International Relations
RELOS and India-Russia Relation
For Prelims: The Indo-Soviet Friendship Treaty of 1971, Quad ,Indian monsoon ,(GSOMIA Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership, Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership, Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP), Agreement on the Programme for Military-Technical Cooperation, MiG-21, Su-30, Ukraine Crisis
For Mains: Strategic Significance of India-Russia Relations, Key Issues and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, the India-Russia mutual logistics agreement named the Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS) is now ready for finalisation. It will facilitate military cooperation between India and Russia, including joint exercises, training, and disaster relief efforts.
What is Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS)?
- About:
- The Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS) between India and Russia is a significant administrative arrangement that will enhance military cooperation between the two nations.
- Purpose:
- This agreement is designed to streamline military logistics support, making joint operations and long-distance missions more efficient and cost-effective for both India and Russia.
- Significance:
- Sustained Operations:
- It will facilitate the replenishment of essential supplies (fuel, rations, spare parts) thus enabling continuous, uninterrupted military presence in crucial regions.
- It will provide berthing facilities for troops, warships, and aircraft.
- It will be applicable during both wartime and peacetime missions.
- Strategic Advantages:
- It will enable smoother utilisation of the host nation's existing logistics networks. Enhances ability to respond swiftly to crises.
- It will provide a strategic edge to the military operations of both countries thereby reducing overall mission costs.
- Expanded Military Reach:
- Enhances India's maritime outreach and influence in strategically important regions.
- Boosts Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) and shared logistics facilities could enable better information exchange about maritime activities, enhancing both countries' situational awareness.
- Balancing Quad Agreements:
- RELOS balances India's logistics agreements with Quad countries and Russia's non-Quad stance.
- Strengthens Russian presence in Indo-Pacific without Quad involvement.
- It Counterbalances US influence and China's regional role for both India and Russia.
- Scientific Interconnections:
- India’s primary engagements in the Arctic are focused on understanding scientific interconnections between Arctic sea ice melting and changes in Indian monsoon systems.
- Sustained Operations:
What are India's Logistics Agreements with Various Countries?
- India and USA:
- General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA): It was signed in 2002, to facilitate sharing military intelligence between India and the USA.
- Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA), 2016: Allows mutual use of military logistics facilities.
- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA), 2020: Provides India access to U.S. geospatial intelligence data.
- Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA), 2018: Enables the transfer of encrypted communication equipment.
- India and France:
- Facilitates logistical support during joint exercises, port visits, and humanitarian efforts
- Promotes stability in the Pacific and Indian Ocean regions.
- Enables maritime intelligence sharing.
- Facilitates logistical support during joint exercises, port visits, and humanitarian efforts
- India and Australia:
- Comprehensive Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA), 2020.
- Emphasises shared vision for Indo-Pacific maritime cooperation.
- Comprehensive Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA), 2020.
- India and Japan:
- Allows Close Coordination of Services (ACSA), 2020 and supplies between armed forces.
How has the Relationship Between India and Russia Evolved?
- Historical Genesis:
- The Indo-Soviet Friendship Treaty of 1971: In the wake of the Indo-Pak war (1971), Russia supported India while the US and China supported Pakistan.
- Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership: In October 2000, India-Russia ties acquired a qualitatively new character with enhanced levels of cooperation in almost all areas of the bilateral relationship.
- Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership: During the visit of the Russian President to India in December 2010, the Strategic Partnership was elevated to the level of a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership”.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Bilateral trade has been substantial, with India's total reaching approximately USD 13 billion in 2021-22.
- Russia ranks as India’s seventh largest trading partner, a significant rise from its position in previous years.
- Political Engagement:
- Politically, both countries engage through annual meetings of two Inter-Governmental Commissions: One focused on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological, and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC) and another on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC).
- Defence and Security Relations: Both countries regularly conduct the Tri-Services exercise ‘INDRA‘.
- The joint military programs between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile program
- 5th generation fighter jet program
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 Triumf
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier program
- AK-203 Rifles
- The joint military programs between India and Russia include:
- Science and Technology:
- The partnership dates back to the early days after India's independence when Soviet assistance was pivotal in establishing institutions like the Bhilai Steel Plant and supporting India's space program.
- Today, collaboration extends to advanced fields such as nanotechnologies, quantum computing, and India’s manned spaceflight program (Gaganyaan).
What are the Key Challenges in India-Russia Relations?
- Strategic Shifts:
- Closer Ties with China: Russia seeks to avoid conflicts on two fronts (West and China).
- Increasing Sino-Russian military and economic cooperation affects India's strategic calculations.
- Improved Relations with Pakistan: It can be due to strengthening US-India ties and it complicates India's regional strategy.
- Closer Ties with China: Russia seeks to avoid conflicts on two fronts (West and China).
- India's Diplomatic Balancing Act:
- India’sgreat power calculations create the dilemma to choose between a “comprehensive global strategic partnership” with the US on one hand, and its “special and privileged partnership” with Russia on the other.
- Russia-Ukraine Crisis Response:
- India faced significant criticism in the West for refraining from condemning the Russian invasion of Ukraine and for its continued expansion of energy and economic cooperation with Moscow.
- Declining Defence Imports:
- There has been a gradual decline in the defence purchase of India from Russia because of its desire to diversify its defence imports which heightened competition for Russia.
- It will also force it to explore other potential buyers like Pakistan.
- There has been a gradual decline in the defence purchase of India from Russia because of its desire to diversify its defence imports which heightened competition for Russia.
Way Forward
- Enduring Defense Partnership: Russia is expected to remain a crucial defence partner for India in the foreseeable future, likely for several decades, due to the substantial Russian inventory in India's defence forces.
- Collaborative Export Strategy: India and Russia are exploring ways to leverage India as a manufacturing hub for Russian-origin defense equipment and services.
- The goal is to export these products to third countries, expanding their market reach.
- Examples like discussions about producing Russian Ka-226T helicopters in India for export to third countries.
- Diversification of Economic Ties: Expand cooperation beyond defense, focusing on areas like energy, technology, and space, like the ongoing partnership in the Sakhalin-1 project.
- Strategic Balancing: Maintain the 'special and privileged partnership' while balancing relations with other powers. Continue participating in forums like BRICS and SCO while also engaging with Quad nations.
- Space Collaboration: Enhance cooperation in space exploration and satellite technology. Joint missions for deep space exploration or satellite-based navigation systems.
|
Drishti Mains Questions: What is the Significance of RELOS and how does the changing global geopolitical landscape affect the dynamics of the India-Russia relationship? Suggest measures to ensure the continued positive trajectory of these bilateral ties. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: B
Mains
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)


Social Justice
High Court Struck Down Bihar 65% Quota Rule
For Prelims: Bihar Reservation Law and Breaching 50% Limit, Supreme Court (SC), Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Castes & Other Backward Classes, 77th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1995, EWS Reservation.
For Mains: Bihar Reservation Law and Breaching 50% Limit, Caste-Based Reservation and Related Issues, Government Policies and Interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Patna High Court struck down the Bihar government's decision to increase the reservation quota from 50% to 65% for Backward Classes (BC), Extremely Backward Classes (EBC), Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) in educational institutions and government jobs.
- This move by the Bihar government has raised important questions about the legal limits on reservation policies in India.
What is the Background of the High Court’s Ruling?
- Background:
- In November 2023, the Bihar government issued gazette notifications to raise the quota for deprived castes from 50% to 65%.
- This decision was taken following a caste-based survey report, which showed the need for increased representation of BC, EBC, SC and ST communities.
- The Bihar Assembly unanimously passed the Bihar Reservation Amendment Bill in November 2023 to implement this 65% quota.
- Key Arguments in Court Verdict:
- A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) was filed challenging the Bihar government's decision to increase reservations beyond 50%.
- The Patna High Court ruled that the 65% quota violated the 50% limit set by the Supreme Court in the Indira Sawhney case (1992).
- The court argued that the state government's decision was not based on "adequate representation" in government jobs, but on the proportional population of these communities.
- The court also noted that together with the 10% Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) quota, the bill has pushed total reservation to 75%, which is unconstitutional.
- Need for Extended Reservation in Bihar:
- Socio Economic Backwardness of the State:
- Bihar has the lowest per capita income in the country (below USD 800 per year), which is 30% of the national average.
- It has the highest fertility rate and only 12% of the population lives in urban areas, compared to the national average of 35%.
- The state has the lowest college density in the country and 30% of the population lives below the poverty line.
- Socio Economic Backwardness of the State:
- Inadequate Representation of Backward Classes:
- SC, STs and Backward Classes constitute 84.46% of Bihar's population, but their representation in government jobs and education was not proportionat
- Other Alternatives to Extending Reservation Limit:
- Building a Strong Foundation:
- Implement recommendations from the Right to Education (RTE) Forum to improve early childhood development (ICDS centres), enhance teacher training, and shift towards interactive and technology-integrated learning methods.
- Building a Strong Foundation:
- Skilling Bihar's Youth for the Future:
- Develop skill-building programs aligned with growing industries alongside fostering entrepreneurship through programs like the SIPB (Single-window Investment Promotion Board) to attract businesses and create a vibrant job market.
- Infrastructure for Inclusive Growth:
- Invest in improved irrigation systems to tackle floods and droughts, and develop a robust transport network connecting rural and urban areas.
- Empowering All Residents of States:
- Promote women's education, skill development, and financial inclusion to increase their participation in the workforce and achieve greater social equality. Enforce laws more strictly to tackle social stratification and promote social harmony.
Note:
- Other states having reservations above the 50% limit are Chhattisgarh (72%), Tamil Nadu (69%).
- North-eastern States including Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland (80% each).
- Lakshadweep has 100% reservations for STs.
What is the Reservation?
- About:
- Reservation is a form of positive discrimination, created to promote equality among marginalised sections and to protect them from social and historical injustice.
- It gives preferential treatment to marginalised sections of society in employment and access to education.
- It was also originally developed to correct years of discrimination and to give a boost to disadvantaged groups.
- Pros and Cons of Reservation:
|
Aspect |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Social Justice |
|
|
|
Meritocracy |
|
|
|
Representation |
|
|
|
Creamy Layer |
|
|
|
Economic Upliftment |
|
|
What are the Constitutional Provisions Related to Reservations in India?
- Part XVI of the Constitution of India deals with the reservation of SC and ST in Central and State legislatures.
- Article 15 of the Constitution empowers the State to make the following provisions:
- Article 15(3) provides special provision for women and children.
- Article 15(4) and Article 15(5) provides special provision for the advancement of any socially and educationally backward classes of citizens or for the SCs and the STs, including their admission to educational institutions, including private ones.
- Article 15(6) provides special provisions for the advancement of any Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) of citizens other than the classes mentioned in clauses (4) and (5).
- Article 16 provides for the grounds of positive discrimination or Reservation in government jobs.
- Article 16(4) provides for the reservation of appointments or posts in favour of any backward class of citizens.
- Article 16(4A) provides for reservation in promotion for Scheduled Castes (SC) and the Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- The Constitution was amended by the Constitution (77th Amendment) Act, 1995 and a new clause (4A) was inserted in Article 16 to enable the government to provide reservation in promotion.
- Later, 16(4A) was modified by the Constitution (85th Amendment) Act, 2001 to provide consequential seniority to SC and ST candidates promoted by giving reservation.
- Article 16 (4B) allows states to consider unfilled reserved vacancies from a previous year meant for SCs and STs.
- It was inserted by the 81st Constitutional Amendment Act, 2000.
- Article 16(6) provides for the reservation of appointments or posts in favour of any Economically Weaker Sections (EWS).
- Article 233T provides reservation of seats for SCs and STs in every Municipality.
- Article 243D provides reservation of seats for SCs and STs in every Panchayat.
- Article 335 of the constitution says that the claims of STs and STs shall be taken into consideration consistently with the maintenance of efficacy of the administration.
- Articles 330 and 332 provide for specific representation through the reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Parliament and in the State Legislative Assemblies respectively.
What are Developments Related to Reservations in India?
- Indra Sawhney Judgment, 1992:
- The court upheld the constitutionality of the 27% reservation for OBCs but put a ceiling of 50% unless exceptional circumstances warranted the breach so that the constitutionally guaranteed Right to Equality under Article 14 would remain secure.
- This 9-judge bench judgement held that Article 16(4) of the Constitution, which allows reservation in appointments, does not extend to promotions.
- The carry forward rule is valid but it is subject to 50%. There should be no reservation in the promotions.
- The court clarified that Article 16(4) is not a separate rule that overrides Article 16(1). Article 16(1) is a fundamental right and Article 16(4) is an enabling provision.
- Article 16(1): It states that there shall be equality of opportunity for all citizens in matters relating to employment or appointment to any office under the State.
- Further, the Court directed to exclude Creamy Layer (economically well-off) from Other Backward Classes (OBCs) from getting reservation benefits.
- However, it specifically excluded SCs and STs from this concept.
85th Amendment Act (2001)
- It introduced the concept of consequential seniority for SC/ST candidates promoted through reservations. This applied retroactively to June 1995.
- "Consequential seniority" refers to the concept of granting seniority to government servants belonging to SC and ST in cases of promotion through reservation rules.
- M. Nagaraj Judgment, 2006:
- This judgment partially overturned Indra Sawhney's judgment.
- It introduced a conditional extension of the "creamy layer" concept to SC/ST communities seeking promotions in government jobs.
- This concept was previously applied only to Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- Judgment laid down 3 conditions to allow states to provide reservations in promotions for SCs/STs.
- Inadequacy of Representation: The state must demonstrate SCs/STs are inadequately represented in promotions.
- Creamy Layer Exclusion: Reservation benefits should not extend to the "creamy layer" within SCs/STs.
- Maintain Efficiency: Reservation should not affect overall administrative efficiency.
- Jarnail Singh vs Union of India, 2018:
- In this case, the SC reversed its stance on data collection.
- States No Longer Need Quantifiable Data: The SC ruled that states no longer needed to collect quantifiable data to prove the backwardness of the SC/ST community when implementing reservation quotas for promotions.
- It allowed the government to implement "accelerated promotion with consequential seniority" for SC/ST members more easily.
103rd Constitution (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- It provides for reservation to EWS in jobs in central government jobs as well as government educational institutions.
- It was introduced by amending Articles 15 and 16 and inserted Article 15 (6) and Article 16 (6).
- It was enacted to promote the welfare of the poor not covered by the 50% reservation policy for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC).
- It enables both the Centre and the States to provide reservations to the EWS of society
- Janhit Abhiyan v. Union of India, 2022:
- It challenged the 103rd Constitutional Amendment. In a 3-2 verdict, the Court upheld the amendment.
- It allowed the government to provide reservation benefits based on economic standing, alongside existing reservations for disadvantaged social groups.
Way Forward
- Focus on Merit with Relaxation: Promoting a system that emphasises merit while allowing for some relaxation in qualifying marks for SC/ST/OBC candidates in promotions, ensuring that qualified candidates from these communities have a better chance while maintaining an acceptable competency level.
- Data-Driven Approach: It is needed to assess the current representation of SC/ST/OBCs across different levels and departments. This data can be used to establish concrete targets for filling reservation quotas.
- Addressing Concerns: Acknowledge concerns about unqualified candidates getting promoted due to reservations.
- Propose solutions like rigorous training and mentorship programs for promoted SC/ST/OBC employees to bridge any skill gaps and ensure they excel in their new roles.
- Long-Term Vision: Emphasise that reservations are a temporary measure to achieve long-term social justice and equal opportunity in promotions.
- Advocate for parallel initiatives that improve education and access to resources for these communities, ultimately leading to a situation where reservations may not be necessary.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyse the role of the reservation policy in promoting social justice and equality, as well as its challenges and limitations. Suggest measures to make the system more effective and equitable. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2009)
- Between Census 1951 and Census 2001, the density of the population of India has increased more than three times.
- Between Census 1951 and Census 2001, the annual growth rate (exponential) of the population of India has doubled.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The Constitution of India defines its ‘basic structure’ in terms of federalism, secularism, fundamental rights and democracy.
- The Constitution of India provides for ‘judicial review’ to safeguard the citizens’ liberties and to preserve the ideals on which the Constitution is based.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. Which of the following are regarded as the main features of the “Rule of Law”? (2018)
- Limitation of powers
- Equality before law
- People’s responsibility to the Government
- Liberty and civil rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Whether the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) can enforce the implementation of constitutional reservation for the Scheduled Castes in the religious minority institutions? Examine. (2018)


International Relations
India-Sri Lanka Relations
For Prelims: Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC), India Sri Lanka Relations, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Buddhism, Renewable energy, Indian Ocean.
For Mains: India Sri Lanka Relations, Bilateral, regional, and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian External Affairs Minister met with the Sri Lankan President to discuss bilateral cooperation in various sectors, including power, energy, connectivity, port infrastructure, aviation, etc.
What are the Recent Developments in India-Sri Lanka Relations?
- Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC): They jointly commissioned MRCC built with a USD 6 million grant from India.
- This includes a centre at Navy Headquarters in Colombo, a sub-centre in Hambantota and unmanned installations at Galle.
- The launch of MRCC is part of the broader initiative under the Colombo Security Conclave, which includes India, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and Mauritius, with Bangladesh and the Seychelles as observers.
- Model Village Housing Project: Both leaders virtually handed over houses constructed under the Model Village Housing Project and Indian Housing Project, with funding from India.
- Energy Sector Initiatives: A plan for an LNG supply, a proposed petroleum pipeline linking the two countries, and advancing oil and gas exploration projects were also discussed.
- The construction of the Sampur Solar Power Plant was also announced.
- Other Developments: Discussions were also held on projects aimed at developing Trincomalee and expanding the Kankesanthurai port, and bolstering Sri Lanka’s liquid milk industry and fertilizer production.
How have Relations Between India and Sri Lanka Been?
- Historical Ties: India and Sri Lanka share deep historical connections through culture, religion, and trade, with many Sri Lankans having Indian roots and Buddhism playing a significant role in both countries.
- Economic Ties:
- Financial Assistance from India: India gave about USD 4 billion in aid to help Sri Lanka through its worst financial crisis since independence in 1948, caused by a severe lack of foreign exchange reserves in 2022.
- India was the first to offer support to Sri Lanka for its debt restructuring, working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and creditors.
- Economic and Technology Cooperation Agreement (ETCA): Both countries are exploring the possibility of an ETCA to integrate their economies and foster development.
- Adoption of India's UPI: Sri Lanka has adopted India's UPI service, which is a significant step towards enhancing fintech connectivity between the two countries.
- The use of the rupee for trade settlement is further helping Sri Lanka’s economy.
- Trade: India is Sri Lanka’s third largest export destination, after the US and UK. More than 60% of Sri Lanka’s exports enjoy the benefits of the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement. India is also a major investor in Sri Lanka.
- Financial Assistance from India: India gave about USD 4 billion in aid to help Sri Lanka through its worst financial crisis since independence in 1948, caused by a severe lack of foreign exchange reserves in 2022.
- Participation in Groupings: Sri Lanka is also a member of groupings like BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) and SAARC in which India plays a leading role.
- Tourism: In 2022, India was the largest source of tourists for Sri Lanka with over 100,000 tourists.
What is the Significance of India and Sri Lanka Relations?
- Focus on Regional Development: India's progress is intricately linked with its neighbouring nations, and Sri Lanka aims to enhance its own growth by integrating with the Southern economy, in South Asia.
- The external Affairs Minister also reaffirmed India’s commitment to its 'Neighbourhood First' Policy, emphasising the importance of Sri Lanka as India's closest maritime neighbour.
- Strategic Location: Sri Lanka, positioned near India's southern coast across the Palk Strait, holds a crucial role in the relationship between the two nations as it is at the crossroads of major shipping lanes making it a critical point of control for India.
- Ease of Doing Business & Tourism: The enhancement of digital payment systems across the two nations will promote economic integration and simplify business transactions between India and Sri Lanka.
- This advancement will not only streamline trade but also improve connectivity for tourism exchanges between the two nations.
Ban on LTTE
- The Indian government has banned the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act 1967.
- The Tamil Nadu Government has also banned it in May 2024 stating that despite their 2009 defeat, the group still pursued their goal of 'Eelam'.
- LTTE was formed in 1976 as the self-styled "national freedom movement of the people of Tamil Eelam" and began a guerilla war on the government and administration.
- It undertook numerous terrorist activities in Srilanka especially against the Sinhalese and executed the assassination of Rajiv Gandhi (the ex Prime Minister of India).
- After a long strife, and millions of casualties, the civil war with LTTE ended in 2009.
What are the Challenges in India-Sri Lanka Relations?
- Tamil Ethnic Issue: India has historically been concerned about the welfare and rights of the Tamil community in Sri Lanka particularly the implementation of the 13th Amendment in its true spirit.
- The 13th Amendment, which led to the creation of Provincial Councils, assured a power-sharing arrangement to enable all nine provinces in the country, including Sinhala majority areas, to self-govern.
- China's Influence: India has concerns about China's investment in Sri Lanka like Hambantota Port due to its proximity.
- Fisheries Dispute: Issues of illegal fishing and arrest of fishermen by both countries on maritime boundaries often led to diplomatic tussles.
- Katchatheevu Island Dispute: The issue revolves around the ownership and usage rights of the uninhabited island of Katchatheevu, located in the Palk Strait between India and Sri Lanka, imposing restrictions on fishing activities without explicit permission.
- Border Security and Smuggling: The porous maritime boundary between India and Sri Lanka has led to issues of border security and the smuggling of goods, including narcotics and illegal immigrants.
Way Forward
- Truth and Reconciliation Commission: India could support the establishment of a truth and reconciliation commission in Sri Lanka to address the legacy of the civil war and promote healing for the Tamil community.
- Joint Maritime Patrols and Training: India and Sri Lanka can enhance cooperation on maritime security by conducting joint patrols in the Indian Ocean region and providing training programs for Sri Lankan coast guard personnel.
- People-to-People Ties: Promote cultural exchange programs, and tourism to foster closer ties between the citizens of both countries.
- Joint Infrastructure Projects: India can invest in infrastructure projects in Sri Lanka while ensuring that the project progresses smoothly from the planning phase to execution.
- Economic and Trade Cooperation Agreement (ETCA) Implementation: Both countries can work towards a swift and smooth implementation of the ETCA to reduce trade barriers, and boost bilateral trade.
- Student Exchange Programs and Skill Development Initiatives: Establish scholarship programs for Sri Lankan students and collaborate on skill development initiatives.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the major challenges in India-Sri Lanka relations. How can both countries work together to overcome these challenges? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Elephant Pass, sometimes seen in the news, is mentioned in the context of the affairs of which one of the following? (2009)
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) Nepal
(d) Sri Lanka
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. ‘India is an age-old friend of Sri Lanka.’ Discuss India's role in the recent crisis in Sri Lanka in the light of the preceding statement. (2022)
Q. In respect of India-Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)


Governance
Reforming Examination System in India
For Prelims: Rethinking India's Examination System, New Education Policy 2020, Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024, UGC, NTA.
For Mains: Rethinking India's Examination System, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education abruptly cancelled the June 2024 edition of the UGC-NET exam. Additionally, there were allegations regarding the fairness of the NEET-UG exam, citing a potential compromise of its integrity and fairness.
- This has led the government to pass the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 as a measure to curb illegal practices in exams.
Note
- NET UGC Exam:
- The University Grants Commission National Eligibility Test (UGC-NET) exam is conducted to fill positions of Junior Research Fellowship and Assistant Professor in Indian universities and colleges.
- It is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) twice every year (June & December).
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament in 1956. It came into existence on 28th December 1953.
- It aims for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of teaching, examination and research in university education.
- NEET UG:
- National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (Undergraduate) or NEET, formerly the All India Pre-Medical Test, is an entrance examination for admission in undergraduate medical programs (MBBS and BDS courses) in India.
- It is conducted by the NTA.
What is the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024?
- About:
- The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 is law passed in the Lok Sabha aimed at addressing the issue of malpractices in government recruitment examinations. It came into effect on 21st June 2024.
- Key Features:
- It defines various offences related to unfair means, such as paper leaks, the use of fake websites, and collusion with service providers.
- It prescribes strict penalties, including a minimum jail term of 3-5 years and a fine up to Rs. 1 crore.
- It holds service providers engaged for exam conduct liable with fines up to Rs 1 crore and a 4-year ban on their involvement in public exams.
- It empowers police officers not below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police or Assistant Commissioner of Police to investigate offences under the Act.
- It will cover a wide range of central government recruitment exams, including those conducted by UPSC, SSC, RRBs, IBPS, and NTA.
- Punishable Offences Defined in the Act:
- Leakage of question paper or answer key
- Directly or indirectly assisting candidates in an unauthorised manner
- Tampering with computer networks, resources, or systems
- Creation of fake websites to cheat or for monetary gain
- Conduct of fake examinations, issuance of fake admit cards or offer letters
- Manipulation of seating arrangements, and allocation of dates and shifts to facilitate unfair means.
- Need for Act:
- Public exams are currently vulnerable to cheating and disruptions, affecting millions of students.
- There's no strong legal framework to deter individuals or groups involved in exam malpractice.
- This bill aims to establish transparency, fairness, and trust in the public examination system.
What are the Issues Related to the Existing Examination System in India?
- Declining Credibility: Lack of credibility and consistency in exams by different boards and universities leads to frequent scandals such as paper leaks, cheating, and fake degrees, eroding public trust.
- Employers often conduct separate assessments of candidates, disregarding university/board certificates.
- More Theoretical in Nature: The current education system focuses heavily on theoretical knowledge and memorisation of facts through textbooks.
- This can lead to graduates who are well-versed in theory but lack the practical skills needed to succeed in their professions.
- Subjectivity: The examiner's biases can influence question phrasing, students answer based on their own understanding, and different graders may award varying marks for the same response.
- This subjectivity creates an unfair and inconsistent evaluation process for students.
- Stifling Creativity and Critical Thinking: The pressure to perform well in standardized tests often discourages students from asking questions, exploring diverse perspectives, or developing critical thinking skills.
- A curriculum focused on rote learning leaves little room for creativity and intellectual curiosity, hindering innovation and problem-solving abilities.
- Impact on Employability: Employers prioritise their evaluations over institutional certifications when assessing candidates, placing importance on higher-order learning for employability.
- This has led to a growing market for coaching for competitive exams and skill development.
What are the Initiatives to Reform the Education System?
What Steps Can Be Taken to Address the Challenges in the Examination System?
- Focus on Understanding and Analytical Ability: Examinations should assess students' comprehension and analytical skills.
- Question papers should include various forms of questions to evaluate different abilities in line with the instructional objectives of each course.
- Memory-based questions should be minimised to encourage deeper learning.
- Subject and Skill-Specific Assessments: Incorporate subject-specific and skill-specific assessments for a comprehensive evaluation of students' learning achievements. Advocate for challenging assessments that distinguish students based on their academic attainments.
- Proper importance should be given to practical components of the curriculum. Practical exams should be designed to assess students' hands-on skills and application of theoretical knowledge.
- Prevent Cheating: Strict measures such as installing CCTV cameras, appointing vigilant invigilators, and providing adequate guidance to students on avoiding unfair means should be implemented to curb cheating.
- Examination centers that fail to prevent cheating should be penalised or cancelled.
- Examinations as a Means, Not an End: The primary purpose of examinations should be to facilitate learning and help students achieve educational objectives. Examinations should not be treated as the final goal but as a tool to promote continuous learning and improvement.
- Leverage Technology for Credibility: Utilise technology in assessments to enhance credibility, standardising question papers and evaluations. Explore market-available software solutions for both centralized and distributed assessment systems.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically examine the challenges posed by exam paper leaks and the shortcomings of the current examination system in India. Suggest strategies for reforming the examination system, aligning it with the objectives of the National Education Policy 2020. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)


Important Facts For Prelims
National Green Hydrogen Mission
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) has increased the yearly allocation of Green Ammonia for the fertiliser sector from 550,000 to 750,000 tonnes to meet rising demand, enhancing support for Green Hydrogen in India.
What is the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM)?
- India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) in January 2023.
- The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) is implementing the NGHM with a target to achieve a production capacity of 5 million tonnes per annum of Green Hydrogen in the country by the year 2030.
- The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme, under NGHM, provides incentives for the manufacturing of electrolysers and the production of green ammonia.
- Under NGHM a dedicated portal was launched to provide information on the mission and steps for developing the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
- India has also released scheme guidelines for the use of Green Hydrogen in steel, transport, and shipping sectors.
- The Department of Science and Technology has initiated Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters to foster innovation and promote the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
Other Initiatives Related to Renewable Energy
What is Green Ammonia?
- About:
- Ammonia is a chemical that is used mainly in the manufacture of nitrogenous fertilisers, like urea and ammonium nitrate, but can be put to other uses too, such as to run engines.
- Green ammonia production is where the process of making ammonia is 100% renewable and carbon-free.
- Method of Production:
- It is produced by using hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air. These are then fed into the Haber process, all powered by sustainable electricity.
- Green ammonia production makes use of renewable energy sources such as hydroelectric, solar power or wind turbines.
- In the Haber process, hydrogen and nitrogen are reacted together at high temperatures and pressures to produce ammonia (NH3).
- It is produced by using hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air. These are then fed into the Haber process, all powered by sustainable electricity.
- Uses:
- Energy Storage: Ammonia is easily stored in bulk as a liquid at modest pressures (10-15 bar) or refrigerated to -33°C. This makes it an ideal chemical store for renewable energy.
- Zero-carbon Fuel: Ammonia can be burnt in an engine or used in a fuel cell to produce electricity. When used, ammonia’s only by-products are water and nitrogen.
- Marine Industry: The maritime industry is likely to be an early adopter, replacing the use of fuel oil in marine engines.
- Significance:
- Green ammonia is intended to be used in the production of carbon-neutral fertiliser products, decarbonizing the food value chain, and also has potential as a future climate-neutral shipping fuel.
- Green ammonia is crucial to tackling the existential challenges of producing enough food to feed a growing global population and generating CO2-free energy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce one of the following as “exhaust” (2010)
(a) NH3
(b) CH4
(c) H2O
(d) H2O2
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved the proposal of the Ministry of Home Affairs for the Central Sector Scheme "National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme (NFIES)".
What is the National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme?
- About:
- This scheme aims to enhance forensic infrastructure across the country by establishing off-campus laboratories of the National Forensic Sciences University in 28 States and all Union Territories.
- Outlay and Duration:
- The scheme has a total financial outlay of Rs. 2,254.43 crore during the period from 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- Components:
- Establishment of Campuses of the National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) across the country.
- Establishment of Central Forensic Science Laboratories in the country.
- Enhancement of existing infrastructure of the Delhi Campus of the NFSU.
- Key Objectives:
- It aims to address the shortage of trained forensic manpower, strengthening the capacity and capabilities of the National Forensic Sciences University.
- The establishment of new Central Forensic Science Laboratories across the country is intended to alleviate the caseload and pendency in the existing forensic laboratories.
- With the enactment of the New Criminal Laws, which mandates forensic investigation for offences involving punishment of 7 years or more, a significant increase in the workload of forensic science laboratories is expected.
- High-quality, trained forensic professionals are expected to contribute to an efficient criminal justice process, leveraging advancements in technology and evolving crime patterns.
- The scheme is intended to support the government's objective of achieving a high conviction rate of more than 90%.
New Criminal Laws in India
- The new criminal laws in India are set to take effect on 1st July 2024. These laws will replace the existing colonial-era legislation.
- The Indian Penal Code (IPC) will be replaced by the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS).
- The Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) will be replaced by the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS).
- The Indian Evidence Act will be replaced by the Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA).
National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU)
- It is the world's first and only university dedicated to forensic sciences.
- It was established in 2009 as Gujarat Forensic Sciences University and was later renamed to NFSU in 2020.
- The university was set up to train professionals in forensic science and is now an institution of national importance under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Its main campus is located in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Forensic Science
- Forensic science is the use of scientific methods or expertise to investigate crimes or examine evidence that might be presented in a court of law.
- It comprises a diverse array of disciplines, from fingerprint and DNA analysis to anthropology and wildlife forensics.
- It is a critical element of the criminal justice system.
- Forensic scientists examine and analyse evidence from crime scenes and elsewhere to develop objective findings that can assist in the investigation and prosecution of perpetrators of crime or absolve an innocent person from suspicion.
Read more: Criminal Justice System, National Forensic Science University
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In addition to fingerprint scanning, which of the following can be used in the biometric identification of a person? (2014)
- Iris scanning
- Retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
US to Train Indian Astronauts at NASA
NASA has stated that it will increase cooperation with India, which will involve a joint project on the International Space Station (ISS) that includes an Indian astronaut.
- The two countries have concluded a Strategic Framework for Human Spaceflight Cooperation, which will involve advanced training for ISRO astronauts at NASA's Johnson Space Center.
- Both countries are also exploring opportunities for India's participation in the Lunar Gateway Programme, which is part of the collaborative Artemis programme led by the US.
- The U.S. and India are also preparing for the launch of the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR), a jointly developed satellite that will map the entirety of the Earth's surface twice every 12 days as part of efforts to combat climate change.
- The India-US initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET) was launched in May 2022 to forge greater collaboration between the two countries in areas of critical technologies such as artificial intelligence, semiconductor, critical minerals, advanced telecommunication and defence space.
- The iCET Dialogue was held on 17th June 2024, in New Delhi in which the US Space Force partnered with Indian startups 114ai and 3rdiTech.


Rapid Fire
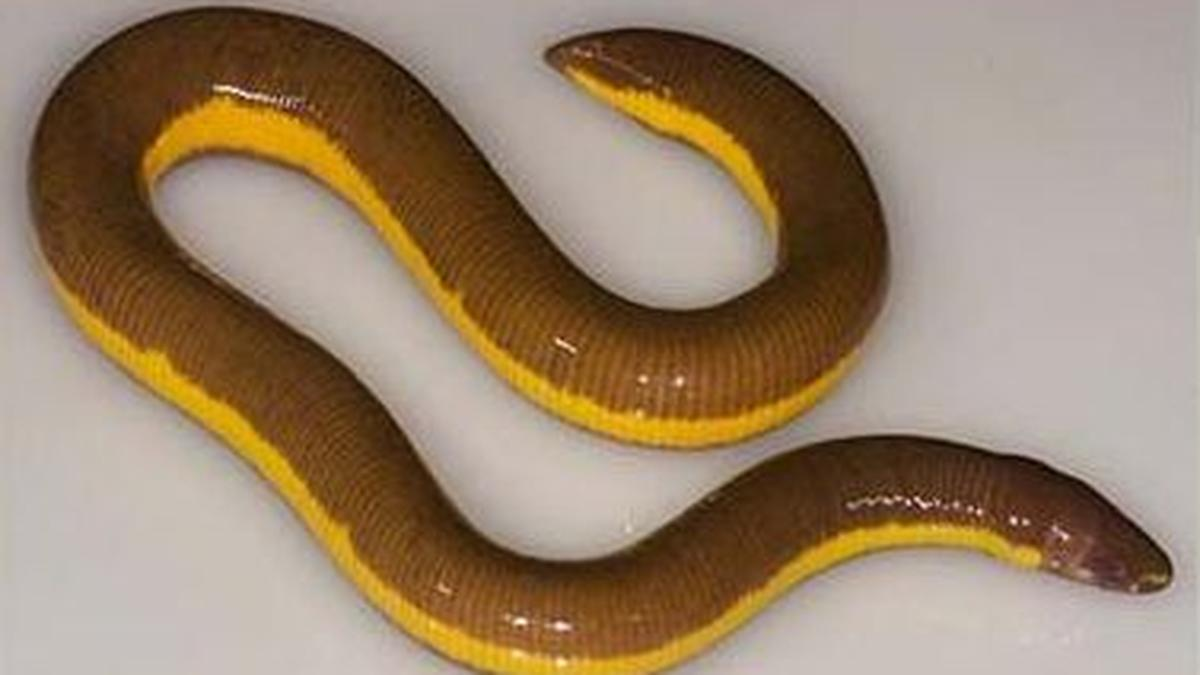
Striped Caecilian
Recently, a limbless amphibian called the Striped Caecilian (Ichthyophis spp) has been discovered for the first time in the Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve, during a rapid herpetofauna survey.
- Reptiles and amphibians are collectively called herpetofauna. Caecilians belong to the family of Ichthyophiidae.
- It is characterised by its worm-like body. They have a limited sense of vision and primarily rely on touch and smell to navigate their environment.
- They spend most of their lives burrowed under soil and are carnivorous.
- Their presence provides critical insights into the evolution and intercontinental speciation due to their ancient lineage.
- They are indicator species for the environment and play a crucial role in controlling pests.
Kaziranga National Park:
- Located between the Brahmaputra River and the Karbi (Mikir) Hills.
- It was declared as a National Park in 1974, and a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1985.
- “Big 5” Species: Rhinoceros, Tiger, Elephant, Wild Water Buffalo, and Swamp deer.
- Major vegetation types: Alluvial inundated grasslands, Tropical wet evergreen forests and Tropical semi-evergreen forests.
Read more: Kaziranga National Park, Amphibians Threatened by Climate Change


Rapid Fire
Odisha Extended Hockey Sponsorship
Recently, the Odisha government decided to extend its hockey sponsorship until 2036, which marks the centenary of Odisha's formation as a state in 1936.
- The Odisha Mining Corporation Ltd (OMC), initially committed to sponsoring Hockey India from 2018 to 2023, later extended to 2033.
- Now, the Odisha government has added three more years to this commitment, stretching it until 2036.
- This new end date aligns with the 2036 Olympic games year.
- OMC is a wholly owned government corporation in Odisha that was established in 1956.
- Odisha Chief Minister inaugurated Birsa Munda Hockey Stadium, one of the largest hockey stadiums in Rourkela on 5th January 2023.
- On 29th August, India observes National Sports Day to commemorate the birth anniversary of hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.


Rapid Fire
Digital Payments Intelligence Platform
The RBI has formed a committee chaired by A.P. Hota to explore a proposal to set up a Digital Payments Intelligence Platform that will harness advanced technologies to mitigate payment fraud risks.
- Domestic payment frauds surged by 70.64% to Rs 2,604 crore in the six months ending March 2024, with the number of cases rising to 15.51 lakh from 11.5 lakh.
Other Proposals:
- Bulk Deposits Limit Raised: The RBI also plans to increase the threshold for bulk deposits from Rs 2 crore to Rs 3 crore for commercial banks and small finance banks, with local area banks set at Rs 1 crore.
- It also allows banks flexibility in setting interest rates based on their needs and Asset-Liability Management (ALM) projections.
- Automatic e-Mandate: The RBI plans to allow automatic balance replenishment for Fastag and NCMC under the e-mandate framework, exempting the need for a 24-hour pre-debit notification.
- UPI Lite e-Mandate: The RBI plans to integrate UPI Lite into the e-mandate framework, enabling automatic reloads of the wallet when its balance drops below a user-set threshold, eliminating the need for extra authentication or pre-debit notifications.
- Export-Import Norms: The Reserve Bank plans to update rules for exporting and importing goods and services to streamline procedures and make business easier for everyone involved.