West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Indian Navy's Motor Car Rally
Why in News?
On 3rd March 2025, Naval Officer-in-Charge (West Bengal) flagged off the Indian Navy's Motor Car Rally Expedition on the East Coast from INS Netaji, Kolkata.
- The rally will cover the route from Kolkata to Chennai, proceed to Kanyakumari, and return to Chennai on 21 March 2025.
Key Points
- Objectives of the Rally:
- Enhance maritime awareness among the public.
- Engage with youth and civil society to inspire participation in naval careers.
- Promote the Agnipath Scheme and other career opportunities in the Indian Navy.
- Advocate for women's empowerment under the Naari Shakti initiative.
- Interact with Naval Veterans and Veer Naaris, updating them on government and naval welfare policies.
- Participation and Coverage:
- A total of 56 Indian Naval personnel, including Officers, Sailors, and their family members, are participating.
- The expedition will traverse approximately 3,800 km through West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, engaging with local communities.
- Historical and Corporate Support:
- The event is supported by M/s Hyundai Ltd.
- The rally will explore India’s rich maritime heritage, visiting historical naval sites and locations along ancient maritime trade routes.
Agnipath Scheme
- The term "Agniveer" translates to "Fire-Warriors" and is a new military rank.
- It is a scheme of recruiting army personnel below officer ranks such as soldiers, airmen, and sailors who are not commissioned officers to the Indian Armed Forces.
- They are recruited for a period of 4 years, after which, up to 25% of these recruits (called Agniveers), can join the services on a permanent commission (another 15 years), subject to merit and organisational requirements.
- At present, all sailors, airmen, and soldiers, except the technical cadre of the medical branch, are recruited to the services under this scheme.


West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Grants for Rural Local Bodies of West Bengal
Why in News?
The Union Government has released the Fifteenth Finance Commission (XV FC) Grants for Rural Local Bodies in West Bengal during the Financial Year 2024-25.
Key Points
- Grant Disbursement:
- The Union Government disbursed the second installment of Untied Grants amounting to Rs 694.4446 crores.
- These funds will support 21 District Panchayats, 326 Block Panchayats, and 3,220 Gram Panchayats.
- Utilization of Grants:
- Untied Grants: Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)/Rural Local Bodies (RLBs) will use these funds for location-specific felt needs, as per the 29 Subjects under the Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution, excluding salaries and establishment costs.
- Tied Grants: These funds will be utilized for essential services, including:
- Sanitation and maintenance of ODF status, covering household waste management, human excreta treatment, and fecal sludge management.
- Drinking water supply, rainwater harvesting, and water recycling to ensure water security in rural areas.
- Role of Government Ministries:
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj and the Ministry of Jal Shakti recommend the release of XV FC Grants to States for Rural Local Bodies.
- The Ministry of Finance subsequently disburses these funds in two installments per Financial Year.
- Impact of the Grants:
- Strengthens rural local governance by enhancing financial resources at the grassroots level.
- Improves accountability and transparency in fund utilization.
- Promotes self-reliance in villages, enabling local bodies to address critical infrastructure and service needs effectively.
15th Finance Commission
- The Finance Commission (FC) is a constitutional body that determines the method and formula for distributing the tax proceeds between the Centre and states, and among the states as per the constitutional arrangement and present requirements.
- Under Article 280 of the Constitution, the President of India is required to constitute a Finance Commission at an interval of five years or earlier.
- The 15th Finance Commission was constituted by the President of India in November 2017, under the chairmanship of NK Singh. Its recommendations will cover a period of five years from the year 2021-22 to 2025-26.
Eleventh Schedule
- The Eleventh Schedule, added by the 73rd Amendment Act in 1992, contains provisions that outline the powers, authority, and responsibilities of Panchayats (rural local governments).
- It places as many as 29 functions within the purview of the Panchayati Raj bodies including agricultural extension, land improvement, implementation of land reforms etc.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Government Seals Multiple Madrasas
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand government has sealed 52 madrasas across the state. Muslim organizations have criticized the crackdown on minority religious institutions.
Key Points
- Madrasas Sealed Across the State:
- Government officials cited illegal and unauthorized construction as the primary reason.
- Some institutions were found unregistered and operating without recognition.
- The identification drive against minority institutions began in January 2024 following orders from the State Chief Minister.
- The CM reiterated the commitment to act against illegal construction and encroachment.
- Statewide Crackdown on Illegal Encroachments:
- In 2023, the government launched a statewide drive against illegal encroachments on forest land.
- Over 450 Mazars (minority religious structures) and 50 temples were demolished across Uttarakhand as part of the campaign.
Madrasas
- Madrasa is an Arabic word for an educational institution.
- Initially, mosques served as educational institutions in early Islam, but by the 10th century, madrasas evolved into distinct entities for both religious and secular learning in the Islamic world.
- The earliest madrasas were found in Khorasan and Transoxania (modern eastern and northern Iran, central Asia, and Afghanistan), with larger institutions providing housing for students, especially those from poor backgrounds.
- Recognized madrasas are under state boards; unrecognized ones follow curricula from major seminaries like Darul Uloom Nadwatul Ulama and Darul Uloom Deoband.
Encroachment
- It is the unauthorised use or occupation of someone else’s property. This can occur on abandoned or unused spaces if the legal owner is not actively involved in its upkeep. It is important for property owners to be aware of the legal steps to take and their rights in such cases.
- Urban encroachment refers to the unauthorised occupation or use of land or property within urban areas.
- This could include illegal construction, squatting, or any other form of occupation without proper permission or legal rights.
- Land encroachment, as defined by Section 441 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), 1860, is the act of unlawfully entering someone else’s property without permission to commit an offence, threaten possession of the property, or stay on the land uninvited.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Solapur Handloom Industry
Why in News?
Weavers have been urging the Maharashtra government to recognize their ‘Solapuri silk saree’ as a traditional textile under the 2023 textile policy.
Key Points
- Inclusion of Solapuri Silk Saree:
- This inclusion would grant access to old-age pension schemes, employment as master trainers in government handloom institutes, and an annual festival allowance of Rs 15,000 for female weavers and Rs 10,000 for male weavers.
- They argue that other textiles, like Himru, are included despite limited production in the state, while their sarees remain unrecognized.
- Challenges in Government Schemes and Weaver ID Cards:
- Weaver’s Pehchan Card is essential to avail benefits under the National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP), including MUDRA loans and workshed support.
- Many applicants face delays in receiving their cards, with some waiting for years before gaining access to central government benefits.
- Weavers struggle to secure loans under the Weavers Mudra Scheme, as banks often reject applications due to high default rates.
- The Pehchan Card also offers financial aid for weavers’ children, covering Rs 2 lakh annually for textile education and a monthly stipend of Rs 5,000.
- Financial Struggles and Seasonal Market Demand:
- Each handloom produces one to two sarees per month, which sell for Rs 12,000 to Rs 15,000 during festive seasons but see minimal demand in off-seasons.
- The community relies on markets in Pune, but buyers frequently reject or undervalue their products, reducing profitability.
- Collective Workshed and Yarn Bank:
- They demand a collective workshed, where multiple handlooms can operate in a shared facility, improving efficiency and working conditions.
- A yarn bank with a 15% subsidy under the Raw Material Supply Scheme (RMSS) is also sought, as middlemen currently exploit subsidies, leaving weavers without direct benefits.
- Lack of Effective Government Marketing Support:
- The government proposed Urban Haat, a dedicated marketplace for handloom products, but its feasibility is questioned due to low financial aid and high infrastructure costs.
- Weavers seek better marketing opportunities and government support to expand their reach and ensure fair pricing for their sarees.
- Future Concerns:
- Many young generations are reluctant to enter weaving, citing unstable income and lack of social security.
- Weavers express concerns over financial insecurity, with no government assistance during medical emergencies or crises.
- They urge policy improvements to protect traditional handloom artisans and sustain their craft for future generations.
National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP)
- Objective:
- NHDP aims to promote the sustainable development of handloom weavers, both within and outside identified handloom clusters, by transforming them into self-managed and competitive socio-economic units.
- Implementation Period:
- The scheme is designed for the 2021-22 to 2025-26 financial years.
- Approach:
- It follows a need-based strategy for the integrated and holistic development of handlooms and the welfare of handloom weavers.
- Target Beneficiaries:
- The scheme benefits individual weavers, cooperatives, and Self-Help Groups (SHGs), both within and outside the cooperative system.
- Key Support Areas:
- Raw material assistance for production sustainability.
- Design inputs to enhance product quality and market appeal.
- Technology upgradation for improved efficiency and competitiveness.
- Marketing support through exhibitions and trade events.
- Permanent infrastructure creation, including Urban Haats and marketing complexes, to provide direct market access to weavers.
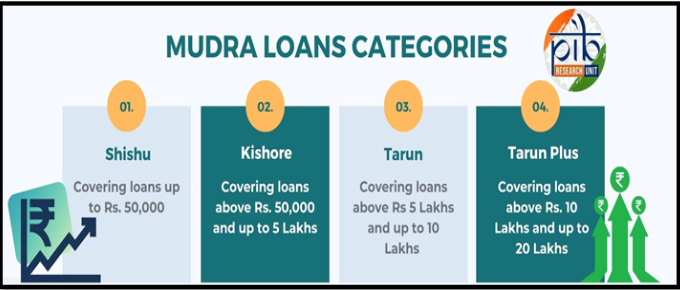
PM MUDRA Yojana
- The aim of PMMY is to facilitate easy collateral-free micro credit to non-corporate, non-farm small and micro entrepreneurs for income generating activities.
- MUDRA (Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency) was launched in 2015, to provide refinance support to financial institutions like banks, micro-finance institutions (MFIs), and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs).
- It provides refinance, credit guarantee, and development support to financial institutions, helping them extend financial services to micro-enterprises in manufacturing, trading, and services.


Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
First Mobile Tower at Remote CRPF Base
Why in News?
The first mobile phone tower was set up inside the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) camp in Tekulagudem village, a remote area in the Naxal-affected Sukma district of Chhattisgarh.
- The initiative aligns with the Union Government’s goal to eliminate Left Wing Extremism (LWE) by March 2026.
Key Points
- BSNL Mobile Tower Operationalized:
- A Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) mobile tower is the first mobile connectivity facility in the area, benefiting both villagers and security personnel.
- The tower will serve Tekulagudem and nearby hamlets, including Timmapuram, Jonaguda, and Puvarti.
- The village is in Sukma district, which has been heavily affected by Naxal violence and shares a border with Bijapur in the Bastar region.
- Special Initiative for Villagers:
- BSNL officials traveled from Sukma headquarters and Raipur to operationalize the tower.
- A special camp was organized to distribute and activate SIM cards for the local population.
Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF)
- Inception and Evolution:
- The CRPF was initially established as the Crown Representatives Police in 1939 in response to political turmoil and unrest within the princely states.
- The force was renamed the Central Reserve Police Force in 1949.
- Sardar Vallabh Bhai Patel, the then Home Minister, envisioned a multifaceted role for the CRPF, aligning its functions with the evolving needs of a newly independent nation.
- Specialised Units:
- The CRPF has several specialised units, including the Rapid Action Force (RAF), Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (CoBRA), VIP Security Wing, and Mahila Battalions.
- Achievements and Contributions:
- The force has thwarted attacks on important national landmarks, controlled militancy in Punjab and insurgency in Tripura, and made significant contributions to eradicating Naxalism.
- Honouring the Bravehearts:
- The CRPF has paid a heavy price, with 2,255 of its soldiers making the supreme sacrifice and being honoured with decorations, including the George Cross, Ashok Chakra, Kirti Chakra, Shaurya Chakra, etc.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
CAG and Finance Commission
Why in News?
A meeting was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh for consultation between Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG) and Sixteenth Finance Commission on public finance.
Key Points
- About the Meeting:
- It focused on three major areas: Union and State finances, local bodies and public sector enterprises.
- It provided a comprehensive framework for making fiscal management, audit, tax policy and public financial management of the Centre and the States more transparent and effective.
- Recommendations:
- Decline in State Tax Revenue (SOTR) : Need for strengthening the tax collection mechanism was emphasized.
- Standardisation of fiscal information : It was proposed to standardise accounting procedures to provide transparent and comparable financial data.
- The CAG stressed the need for further reforms in areas such as stamp duty, registration fee and state excise duty .
- Also recommended adopting modern technologies like QR codes and sensor-based systems.
- It was recommended that states with surplus revenue should create a Budget Stabilization Fund to avoid financial instability.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) reforms recommended strengthening the taxpayer verification process, integration of unregistered units and use of automated data collection and real-time information systems.
Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)
- Introduction:
- According to Article 148 of the Constitution , the CAG of India is the head of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department (IA-AD) .
- He is responsible for the safeguarding of public funds and overseeing the financial system at both the central and state levels.
- The CAG of India is governed by the Comptroller and Auditor General (Duties, Powers and Conditions of Service) Act, 1971, which was significantly amended in the years 1976, 1984 and 1987 .
- Appointment and Tenure:
- The CAG of India is appointed by the President of India by a warrant under his signature and seal .
- The CAG holds office for a term of six years or till the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CAG shall be removed from his office by the President only in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
- The CAG can resign from his office at any time by submitting his resignation to the President.
- After leaving the office, the CAG is not eligible for any other post under the Government of India or any State Government.
- Pay and Allowances:
- The salary of the CAG is determined by the Parliament, which is equal to the salary of a Supreme Court judge.
- The CAG's administrative expenses, including salary, allowances and pension, are charged on the Consolidated Fund of India , which is not subject to parliamentary vote.
- Duties and Powers: The CAG audits the accounts relating to expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India and State funds .
- It also audits the accounts of Government corporations , public sector undertakings and government-financed bodies.
- The CAG submits audit reports to the President , who lays them before Parliament. These reports are scrutinised by the Public Accounts Committee.
Finance Commission
- Constitutional Basis: It is a constitutional body established under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution .
- It is appointed by the President every five years or earlier as the President considers necessary.
- Composition: The Commission consists of a Chairman and four other members appointed by the President.
- The Chairman should be a person who has experience in public affairs .
- Functions and Duties : The primary function of the Finance Commission is to make recommendations to the President on various financial matters .
- Distribution of Taxes: It recommends the distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes . This includes allocation of shares among the States from tax proceeds.
- Grants-in-aid: The Bill suggests principles for providing grants-in-aid to States from the Consolidated Fund of India .
- This includes establishing the principles governing grants-in-aid to the states from the Consolidated Fund of India.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Swavalambini
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship ( MSDE ) in collaboration with NITI Aayog launched the women entrepreneurship programme Swavalambini at Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut .
Key Points
- About Swavalambini:
- Swavalambani It is a women entrepreneurship program aimed at empowering women by helping them develop an entrepreneurial mindset, providing necessary resources and guidance for business success.
- Program structure:
- A phase-wise entrepreneurship process is initiated comprising Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP), Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP), Faculty Development Programme (FDP ) and Financing .
- This will involve recognising and rewarding successful enterprises, which will inspire others and establish a clear framework for promoting women-led enterprises in India.
- Strengthen the culture of entrepreneurship in higher education institutions, making business creation a viable career path for women.
- Promote women-led enterprises as a key driver of India's economic transformation.
- Aligned with national policies:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 promotes skill integration, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-driven education.
- Swavalambanni works on this by ensuring financial and consultancy support for women entrepreneurs .
- It strengthens initiatives like Start-up India , Stand-up India , PM Mudra Yojana and Women Entrepreneurship Platform .
- Swavalambanni is in line with Union Budget 2025 , which launches a Rs 10,000 crore start-up fund and 100% tax exemption on start-up dividends for the first five years , providing crucial financial support to emerging women-led enterprises.
Women Entrepreneurship Scenario in India
- Total MSMEs in India: Over 63 million, Women-owned MSMEs 20% (12.39 million).
- Employment Contribution: Women-led MSMEs provide employment to 22-27 million people.
- India Ranking in Women Entrepreneurship: India is currently ranked 57th out of 65 countries in the Mastercard Index on Women Entrepreneurship (MIWE) 2021 .
- India ranks 70th among 77 nations in the Global Female Entrepreneurship Index (FEI) as estimated by the Global Entrepreneurship and Development Institute.
- Top states with highest participation of women-led MSMEs: West Bengal (23.42%), Tamil Nadu (10.37%), Telangana (7.85%), Karnataka (7.56%), and Andhra Pradesh (6.76%).


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Multi-Modal Logistics Park in Varanasi
Why in News?
An Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between National Highways Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) and Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) to develop a state-of-the-art Multi-Modal Logistics Park (MMLP) at Varanasi
Key Points
- About MMLP:
- Objective:
- It aims to strengthen the supply chain by seamless freight movement through road, rail and water routes, reducing costs and increasing business efficiency.
- Significance and Impact:
- Spread over 150 acres, the park will have direct connectivity to NH7 and Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) , making freight transportation smooth and affordable.
- Connectivity with National Waterway-1 (NW-1) will facilitate cargo transportation through waterways , thereby reducing transportation costs .
- The construction of this logistics park will attract significant investments , which will give a boost to the economy of Uttar Pradesh.
- Traders, industries and MSMEs will benefit at local and national level , leading to increased production and exports .
- This project will generate direct and indirect employment opportunities at the local level .
- The logistics sector will be modernized , which will pave the way for developing such centres in other cities in the future.
- It will act as a model under the Gati Shakti scheme and multi-modal connectivity, promoting such projects in other states as well.
- Objective:
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI)
- IWAI is a statutory body under the Ministry of Shipping .
- It develops and maintains inland water transport infrastructure on national waterways through grants received from the Ministry of Shipping.
- The Authority has its head office at Noida (Uttar Pradesh) with regional offices at Patna, Kolkata, Guwahati and Kochi and sub-offices at Prayagraj (formerly Allahabad), Varanasi, Bhagalpur, Rakka and Kollam.
Prime Minister's Gati Shakti scheme
- Objective: To ensure integrated planning and implementation of basic infrastructure projects over the next four years with a focus on accelerating work on the ground, reducing costs and creating employment.
- The Gati Shakti plan subsumes the Rs 110 lakh crore ' National Infrastructure Pipeline ' launched in the year 2019 .
- Apart from cutting logistics costs, the scheme aims to increase cargo handling capacity and reduce turnaround time at ports to boost trade.
- It also aims to build 11 industrial corridors and two new defence corridors (one in Tamil Nadu and the other in Uttar Pradesh). Under this, 4G connectivity will be expanded to all villages.
- Also, a plan is being made to add 17,000 km of capacity to the gas pipeline network.
- Integrated Approach: It entails bringing together 16 ministries dealing with infrastructure.
- Gati Shakti Digital Platform: It involves creation of an umbrella platform through which basic infrastructure projects can be created and implemented effectively through real-time coordination between various ministries/departments.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
The Rise App
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has implemented the RISE app (Rapid Immunization Skill Enhancement - RISE) to ensure regular vaccination of children.
Key Points
- About RISE App:
- RISE (Responsive Immunization Support for Everyone) is a digital training and monitoring platform developed for effective implementation of immunization programs .
- The app provides real-time updates to help health workers monitor vaccination schedules, safety protocols, cold chain management , and adverse effects following immunization .
- RISE App plays a vital role in strengthening Mission Indradhanush of the Government of India .
- This digital platform has been developed for staff nurses, auxiliary nurse midwives ( ANM ) and health workers to enable them to accurately monitor and effectively manage routine immunization of children.
- Aim:
- The initiative aims to increase vaccination coverage , identify hesitant families and ensure proper vaccination .
- This app will further strengthen the safety and effectiveness of vaccination by replacing traditional training methods with a digital learning system .
- The initiative aims to increase vaccination coverage , identify hesitant families and ensure proper vaccination .
- Training and Implementation Process:
- The process of training health workers is being carried out in three phases:
- District level officers have been successfully trained in all the 75 districts of the state.
- Training of block-level officers is currently underway to ensure effective implementation of the programme at the ground level .
- After full implementation of the plan, around 52,175 vaccination personnel will be equipped with digital devices , which will increase their efficiency and data management efficiency.
- The process of training health workers is being carried out in three phases:
Mission Indradhanush
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India launched 'Mission Indradhanush' on 25 December 2014.
- Mission Indradhanush is a booster vaccination programme, which was launched in 201 districts with low vaccination coverage.
- It represents 7 vaccines against 7 diseases covered in the Universal Immunization Programme.
- These diseases are Tuberculosis, Poliomyelitis, Hepatitis B, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus and Measles.
- Apart from this, after inclusion of vaccines against Measles Rubella, Rotavirus, Haemophilus Influenzae Type-B and Polio, the number of these vaccines has increased to 12.
- In some selected states and districts, vaccines are also given against Japanese Encephalitis and Pneumococcus.
- To accelerate full immunization coverage, India has launched an ambitious plan – Intensified Mission Indradhanush .






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan