Infographics
Biodiversity & Environment
Rising Methane Levels and the Threat to Climate Stability
For Prelims: Termination-Level Transition, Methane, Greenhouse Gas
For Mains: Impacts of methane emissions on global warming, Role of hydrocarbons in termination-level transition
Why in News?
The surge in methane levels in Earth's atmosphere has raised concerns about the planet's ongoing climate transition.
- As methane, a potent greenhouse gas, gains momentum in its growth, it raises questions about whether Earth is undergoing a 'termination-level transition' similar to past climate shifts.
What is Termination-Level Transition?
- The concept of a "termination-level transition" refers to a significant and abrupt shift in Earth's climate from one state to another.
- These transitions are marked by rapid and substantial changes in various climatic factors, which can have far-reaching consequences for the planet's ecosystems, weather patterns, and overall environmental stability.
- Earth's climate has undergone termination-level transitions throughout its history.
- These transitions are often associated with the end of ice ages (It was during the Pleistocene, epoch spanning from approximately 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, which witnessed the most recent instances of global cooling, or ice ages) and the subsequent shift to warmer interglacial periods.
- Various factors, including changes in ocean currents, and atmospheric composition, can trigger termination-level transitions.
How Does Methane Threaten Warming Limits?
- Potency of Methane as a Greenhouse Gas:
- Methane is much more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide(CO₂).
- It has a shorter atmospheric lifespan of less than a decade compared to CO₂'s centuries.
- While present in smaller quantities than CO₂, methane's heat-trapping capacity is approximately 28-36 times stronger over a 100-year period.
- Methane was about 0.7 parts per million (ppm) in the air before humans began burning fossil fuels. Now it is over 1.9 ppm and rising fast.
- This enhanced warming potential intensifies its impact on the greenhouse effect.
- Challenges in Limiting Warming:
- The rapid increase in methane levels complicates efforts to limit global warming to safe levels.
- Elevated methane concentrations contribute to the overall greenhouse gas effect, exacerbating temperature rise.
- Rising methane levels can push the planet closer to dangerous temperature thresholds.
- Warming caused by methane can lead to further methane release from thawing permafrost and melting Arctic ice, amplifying its warming effects.
- Effects on Ecosystems:
- The increased methane concentrations can impact ecosystems, disrupt natural processes, and affect biodiversity.
- Vulnerable ecosystems, such as wetlands, are particularly sensitive to methane-related changes.
- Implications for Sea-Level Rise:
- Elevated methane levels can contribute to sea-level rise by accelerating the melting of polar ice and glaciers.
- Sea-level rise threatens coastal communities and exacerbates the impacts of climate change.
Methane
- Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
- It is flammable and is used as a fuel worldwide.
- Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas.
- Methane has more than 80 times the warming power of carbon dioxide over the first 20 years of its lifetime in the atmosphere.
- Roughly three-fifths of methane emissions come from fossil fuel use, farming, landfills and waste. The remainder is from natural sources, especially vegetation rotting in tropical and northern wetlands.
What are the Initiatives to Tackle Methane Emissions?
- Indian:
- ‘Harit Dhara’ (HD): Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has developed an anti-methanogenic feed supplement ‘Harit Dhara’ (HD), which can cut down cattle methane emissions by 17-20% and can also result in higher milk production.
- India Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Program: The India GHG Program led by WRI India (non-profit organization), Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) is an industry-led voluntary framework to measure and manage greenhouse gas emissions.
- The programme builds comprehensive measurement and management strategies to reduce emissions and drive more profitable, competitive and sustainable businesses and organisations in India.
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): NAPCC was launched in 2008 which aims at creating awareness among the representatives of the public, different agencies of the government, scientists, industry and the communities on the threat posed by climate change and the steps to counter it.
- Bharat Stage-VI Norms: India shifted from Bharat Stage-IV (BS-IV) to Bharat Stage-VI (BS-VI) emission norms.
- Global:
- Methane Alert and Response System (MARS): MARS will integrate data from a large number of existing and future satellites that have the ability to detect methane emission events anywhere in the world, send out notifications to the relevant stakeholders to act on it.
- Global Methane Pledge: At the Glasgow climate conference (UNFCCC COP 26) in 2021, nearly 100 countries had come together in a voluntary pledge, referred to as the Global Methane Pledge, to cut methane emissions by at least 30% by 2030 from the 2020 levels.
- India is not a part of the Global Methane Pledge.
- Global Methane Initiative (GMI): It is an international public-private partnership focused on reducing barriers to the recovery and use of methane as a clean energy source.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid that consists of a methane molecule surrounded by a cage of interlocking water molecules. It is an “ice” that only occurs naturally in subsurface deposits where temperature and pressure conditions are favourable for its formation.
- Regions with suitable temperature and pressure conditions for the formation and stability of methane hydrate– sediment and sedimentary rock units below the Arctic permafrost, sedimentary deposits along continental margins, deep-water sediments of inland lakes and seas, and, under Antarctic ice. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Methane hydrates, the sensitive sediments, can rapidly dissociate with an increase in temperature or a decrease in pressure. The dissociation produces free methane and water, which can be triggered by global warming. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Methane is removed from the atmosphere in about 9 to 12 year period by oxidation reaction where it is converted into Carbon Dioxide. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Q2. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)


Biodiversity & Environment
Unveiling California's Past Extinction to Illuminate Modern Challenges
For Prelims: Forestfires, Pleistocene Epoch, La Brea Tar Pits , Holocene Epoch, Geological Time Scale, Mammoths, Giant bears, Dire wolves, Camels.
For Mains: Priorities to Prevent Future Mass Extinctions
Why in News?
As the prevalence of deadly wildfires has surged, driven by the combined forces of human-caused climate change and disruptive land management practices, a new study delves into California's history during the Pleistocene epoch, a time marked by profound climatic shifts and Earth's largest extinction event in over 60 million years.
What is the Pleistocene Epoch?
- It is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations.
- It was during the Pleistocene that the most recent episodes of global cooling, or ice ages, took place.
- The epoch featured ice age giants, such as woolly mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) giant bears, dire wolves and camels, many of which disappeared at the end of the Pleistocene in a major extinction event.
- The extinction resulted in substantial losses, North America lost over 70% of mammals weighing more than 97 pounds, South America lost over 80%, and Australia nearly 90%.
- The end of the Pleistocene epoch also marks the beginning of the Holocene epoch, which is the current epoch we are living in.
What are the Major Highlights of the Study?
- Revealing Insights from the La Brea Tar Pits: La Brea Tar Pits is a prolific ice age fossil site in Los Angeles,US home to preserved remains of thousands of large mammals trapped in asphalt seeps.
- By analyzing proteins in the fossils, the study reveals a deadly combination of a warming climate marked by prolonged droughts and rapid human population growth.
- These factors pushed Southern California's ecosystem to a tipping point, causing irreversible changes in vegetation and mega-mammal populations.
- As California warmed coming out of the last ice age, the landscape became drier and forests receded.
- At La Brea, herbivore populations also declined, probably from a combination of human hunting and habitat loss. Species associated with trees, like camels, disappeared entirely.
- By analyzing proteins in the fossils, the study reveals a deadly combination of a warming climate marked by prolonged droughts and rapid human population growth.
- A New Paradigm: Fire's Role: The study highlights that fire is a relatively recent phenomenon in Southern California, with fire becoming frequent only after human arrival.
- Over 90% of wildfires in coastal California are ignited by human activities such as downed power lines and campfires.
- Parallels between Pleistocene extinctions and contemporary crises underscore the vulnerability of ecosystems under compounded stress.
- Relevance for Today's Climate and Biodiversity Crisis: Today's convergence of climate warming, human population expansion, biodiversity loss, and human-triggered fires mirrors the past.
- The pace of current temperature rise, primarily fueled by fossil fuel burning, far surpasses that of the ice age's end.
- The study underscores the need to intensify efforts to curtail greenhouse gas emissions, prevent reckless fire ignitions, and safeguard megafauna.
What is the Geological Time Scale?
- The Geological Time Scale is like a vast timeline that helps us understand the history of our planet.
- Just as a calendar breaks down years, months, and days, the Geological Time Scale breaks down Earth's history into eons, eras, periods, and epochs.
- Eons are divided into Eras, Eras into Periods, Periods into Epochs, and Epochs into Ages.
What Should be the Priorities to Prevent Future Mass Extinctions?
- Holistic Ecosystem Restoration and Preservation:
- Innovative Ecosystem Mapping: Develop advanced mapping technologies to assess ecosystem health and identify critical areas for restoration.
- Bio-corridor Creation: Establish ecological corridors to connect fragmented habitats, enabling species to migrate and thrive across diverse environments.
- Preemptive Conservation: Prioritize conservation of keystone species to maintain the ecological balance crucial for long-term ecosystem resilience.
- Synthetic Biology for Species Resilience:
- Genetic Augmentation: Employ synthetic biology techniques to enhance genetic diversity within vulnerable species, bolstering their adaptability to changing conditions.
- Assisted Evolution: Proactively guide species adaptation through controlled interventions, accelerating their response to environmental shifts.
- Ethical Considerations: Forge a global ethical framework to guide the responsible use of synthetic biology in conservation efforts.
- Green Innovation for Sustainable Resource Utilization:
- Circular Economies: Promote circular economies to minimize resource depletion and waste, thereby reducing stress on ecosystems.
- Biomimicry and Sustainable Design: Harness nature-inspired designs to develop eco-friendly products, reducing environmental impacts across industries.
- Green Infrastructure: Invest in sustainable infrastructure that reduces habitat destruction, such as wildlife-friendly roadways and energy installations.
- Data-Driven Conservation Management
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize machine learning and AI to model ecosystem dynamics, enabling timely interventions to prevent disruptions.
- Real-time Monitoring: Implement remote sensors and satellite technology for real-time monitoring of ecosystems and early detection of stressors.
- There is a need to establish interconnected data-sharing networks to facilitate collaborative conservation efforts across borders.
- Youth and Community Empowerment:
- Environmental Education Reform: Revamp educational curricula to foster a deep understanding of biodiversity's importance and instill a sense of stewardship from an early age.
- Youth-Driven Initiatives: Encourage youth-led conservation projects and platforms to amplify their influence and involvement in shaping policies.
- Cultural Integration: Integrate indigenous and local knowledge systems into conservation strategies, promoting community ownership and sustainable practices.


Indian Economy
Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit
For Prelims: Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Credit Appraisal, Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), Frictionless Credit, Reserve Bank Innovation Hub, Account Aggregators.
For Mains: Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit, its Significance.
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has initiated a pilot programme aimed at evaluating the feasibility of a 'Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit', seeking to facilitate seamless and efficient credit delivery by lenders for Credit Appraisal, and therefore boosting Financial Inclusion in India.
- The initiative comes as part of RBI's developmental and regulatory policies and was introduced following the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting in August 2023.
Note: Frictionless credit is a borrowing approach that seeks to streamline the lending process for consumers. Unlike the traditional credit systems, where individuals need to go through extensive paperwork, credit checks, and lengthy approval procedures, frictionless credit promises a smoother and faster experience.
What is the Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit?
- About:
- Developed by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH), It is an end-to-end digital platform that will have an open architecture, open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), and standards to which all banks can connect in a "Plug and Play" Model.
- The public tech platform seeks to make this process seamless by providing all the required information in one place to facilitate credit.
- Process:
- The process of delivering credit through digital means involves Credit Appraisal, which evaluates the borrower's ability to repay the loan and adhere to the credit agreement.
- This process rests on three pillars:
- Adverse selection (information asymmetry between borrowers and lenders)
- Exposure risk measurement
- Default risk assessment.
- Key Data Sources:
- The platform would integrate data from central and state governments, Account Aggregators (AA), banks, credit information companies, and digital identity authorities.
- This consolidation would eliminate hindrances and streamline rule-based lending processes.
- Scope and Coverage:
- Diverse Loan Types: The platform's scope encompasses digital loans beyond KCC (Kisan Credit Card), including dairy loans, MSME loans without collateral, personal loans, and home loans.
- Data Integration: It will link with various services like Aadhar e-KYC, Aadhar e-signing, land records, satellite data, PAN validation, transliteration, account aggregation by account aggregators (AAs), and more.
What are the Benefits and Outcomes?
- Enhanced Credit Portfolio Management:
- The platform's data consolidation will enable improved credit risk assessment and efficient credit portfolio management.
- Improved Access to Credit:
- Access to accurate information supports informed and swift credit assessments. This expansion of credit availability benefits borrowers by lowering the cost of capital access.
- Reduced Operational Costs:
- The platform addresses operational challenges such as multiple visits and documentation requirements, leading to cost reduction for both lenders and borrowers.
- RBI’s survey indicated that processing of farm loans took two to four weeks and cost about 6% of the loan’s total value.
- The platform addresses operational challenges such as multiple visits and documentation requirements, leading to cost reduction for both lenders and borrowers.
- Efficiency and Scalability:
- The platform's streamlined processes lead to quicker disbursement and scalability, resulting in a more efficient credit ecosystem.
What is the Significance of Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit in Economic Growth?
- Reduced Income Inequality:
- Financial inclusion ensures that all segments of society, including low-income individuals and marginalized groups, have access to essential financial services.
- This empowers them to save, invest, and access credit, reducing income disparities and fostering more equitable economic growth.
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation:
- Access to credit enables aspiring entrepreneurs to start and expand businesses.
- This leads to increased job creation, innovation, and economic diversification, all of which contribute to higher GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth and overall prosperity.
- Poverty Alleviation:
- Financially excluded individuals often face barriers to economic progress.
- Providing access to credit allows them to invest in education, healthcare, and income-generating activities, breaking the cycle of poverty and enhancing overall human development.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Adequate credit access is essential for funding large-scale infrastructure projects. These projects, such as transportation, energy, and communication networks, provide the necessary backbone for sustained economic growth.
- Rural Development:
- In agrarian economies, access to credit can enable farmers to invest in modern agricultural practices, leading to increased productivity and rural development. This, in turn, supports overall economic growth.
- Financial Stability:
- A well-functioning credit market contributes to financial stability by diversifying funding sources for individuals and businesses. It reduces dependence on informal lending, which can be more volatile and risky.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (2016)


International Relations
Challenges in Major Defence Deals with Russia
For Prelims: Challenges in Major Defence Deals with Russia, S-400 Deal, War in Ukraine, Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA), Rupee-Rouble Arrangement, Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT).
For Mains: Challenges in Major Defence Deals with Russia
Why in News?
Major defence deals between India and Russia, particularly the S-400 Deal, are facing uncertainties due to various factors including the ongoing War in Ukraine and payment challenges.
- The S-400 deal involves the procurement of advanced air defense systems from Russia. Three out of the contracted five S-400 regiments have been delivered as part of a deal signed in 2018.
What are the Challenges Faced by the Defense Deals?:
- S-400 Deal Complexities:
- The S-400 deal has faced complications, including concerns about U.S. sanctions Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) and delays in milestone payments.
- The war in Ukraine has compounded challenges in executing the deal.
- The S-400 deal has faced complications, including concerns about U.S. sanctions Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) and delays in milestone payments.
- Payment Crisis:
- An estimated USD 3 billion payments are currently held up due to payment challenges. Efforts to resolve this crisis through a Rupee-Rouble Arrangement have not been successful due to trade imbalances and accumulating Rupees on the Russian side.
- Due to Russia's Exclusion from the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) system, India and Russia had adopted a Rupee-Rouble payment mechanism to settle payments for defence deals.
- While small payments have resumed, larger payments remain stuck, creating challenges in completing ongoing and future deals.
- An estimated USD 3 billion payments are currently held up due to payment challenges. Efforts to resolve this crisis through a Rupee-Rouble Arrangement have not been successful due to trade imbalances and accumulating Rupees on the Russian side.
- Delays in S-400 Deliveries and Frigates:
- While three regiments have been delivered, the delivery of the remaining two regiments is delayed. The revised schedule remains uncertain until payment issues are resolved.
- Delivery of two Krivak-Class Stealth Frigates under construction in Russia for the Indian Navy is further delayed.
- While three regiments have been delivered, the delivery of the remaining two regiments is delayed. The revised schedule remains uncertain until payment issues are resolved.
How is the Defence Trade Dynamics Between India and Russia?
- Buyer-Seller Framework to Joint Research:
- India-Russia military-technical cooperation has evolved from a buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems.
- Joint Military Programmes:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- Ilyushin/HAL Tactical Transport Aircraft
- KA-226T twin-engine utility helicopters
- Some frigates
- Military Hardware:
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 Triumf
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- Submarine Programmes:
- Russia also plays a very important role in assisting the Indian Navy with its submarine programmes:
- Indian Navy’s first submarine, ‘Foxtrot Class’ came from Russia
- INS Vikramaditya, the sole aircraft carrier operated by India, is of Russian origin.
- India operates nine of the fourteen conventional submarines sourced from Russia.
- Russia also plays a very important role in assisting the Indian Navy with its submarine programmes:
- Recent Development:
- Between 2018 and 2021, defence trade between India and Russia amounted to approximately USD 15 billion, encompassing significant deals including S-400, frigates, AK-203 assault rifles, and emergency procurements.
- The defence trade relationship has been influenced by geopolitical dynamics, including the Balakot air strike in 2019 and the standoff with China in Eastern Ladakh in 2020.
What is Russia’s S-400 Deal?
- About:
- Russia's S-400 deal refers to the procurement of the S-400 Triumf, a highly advanced mobile Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system.
- In October 2018, India signed a 5.43 billion USD deal with Russia for the S-400 Triumf missile system despite objections from the US and the threat of sanctions under Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
- Features:
- The system can engage all types of aerial targets including aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) and ballistic and cruise missiles within the range of 400km, at an altitude of up to 30 km.
- The system can track 100 airborne targets and engage six of them simultaneously.
Way Forward
- Apprehensions among companies and traders about sanctions are hindering trade expansion. The Reserve Bank of India's intervention is necessary to address these apprehensions and promote bilateral trade.
- Officials acknowledge the need for a comprehensive approach to resolve the payment crisis, as no single measure may be sufficient.
- Currency diversification, including the use of Yuan, is considered to mitigate payment challenges and expand trade options.
- Resolving payment issues and streamlining mechanisms for executing major defence deals are critical for ensuring the timely delivery of advanced defence systems, bolstering national security, and enhancing the capabilities of the Indian armed forces.


Science & Technology
Challenges in Lunar Landing Missions
For Prelims: Challenges in Lunar Landing Missions, Russia's Luna-25, Soviet Union, India’s Chandrayaan-3, Lunar South Pole, International Lunar Research Station, ISRO's Chandrayaan-2.
For Mains: Challenges in Lunar Landing Missions.
Why in News?
Recently, Russia's Luna-25 crashed on the Moon’s surface, ending its first mission to the lunar surface 47 years after the last landing by the former Soviet Union.
- This leaves India’s Chandrayaan-3 on course to become the first spacecraft to land near the Lunar South Pole.
- Russia's Luna-25 marked the resumption of lunar interest and plans to continue the Luna series.
What is the Luna-25 Mission?
- About:
- The Luna 25 mission, originally named Luna-Glob, underwent over two decades of development before joining the historic Luna series initiated in 1976.
- The mission aimed to secure Russia's access to the Moon's surface amid its significance in space exploration and geopolitical rivalry.
- While Russia and China lead the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), the U.S. heads the Artemis Accords.
- Failure:
- The Luna 25 spacecraft encountered a technical glitch, surpassing its operational limits.
- The failure appears linked to an attempt to shift its circular orbit to a lower pre-landing orbit.
- Excessive thrust during this maneuver caused a trajectory deviation, causing the craft to crash onto the Moon's surface.
- Roscosmos lost communication during this critical event.
- Due to the Russia-Ukraine war, Russia lost its privileges to use satellite tracking systems operated by countries in different parts of the world. Roscosmos could contact Luna 25, and receive signals from the spacecraft, only at three stations: two in Russia and one in Russian-occupied Crimea.
- ISRO, unlike Russia, is receiving help from National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the European Space Agency (ESA) to track Chandrayaan 3 around the moon.
What are the Complexities in Successful Lunar Landing?
- Complexity of Lunar Descent:
- Lunar landings involve a challenging descent from lunar orbit to the Moon's surface, often referred to as the "15 minutes of terror."
- The complexity arises from the need to precisely control the spacecraft's speed, trajectory, and altitude during this crucial phase.
- Historical Perspective:
- Despite more than 20 successful landings, including six with human crew, the technology remains imperfect.
- Most successful lunar landings occurred within a decade between 1966 and 1976, with three Chinese landings in the past decade as exceptions.
- Lunar landing technology during the 1960s and 1970s was far from perfected, with a 50% success rate among 42 attempts.
- Contemporary lunar missions deploy safer, cost-efficient, and fuel-efficient technologies but require testing and validation.
- Despite more than 20 successful landings, including six with human crew, the technology remains imperfect.
- Complex Propulsion:
- Lunar landing involves a sequence of controlled maneuvers, from deceleration to final touchdown. Precise propulsion systems must be employed to manage speed and altitude accurately.
- Thermal Challenges:
- Extreme temperature variations on the Moon, from scorching heat to freezing cold, pose challenges for spacecraft systems. Thermal protection and insulation are critical to prevent equipment malfunctions.
What are the Recent Failures and Successes in Lunar Landing Attempts?
- Failure:
- Missions from India, Israel, Japan, and Russia all faced challenges during the landing process, resulting in crashes on the Moon's surface.
- ISRO's Chandrayaan-2: Malfunctions prevented the desired speed levels from being achieved.
- Beresheet (Israel), Hakuto-R (Japan): Different kinds of malfunctions disrupted landing plans.
- Missions from India, Israel, Japan, and Russia all faced challenges during the landing process, resulting in crashes on the Moon's surface.
- Successes:
- China's Chang'e-3, Chang'e-4, and Chang'e-5 missions achieved successful lunar landings.
Way Forward
- India's Chandrayaan-3 exemplifies the importance of learning from failures. After the Chandrayaan-2 setback.
- While recent failures underscore the complexity of soft-landing on the Moon, they also reflect the determination of space agencies to push boundaries and advance the field of lunar exploration.
- The lessons learned from these attempts will contribute to the development of more reliable and successful lunar landing technologies in the future.


Important Facts For Prelims
RBI Study on Investment Trends in India for FY 2022-23
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) recent study sheds light on the state-wise distribution of capital investments in India during the fiscal year 2022-23.
- The study examines the geographical and sectoral trends that shape the landscape of project funding across the country.
What are the Highlights of the Study?
- Investment Surge and Capital Outlay:
- Credit offtake soared by 19.7% in July 2023, amidst a 250 basis points hike in the repo rate by the RBI since April 2022, indicating robust investment momentum.
- The aggregate capital outlay reached an impressive of over Rs 3.5 lakh crores, reflecting a significant increase compared to the previous years.
- State-wise Share in Total Project Costs:
- Top Performers:
- Uttar Pradesh emerges as the frontrunner, accounting for the highest share of 16.2% in the total cost of projects sanctioned by banks and financial institutions.
- Following closely are Gujarat (14%), Odisha (11.8%), Maharashtra (7.9%), and Karnataka (7.3%), showcasing a dynamic distribution of investments.
- Bottom Performers:
- Kerala, Goa, and Assam secured the lowest shares, with Kerala receiving just 0.9% of the total investment plans.
- Haryana and West Bengal also fell within the 1% bracket of the total investment projects.
- Top Performers:
- Sectors Driving Investments:
- The infrastructure sector played a pivotal role, accounting for 60% of the total project cost in 2022-23.
- Notably, road and bridge projects within the infrastructure sector garnered significant attention, benefiting from the "Bharatmala" initiative.
- Factors Influencing Investment Momentum:
- Government capital expenditure, rising business optimism, and a revival of private capital expenditure in select sectors have fueled investment activity.
- Despite the upward revision of the repo rate, credit offtake experienced robust growth, reflecting the confidence in investment opportunities.
- Outlook and Future Trends:
- The RBI study provides a positive outlook for private investment, attributing the surge to increased government spending, improved business sentiments, and policy support.
- Greenfield projects, constituting 93.1% of total project costs financed by banks and financial institutions, underscore the focus on new initiatives.
- Greenfield project refers to investment in a manufacturing, office, or other physical company-related structure or group of structures in an area where no previous facilities exist.


Important Facts For Prelims
India Sets Emission Threshold in Green Hydrogen Standard
Why in News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) recently defined a clear Green Hydrogen Standard, which establishes emission thresholds for hydrogen production categorized as 'green'.
- This significant development positions India at the forefront of global efforts towards sustainable energy solutions.
What is Green Hydrogen, and its Emission Threshold?
- Definition of Green Hydrogen:
- “Green Hydrogen” shall mean Hydrogen produced using renewable energy, including, but not limited to, production through electrolysis or conversion of biomass.
- Renewable energy also includes such electricity generated from renewable sources which is stored in an energy storage system or banked with the grid in accordance with applicable regulations.
- “Green Hydrogen” shall mean Hydrogen produced using renewable energy, including, but not limited to, production through electrolysis or conversion of biomass.
- Emission Threshold :
- The MNRE has determined that Green Hydrogen should have a well-to-gate emission of not exceeding 2 kg carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent per kg Hydrogen(H2), taken as an average over the last 12-month period.
- The well-to-gate emission includes water treatment, electrolysis, gas purification, drying and compression of hydrogen.
- Methodology and Monitoring:
- The MNRE will specify a detailed methodology for measuring, reporting, monitoring, on-site verification, and certification of green hydrogen and its derivatives.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), Ministry of Power, will serve as the Nodal Authority for accrediting agencies overseeing monitoring, verification, and certification of green hydrogen production projects.
- The MNRE has determined that Green Hydrogen should have a well-to-gate emission of not exceeding 2 kg carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent per kg Hydrogen(H2), taken as an average over the last 12-month period.
What are India's Initiatives to Promote Green Hydrogen?
- National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission with the objective of producing 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030.
- The mission aligns with a target of about 125 gigawatts of associated renewable energy capacity.
- The program offers financial incentives to promote domestic production of electrolysers and green hydrogen.
- These incentives are designed to facilitate rapid scale-up, technology development, and cost reduction.
- Green Hydrogen Consumption Obligations:
- The MNRE has proposed to introduce green hydrogen consumption obligations for fertilizer and the petroleum refining industry, like the renewable purchase obligations for electricity distribution companies.
- The obligations will require these industries to consume a certain percentage of green hydrogen in their total hydrogen consumption.
- The MNRE has proposed to introduce green hydrogen consumption obligations for fertilizer and the petroleum refining industry, like the renewable purchase obligations for electricity distribution companies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following heavy industries: (2023)
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decarbonizing how many of the above industries?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Need for Producing Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen in particular is one of the cleanest sources of energy with close to zero emission. It can be used in fuel cells for cars or in energy-guzzling industries like fertilizers and steel manufacturing.
- Green Hydrogen can aid the desulfurisation of crude oil, without the output of CO2 into the atmosphere hence it can provide a clean, on-site green hydrogen supply which will decarbonise the refining process and reduce emissions.
- Hence option (c) is correct.
Q. With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Namoh 108 Lotus Variety
- Recently, the Union Minister of Science & Technology, unveiled the innovative 'Namoh 108' lotus variety, developed by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research -National Botanical Research Institute (CSIR-NBRI), Lucknow.
- Having been discovered in Manipur several years ago, this lotus variety boasts 108 petals, leading to its designation as 'NBRI Namoh 108,' a name derived from both its petal count and its religious significance.
- Blossoms from March to December, rich in nutrients.
- The flower's genome was sequenced, making it the only Indian lotus variety with a sequenced genome.
- The flower's characteristics were modified to facilitate cultivation outside Manipur.
Chess World Cup 2023
- Grandmaster Rameshbabu Praggnanandhaa wins over World No. 3 Fabiano Caruana in the tie-breaker round of the World Cup 2023, chess tournament at Baku, Azerbaijan.
- The World Cup 2023 is organised by the International Chess Federation (FIDE), the governing body of chess in the world.
- It's constituted as a non-governmental institution.
- FIDE currently has its headquarters in Lausanne (Switzerland), but it was initially founded in 1924 in Paris under the motto “Gens Una Sumus” (Latin for “We are one Family”).
- The World Cup 2023 is organised by the International Chess Federation (FIDE), the governing body of chess in the world.
- Praggnanandhaa, the youngest Indian grandmaster and the youngest international master is among the most promising talents in the world of chess.
- He achieved significant victories such as winning the World Youth Chess Championship (under-18) in 2019 and emerging victorious in the Asian Continental Chess Championship (open) in 2021.
Read more: The Rising Popularity of Chess in India
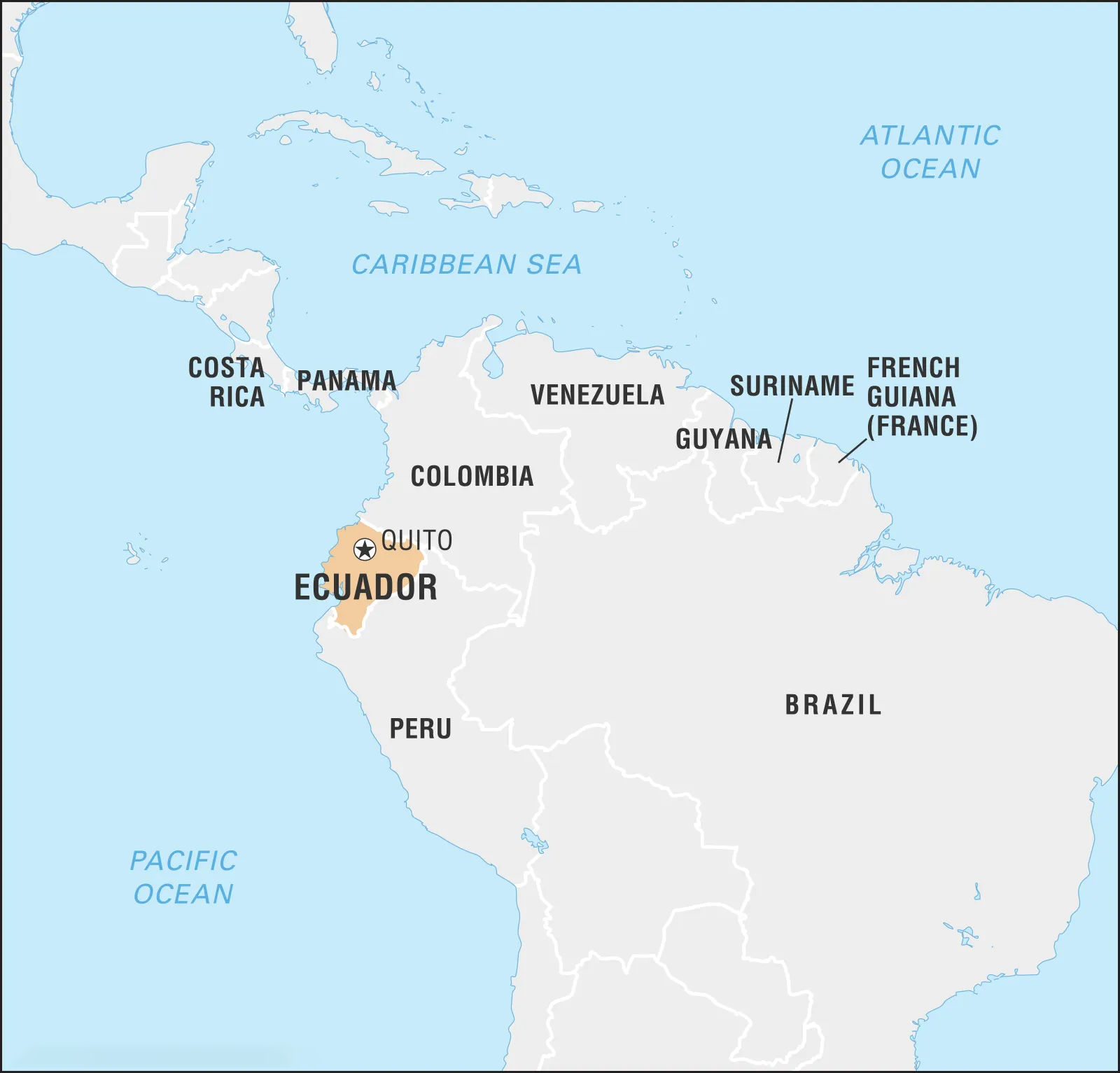
Ecuador Rejects Amazon Oil Drilling
Ecuadorians have spoken out against the oil drilling of a protected Amazon area housing uncontacted tribes and remarkable biodiversity.
- Over 90% of ballots rejected oil exploration in the area located within the renowned Yasuni National Park, a global biodiversity hotspot.
- This area is the habitat of the isolated Tagaeri and Taromenani tribes, and its significance led to its designation as a UNESCO world biosphere reserve in 1989.
Read more: Biodiversity hotspot
Student-Led Water Parliament Spurs Water Conservation
In just one year, Shyam Sadan School in Rajasthan's Jodhpur district has witnessed a transformative shift in water practices .
- The school's "Jal Sansad" (water parliament) was established in mid-2022, engaging students in a range of water conservation activities. Students conduct audits to track water usage, organize awareness campaigns, and maintain digital records.
- Rainwater harvesting irrigates the school's nutrition garden, showcasing innovative integration of water-saving practices.
Read more: Catch the Rain: National Water Mission












-min.jpg)