Important Facts For Prelims
Empowering Minority Communities
- 03 Feb 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Ministry of Minority Affairs (MoMA) shed light on India’s ongoing efforts to empower minority communities.
What are the Highlighted Initiatives Related to Minority Communities?
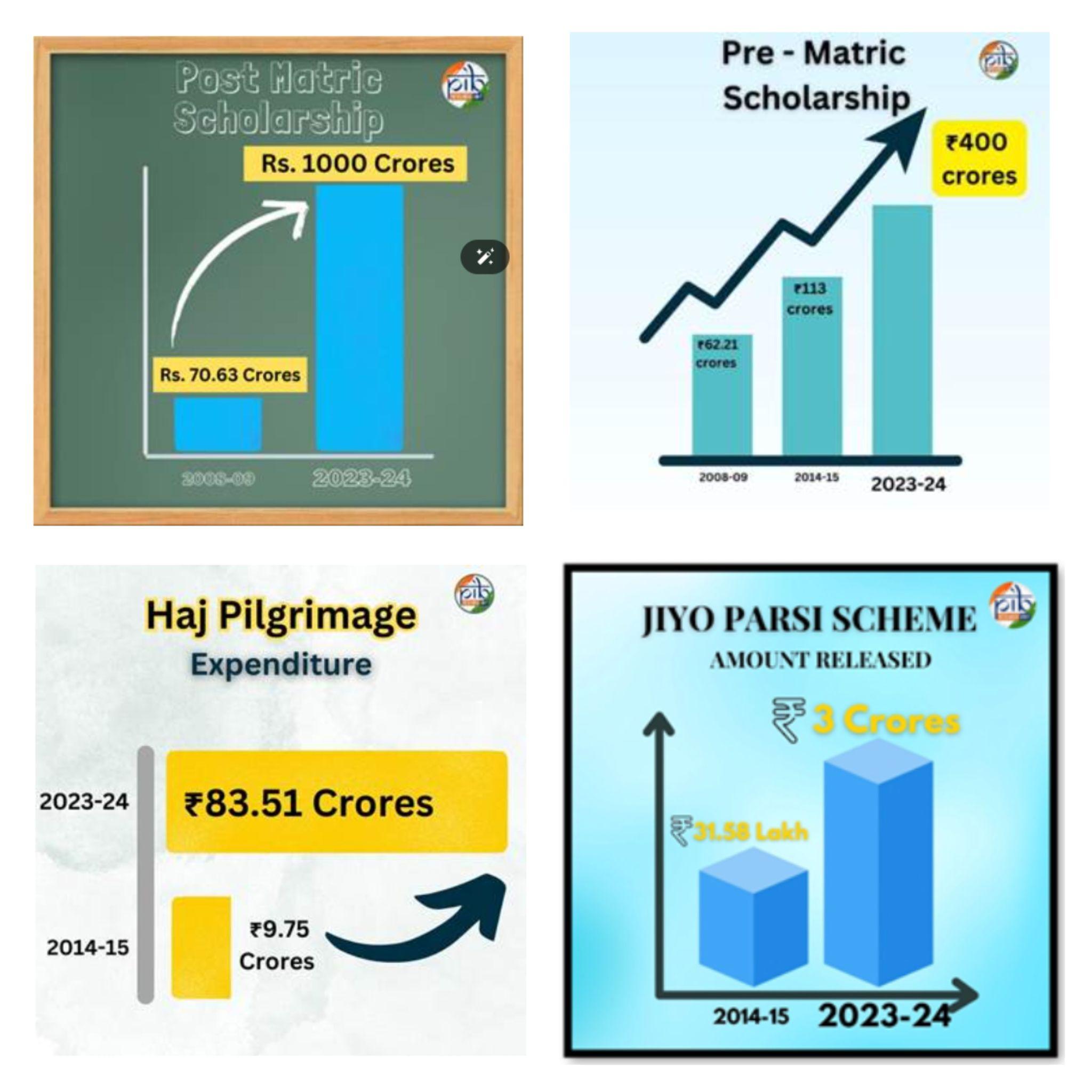
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme (2007): Provides scholarships to meritorious students from economically weaker sections of minority communities to enhance higher education and employability.
- Allocation increased from Rs 70.63 crores in 2008-09 to Rs 1000 crores in 2023-24.
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme (2008): Encourages parents to send children from minority communities to school and lightens financial burdens for school education.
- Allocation increased from Rs 62.21 crores in 2008-09 to Rs 400 crores in 2023-24.
- National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC) (1994): Provides concessional credit for self-employment and income-generating activities for the socio-economic development of backward sections of minorities.
- Allocation rose from Rs 2 crores in 2014-15 to Rs 3 crores in 2023-24.
- Haj Pilgrimage Support (2016): Facilitates Haj pilgrimage (to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia) for low-income individuals.
- Expenditure increased from Rs 9.75 crores in 2014-15 to Rs 83.51 crores in 2023-24.
- Jiyo Parsi Scheme (2013): Aims to reverse the declining Parsi population through scientific interventions.
- As of March 2024, the scheme has enabled the birth of over 400 Parsi children since its inception, with Rs 3 crores allocated in 2023-24.
- Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS): The PM VIKAS combining 5 existing schemes of MoMA like USTTAD (Upgrading the Skills & Training in Traditional Arts/Crafts for Development), Nai Manzil, Nai Roshni, and Hamari Dharohar to empower minorities through skill development and cultural preservation.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK): The PMJVK focuses on developing community infrastructure in minority-concentrated areas, covering health, skill development, women's projects, water supply, sanitation, and sports.
India's Minority Communities
- Minority Communities: The Central Government determines minority status under the National Commission for Minorities Act (NCMA), 1992, officially recognizing Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, Jains (added in 2014), and Zoroastrians (Parsis) as minority communities.
- Together, they constitute around 19.3% of India’s total population (Census 2011).
- While most states follow the central list, some, like Maharashtra, may have their own (e.g., Jews are a notified minority in Maharashtra).
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 29 protects minorities' rights to preserve their distinct language, script, and culture, and prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, or language.
- Article 30 grants minorities the right to establish and manage educational institutions.
- Institutions to Protect Minority Rights:
- Ministry of Minority Affairs: Established in 2006, carved out from the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, coordinates programs for the socio-economic development of minority communities in India.
- National Commission for Minorities (NCM): Created under the NCMA 1992, the NCM safeguards the interests of minority groups in line with the Constitution and laws enacted by the Parliament.
- Waqf Act, 1995: Governs the management and development of Waqf properties.
- The Central Waqf Council (CWC) implements schemes for the modernization and digitalization of Waqf properties, supporting state-level Waqf boards.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In India, if a religious sect/community is given the status of a national minority, what special advantages it is entitled to? (2011)
- It can establish and administer exclusive educational institutions.
- The President of India automatically nominates a representative of the community to Lok Sabha.
- It can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- At present Muslims, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Christians, and Parsis (Zoroastrians) are notified as minority religious communities by GoI. There are certain special advantages that these communities are entitled by the Constitution of India as well as various other legislative and administrative measures.
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution upholds the right of religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice. Hence, statement 1 is correct. There is no provision for the President of India to automatically nominate a member of a minority religious community to the Lok Sabha. This provision was earlier available for members of Anglo-Indian community under Article 331 of the Constitution. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Religious minorities can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme. The programme was launched in 2005 to ensure the welfare of minorities in the fields of education, skill development, employment and prevention of communal conflicts. Hence, statement 3 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.