Facts for UPSC Mains
IMF Report on India's Financial System
- 07 Mar 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF), in its report titled "India Financial System Stability Assessment", has flagged concerns about the stress in Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and its potential risks to India's financial system.
What are the Key Highlights of the IMF Report on India Financial System?
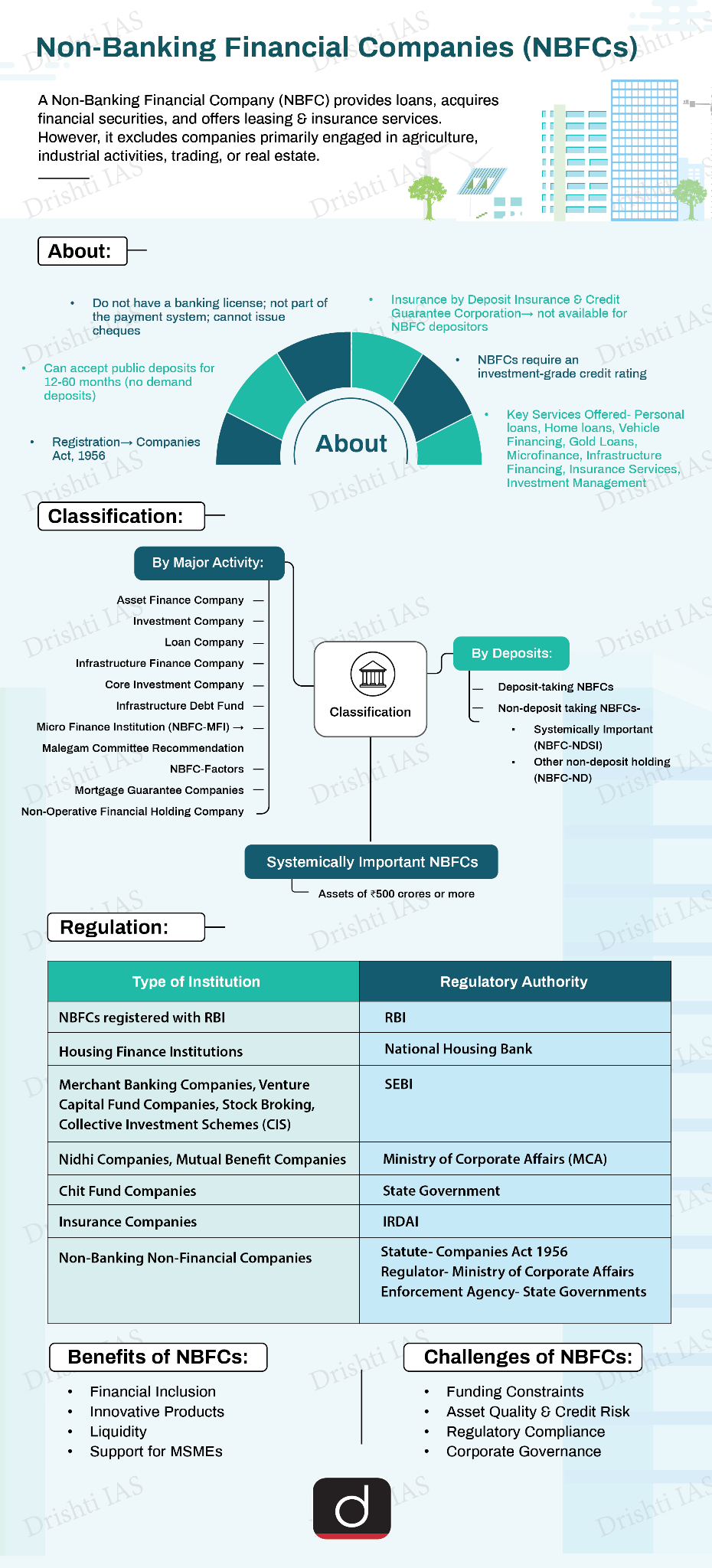
- NBFC Stress and Systemic Risk: 63% of power sector loans in FY 2024 were from the three largest Infrastructure Financing NBFCs, up from 55% in 2019-20.
- 56% of NBFC lending is financed by market instruments (mutual funds, and corporate bond markets), with the remaining from bank borrowings.
- State-owned NBFCs like Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) are at higher risk due to their exposure to the power sector which face delays, and financial stress. Without expected revenues, NBFCs asset-liability mismatches that hinder repayments.
- NBFCs can't accept demand deposits, lack deposit insurance, and have no direct Reserve Bank of India (RBI) liquidity access, making them vulnerable to financial stress.
- Stagflation Risk and Impact on PSBs: The report warns that geopolitical risks and miscalculated monetary policies by major central banks could lead to rising interest rates and slow economic growth, affecting both NBFCs and banks.
- IMF stress tests indicate that Public Sector Banks (PSBs) may struggle to maintain the 9% Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) if stagflation (slow growth + high inflation) occurs.
- RBI mandates 12% CAR for PSBs and 9% for scheduled commercial banks.
- Financial Inclusion Growth: Nearly 80% of Indian adults have financial accounts, supported by an extensive banking network and digital infrastructure like Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- The rapid rise of retail investors in equities has transformed India into one of the world's largest equity options trading markets.
- Financial System Assets: India’s financial system assets (including banks, NBFCs, insurance companies, mutual funds, and pension funds) amount to nearly 190% of GDP, with banks holding 60% of total financial assets.
- Recommendations For Financial Stability: Instead of paying dividends to the government, PSBs should retain earnings to bolster their capital reserves and support economic recovery in case of downturns.
- Improve data sharing on NBFC credit and exposure to assess risks better.
- IMF recommends state-owned NBFCs should have the same regulatory burden as private sector NBFCs to create a level playing field.
- IMF recommends prioritizing financial stability over aggressive lending for economic development.
- Improve data sharing on NBFC credit and exposure to assess risks better.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does the high exposure of NBFCs to power and infrastructure sectors pose financial risks? Suggest regulatory measures to mitigate these risks. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. "Rapid Financing Instrument" and "Rapid Credit Facility" are related to the provisions of lending by which one of the following? (2022)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
(d) World Bank
Ans: (b)
Q2. “Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to (2020)
(a) a loan system of the World Bank
(b) one of the operations of a Central Bank
(c) a credit system granted by WTO to its members
(d) a credit system granted by IMF to its members
Ans: (d)
Q3. ‘Global Financial Stability Report’ is prepared by the (2016)
(a) European Central Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
(d) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. The World Bank and the IMF, collectively known as the Bretton Woods Institutions, are the two inter-governmental pillars supporting the structure of the world’s economic and financial order. Superficially, the World Bank and the IMF exhibit many common characteristics, yet their role, functions and mandate are distinctly different. Elucidate. (2013)