Governance
Need for Balanced Cryptocurrency Regulation
- 08 Mar 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Cryptocurrency, Blockchain, Bitcoin, Money Laundering, Digital Rupee, Taxation
For Mains: Issues in Regulating Cryptocurrency
Why in News?
The US administration has embraced crypto assets, solidifying their place in global finance. While countries like Vietnam push for clear regulations and the EU sets global standards with MiCA, India still waits for a discussion paper.
What is Cryptocurrency?
About
- A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure transactions. It is a decentralized currency (not controlled by any government or institution).
- Transactions with cryptocurrency are recorded on a public digital ledger called blockchain.
- This ledger is maintained by a network of computers around the world, and each new transaction is verified and added to the blockchain by these computers.
- The decentralization and use of cryptography make it difficult for anyone to manipulate the currency or the transactions recorded on the blockchain.
- Some examples of cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Difference Between Cryptocurrency, e-Money, Physical Currency
|
Category |
Cryptocurrency |
e-Money |
Physical Currency (Rs) |
|
Accessibility |
Largely limited to Internet connection |
Access to e-devices such as mobile phones and an agent network |
Physical access to cash, ATMs, and bank branches |
|
Value |
Determined by supply, demand and trust in the system |
Equal to amount of fiat currency exchanged into electronic form |
Backed by the government, determined by monetary policy |
|
Customer ID |
Anonymous |
Required adequate customer identification |
Not required for transactions, but required for bank accounts |
|
Production/ Issuer |
Mathematically generated ("mined") by community of developers, called "miners" |
Digitally issued against receipt of equal value of fiat currency of central authority by RBI |
Central bank (RBI) |
|
Regulator or Oversight |
Mostly Unregulated |
Central Bank/Board |
Central Bank (RBI) |
Regulations
- Global: Most cryptocurrencies operate outside national government regulations, serving as alternative currencies beyond state monetary policies.
- Switzerland has embraced crypto with a well-defined regulatory framework, ensuring investor protection while fostering blockchain innovation.
In September 2021, El Salvador became the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
- Switzerland has embraced crypto with a well-defined regulatory framework, ensuring investor protection while fostering blockchain innovation.
- India: Cryptocurrency in India is unregulated but not specifically banned.
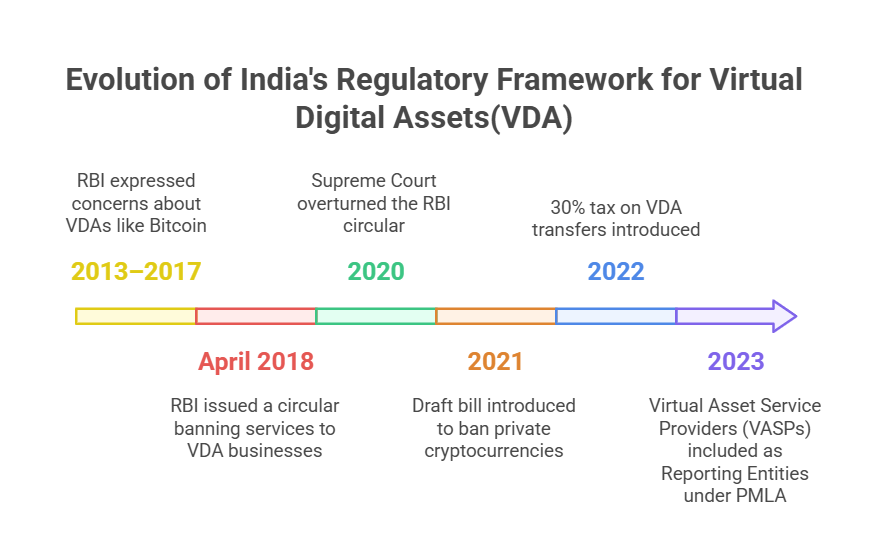
- Timeline:
Why Does India Need a Policy for Cryptocurrency?
- Preventing Talent Exodus: A blanket ban on cryptocurrencies could lead to a significant brain drain, along with the flight of capital as seen after the RBI's 2018 ban, with blockchain experts moving to crypto-friendly countries and halting blockchain innovation in India.
- Integrating into the Global Financial Ecosystem: By embracing cryptocurrency, India can position itself as a key player in the global financial ecosystem, attracting investments and fostering growth in crypto startups through initiatives like 'crypto export zones.'
- Leveraging New Technology and Services: The growing demand for blockchain applications in scalability, security, and analytics presents an opportunity for India to develop a large talent pool with expertise in crypto technologies, driving technological advancement.
- Encouraging Financial Innovation: The dynamic nature of blockchain technology offers vast potential for innovative business models and applications, with long-term impacts that could revolutionize various sectors, necessitating a balanced regulatory approach.
- Enhancing Investor Protections: To safeguard investors, India needs to implement robust education and guidelines against mis-selling, regulate crypto assets as commodities, which can also boost government tax revenues by increasing tax base.
- Stricter oversight is also needed to prevent their use in sophisticated fraud schemes, including ransomware attacks and investment scams.
What are the Challenges Cryptocurrency Poses?
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency is highly speculative, leading to significant price fluctuations and potential for substantial losses when investing large amounts.
- Risk of Misuse: The ease of transferring cryptocurrency across borders without accountability increases the risk of it being used for money laundering and terror financing.
- Scalability Issues: Blockchain's growing data size limits capacity, making rapid large-scale transactions challenging, especially during national emergencies.
- Economic Imbalance: The rise of the cryptocurrency market can disrupt the circular flow of money in the Indian economy, differing significantly from traditional cash creation processes.
- Lack of Regulatory Oversight: The absence of a dedicated forum or grievance redressal mechanism for crypto assets leaves consumers vulnerable to transactional and informational risks.
Way Forward
- Regulatory Clarity: A comprehensive crypto regulation bill must differentiate between crypto assets on use cases.
- Investor Protection: Establishing mechanisms for dispute resolution, fraud prevention, and risk disclosures will ensure that retail investors are protected from bad actors.
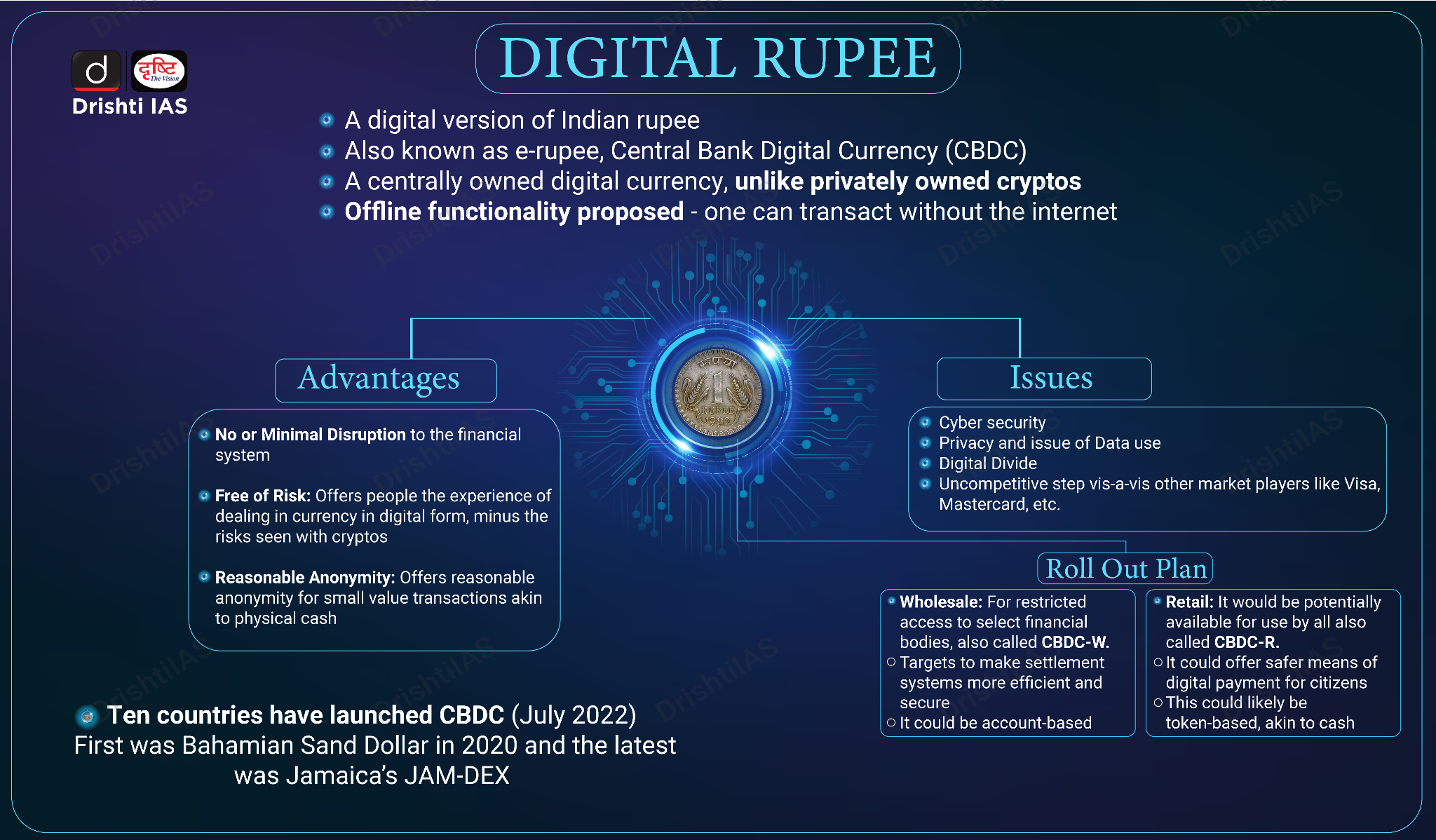
- Stablecoin and CBDC Integration: India’s digital rupee initiative (CBDC) can coexist with crypto assets, provided there are clear regulatory distinctions and interoperability guidelines.
- Additionally, the government can adopt a stage-based approach to the use of crypto assets, allowing for phased integration based on risk assessment, regulatory readiness, and technological advancements.
- Taxation Reform: The current high tax regime in crypto is pushing businesses offshore. A more balanced tax structure can encourage domestic innovation while ensuring government revenue
- Public-private Collaboration: Engaging with industry leaders, blockchain startups, and international regulatory bodies will help India craft policies that foster innovation while mitigating risks.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the current regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies in India. Evaluate the challenges and suggest measures to ensure a balanced approach that fosters innovation while protecting investors. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Terms sometimes seen in news Context/Topic
- Belle II experiment — Artificial Intelligence
- Blockchain technology — Digital/ Cryptocurrency
- CRISPR – Cas9 — Particle Physics
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2020)
Q. What is Cryptocurrency? How does it affect global society? Has it been affecting Indian society also? (2019)