for delays in providing information.
Key Points
- Pending Appeal Cases:
- It was revealed that 8,340 appeal cases were pending before the Chief Information Commissioner and seven State Information Commissioners in January 2024.
- By December 2024, the number decreased to 7,216, with only around 1,000 cases resolved in a year.
- Limited Awareness Campaigns:
- According to the RTI reply, only five workshops have been conducted since 2005, with 896 participants, the last of which was held in Panchkula in 2011.
- Penalty and Recovery Details:
- Over the last 20 years, the Commission imposed Rs 5.86 crore in penalties across 3,611 cases for delays in providing information.
- However, only Rs 2.84 crore has been recovered so far.
- The Commission has awarded Rs 92 lakh in compensation across 1,974 cases for the failure to provide information in a timely manner.
- Over the last 20 years, the Commission imposed Rs 5.86 crore in penalties across 3,611 cases for delays in providing information.
The Right to Information (RTI) Act
- About:
- The Right to Information Act 2005 mandates timely response to citizen requests for government information.
- The basic object of the Right to Information Act is to empower the citizens, promote transparency and accountability in the working of the Government, contain corruption, and make our democracy work for the people in a real sense.
- Right to Information (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- It provided that the Chief Information Commissioner and an Information Commissioner (of Centre as well as States) shall hold office for such term as prescribed by the Central Government. Before this amendment, their term was fixed for 5 years.
- It provided that the salary, allowances and other service conditions of the Chief Information Commissioner and an Information Commissioner (of Centre as well as States) shall be such as prescribed by the Central Government.
- It removed the provisions regarding deductions in salary of the Chief Information Commissioner, an Information Commissioner, the State Chief Information Commissioner and a State Information Commissioner due to pension or any other retirement benefits received by them for their previous government service.
- The RTI (Amendment) Act, 2019 was criticized on grounds of diluting the law and giving more powers to the central government.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
RuTAG Smart Village Center
Why in News?
Recently, the Rural Technology Action Group (RuTAG) Smart Village Center (RSVC) was launched in Mandaura village of Sonipat, Haryana.
Key Points
- About RSVC:
- The RuTAG Smart Village Center (RSVC) aims to introduce innovative solutions to solve everyday challenges in rural areas, such as preventing animal intrusion, promoting organic farming, and supporting small businesses like bakery production.
- The center will benefit farmers, artisans, and rural entrepreneurs by providing technology solutions directly to their doorsteps.
- Technological Solutions:
- Developed under the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser, RSVC will introduce technologies like satellite data for farming, water monitoring kits, solar power, Internet of Things applications, and organic fertilizers.
- The initiative also includes assistive technologies for differently-abled individuals and financial inclusion apps, ensuring access to modern advancements for everyone.
- It will address rural challenges with improved agricultural practices, waste management, renewable energy solutions, and affordable housing innovations.
- Farmers will benefit from advanced post-harvest technologies, and the center will provide information on government welfare schemes through citizen-centric apps.
- This initiative will also enhance income for local artisans and farmers by improving market access.
- The center will collaborate with institutions like IIT Madras, and the Assistive Technology Foundation to provide practical solutions and training in various skills, including bakery, bread-making, and financial literacy.
- Government and Institutional Support:
- The initiative aligns with the Rural Development, Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, and Labour ministries to enhance rural welfare.
- There are plans to expand RSVC across India, with 20 more centers in development.
- The "Techpreneurs" program will empower women to promote these technologies within their communities, ensuring sustainability and long-term success.
Rural Technology Action Group (RuTAG)
- RuTAG is an initiative of the office of the Principal Scientific Advisor (PSA) since 2004.
- It was conceptualized as a mechanism to provide a higher level of science and technology intervention and support for rural areas.
- Under this initiative, the interventions are designed to be primarily demand-driven, focusing on bridging technology gaps at the grassroots level, upgrading technology, and providing training and demonstrations through innovative projects.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
14th Mid Career Course (Phase III)
Why in News?
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), India, organized a training programme for Indian Forest Service (IFS) officers as part of the 14th Mid Career Course (Phase III) at the Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy, Dehradun.
Key Points
- Importance of IFS Officers:
- The Chairperson of NHRC emphasized the key role of Indian Forest Service officers in safeguarding the nation’s natural heritage. He highlighted their responsibility to balance development needs with conservation priorities.
- He stressed the need for officers to understand the historical context of forest legislation, the evolving challenges in forest management, and the relationship between law, policy, and enforcement to carry out their duties effectively.
- Historical Evolution of Forest Legislation:
- The Chairman also discussed the historical development of forest legislation, from the British era to the present. The changing balance between development and conservation was also highlighted.
- The impact of the 2013 Land Acquisition Act on forest land acquisition was examined, which eventually led to the 2023 amendment of the Forest Conservation Act.
- Judicial Impact on Forest Conservation:
- The Chairperson emphasized the role of the courts in shaping forest conservation, citing the landmark T. N. Godavarman case of 1995. This case reduced the timber industry’s detrimental effects on forest cover.
- The importance of strong laws and effective enforcement mechanisms was highlighted, noting that the ongoing involvement of the court through 'continuing mandamus' highlights the persistent challenges in balancing development with conservation.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- About:
- It ensures the protection of rights related to life, liberty, equality, and dignity of individuals.
- Rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and international covenants enforceable by Indian courts.
- Establishment:
- Established on 12th October 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Amended by the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006, and Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- Established in conformity with the Paris Principles, adopted for promoting and protecting human rights.
Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy
- It is a forest service training institute under the Ministry of Environment and Forests of India, which was originally as Indian Forest College, established in 1938 for training of senior forest officers.
- It is situated in the New Forest campus of Forest Research Institute, Dehradun.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
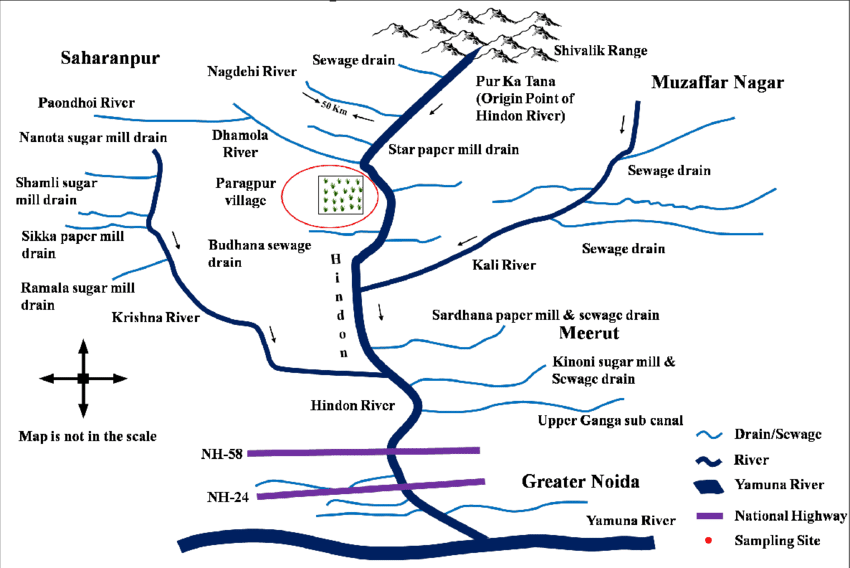
Hindon River
Why in News?
Recently, a large amount of silt and religious material has been dumped into the Hindon River in Ghaziabad, further polluting the river.
Key Points
- The Uttar Pradesh Irrigation Department attributed the river's pollution to the release of untreated drains into it, along with mismanagement and neglect of water quality.
- Pollution in the river:
- Dissolved oxygen (DO) ranged from 1.43 to 4.22 mg/l, while the minimum DO required for aquatic life should be 4 mg/l.
- Total coliform levels range from 260,000 to 380,000 MPN/100 ML, while the standard limit is 1,000 MPN/100 ML.
- The Uttar Pradesh Pollution Control Board (UPPCB) has categorised the river's water quality as 'E', which means the water is suitable only for irrigation, industrial cooling and controlled waste disposal.
- In 2015, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) declared the Hindon River a dead river , stating that it had high levels of pollution and was unfit for bathing in many parts.
Hindon River
- This river originates from the Shivalik Hills in Saharanpur district of Uttar Pradesh and flows for about 400 km in the industrial area of western Uttar Pradesh and merges with the Yamuna River in Noida.
- Hence it is a tributary of Yamuna River.
- It is a monsoon fed river.
- Its catchment area is approximately 7,083 sq. km.
- The Kali (West) River and the Krishna River are the main tributaries of the Hindon River.
- Evidence of the Harappan civilization has been found on the banks of this river, which dates back to 2500 BC.
- Ghaziabad and Noida are situated on the banks of this river.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Exhibition of Schemes in Maha Kumbh
Why in News?
Recently, an exhibition was organised in the Mahakumbh Mela on the implementation of important schemes by the Central Government and the Uttar Pradesh Government.
Key Points
- About the exhibition:
- This exhibition was organized by the Rural Development Department of the Government of India and the Rural Development Department of the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- Through this an attempt has been made to depict the implementation of various schemes and the changing environment of the rural areas through them.
- The important schemes among them are:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act(MGNREGA): Under MGNREGA, various development works were carried out in rural areas such as Amrit-Sarovar, soak pit, rain water harvesting, construction of drains, tree plantation,etc. which changed the face of the rural area and led to development.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): Through Saras Haat of NRLM, women's livelihood was enhanced by promoting their products.
- Programs like BC Sakhi and Drone Sakhi showed improvement in the economic and social life of women
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Rural): The goal of changing the face of housing in rural areas and giving every family its own pucca house was achieved through model houses under this scheme.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY): Under PMGSY, rural areas with a population of more than 250 are connected with all-weather roads.
- Integrated Watershed Management System
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin
- Under the MNREGA scheme, various development works were carried out in rural areas such as Amrit-Sarovar, soak pit, rain water harvesting, construction of drains, tree plantation,etc. which changed the face of the rural area and led to development.
Saras Haat
- About:
- It is a programme to transform rural India in general and the lives of rural women in particular.
- During the Mela, workshops on product packaging and design, communication skills, social media publicity and Business to Business marketing will be organised to educate the rural self-help groups and craftsmen.
- Organiser:
- It is an initiative by the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) under the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) organised by the Council for Advancement of People’s Action and Rural Technology (CAPART).
- CAPART is an autonomous body set up by the Ministry of Rural Development to interface between the government and Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs) that seek to improve the quality of life in India's rural areas.
- Objective:
- To bring the rural women Self Help Groups (SHGs) under one platform so that they can showcase their skills, sell their products, and help them build linkages with bulk buyers.
- Through participation in SARAS Aajeevika Mela, these rural SHG women will get vital national level exposure to understand the demand and taste of urban customers.
Kumbh Mela
- In the year 2025, Maha Kumbh Mela is being organized in Prayagraj from 13 January to 26 February 2025, in which millions of pilgrims are coming every day as a symbol of spiritual purification, cultural celebration and unity.
- The word 'Kumbh' is derived from the metal 'Kumbhaka' (sacred pot of the nectar of immortality).
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims during which the participants take a bath or dip in the holy river. This congregation takes place at 4 different places, namely:
- On the banks of the Ganga at Haridwar .
- On the banks of the Shipra River in Ujjain .
- On the banks of the Godavari (South Ganga) at Nasik .
- At the confluence of Ganga, Yamuna and the mythical invisible Saraswati in Prayagraj
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Removal of a High Court Judge
Why in News?
Recently, after the controversial statement of Allahabad High Court judge, an impeachment motion signed by 55 members has been introduced in the Rajya Sabha to remove him from his post.
Key Points
- About the issue:
- The Judge had allegedly made some communal remarks at a Vishwa Hindu Parishad event in December 2024.
- Under the Judges Inquiry Act 1968, 55 opposition MPs in the Rajya Sabha have given a notice to introduce a motion to remove Justice from the office of judge for his alleged misconduct.
- Procedure for removal of Judges:
- Under Articles 124 and 218 , judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts can be removed by the President on grounds of “proven misbehaviour” or “incapacity”.
- To remove this, a resolution must be passed by both houses of the Parliament:
- Majority of the total membership of the House.
- A special majority of not less than two-thirds of the members present and voting at the same session .
- The words “proven misbehaviour” and “incapacity” are not defined in the Constitution.
- Misconduct, as interpreted by the Supreme Court, includes wilful misconduct, corruption, lack of integrity or moral turpitude .
- Incapacity refers to a physical or mental condition that impedes judicial functioning.
- Procedure under the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968:
- Notice of Offer:
- Inquiry Committee constituted:
- If the proposal is accepted then a three-member committee consisting of judges and a renowned jurist is formed.
- The committee investigates allegations of:
- If the judge is acquitted, the motion is dismissed.
- If found guilty then the committee report is sent to the Parliament for voting.
- If the judge is acquitted, the motion is dismissed.
- Parliamentary approval:
- For the President to remove a judge , both the Houses will have to pass a resolution with a special majority.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Regional Official Language Conference
Why in News?
Recently, a joint regional official language conference was organized in Jaipur.
Key Points
- About the conference:
- This conference was organised by the Official Language Department of the Home Ministry .
- About 3000 people from Central Government offices, Nationalized Banks, Public Sector Undertakings and Town Official Language Implementation Committees participated in the conference .
- The best performing institutions were also honoured for promoting greater use of Hindi in government work .
- Objective:
- The objective of this conference was to promote the use of Hindi in government departments .
Hindi Language
- Introduction :
- Hindi is an Indo-Aryan language, spoken mainly in the Indian subcontinent .
- It is the official language of India according to the Indian Constitution , and it holds an important place in Indian society , culture and literature .
- It is the third most widely spoken language in the world and one of the ten official languages of the UNESCO General Conference.
- History :
- Hindi evolved from Sanskrit and has been spoken in the Indian subcontinent since ancient times. Over time, Hindi has also adopted words from Persian , Arabic , and English , especially during the Mughal Empire and British rule .
- Script :
- The script of Hindi is Devanagari , which is developed from the Sanskrit script. It has 11 vowels and 33 consonants . Devanagari script is used not only for Hindi but also for many other Indian languages.
- Linguistic Diversity :
- Hindi language has many dialects, such as Awadhi , Bhojpuri , Braj , Haryanvi , Marwari etc.
- Expansion :
- Hindi is spoken not only in India but also in Nepal , Pakistan , Malaysia , Thailand , Fiji and other countries.
- Place in the Constitution :
- Hindi has been accepted as the official language of the Union under Article 343 of the Indian Constitution.
- Apart from this, Hindi has been recognized as one of the 22 scheduled languages listed in the Eighth Schedule.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Madhubani Painting
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India gifted a wooden railway toy set and a jigsaw puzzle based on Indian folk art to US Vice President J D Vance’s Kids in France during his two-day visit to the European country.
Key Points
- About the Gifts:
- Wooden Railway Toy:
- Crafted from natural wood and painted with eco-friendly vegetable dyes, this toy ensures child safety and environmental awareness.
- This wooden railway toy was described as "a timeless classic" that combines nostalgia with sustainability.
- Wooden Railway Toy:
- Jigsaw Puzzle:
- It depicts the rich art heritage of India by incorporating various folk painting styles like Kalighat art of West Bengal, Santhal paintings of Santhal tribe and Madhubani paintings of Bihar.
- Wooden Alphabet Set:
- It is a durable, safe, and engaging learning tool, which enhances skills and cognitive abilities.
Madhubani Art
- Origin:
- Madhubani painting originated in the Mithila region of Bihar .
- This painting is one of the oldest and most famous Indian art forms, which is also practiced in Nepal.
- Traces of Madhubani art can also be seen in the Indian epic Ramayana.
- It is also known as Mithila or Madhubani art.
- Features:
- These paintings are popular due to their tribal motifs and use of bright earthy colours.
- Traditionally village women used to draw these paintings on the walls of their homes as a display of their feelings, hopes and thoughts.
- Style:
- It includes geometric patterns, floral, animal and bird motifs.
- Colours:
- The colours used in the paintings are made from natural extracts obtained from plants and other natural sources.
- For example: black colour is made by mixing soot with cow dung; blue colour is made from indigo; white colour is made from rice powder; orange colour is made from palash flowers, etc.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan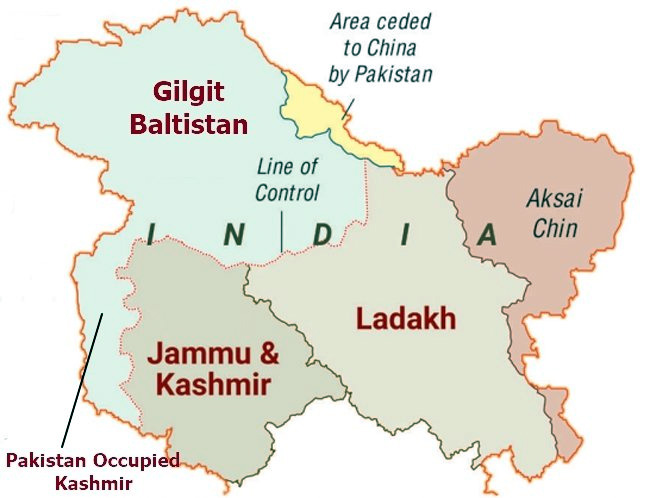
.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
 (2).jpg)
.jpg)



