West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Surface Ozone Pollution
Why in News?
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur study reveals that surface ozone pollution is severely affecting India's major food crops, especially in the Indo-Gangetic Plain and central India.
Key Points
- About Surface Ozone Pollution:
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- Unlike the ozone layer in the stratosphere, which protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation, Surface ozone is a harmful pollutant that poses significant health risks and environmental damage.
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- About the study:
- Surface ozone pollution is damaging major food crops such as wheat, rice, and maize.
- The study argues that rising ozone pollution jeopardizes India's progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 1 (No Poverty) and Goal 2 (Zero Hunger) by 2030.
- Declining crop yields could directly affect livelihoods and food access, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Key Findings of the Study:
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Ozone acts as a strong oxidant that damages plant tissues, causes foliar injuries, and leads to significant drops in crop productivity.
- Using data from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase-6 (CMIP6), the study assessed both historical and future trends of ozone-induced damage.
- Without adequate mitigation, wheat yields may decline by up to 20%, while rice and maize could see losses of around 7%.
- In the worst-case scenarios, ozone exposure in key agricultural zones could exceed safe limits by six times.
- The research warns that ozone-related yield losses could undermine India’s ability to ensure food security at home and impact food grain exports to Asian and African nations.
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Gaps in Current Air Quality Initiatives:
- The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) largely focuses on urban air pollution, leaving agricultural regions underserved.
- The study highlights the need for targeted interventions to monitor and curb surface ozone pollution in farmlands.
- Call for Policy Action:
- The researchers advocate for urgent policy measures to reduce ozone emissions and protect crop health.
- Effective pollution control strategies in agricultural areas could boost food production and help meet both national and global food security goals.
Formation of Surface Level Ozone
- Surface-level ozone is a secondary pollutant, meaning it is not directly emitted but formed through chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- NOx (emitted by vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes) and VOCs (emitted from vehicles, petrol pumps, solvents, and waste burning).
- These reactions occur in the presence of sunlight, making ozone formation more significant during sunny days and warmer seasons.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- About:
- The NCAP aims to systematically address air pollution by involving all stakeholders and ensuring necessary action.
- Under NCAP, 131 cities have been identified for implementation of city specific action plans.
- Objective:
- This is the first attempt in the country to develop a national framework for air quality management with the goal of time-bound reduction .
- It aims to reduce the concentration of coarse (PM10) and fine particles (PM2.5) by at least 20% over the next five years (base year for comparison – 2017).


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Approval for Zirakpur Bypass
Why in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved the construction of a six-lane Zirakpur bypass at a capital cost of Rs 1,878.31 crore.
- The project aims to ease congestion in cities like Zirakpur and Panchkula by redirecting traffic bound for Himachal Pradesh.
Key Points
- Route and Specifications:
- The six-lane Zirakpur bypass will start from the Zirakpur–Patiala junction on NH-7 and end at the Zirakpur–Parwanoo junction on NH-5.
- The bypass will cover a total length of 19.2 km, passing through Punjab and Haryana.
- The project will be developed using the Hybrid Annuity Mode (HAM) as part of the National Highway (Original) [NH(O)] programme.
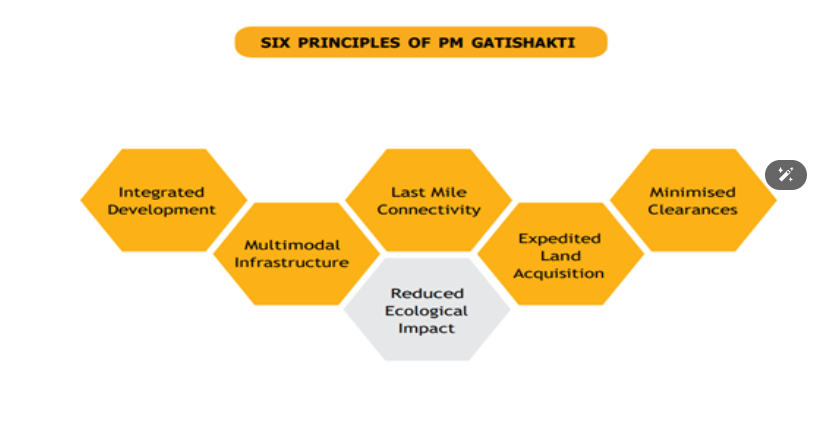
- Strategic Importance under PM GatiShakti:
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways described the project as a key step in building integrated transport infrastructure.
- It aligns with the objectives of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, which seeks to synchronise infrastructure planning and boost multi-modal connectivity.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, launched in October 2021 is a transformative Rs. 100 lakh crore initiative aimed at revolutionising India’s infrastructure over the next five years.
- It has been developed as a Digital Master Planning tool by BISAG-N (Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics).
- It has been prepared in a dynamic Geographic Information System (GIS) platform wherein data on specific action plans of all the Ministries/Departments have been incorporated within a comprehensive database.
- The plan seeks to accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by breaking down inter-ministerial obstacles.
- The vision of PM GatiShakti is to create a world-class infrastructure that improves the ease of living, boosts economic growth and makes Indian businesses more competitive.
Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM)
- It is a mix of EPC and BOT-Annuity models. As per the design, the government will contribute 40% of the project cost in the first five years through annual payments (annuity).
- The remaining payment will be made on the basis of the assets created and the performance of the developer.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Mining Activities Prohibited in Aravalli
Why in News?
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has issued a show-cause notice to the Haryana Government and the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change over alleged mining on protected Aravalli forest land.
- It also directed the state to halt all mining and stone-crushing activities until 7th August 2025.
Key Points
- About the Issue:
- It was alleged that the Haryana Government auctioned 25% of 506.33 acres of notified protected forest land to stone crushing units.
- This land had been declared a protected forest as part of compensatory afforestation for the Great Nicobar Island project.
- The case highlights potential violations of the Forest (Conservation) Act 1980 and questions the legality of the auction process.
- Petitioners and environmentalists pointed out that mining and stone crushing have severely impacted the local water table, flora, and fauna.
- They also stressed that while the country is losing dense forests in Great Nicobar, the ‘Nicobar swap’ land meant to restore the Aravallis is being sabotaged by illegal mining.
- About Aravallis:
- The Aravalli Range extends from Gujarat to Delhi through Rajasthan, 692 km in length and varies between 10 to 120 km in width.
- The range acts as a natural green wall, with 80% located in Rajasthan and 20% in Haryana, Delhi, and Gujarat.
- The Aravalli mountains are divided into two main ranges – the Sambhar Sirohi Range and the Sambhar Khetri Range in Rajasthan, where their extension is about 560 km.
- It serves as an ecotone between the Thar Desert and the Gangetic Plain.
- Ecotones are areas where two or more ecosystems, biological communities, or biotic regions meet.
- Gurusikhar (Rajasthan), the highest peak in the range, reaches an elevation of 1,722 meters.
- The Aravalli Range extends from Gujarat to Delhi through Rajasthan, 692 km in length and varies between 10 to 120 km in width.
- It was alleged that the Haryana Government auctioned 25% of 506.33 acres of notified protected forest land to stone crushing units.
Great Nicobar Island Project
- The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) project, launched in 2021, is a mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- It involves developing a trans-shipment port, an international airport, township development, and a 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant on the island.
- The project was implemented after a report by NITI Aayog which identified the potential to utilise the advantageous position of the island, which is approximately equidistant from Colombo in Sri Lanka to the southwest and Port Klang (Malaysia) and Singapore to the southeast.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Acting Chief Justice of J&K Appointed
Why in News?
On 9th April 2025, the Law Ministry announced that Justice Sanjeev Kumar has taken charge as the acting Chief Justice of the Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh High Court.
Key Points
- Appointment of Acting Chief Justice:
- Article 223 of the Constitution of India deals with the appointment of an acting Chief Justice.
- According to this, when the office of the Chief Justice of a High Court is vacant or when such a Chief Justice, on account of absence or otherwise, is unable to perform the duties of his office, the duties of the office shall be performed by such person. Other judges of the Court may be appointed by the President for this purpose.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
India's First Sickle Cell Hub
Why in News?
Recently, India's first sickle cell wellness hub was established at the Sickle Cell Excellence Center located at Bal Chikitsalaya in Udaipur district of Rajasthan. It was inaugurated by the Tribal Minister of Rajasthan .
Key Points
- About Wellness Hub:
- This hub is the country's first digital active centre , which provides facilities ranging from screening to consultation for sickle cell patients.
- Its main objective is to ensure prevention, timely detection and effective treatment of serious disease like sickle cell which is widely spread in tribal communities .
- This center will provide screening, counselling, and OPD (Outpatient Department) services to patients at one place through digital medium , so that even remote areas can be connected to health services.
- This initiative will act as a model system in the field of health, through joint efforts of the State and Central Governments and collaboration with social organizations.
Sickle cell disease (SCD)
- Introduction:
- SCD is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. The disease involves abnormalities in hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen. In SCD, the red blood cells become stiff and sticky and look like a C-shaped agricultural tool called a "sickle."
- Symptoms:
- The symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary, but some common symptoms include:
- Chronic anemia: It causes fatigue, weakness and paleness in the body.
- Acute pain (also known as sickle cell crisis): This can cause sudden, unbearable pain in the bones, chest, back, arms, and legs.
- Delay in puberty and physical development.
- The symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary, but some common symptoms include:
- Treatment:
- Blood transfusions: These can help relieve anemia and reduce the risk of acute pain.
- Hydroxyurea: This medication can help reduce the frequency of pain episodes and control long-term complications of the disease.
- It can also be treated by bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP First Bio-CNG Plant
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh's first and the country's second waste-to-CNG plant is being set up in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh .
Key Points
- About the Plant:
- This plant will produce bio-fuel (Bio-CNG) from straw, poultry litter, cow dung and wet waste .
- It will produce 21.5 tonnes of bio-CNG , 200 tonnes of organic manure and 30 metric tonnes of briquettes per day.
- It will be operated on the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model .
- To supply biofuel, a pipeline will be laid in the area by Adani Gas Limited .
- This will result in annual savings of about Rs 5 crore on waste disposal .
- About one-third of the city's waste will be used in this plant.
- Objective:
- Streamlining waste management.
- Promoting renewable and clean energy sources.
- Reducing environmental pollution (especially caused by stubble burning).
- Making city gas supply accessible and affordable.
Bio-CNG
- Bio-CNG , also known as 'Biomethane', is a renewable and clean burning transportation fuel produced through the conversion of biogas to natural gas quality.
- It is essentially purified biogas, made from the following organic waste materials:
- Agricultural waste: crop residues, straw, manure
- Food waste: spoiled food, leftovers
- Sewage sludge: Solid waste from wastewater treatment plants


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
15th Hockey Men's National Championship 2025
Why in News?
The 15th Men's National Championship 2025 is going to be held from 4 to 15 April at the Major Dhyan Chand Hockey Stadium in Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh .
Key Points
- About the Championship:
- According to Hockey India, the tournament will follow the same division-based format that was followed in the Senior Women's National Championship.
- The competition will include promotion and relegation competitions , with a total of 30 teams participating and divided into three divisions – Division A, Division B and Division C.
- Division A is the highest level of the competition, where teams will compete for the championship title . Division B teams will play with the aim of gaining promotion to Division A in the next season, while Division C teams will fight to secure a place in Division B in the upcoming edition.
Major Dhyan Chand
- Major Dhyan Chand was a field hockey player who played international hockey from the year 1926 to 1949 .
- He was a three-time Olympic gold medalist , winning gold in the 1928, 1932, and 1936 Olympic editions.
- His exceptional skills in the game earned him the title of ‘Hockey Wizard’.
- Dhyan Chand, along with his brother Roop Singh, contributed significantly to India's tally of 35 goals, leading to them being known as the 'Hockey Twins' .
- In the year 1934, Dhyan Chand was honoured with the captaincy of the Indian team .
- Major Dhyan Chand retired from the Army as a Major in the year 1956 and was awarded the Padma Bhushan.
- National Sports Day is celebrated every year on 29 August on the birth anniversary of Major Dhyan Chand to honour his contribution and promote sports culture .


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
First in Digital Transactions and DBT
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh has secured first place in the country in terms of digital transactions .
Key Points
- About the issue:
- Under the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme, the state government has transferred Rs 1,11,637 crore directly into the accounts of 9.08 crore beneficiaries through 207 schemes of 11 departments.
- This has not only brought transparency in the system but has also resulted in saving of Rs 10,000 crore by eliminating middlemen .
- Uttar Pradesh has now become the second largest economic contributor to the country with a 9.2% share in the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- While the country's GDP growth rate was 9.6% in the year 2023-24, UP's growth rate was 11.6%.
- According to the NITI Aayog report, Uttar Pradesh has been declared a ' front runner' in terms of 'fiscal position'.
- The role of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) was also important in this remarkable growth . Easy access to digital banking , availability of internet in villages and financial awareness further accelerated this progress.
- Under the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme, the state government has transferred Rs 1,11,637 crore directly into the accounts of 9.08 crore beneficiaries through 207 schemes of 11 departments.
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme
- Objective : The scheme is designed to aid faster flow of information and funds to the beneficiaries and to reduce fraud in the distribution system.
- Implementation : It was launched by the Government of India on January 1, 2013 as a mission to reform the government delivery system.
- The old version of the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Accountant General's Office i.e. 'Central Plan Scheme Monitoring System' was chosen as a platform for direct benefit transfer.
- Components of DBT: The primary components for implementation of Direct Benefit Scheme include beneficiary account verification system; integrated, stable payment and settlement platform with RBI , NPCI , public and private sector banks, Regional Rural Banks and Co-operative Banks (viz. Core Banking Solution of banks, settlement systems of RBI and Aadhaar Payment System of NPCI etc.).
- Aadhaar not mandatory: Aadhaar is not mandatory in DBT schemes. Since Aadhaar provides unique identification and is useful in targeting the intended beneficiaries, Aadhaar is preferred and beneficiaries are encouraged to have Aadhaar.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Birth Anniversary of Emperor Ashoka
Why in News?
On the birth anniversary Emperor Ashoka, the Bihar Governor and Chief Minister paid floral tributes at his statue at the Ashoka Convention Center.
Key Points
- About Ashoka:
- Every year the Ashtami of Chaitra month is celebrated as Ashok Jayanti. This time it was celebrated on 5th April 2025.
- Ashoka was the son of Maurya emperor Bindusara . He displayed extraordinary talent in administrative work .
- Impressed by his ability and knowledge, Bindusara appointed him the governor of Ujjain (Avanti) .
- Ashoka fought only one major war , the Kalinga War , which is mentioned in his 13th major rock edict .
- He fought this war in the eighth year of his reign (261 BC) . Ashoka was deeply saddened by the destruction and bloodshed in this war, due to which his personality changed from a warrior to a saint .
- As a result, he abandoned the policy of Digvijaya and adopted the policy of Dhammavijaya .
- Ashoka's Dhamma:
- After conversion to Buddhism, he remained a simple worshipper for about two and a half years . After that, he joined the Buddhist Sangha and became a Bhikshu Gatika (those who live in a monastery for a limited time are called Bhikshu Gatika).
- Ashoka never fully adopted the life of a Buddhist monk , but rather he always remained a worshipper .
- Definition of Dhamma:
- Ashoka has presented the definition of Dhamma in his second and seventh pillar inscriptions .
- According to him, Dhamma includes the following principles:
- No human being will be killed .
- There will be no destruction of property .
- Service and respect for parents and elders .
- Respect for elders and teachers .
- Good treatment of slaves and servants .
- Spend less and live a simple life .
- In the 13th major rock edict, Ashoka has described Dhammavijaya as the greatest victory. He was the first ruler in world history who adopted the Dhamma based imperialist policy through non-violence.
- For the propagation of Dhamma, Ashoka created a new administrative category which was called 'Dhammamahamatra' .
- In the fifth major inscription, Ashoka has mentioned that these officers were appointed in the 13th year of the reign (256 BC).
- Apart from this, other officers like Yukta , Rajukka , and Pradeshik were also given the responsibility of propagating the principles of Dhamma .






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan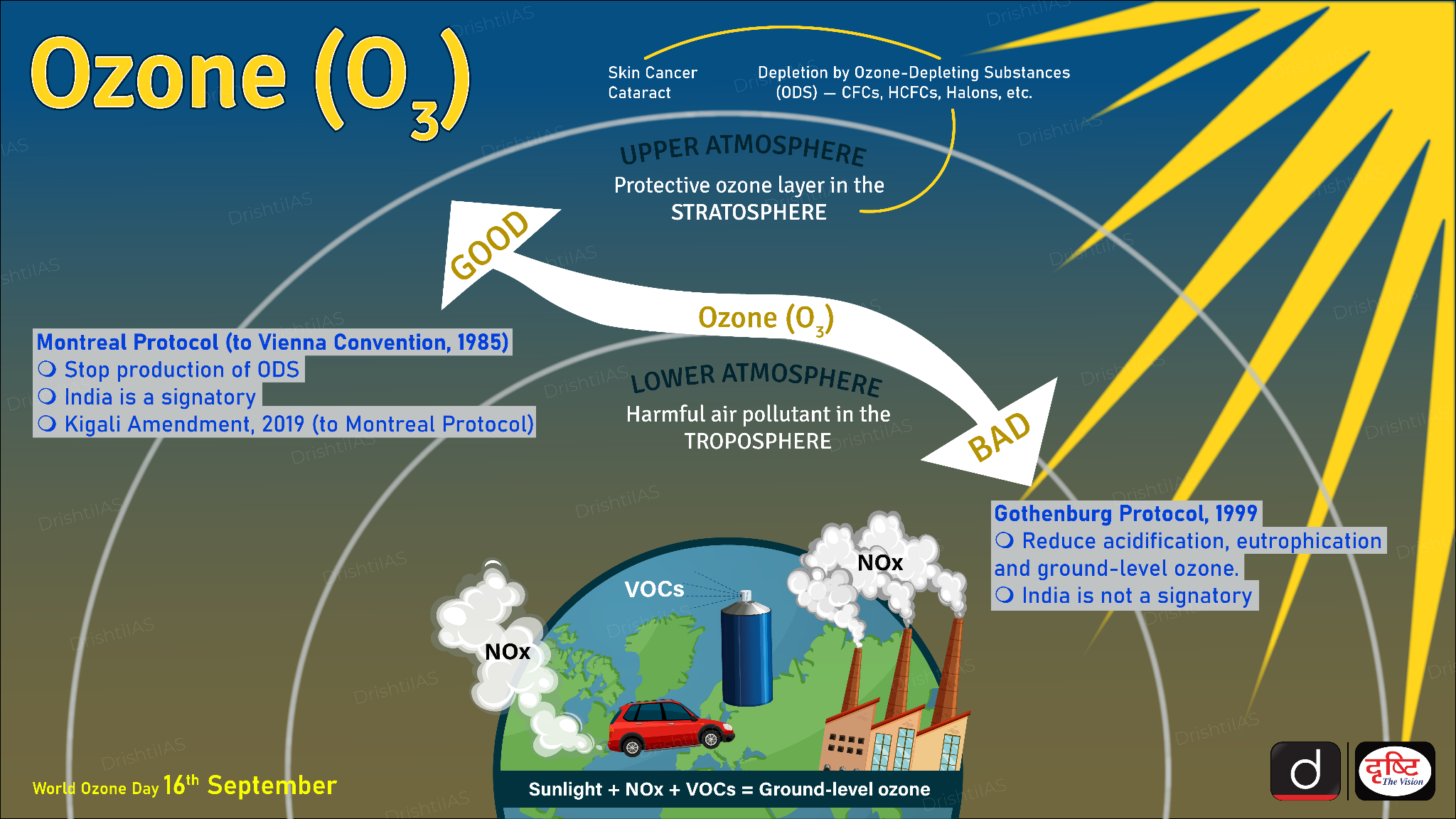
.png)


