Internal Security
Transnational Organised Crime
For Prelims: Financial Action Task Force (FATF), United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, Transnational Organized Crime, Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre, UN Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime, Cybercrime
For Mains: Impact of Transnational Organized Crime and challenges in controlling, Cybercrimes and their effects, International cooperation, Money Laundering
Why in News?
Recently, the heads of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Interpol, and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) have emphasised the urgent need to intensify efforts to target the massive illicit profits generated by transnational organized crime (TOC).
- Additionally, the recent revelations from the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), a division under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), have shed light on the escalating threat of cybercrime targeting Indian citizens.
What is Transnational Organised Crime?
- About: Organised crime is defined as illegal activities carried out by groups or networks working together, often involving violence, corruption, or related actions to gain financial or material benefits.
- Transnational organised crime (TOC) occurs when activities or groups operate in multiple countries.
- Different Forms:
- Money Laundering: It disguises financial assets to use them without detection of the illegal activity that produced them. Criminals transform the proceeds of criminal activity into funds with a seemingly legal source.
- The estimated amount of money laundered globally exceeds 2% to 5% of the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or approximately USD 800 billion to USD 2 trillion in just one year.
- Drug Trafficking: It continues to be the most lucrative form of business for criminals,
- Global drug trafficking is estimated to be worth USD 650 billion, contributing 30% of the overall illicit economy.
- Human Trafficking: A global crime where men, women, and children are used for sexual or labour-based exploitation.
- Human traffickers are in it for the money, with estimated annual global profits of USD 150 billion.
- They victimise an estimated 25 million people worldwide, with 80% in forced labour and 20% in sex trafficking.
- Smuggling of Migrants: A well-organised business moving people around the globe through criminal networks, groups, and routes.
- In 2009, USD 6.6 billion was generated through the illegal smuggling of 3 million migrants from Latin America to North America.
- Illicit Firearms Trafficking: Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms, explosives, and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organisations.
- Brings in around USD 170 million to USD 320 million annually.
- Trafficking in Natural Resources: It involves the trade of non-renewable resources like minerals and fuels, and renewable resources like wildlife(skins and body parts for export to foreign markets), forestry, and fishery.
- This trade is often called an "environmental crime" by international organisations.
- The sale of elephant ivory, rhino horn and tiger parts in Asia alone was worth an estimated US USD 75 million in 2010.
- Fraudulent Medicines: These include counterfeit medicines and medicines diverted from legal and regulated supply chains.
- Instead of curing people, fraudulent medicines can result in death or cause resistance to drugs used to treat deadly infectious diseases.
- Cybercrime and Identity Theft: Criminals exploit the Internet to steal private data, access bank accounts, and fraudulently obtain payment card details.
- Money Laundering: It disguises financial assets to use them without detection of the illegal activity that produced them. Criminals transform the proceeds of criminal activity into funds with a seemingly legal source.
Cybercrimes Targeting Indian Citizens
- Surge in Cybercrime Incidents: I4C reports an average of around 7,000 cyber-related complaints daily, indicating a significant increase in cybercrime incidents.
- Various types of cybercrimes, including digital arrest, trading scams, investment scams, and dating scams, have been identified, highlighting the diverse tactics employed by cybercriminals.
- Origin in Southeast Asia: Nearly 45% of cybercrimes targeting Indian citizens originate from Southeast Asian countries, particularly Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos.
What is the Impact of Transnational Organized Crime?
- Global Public Health: Counterfeit medicines, especially prevalent in low- and middle-income countries, can be ineffective or harmful, leading to an estimated 1 million deaths per year globally.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 1 million people die each year from falsified or substandard medicines, with 200,000 of those deaths in Africa.
- Resilient and Inclusive Global Economy: Money laundering and illicit financial flows undermine financial integrity and state public financing capacities, obstructing economic development.
- TOC can drain foreign exchange reserves and affect asset prices, undermining economic stability.
- The global offshore economy conceals an estimated 10% of the world's wealth, including proceeds from organized crime.
- Planet Health: Organized environmental crime drives deforestation, biodiversity loss, and carbon emissions contributing to climate change.
- Illicit production and smuggling of synthetic refrigerants (HFCs) undermine the Montreal Protocol and contribute to climate change.
- Lack of consensus on defining and criminalizing environmental crimes enables criminals to evade enforcement efforts.
- International Peace and Security: The illicit arms trade fuels armed conflicts, violent crime, and other organized criminal activities.
- Non-state armed groups engage in illicit markets to support their activities, including natural resource extraction and smuggling.
- Organized crime-related violence, particularly in Central and South America, often exceeds casualties from armed conflicts.
- Local Effects: While transnational organized crime is a global threat, its effects are felt locally.
- It can destabilize countries and entire regions, undermining development assistance in those areas.
- Organized crime groups can work with local criminals, leading to an increase in corruption, extortion, racketeering, and violence, as well as other sophisticated crimes.
- It adds to public spending for security and policing and undermines human rights standards.
Why is it Crucial to Target Illicit Profits?
- Sustainable Development Goals: Disincentivizing criminal activity by targeting illicit profits would positively impact the goals of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda, including Financial stability, Inclusive economic growth, and Strengthened institutions and governance.
- Disrupts Criminal Activities: By targeting the financial gains from illegal activities, it becomes more difficult for criminals to fund their operations and sustain their networks.
- Illicit profits often fuel other illegal activities. Cutting off these funds helps in preventing further crimes.
- Promotes Rule of Law: Confiscating illicit profits supports the rule of law and demonstrates that crime does not pay.
- Aids Development Goals: Redirecting illicit funds towards legitimate purposes can support economic growth and development initiatives.
- Enhances Global Security: Money laundering and terrorism financing pose threats to international peace and security. Targeting illicit profits helps in combating these threats.
- Safeguards Vulnerable Populations: Criminal activities financed by illicit profits often exploit the most vulnerable. By targeting these profits, we can protect these populations.
- International Cooperation: It encourages international cooperation in fighting transnational organized crime and terrorism financing.
What are the Challenges Regarding Controlling TOC?
- Diverse Legal Systems: Variations in legal frameworks across countries complicate international efforts to combat TOC.
- Lack of Consensus: Achieving global consensus on strategies to address TOC is difficult due to varying national interests and priorities.
- The UN Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the main legal instrument, but its implementation and cooperation regime are ineffective.
- The UNODC and other bodies lack a coherent strategy, taking a piecemeal approach.
- Powerful states prefer informal, unilateral solutions, which often lack oversight and pose challenges to the rule of law and human rights.
- Corruption: TOC often involves corruption, which infiltrates and undermines law enforcement and governance structures.
- Technological Advancements: Criminals exploit technology for illicit activities, staying ahead of law enforcement capabilities.
- Armed Conflict: In regions of conflict, TOC can fuel violence and instability, complicating efforts to control it.
- The connection between TOC and terrorism, where criminal profits fund terrorist activities, poses a significant threat.
Legal Position In India on Organized Crime
- Organized crime has historically existed in India, but it has become more prominent in modern times due to various socio-economic and political factors and advancements in science and technology.
- At the national level, India lacks a specific law to address organized crime, and existing laws like the National Security Act, of 1980, and the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, of 1985 are insufficient as they focus on individuals rather than criminal groups.
- Some states, such as Gujarat, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh, have implemented their laws to combat organized crime.
- India is a party to international conventions and treaties aimed at preventing and suppressing organized crime globally. These include the UNTOC, the UNCAC, and the UNODC.
Way Forward
- Blockchain Forensics: Leverage blockchain technology to track illicit cryptocurrency flows, a growing revenue stream for TOC.
- Identify and dismantle money laundering networks through advanced tracing methods.
- Dark Web Infiltration: Develop specialized units trained to navigate the dark web, infiltrate online marketplaces used by TOC, and gather crucial intelligence on their operations.
- Transparency Initiatives: Support and promote transparency measures in government institutions to reduce opportunities for bribery and collusion with TOC.
- Empower citizens to report corruption through secure channels.
- Political Will: Develop a comprehensive understanding of how transnational organized crime and corruption undermine global public goods.
- Build political will for effective international cooperation through multilateral instruments.
- Integrate strategies to combat transnational organized crime in conflict prevention, peace operations, and peacebuilding efforts.
- Adopt a holistic vision and approach beyond criminal justice responses, addressing developmental, human rights, and security implications.
- Real-Time Fusion Centers: Create real-time fusion centers to facilitate immediate collaboration between law enforcement, intelligence agencies, and private sector partners for swift analysis of data, identification of trends, and coordinated responses to organized crime activity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Assess the impact of transnational organized crime on sustainable development, particularly in the context of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda. Explain how targeting the illicit profits of TOC can support the achievement of development goals. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. India’s proximity to two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)


Geography
Influence of Wind Shear on Hurricanes
For Prelims: Wind Shear, Hurricane, Jet streams, Temperature Inversion, Doppler Radar, LIDAR, El Nino and La Lina.
For Mains: Important Geophysical phenomena Impacting Precipitation and Weather Patterns.
Why in News?
Recently, the concept of wind shear has gained increased attention due to its crucial role in determining whether a storm intensifies into a destructive hurricane.
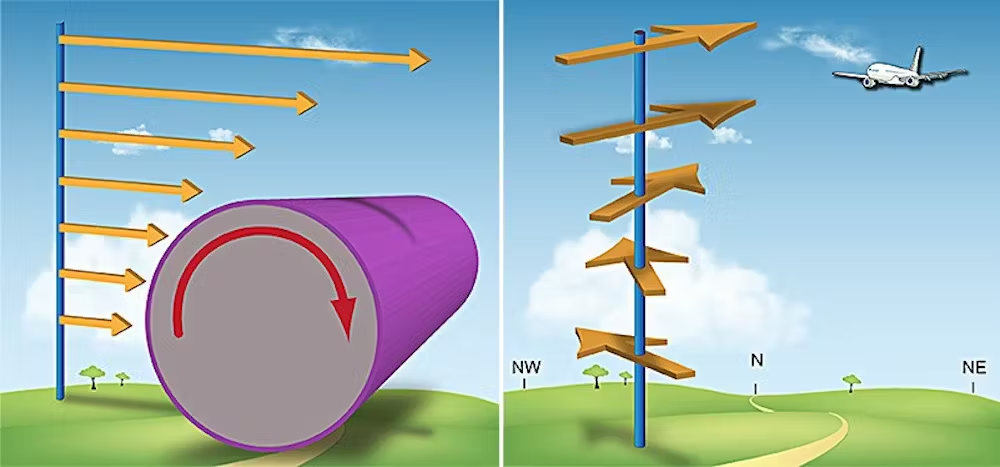
What is Wind Shear?
- About: Wind shear is a meteorological phenomenon that refers to a sudden change in wind speed and/or wind direction over a relatively small distance.
- Types: It is mainly of 2 types:
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.
- Common examples include low-level jet streams and wind shear associated with thunderstorms.
- Horizontal Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly over a horizontal distance.
- In this case, the wind might be blowing from the west at one spot, but then suddenly switch to blowing from the north just a bit further on.
- Common examples include frontal systems and sea breezes.
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.
- Major Causes:
- Temperature Inversion: During calm nights, warm air near the ground traps cooler air above, creating strong vertical wind shear, which could be a hazard for aircraft taking off and landing.
- Thunderstorms: Powerful updrafts and downdrafts within thunderstorms cause both horizontal and vertical wind shear, making flying near them dangerous.
- Frontal Systems: Boundaries between warm and cold air masses (fronts) create rapid changes in wind speed and direction, resulting in horizontal wind shear that can challenge aircraft navigation.
- Detection Methods:
- Low-Level Wind Shear Alert System (LLWAS): This network of ground-based towers uses anemometers (wind speed sensors) and wind direction sensors to measure wind speed and direction at multiple points around an airport.
- Doppler Radar: On the ground, these radars track wind speed and direction to spot wind shear zones.
- LIDAR: This uses light to detect wind shear, especially helpful for clear air turbulence.
What are the Effects of Wind Shear on Hurricanes?
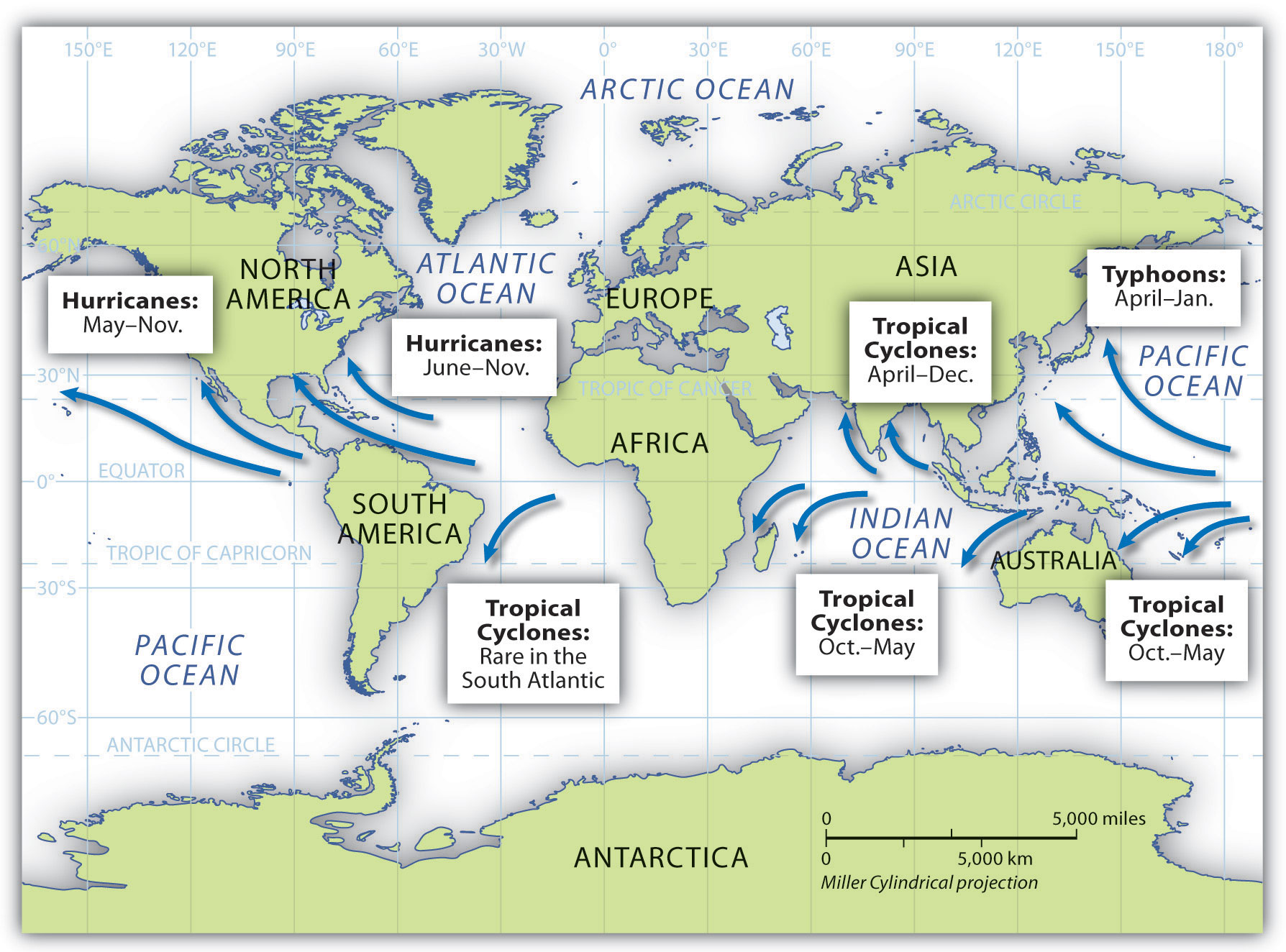
- About Hurricanes: Hurricanes or Tropical Cyclones are violent storms that originate over oceans in tropical areas and move over to the coastal areas bringing about large scale destruction caused by violent winds, very heavy rainfall and storm surges.
- Its formation and initial development depends upon the transfer of water vapor and heat from the warm ocean to the overlying air, primarily by evaporation from the sea surface.
- They are given many names in different regions of the world such as:
- Effects of Wind Shear on Hurricanes:
- Hurricanes thrive in environments with minimal vertical wind shear, as it allows for a symmetrical structure and efficient rotation.
- Strong vertical wind shear can disrupt the hurricane's vertical structure, offsetting the top of the storm from the bottom.
- This weakens the wind circulation, heat transport, and moisture supply, which are essential for fueling the hurricane.
- Excessive vertical wind shear can potentially tear a hurricane apart.
- Other Factors Affecting Hurricane Intensity:
- While vertical wind shear is a significant factor, it is not the only determinant of hurricane intensity.
- Other factors, such as sea surface temperatures, atmospheric moisture content, and pressure systems, also play crucial roles in hurricane development and strengthening.
- In some cases, exceptionally warm sea surface temperatures can overcome the effects of increased wind shear, as witnessed during the 2023 hurricane season.
- While vertical wind shear is a significant factor, it is not the only determinant of hurricane intensity.
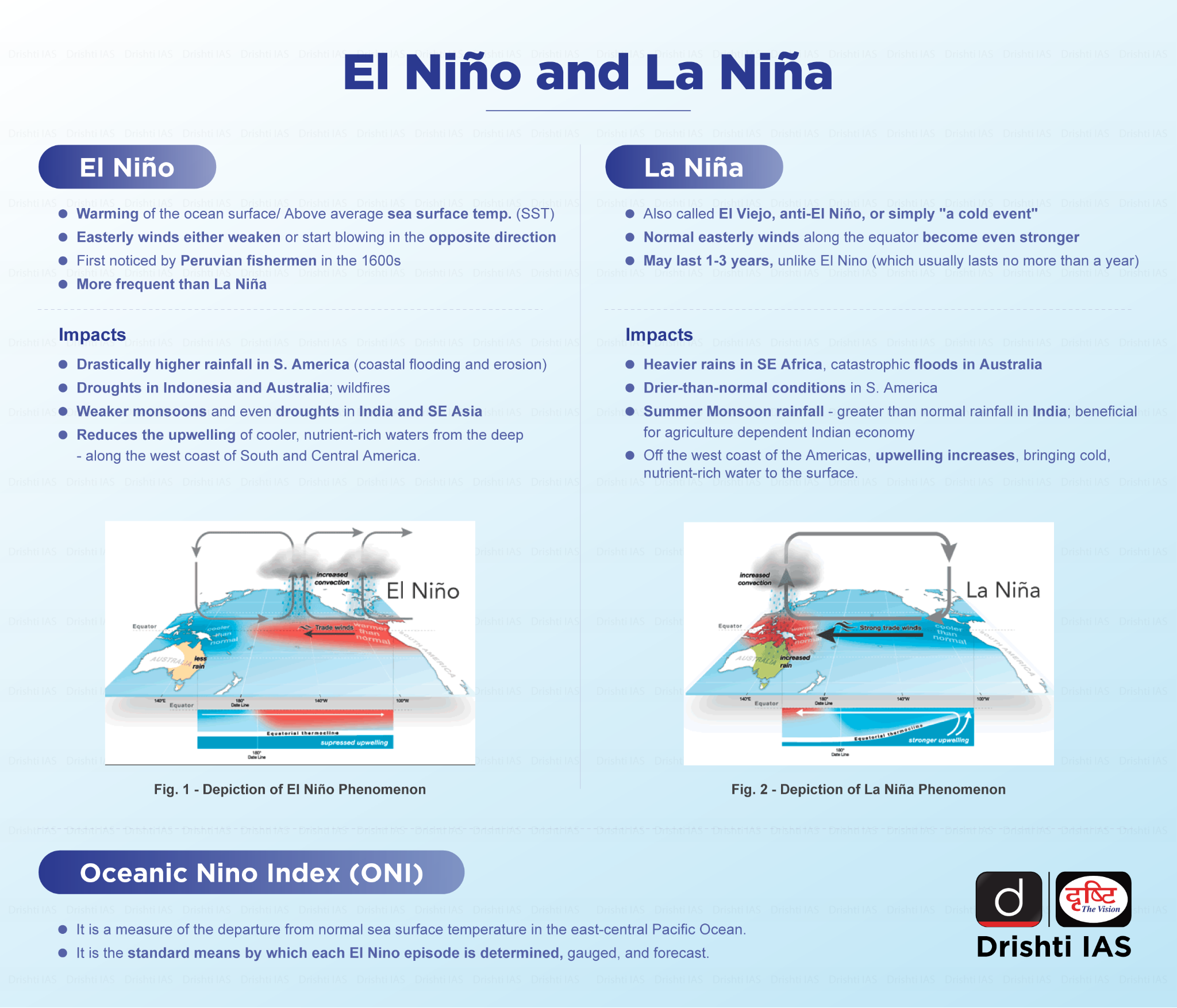
What is the Influence of EL Nino and La Lina on Wind Shear?
- El Nino's Influence on Wind Shear: During El Nino years, stronger-than-usual vertical wind shear is typically observed over the Atlantic Ocean during hurricane season.
- El Nino events are characterised by warmer sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean and cooler temperatures in the western Pacific.
- This pattern leads to stronger upper-level winds over the Atlantic, resulting in increased vertical wind shear.
- The increased wind shear during El Nino years can make it more challenging for hurricanes to develop and intensify in the Atlantic basin.
- La Nina's Influence on Wind Shear: La Nina conditions, which are the opposite of El Nino, tend to be more favorable for hurricane development in the Atlantic.
- During La Nina years, vertical wind shear is generally weaker over the Atlantic, allowing for more active hurricane seasons.
- The record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season occurred during a La Nina event.
Read More: Cyclone
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Prelims
Q. In the South Atlantic and South-Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclones do not originate. What is the reason? (2015)
(a) Sea surface temperatures are low
(b) Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
(c) Coriolis force is too weak
(d) Absence of land in those regions
Ans: (b)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulfate aerosol into the stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
- Only some cyclones develop an eye.
- The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10ºC lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (c)


Science & Technology
Space Tourism
For Prelims: Space Missions in 2024, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx Mission, NASA’s Artemis plan, India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission.
For Mains: Space Missions in 2024, Achievements of Indians in science & technology.
Why in News?
Recently, Gopi Thotakura, an India-born commercial pilot based in the US, became the first space tourist from India. She, along with five other space tourists, made a short recreational trip to space.
What is Space Tourism?
- About:
- Space tourism is a niche segment of the aviation industry that seeks to give tourists an experience of space travel for recreational, leisure, or business purposes.
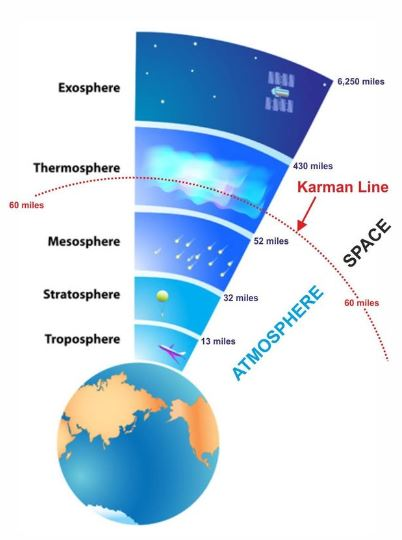
- Space travel begins at about 100 km altitude from Earth, after crossing the Karman line, which is widely accepted as the boundary line separating the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space.
- Anything flying below this altitude is called an aircraft while those crossing this line get classified as a spacecraft.
- Types:
- Suborbital: Here, flights take passengers to the edge of space, where they can experience weightlessness for a few minutes.
- Orbital: Here, flights take passengers into orbit around the Earth. This gives them a chance to see the planet from space and experience weightlessness for a longer period of time.
- Entry of Private Space Players:
- In 2021, Virgin Galactic's founder Richard Branson and Blue Origin's founder Jeff Bezos first rocketed into space on brief suborbital flights.
- More recently NASA funded three companies to develop commercial space stations, totaling USD 415M.
- Blue Origin received USD 130 million, Nanoracks received USD 160 million, and Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation received USD 125.6 million. These developments help support growing demand for space tourism, providing the necessary infrastructure to support it.
- Market Size:
- While the industry is still in its infancy, it is rapidly growing as the demand for space travel is growing, and it is expected to continue to expand at an annual growth rate of 40.2% from 2023 to 2030.
- In 2022, the global space tourism market was valued at USD 695.1 million, and it is projected to reach USD 8,669.2 million by 2030.
- The sub-orbital segment dominated the market in 2022, accounting for 49.3% of the overall market share.
- The orbital segment, on the other hand, is expected to witness the fastest growth of 41.0% throughout the forecast period.
Karman Line
- The Karman line is the internationally recognised boundary of space.
- The line is named after Theodore von Kármán (1881–1963), a Hungarian American engineer and physicist, who was active primarily in aeronautics and astronautics.
- He was the first person to calculate the altitude at which the atmosphere becomes too thin to support aeronautical flight and arrived at 83.6 km himself.
- The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) defines Karman Line as the altitude of 100 kilometres above Earth’s mean sea level.
- FAI is the world governing body for air sports, and also stewards definitions regarding human spaceflight.
- However, other organisations do not use this definition. There is no international law defining the edge of space, and therefore the limit of national airspace.
What are Challenges to Space Tourism?
- Environmental Impact:
- Launching spacecraft and rockets require a lot of energy and can produce significant amounts of air and noise pollution.
- These emissions can contribute to climate change and harm the atmosphere.
- Safety Concerns:
- Despite safety protocols, there is always a risk of a mishap the consequences for which could be catastrophic.
- Cost:
- At present, space tourism is an expensive venture that is accessible only to the wealthy. As a result, many people will not be able to experience space travel, which can create feelings of inequality and elitism.
- A recent NASA paper mentions that space companies SpaceX and Space Adventures were planning to offer a journey around the Moon for about USD 70 to 100 million (about Rs 600 to 850 crore).
- Space Debris:
- Every launch of a spacecraft generates debris that can stay in orbit for many years, and as the number of space launches increases, the amount of debris grows.
- This debris can cause problems for other spacecraft, and even small debris can cause damage.
- Resource Depletion:
- Space travel requires a vast amount of resources, including energy, fuel, and materials.
- The depletion of these resources could have long-term consequences and could negatively impact the environment and the availability of resources for future generations.
- Legal Issues:
- The legal framework for space tourism is still in progress, creating uncertainty about liability if any issues arise.
- There are also concerns about the impact of space tourism on international space laws and the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies.
- It is also called the Outer Space Treaty. It is a multilateral treaty that forms the basis of international space law, signed in 1967.
What are the Opportunities for India in the Space Tourism Sector?
- Leveraging ISRO's Expertise:
- The ISRO has a successful history in space missions, including the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), demonstrating its technological capabilities. This inspires confidence for future human space endeavours.
- ISRO's cost-efficient space programs could lead to competitive pricing for future space tourism, increasing accessibility for a wider range of participants.
- Fostering a Thriving Public- Private Space Partnership:
- The Indian government is actively encouraging private participation in the space sector. Initiatives like New Space India Limited (NSIL) by ISRO and supportive policies are attracting investments and propelling innovation.
- Eg: PSLV-C53 is the first official public-private collaboration for a space launcher in India.
- Private firms like SpaceX and Blue Origin have demonstrated the viability of such partnerships.
- Future Plans:
- The ISRO is also developing a reusable space tourism module for an estimated cost of Rs 6 crore per trip, which is expected to be launched by 2030.
What is the Future of Space Tourism?
- Accessible to Wealthy:
- By 2030, ISRO predicts that space tourism will be accessible to the wealthy with an average ticket cost of around 6 crores. ISRO is working towards commercialising space tourism in India in the near future.
- Beyond Earth's Orbit:
- The current focus on suborbital and orbital flights is just the beginning.
- Companies are already setting their sights on lunar adventures and, ultimately, deep space exploration like missions to Mars such as Mangalyaan (India), Mariner 4(NASA), ExoMars (ESA), Tianwen-1 (China), Hope(UAE).
- Space Staycations:
- The concept of space tourism is expanding beyond brief trips with companies now designing modules for space tourists to stay in for longer periods.
- Focus on Sustainability:
- Greater emphasis will likely be placed on developing fully reusable rockets to minimise space debris and make space travel more environmentally friendly.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the potential benefits and challenges of space tourism as an emerging industry. What are the implications for countries like India in participating in and regulating this sector? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q.1 What is the main task of India’s third mood mission which could not be achieved in its earlier mission? List the countries that have achieved this task. Introduce the subsystems in the spacecraft launched and explain the role of the ‘Virtual Launch Control Centre’ at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre which contributed to the successful launch from Sriharikota. (2023)
Q.2 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.3 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)


Indian Economy
US Federal Reserve Keeps Rates Steady as Inflation Persists
For Prelims: US Federal Reserve, Retail Inflation, Reserve Bank of India, Monetary Policy Committee, Wholesale Price Index (WPI), Consumer Price Index, Core Inflation, Headline Inflation,
For Mains: US Fed Rate Hike’s impact on Indian Economy
Why in News?
Recently, the US Federal Reserve maintained interest rates in a target range between 5.25%-5.5% and indicated that borrowing costs are likely to stay higher. Annual inflation in the US is currently at 3.5%, compared to 3.2% in the UK and 2.4% in the eurozone.
What are the Reasons Behind the Recent US Federal Reserve Decision?
- Inflationary Pressures:
- The US inflation rate peaked in 2021 and 2022 at 7.0% and 6.5% respectively, and then declined at the end of 2023 but it still remains stubbornly high at 3.5%.
- This is significantly above the US Fed's target of 2%.
- This persistent inflation suggests that previous measures, like raising interest rates, haven't brought inflation down as quickly as hoped.
- The US inflation rate peaked in 2021 and 2022 at 7.0% and 6.5% respectively, and then declined at the end of 2023 but it still remains stubbornly high at 3.5%.
- The Wait-and-See Approach:
- Earlier in the year, the fed anticipated inflation would decline and projected rate cuts. However, the current situation has forced them to reconsider.
- By holding rates, the US Fed buys itself time to gather more data. They'll be closely monitoring inflation metrics, employment figures, and consumer spending patterns.
- This data will guide their future decisions on whether to raise rates to combat inflation or leave them unchanged to support economic growth.
Why do Central Banks Resort to a Rate Hike?
- The central bank may increase interest rates to control inflation.
- This is being done to reduce the amount of money available for borrowing, which can help to cool down the economy and prevent prices from rising too quickly.
- With higher borrowing costs, people and companies may be less willing to borrow, which can slow down economic activity and growth.
- Businesses may take fewer loans, hire fewer people, and reduce production in response to the increased costs of borrowing.
How do US Fed Rates Impact the Indian Economy?
- Capital Outflows:
- The Fed's rate hikes make US dollar-denominated assets (bonds, treasuries) more attractive. This triggers a phenomenon called the "carry trade."
- Investors borrow money in low-interest-rate countries like India and invest it in the US to earn higher returns. This outflow of capital (capital flight) from other countries can:
- Slow Economic Growth: Reduced foreign investment can hinder the growth of Indian companies and the overall economy.
- Impact on stock markets: The sudden withdrawal of foreign investment can lead to stock market volatility and potentially decreased valuations.
- Inflation:
- Changes in the US Fed rates can have significant effects on capital flows and the exchange rate which can result in inflation.
- By adjusting domestic interest rates and liquidity measures, the RBI can try to mitigate the inflationary impacts of a weaker rupee.
- Weaker Rupee:
- When foreign investors pull their money out of India due to the higher US returns, it reduces the supply of USD in India and increases the supply of INR. This imbalance weakens the Indian rupee.
- This has a double-edged effect:
- Imported Inflation: Cheaper rupees make imports more expensive, especially for crucial resources like oil. This can push up the overall cost of living in India.
- Potential Export Boost: A weaker rupee can make Indian exports cheaper in the global market, potentially increasing their competitiveness.
- Higher Borrowing Costs:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might raise interest rates in India to match the Fed's move to:
- Control Inflation: Higher interest rates discourage borrowing and spending, potentially helping to curb inflation.
- Stem Capital Flight: The RBI aims to prevent further outflow of capital from India by making domestic investments more attractive
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might raise interest rates in India to match the Fed's move to:
- Stock Market Fluctuations:
- As investors chase higher US returns, the Stock Indian stock market might experience:
- Decreased Demand: Reduced foreign investment can lead to lower demand for Indian stocks, potentially causing a decline in their prices.
- As investors chase higher US returns, the Stock Indian stock market might experience:
- Increased Debt Burden:
- A weaker rupee can make it more expensive for India to service its external debt, which is mostly denominated in US dollars. This can:
- Strain Public Finances: The government may need to spend more to pay off its debts, impacting other crucial developmental plans.
- A weaker rupee can make it more expensive for India to service its external debt, which is mostly denominated in US dollars. This can:
- Benefits for Banks:
- The banking industry gets benefits from the interest rates rise, as banks re-price their loan portfolio much quicker than their deposit rates, which helps them to increase their net interest margin.
How can India Reduce the Impact of the US Federal Reserve Decisions on its Economy?
- Balancing Interest Rates:
- Raising Rates: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) can replicate the US Fed's hike to:
- Attract Foreign Investment: Higher interest rates can make Indian bonds and other investments more attractive to foreign investors, potentially increasing demand for the rupee and stabilizing its value.
- Control Inflation: Increased interest rates can deter borrowing and spending, potentially aiding in the control of inflation, particularly when coupled with a depreciating rupee.
- Raising Rates: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) can replicate the US Fed's hike to:
- Diversifying the Reserve Basket:
- Reducing Dollar Dependence: India can diversify its foreign exchange reserves by increasing holdings of other major currencies like the Euro, Yen, or Yuan.
- This reduces India's vulnerability to US dollar fluctuations. However, managing a diversified reserve basket can be complex.
- Reducing Dollar Dependence: India can diversify its foreign exchange reserves by increasing holdings of other major currencies like the Euro, Yen, or Yuan.
- Expanding Trade Horizons:
- Exploring Export Markets: Identifying and entering new markets for Indian exports can help diversify India's trade base and reduce its reliance on US markets.
- Trade Agreements: Negotiating bilateral trade agreements with other countries can reduce trade barriers and boost trade flows with non-US countries.
- This reduces dependence on the US Dollar.
- Trade Agreements: Negotiating bilateral trade agreements with other countries can reduce trade barriers and boost trade flows with non-US countries.
- Exploring Export Markets: Identifying and entering new markets for Indian exports can help diversify India's trade base and reduce its reliance on US markets.
- Stimulating Domestic Consumption:
- Boosting Demand: If the US Fed hike slows down the economy, the government can implement measures to encourage domestic consumption:
- Tax Cuts: Reducing taxes can put more money in people's pockets, potentially increasing spending and stimulating economic activity.
- In 2020, the Indian government increased the tax rebate for income tax payers in the lower tax brackets. This aimed to boost consumption spending during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Subsidies: Targeted subsidies for essential goods and services can help ease the burden on consumers and maintain purchasing power.Public Distribution System (PDS),Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) are examples of such governmental initiatives.
- Tax Cuts: Reducing taxes can put more money in people's pockets, potentially increasing spending and stimulating economic activity.
- Boosting Demand: If the US Fed hike slows down the economy, the government can implement measures to encourage domestic consumption:
- Reducing Reliance on Oil:
- Embracing Renewables: A strong dollar often leads to higher oil prices. India can mitigate this by investing in solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources. It can reduce dependence on imported oil and shield the economy from oil price fluctuations.
- Exploring Biofuels: Developing biofuels like ethanol can provide an alternative fuel source, reducing reliance on imported oil.
- Embracing Renewables: A strong dollar often leads to higher oil prices. India can mitigate this by investing in solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources. It can reduce dependence on imported oil and shield the economy from oil price fluctuations.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss about the US Fed Rate Hike’s impact on the Indian Economy. How can India tackle the impact of the US Federal Reserve decisions on its economy? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
- Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
- Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Tight monetary policy of US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
- Capital flight may increase cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBs
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)


Important Facts For Prelims
Indian Navy Sheds Colonial Legacy
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Navy has taken significant steps to shed its British colonial legacies by renaming traditional naval symbols and introducing new insignias.
- This transformation underscores India's efforts to redefine its naval identity to reflect its national heritage and aspirations better.
What are the Recent Changes in Nomenclature?
- New Nomenclature: To indigenize and reflect national pride, the Indian Navy has renamed ‘Jack’ to ‘National Flag’ and ‘Jackstaff’ to ‘National Flag Staff’.
- Old Terms and Their Origins: The terms 'Jack' and 'Jackstaff' are deeply rooted in British naval history and have been adopted by navies worldwide, including India, as remnants of British naval practices.
- ‘Jack’ typically refers to a flag, and the ‘Jackstaff’ is a short pole from which this flag is flown, positioned at the bow of a ship.
- Regulatory Framework and Legal Amendments: The change in nomenclature was formalised through an amendment to the "Regulations for the Navy (Ceremonial, Conditions and Service and Miscellaneous Regulation) 1963", leveraging the powers granted by the Naval Act of 1957.
What are Other Symbolic Changes Across the Armed Forces?
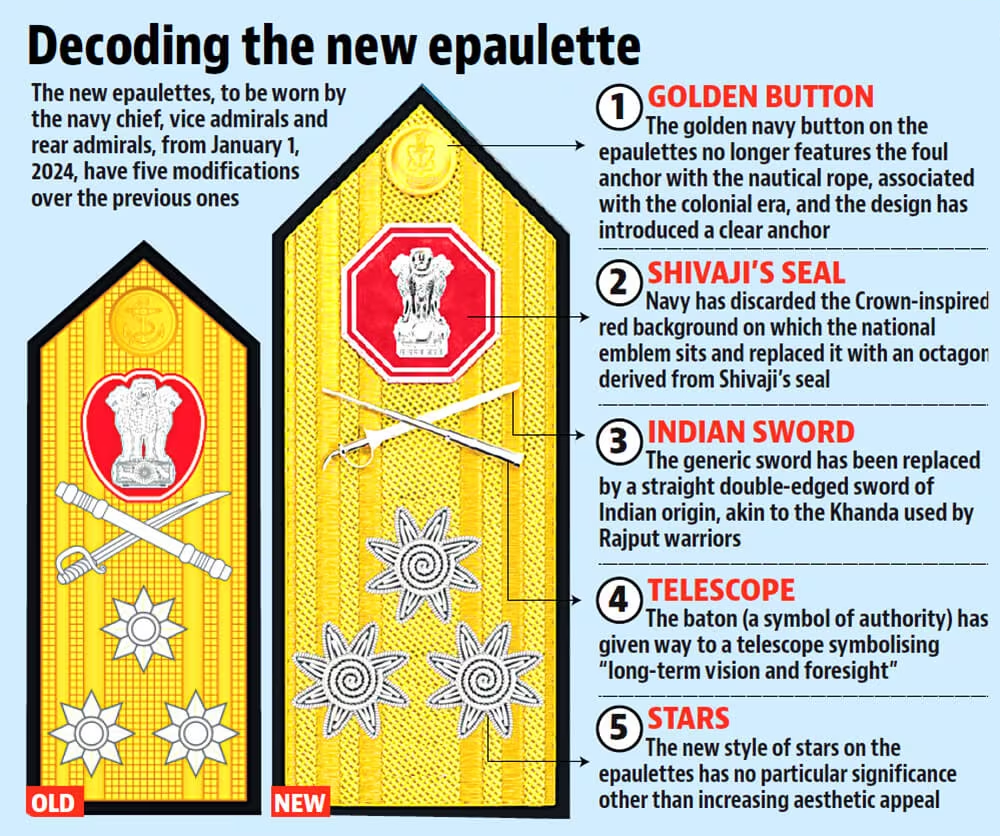
- Changes in Naval Insignia: In September 2022, the Indian Navy adopted a new naval ensign, discarding the British-inspired George's Cross for a design that includes a blue octagon with twin golden borders, the national emblem, and the motto ‘Satyamev Jayate’.
- This insignia draws inspiration from the seal of Shivaji Maharaj, symbolising the Navy's reach in all eight directions (four cardinal and four intercardinal).
- Change in Epaulettes of Naval Officers: The Indian Navy also unveiled new senior officers' epaulettes inspired by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's seal, symbolising a break from colonial legacies and a celebration of India's maritime heritage, with five modifications from the previous design for the navy chief, vice admirals, and rear admirals.
- New Dress Code in Messes: The Indian Navy has embraced its heritage by introducing the Kurta-Pyjama in naval messes, with senior officers among the first to don the traditional attire.
- Changes in Indian Army: The Indian Army has also started phasing out traditional practices such as horse-drawn buggies at events, retirement ceremonies, and pipe bands at dinners.
- Significance:
- Renaming and redesigning naval symbols indicate both distance from colonial ties and reasserting Indian sovereignty and maritime heritage.
- These steps align with India's Prime Minister's "Panch Pran" pledges for the nation's development by its 100th year of independence.
National Flag
- The design of the Indian tricolour is largely attributed to Pingali Venkayya, an Indian freedom fighter.
- Arguably the first national flag of India is said to have been hoisted on 7th August 1906, in Kolkata at the Parsee Bagan Square (Green Park).
- The National Flag is rectangular with a length-to-width ratio of 3:2.
- According to Article 51A (a), it shall be the duty of every citizen of India to abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag, and the National Anthem.
- A person who is convicted for the following offences under the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act of 1971 is disqualified to contest in the elections to the Parliament and state legislature for 6 years.
- Offence of insulting the National Flag
- Offence of insulting the Constitution of India
- Offence of preventing the singing of the National Anthem
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the National Flag of India according to the Flag Code of India, 2002: (2023)
Statement-I: One of the standard sizes of the National Flag of India is 600 mm x 400 mm.
Statement-II: The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the Flag shall be 3 : 2.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement- II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement- I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement- II is correct
Ans: (d)
Q. Department of Border Management is a Department of which one of the following Union Ministries? (2008)
(a) Ministry of Defence
(b) Ministry of Home Affairs
(c) Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways
(d) Ministry of Environment and Forests
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Cyclone Remal
Why in News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has issued a warning for a potential severe cyclonic storm, named Cyclone Remal, that could impact the coasts of West Bengal and Bangladesh.
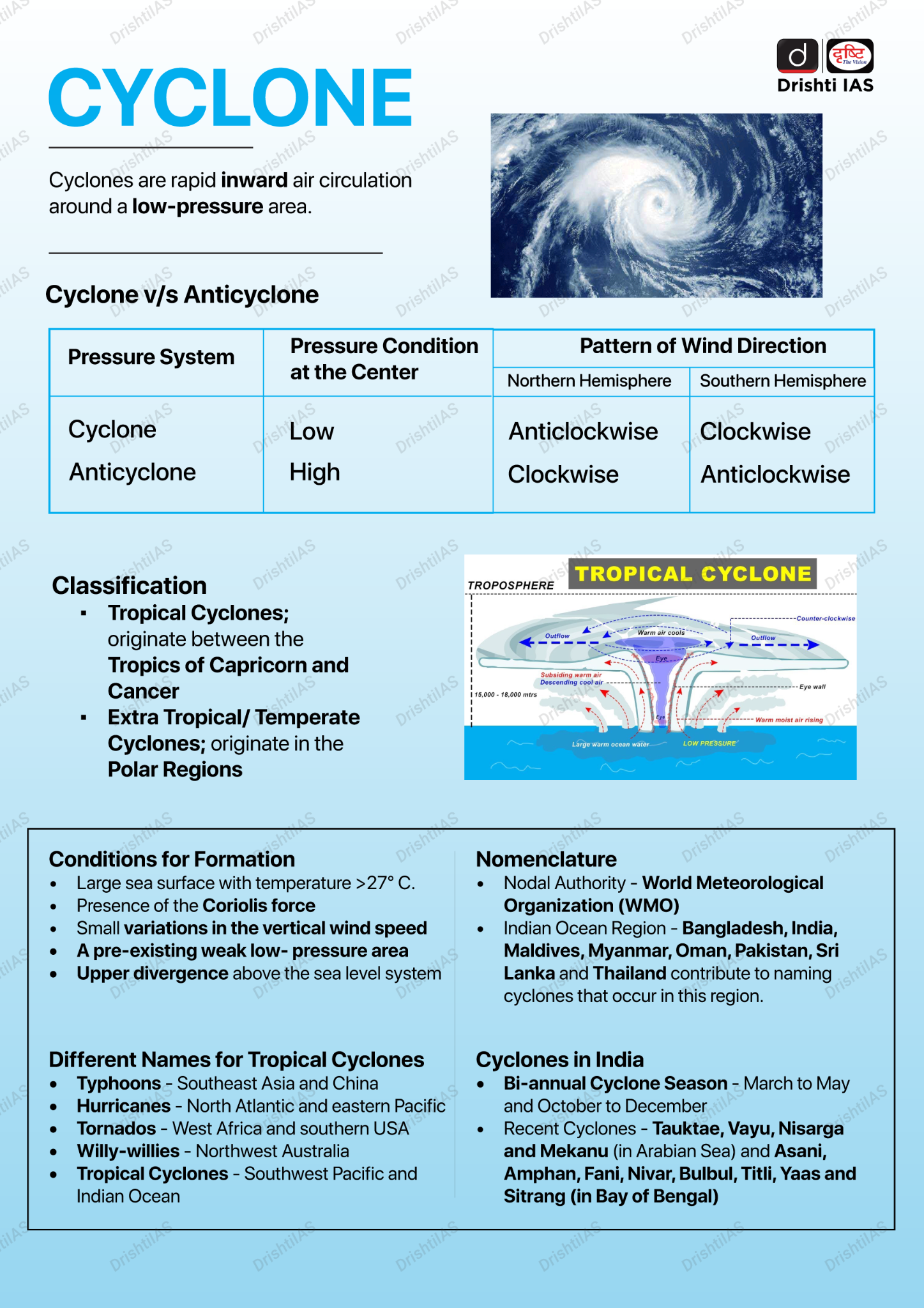
What are the Key Insights About Cyclone Remal?
- Naming: The name 'Remal' in the list of tropical cyclones is given by Oman. It will be the first cyclone to hit the region this 2024 pre-monsoon season.
- 'Remal,' meaning 'sand' in Arabic.
- Origin: Bay of Bengal (BoB).
- Factors Contributing to the Formation:
- A depression (an area of low pressure characterised by circulating winds and atmospheric instability) has formed over the central Bay of Bengal, serving as the genesis for Cyclone Remal.
- The Bay of Bengal, experiences water temperatures higher(2–3°C) warmer than average. This warm water provides the energy needed for cyclones to form and intensify.
- The Madden Julian Oscillation, a band of clouds moving eastward, along with the winds and warm ocean waters, is currently moving south of the Bay of Bengal. These winds play a role in initiating cyclones due to their rotational effect.
- Potential Impact: The cyclone may impact the Sundarbans region if the landfall happens on the Indian coast and coincides with high tide, potentially causing partial damage to the fragile ecosystem.
- The shallow bathymetry and the funnel-shaped geography of the northern Bay of Bengal can amplify the intensity of the cyclone as it approaches the coast, increasing the risk of storm surges and flooding.
- Previous Cyclones: The cyclone scare comes close to the anniversaries of previous devastating cyclones, such as Yaas (2021), Amphan (2020), Cyclone Fani( 2019), and Aila (2009) which caused massive damage in the Sundarbans and other parts of West Bengal.
- The state's disaster management authorities and local communities are drawing on the lessons learned from these past experiences to better prepare for and mitigate the potential impact of Cyclone Remal.
Note:
- The Bay of Bengal (BoB) experiences more cyclones than the Arabian Sea (A.S.) by a ratio of about 4:1. However, a 2022 study found that the frequency of cyclones in the A.S. has increased by 52% from 2001–2019, while the Bay of Bengal’s frequency has slightly decreased.
- The BoB is relatively shallower than the A.S. The larger surface area of the BoB allows faster heating causing higher evaporation. Inturn forms a high-pressure zone in the area causing instability in the region. All these factors make it suitable for cyclone formation.
- The A.S. has traditionally seen fewer cyclones due to higher salinity, lower sea surface temperatures, and disadvantageous wind systems.
- However, changes in ocean and atmosphere warming patterns are leading to more frequent and severe tropical cyclones in the Arabian Sea.
- The positive phase of the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and human-induced climate change are contributing to the intensification and higher frequency of cyclones in the Arabian Sea.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the South Atlantic and South-Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclone does not originate. What is the reason? (2015)
(a) Sea surface temperatures are low
(b) Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
(c) Coriolis force is too weak
(d) Absence of land in those regions
Ans: (b)
Ans:
- The most proximate reasons for the lack of cyclones in the South Atlantic and South Eastern Pacific ocean is the rare occurrence of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) over the region.
- It becomes very difficult or nearly impossible to have genesis of tropical cyclones, unless synoptic vorticity (it is a clockwise or counterclockwise spin in the troposphere) and convergence (i.e., large scale spin and thunderstorm activity) are provided by ITCZ.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Rapid Fire
Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC)
India's main opposition party has called for setting up a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC) to investigate claims that the Adani Group sold low-grade coal to a state-run company in Tamil Nadu, pretending it was of higher quality.
- The JPC is an ad-hoc Committee, established by the Parliament to conduct a thorough examination of a specific subject or Bill.
- It consists of members from both Houses as well as from the ruling and opposition parties and is chaired by a member of the Lok Sabha (appointed by Speaker of the Lok Sabha).
- The Parliament determines the composition of the JPC, and there is no set limit on the number of members.
- The committee is dissolved after completing its term or task.
- The committee's recommendations are advisory and not mandatory for the government to follow.
- However, suggestions by the Select Committees and JPCs — which have a majority of MPs and heads from the ruling party — are accepted more frequently.
- The JPC has the authority to gather evidence from experts, public bodies, associations, individuals, or interested parties either on its own initiative or in response to their requests.
- Some of the cases in which JPC were formed include:
- Bofors scandal (1987)
- Harshad Mehta Stock market scam (1992)
- Ketan Parekh share market scam (2001)
- National Register of Citizens (NRC, 2016)
- Personal Data Protection Bill (2019)
Read More: Parliament Committees, Select Committee Of Parliament


Rapid Fire
Explosive Substances Act and Peroxide Chemicals
A chemical explosion in a Thane (Maharashtra)-based factory, claiming 11 lives, highlights critical safety flaws. Caused by reactive peroxide chemicals, the accused have been charged under Explosive Act 1884, and Explosive Substances Act 1908.
- The Explosives Act of 1884, enacted by the British colonial government in India, regulates the manufacture, storage, possession, use, sale, import, and export of explosives. It sets safety standards for handling, transportation, and storage of explosives to prevent accidents.
- The Explosive Substances Act of 1908 encompasses provisions defining explosive substances and special category explosive substances, including notable compounds like RDX.
- The Act delineates punishments for causing explosions likely to endanger life or property, along with penalties for attempts to cause explosions or possession of explosives with malicious intent.
- Peroxide chemicals are organic compounds that contain a peroxide functional group, which is characterised by two oxygen atoms linked together.
- The general structure for peroxides can be represented as R−O−O−R, where ‘R’ can be any element. The linkage between the two oxygen atoms (O−O) is known as the peroxide group or peroxy group.
- Example: Hydrogen peroxide, Benzoyl peroxide.
- The bond in peroxides is weak, making them very reactive and allowing other chemicals to alter their structure.
- Peroxides can be hazardous and can cause fires and explosions when exposed to heat, shock, or friction.
- The general structure for peroxides can be represented as R−O−O−R, where ‘R’ can be any element. The linkage between the two oxygen atoms (O−O) is known as the peroxide group or peroxy group.
Read More: Forever Chemicals


Rapid Fire
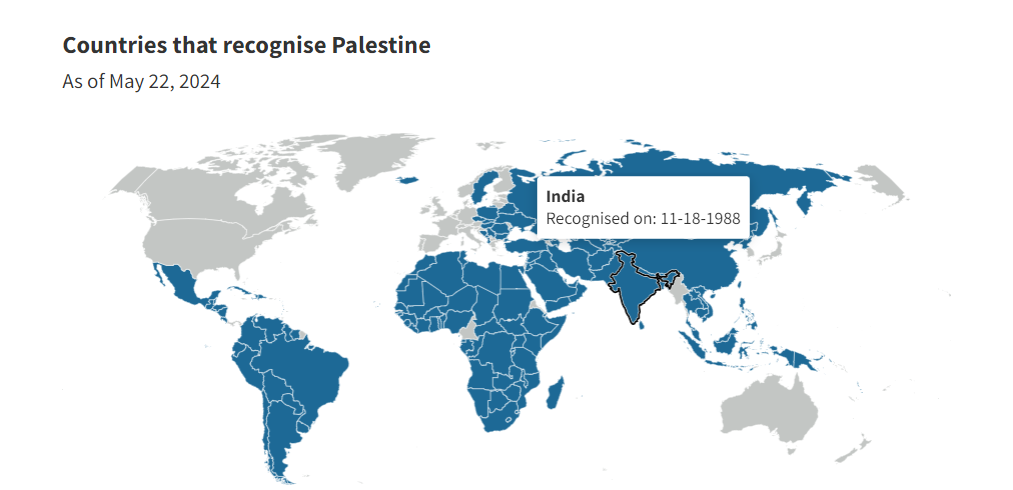
Ireland, Norway, and Spain to Recognize Palestine
Recently, Ireland, Norway, and Spain have announced that they will formally recognize the state of Palestine on 28th May 2024.
- In response, Israel ordered the immediate return of its ambassadors from Ireland, Norway, and Spain, expressing strong opposition and dissatisfaction.
- Also, recently at the United Nations General Assembly, 143 of 193 UN member countries voted in favor of granting full membership to Palestine.
- India has always supported the two-state solution and was one of the first non-Arab nations to recognise Palestine as a state in 1988.
- India has also recognised the Palestine Liberation Organization.
- India has always supported the two-state solution and was one of the first non-Arab nations to recognise Palestine as a state in 1988.
Read more: Israel-Palestine Conflict


Rapid Fire
Brain-eating Amoeba
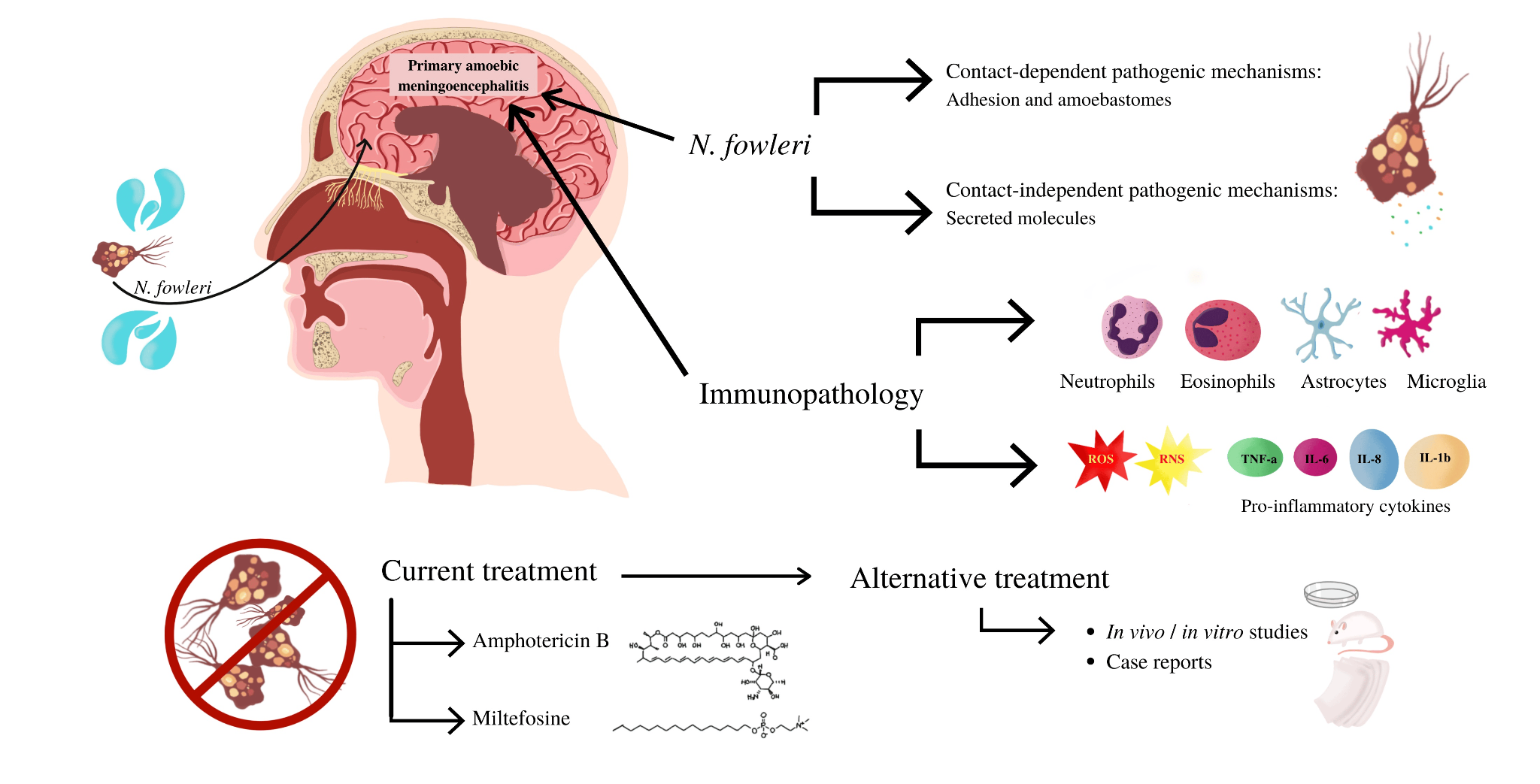
The recent death of a 5-year-old girl in Kerala due to primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) caused by the Naegleria fowleri amoeba, often referred to as the "brain-eating amoeba," has highlighted the rare yet fatal nature of this devastating infection.
- Naegleria fowleri is a free-living amoeba that thrives in warm freshwater and soil around the world.
- The amoeba enters the body through the nose, typically during activities like swimming, and then travels to the brain, where it destroys brain tissue and causes swelling.
- Symptoms: The initial symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, and vomiting, followed by a stiff neck, confusion, seizures, hallucinations, and eventually coma.
- Mortality Rate: Most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after the onset of symptoms, and the disease usually leads to coma and death within 5 days.
- Treatment Challenges: There is currently no effective treatment for PAM, and doctors rely on a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, and others, to try to manage the infection.
Read More: Naegleria fowleri: The Brain-Eating Amoeba