Important Facts For Prelims
Ground Level Ozone Pollution
- 11 Dec 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) highlighted the steps being taken to control Ground Level Ozone Pollution(GLOP) in India.
What is Ground Level Ozone Pollution?
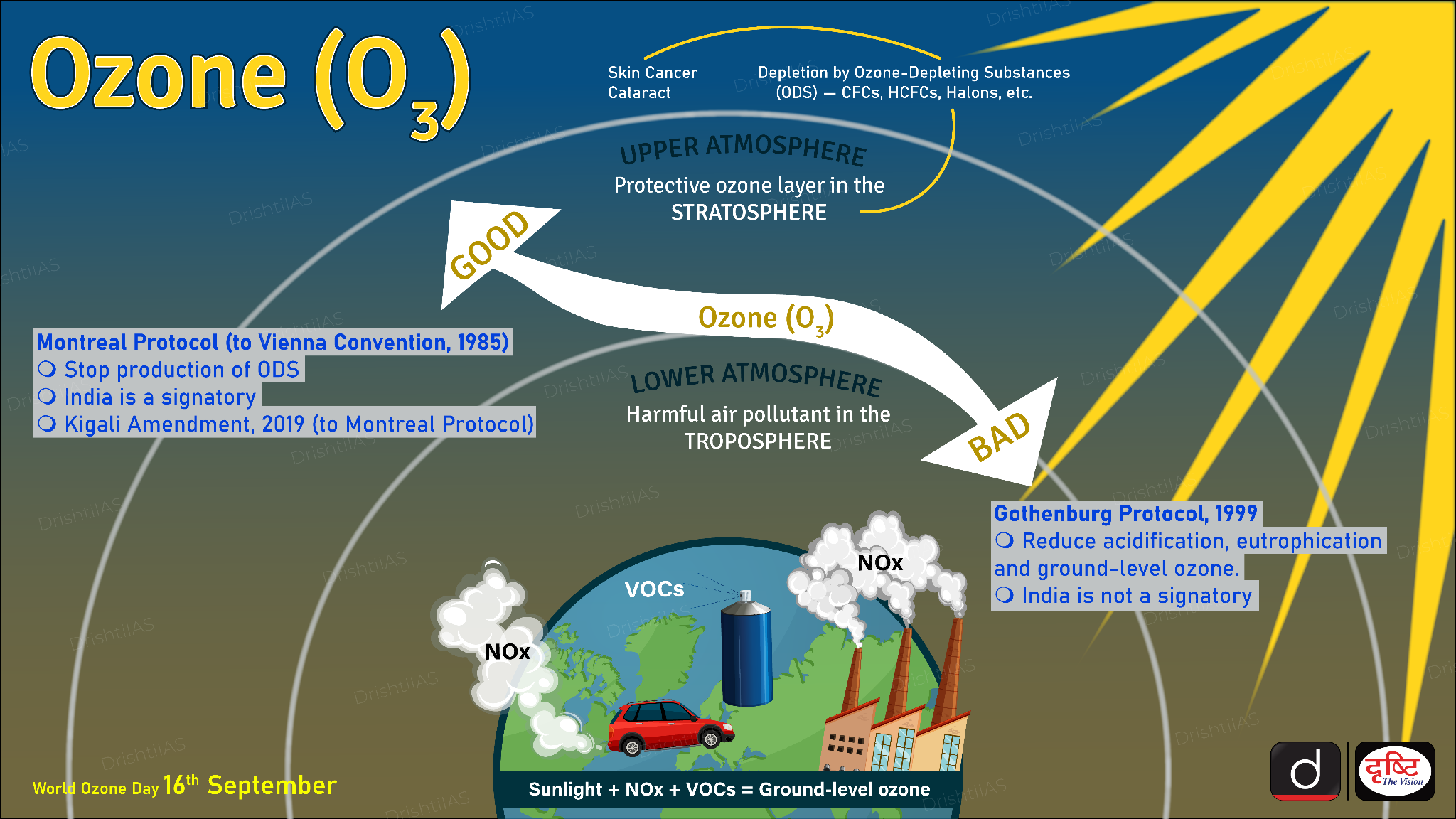
- Ground Level Ozone Pollution: Ground-level ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- Unlike the ozone layer in the stratosphere, which protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation, ground-level ozone is a harmful pollutant that poses significant health risks and environmental damage.
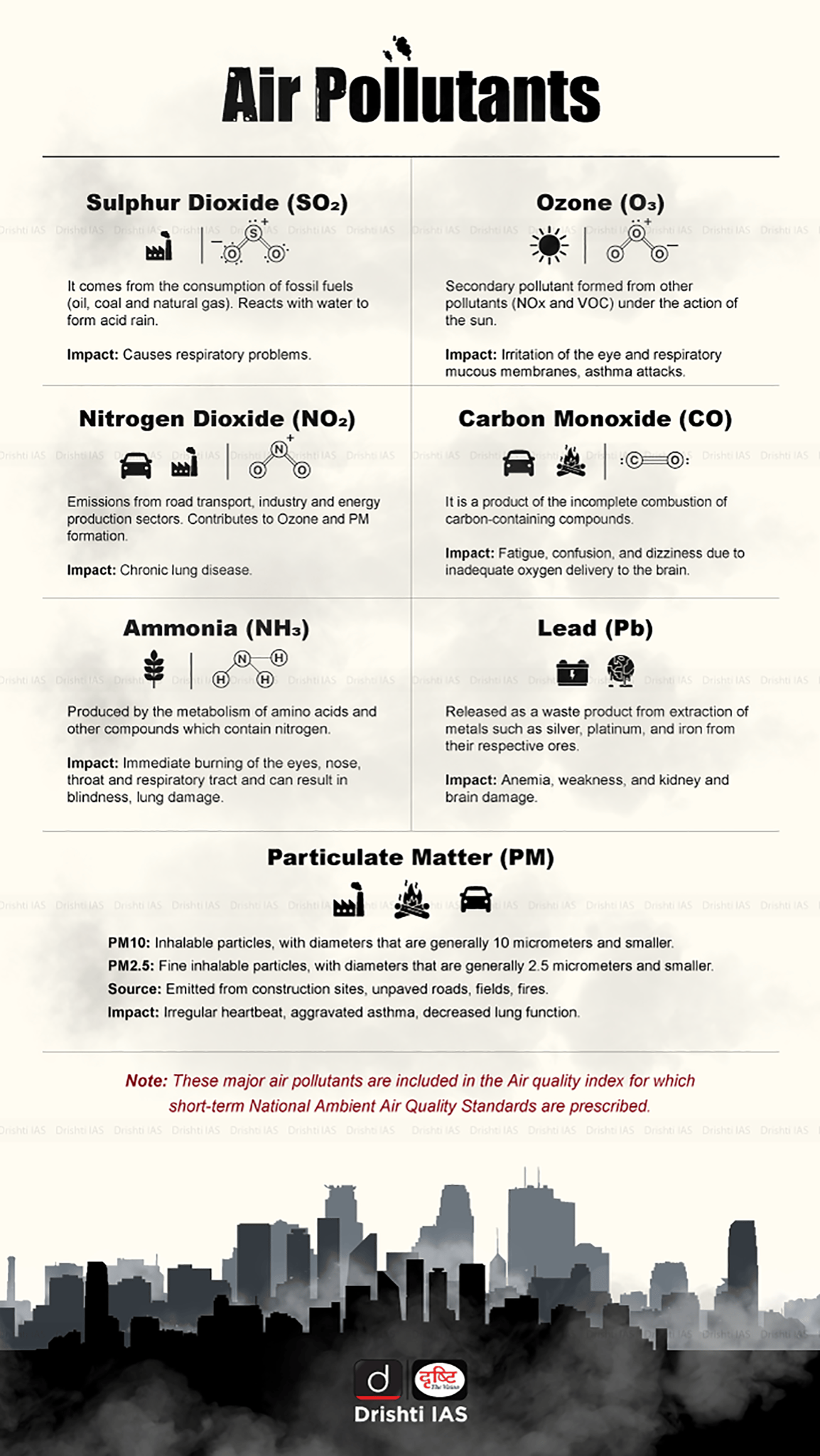
- Formation of Ground Level Ozone: Ground-level ozone is a secondary pollutant, meaning it is not directly emitted but formed through chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- NOx (emitted by vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes) and VOCs (emitted from vehicles, petrol pumps, solvents, and waste burning).
- These reactions occur in the presence of sunlight, making ozone formation more significant during sunny days and warmer seasons.
- Regulation: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in India has set National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for ozone, including an 8-hour average limit of 100 µg/m³ and a 1-hour limit of 180 µg/m³.
- Ground-level ozone is monitored under the National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP), managed by CPCB in collaboration with State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) and the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI).
- Impact:
- Health Effects: Ground-level ozone causes respiratory issues and worsen conditions like asthma and heart disease. Chronic exposure may reduce lung capacity, cause permanent damage.
- By 2050, ozone exposure could lead to over a million deaths in India if emissions are not controlled.
- Environmental Impact: Ozone damages crops, reducing agricultural productivity, and harms forests by inhibiting growth and photosynthesis.
- Measures to Control GLOP:
- Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS): MoEF&CC has notified the Ozone Depleting Substances (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000, to regulate the use, import, and export of ODSs in India.
- ODS, like Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), harm the ozone layer. They are stable in the troposphere but break down under UV light in the stratosphere, leading to ozone depletion.
- Cleaner Fuels: The government has encouraged the use of Compressed Natural Gas, Liquefied Petroleum Gas, and ethanol-blended fuels to reduce vehicular and industrial emissions.
- Vapour Recovery Systems (VRS): Installation of VRS at petrol pumps, particularly in Delhi-NCR, to minimize VOC emissions during refueling operations.
- PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM-E Drive)
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP
- Bharat Stage - VI(BS-VI) compliant vehicles
- Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS): MoEF&CC has notified the Ozone Depleting Substances (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000, to regulate the use, import, and export of ODSs in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)