Rising Digital Arrests | 30 Nov 2024
For Prelims: Digital Arrest, CBI, Enforcement Directorate, Narcotics Bureau, Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre, CBDC, Cryptocurrency, National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal, Virtual Private Network, Ponzi or Pyramid Schemes, National Cyber Crime Helpline, Aadhaar
For Mains: Economic cost of cyber fraud, threats and way forward.
Why in News?
Digital arrests are the newest form of cyber scam that has affected more than 92,000 Indians in 2024 in which money is extracted through online transfers under the guise of resolving tax or legal dues.
What are Key Facts About Digital Arrest?
- About: Digital arrest scams involve cybercriminals impersonating law enforcement officials or government agencies such as the State police, CBI, ED, and Narcotics Bureau defrauding gullible victims of their hard-earned money.
- Scammers call unsuspecting people, claiming a case has been filed against them and even use a fake police station to give credence to their allegations.
- Modus Operandi: Cybercriminals contact victims by phone or email, starting with audio calls and then video calls from places like airports, police stations, or courts.
- They use photos of police officers, lawyers, and judges as display pictures on their social media accounts to appear legitimate.
- They may also send fake arrest warrants, legal notices, or official-looking documents via email or messaging apps.
- Trapping Victims: The cybercriminals typically accuse victims of serious crimes such as money laundering, drug trafficking, or cybercrime.
- They may fabricate evidence to make their accusations seem credible.
- Vulnerability of People:
- Fear and Panic: Fear of arrest threats push victims to comply without rational thought.
- Lack of Knowledge: Unfamiliarity with law enforcement procedures makes it difficult for victims to distinguish legitimate claims from fraud.
- Social Stigma: Fear of social stigma and impact on family motivates victims to comply to avoid embarrassment.
- Manipulative Techniques: Use of AI voices, professional logos, and simulated video calls to appear credible and increase victim compliance.
- Isolation and Control: Scammers isolate victims by preventing them from seeking verification, making it easier to control them.
- Increased Target Vulnerability: Trusting, less tech-savvy, or stressed individuals are prime targets for easier deception.
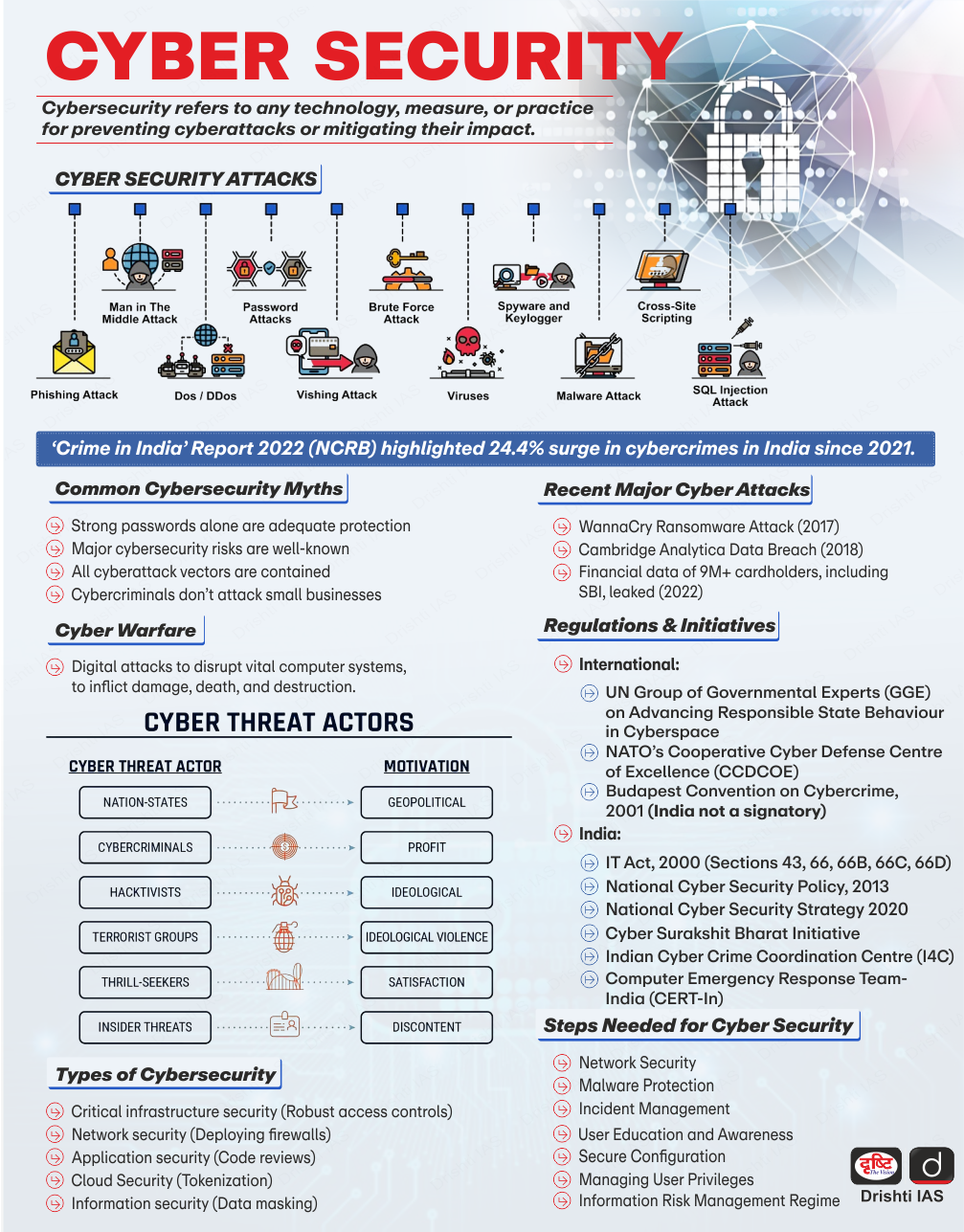
What is the Status of Cyber Scams in India?
- Overview: According to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), cyber scams in India have shown a significant rise in both frequency and financial impact.
- This alarming trend indicates a persistent and evolving threat landscape in India’s digital ecosystem.
- Complaints and Losses: The number of complaints increased significantly over the years, with 1,35,242 complaints in 2021, 5,14,741 in 2022, and 11,31,221 in 2023.
- The total monetary loss from cyber frauds has reached Rs 27,914 crore between 2021 and September 2024.
- Major Scams:
- Stock Trading Scams: It is the most significant source of loss with Rs 4,636 crore from 2,28,094 complaints.
- Under it, scammers offer unrealistic returns trading stocks, foreign currencies, or cryptocurrencies but victims end up being defrauded.
- Ponzi Scheme Scam: Caused Rs 3,216 crore in losses with 1,00,360 complaints.
- “Digital Arrest” Frauds: Accounted for Rs 1,616 crore in losses from 63,481 complaints.
- Stock Trading Scams: It is the most significant source of loss with Rs 4,636 crore from 2,28,094 complaints.
- New Money Siphoning off Tactics: Cybercriminals have adapted their strategies to siphon off money.
- Withdrawal Methods: Stolen money is often withdrawn through various channels, including cheques, CBDC, fintech cryptocurrencies, ATMs, merchant payments, and e-wallets.
- Mule Accounts: The I4C has identified and frozen around 4.5 lakh mule bank accounts, used primarily for laundering funds from cybercrime.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- About: I4C was launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs in 2020 to deal with all types of cyber crimes including cyber fraud in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- Objectives of I4C:
- To act as a nodal point to curb Cybercrime in the country.
- To strengthen the fight against Cybercrime committed against women and children.
- Facilitate easy filing Cybercrime related complaints and identifying Cybercrime trends and patterns.
- To act as an early warning system for Law Enforcement Agencies for proactive Cybercrime prevention and detection.
- Awareness creation among the public about preventing Cybercrime.
- Assist States/UTs in capacity building of Police Officers, Public Prosecutors and Judicial Officers in the area of cyber forensic, investigation, cyber hygiene, cyber-criminology, etc
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal:
- Under I4C, the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal is a citizen-centric initiative which will enable citizens to report cyber fraud online and all the complaints will be accessed by the concerned law enforcement agencies for taking action as per law.
What are Challenges in Addressing Cyber Scams?
- Anonymity and Privacy: Cybercriminals use tools such as virtual private networks (VPNs) and encrypted messaging apps to conceal their identity and location, complicating efforts to trace and arrest them.
- International Scope: Cyber scams often span multiple countries, making it difficult for local law enforcement to take action.
- A significant portion of scams originates from Southeast Asia and China.
- Rapidly Evolving Tactics: Phishing scams have advanced from simple emails to more sophisticated tactics, including social engineering, text messages, and voice calls, making fraud harder to detect.
- Advanced Malware: Cyber scams use advanced malware that can bypass antivirus programs and firewalls to steal data or gain unauthorized access.
- Regulatory Fragmentation: Different countries have different regulations, making it difficult to create cohesive international strategies for combating cybercrime.
- Also, countries lack comprehensive threat intelligence to identify emerging cyber scam trends and tactics without sharing data.
- Growing Digital Market: The growth of e-commerce and digital payment systems has led to an increase in scams such as fake online stores, card skimming, and fraudulent payment schemes.
Types of Cyber Scams
- Phishing Scams: Fraudsters send fake emails or messages that mimic trusted organizations to trick victims into sharing sensitive information like passwords or financial details.
- Lottery and Prize Scams: Victims receive notifications claiming they have won a significant prize and are asked to pay a processing fee or taxes to claim it.
- Emotional Manipulation Scams: Scammers on dating apps build relationships with victims and later ask for money for emergencies, often demanding payments in cryptocurrency.
- Job Scams: Scammers post fake job listings on hiring platforms or social media to trick job seekers, especially fresh graduates, into giving personal information or money.
- Investment Scams: These scams appeal to a victim’s desire for quick money by promising high, unrealistic returns through Ponzi or pyramid schemes.
- Cash-on-Delivery (CoD) Scams: Scammers set up fake online stores that accept CoD orders. When the product is delivered, it is either counterfeit or not as advertised.
- Fake Charity Appeal Scams: Scammers create fake websites or social media pages for bogus causes like disaster relief or health initiatives, using emotional stories or images to create urgency and sympathy.
- Mistaken Money-Transfer Scams: Scammers contact victims claiming money was mistakenly sent to their account and using fake transaction receipts to pressure them into returning it to avoid legal trouble.
- Credit Card Scams: Fraudsters offer loans at low interest rates with quick approval. After the victim pays an upfront fee to secure the loan, the scammers disappear.
What are the Key Government Initiatives Related to Cyber Scam in India?
- National Cyber Security Policy
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India (CERT-In)
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Cyber Crime Coordination Centre
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System
Way Forward
- Digital Safety: India’s PM outlined a simple three-step safety protocol to protect against digital arrests.
- Stop: Remain calm and avoid giving out personal information immediately.
- Think: Be aware that legitimate agencies don’t conduct such inquiries over calls or demand payments through calls.
- Take Action: Report incidents on the National Cyber Crime Helpline (1930) or at National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal, inform family members, and record evidence.
- Cybersecurity Best Practices: Use firewalls that act as the first line of defence for computers, monitoring and filtering network traffic to prevent unauthorised access.
- Keep all software and hardware systems up-to-date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Enhanced Security: Implement two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security. Use encryption to protect sensitive data, including financial records.
- Heightened Alertness: Banks should monitor high-value transactions in low-balance or salaried accounts and alert authorities, as stolen money is often moved to these accounts before being converted to cryptocurrency and sent abroad.
- Awareness: Don’t give out any personal information (such as Aadhaar or PAN card details). Do not send any money.
- Always independently verify the caller’s identity through official channels.
- Learn about common scam tactics and share this information with your family and friends to prevent such events.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration between nations to create common laws, share intelligence, and coordinate responses can help combat cross-border cybercrime.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. What are the different types of Cyber Scams? What are the challenges in addressing cyber scams? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
1. Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
2. Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
3. Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
4. Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents?(2017)
1. Service providers
2. Data centres
3. Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)