Indian Polity
22nd Foundation Day of NCST
For Prelims: National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Castes, Provisions Related to STs
For Mains: Significance of NCST in tribal welfare, Safeguarding Scheduled Tribes' rights
Why in News?
The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) celebrated its 22nd Foundation Day on 19th February 2025, highlighting the Commission’s role in protecting Scheduled Tribes(ST) rights.
What are the Key Facts About the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes?
- Origin and Evolution: In 1992, a statutory National Commission for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and STs was established. Later, to address the distinct needs of STs, the NCST was established on 19th February 2004, through the 89th Constitutional Amendment Act, amending Article 338 and adding Article 338A to the Constitution.
- Composition and Tenure:
- Structure: NCST comprises a Chairperson (Cabinet Minister rank), a Vice-Chairperson (Minister of State rank), and three Members (Secretary rank), all appointed by the President.
- At least one other Member shall be appointed from amongst women.
- Tenure & Reappointments: The term of office for all members is three years. A member can be reappointed for a maximum of two terms.
- Structure: NCST comprises a Chairperson (Cabinet Minister rank), a Vice-Chairperson (Minister of State rank), and three Members (Secretary rank), all appointed by the President.
- Key Functions: Under Article 338A(5), the NCST monitors constitutional safeguards for STs, addresses tribal rights issues, advises on socio-economic development.
- Reports to the President on tribal welfare, suggests policy measures, and oversees ST welfare programs.
- Additionally, under the NCST (Specification of Other Functions) Rules, 2005, the commission recommends land ownership rights for tribals (Forest Rights Act, 2006), and suggests alternative livelihood strategies.
- Advocates for full implementation of the Panchayat (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA), and seeks solutions to reduce and eliminate shifting cultivation.
Who are the Provisions Related to Scheduled Tribes in India?Click here to Read: Provisions Related to STs in India |
What are the Challenges Regarding the NCST?
- Administrative and Financial Constraints: The NCST functions under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, lacking financial and operational autonomy, affecting its independence in budgeting, and operations.
- Article 338A(9) of the Constitution mandates that the Union and State Governments consult the NCST on all major policy matters affecting STs.
- However, many states and departments fail to seek its advice, leading to tribal welfare policies being designed without the Commission’s input .
- Article 338A(9) of the Constitution mandates that the Union and State Governments consult the NCST on all major policy matters affecting STs.
- Manpower Shortages: The NCST reviews tribal welfare schemes, but its effectiveness is hindered by limited staff and poor coordination.
- Historically, the NCST has faced prolonged vacancies in key positions like Chairperson and Members.
- Manpower shortages and bureaucratic delays result in prolonged resolution times, leaving many cases pending for years and weakening public trust.
- Weak Enforcement Powers: The recommendations of NCST are not binding, limiting its ability to enforce protective measures for STs.
- Despite receiving numerous petitions on atrocities against tribals, land alienation, and denial of reservation benefits, the NCST lacks the power to enforce its directives.
- This weakens its authority and reduces accountability among government agencies.
- Lack of Awareness and Outreach: Many tribals are unaware of their rights and the existence of NCST, the Commission lacks a strong grassroots presence .
Way Forward
- Strengthening Legal Mandate: The NCST should be empowered to award penalties on the lines of the powers given to the Central Information Commission in the context of the implementation of the various provisions of the Rights to Information Act, 2005.
- Capacity Building: A separate cadre for NCST personnel should be created to ensure staffing shortages do not affect its operations .
- Mandatory Consultation on Policies: The government should ensure compliance with Article 338A(9), making it compulsory for ministries and states to consult NCST on all tribal welfare policies .
- Grievances: NCST should have a dedicated grievance redressal cell to follow up on cases of violence, displacement, and human rights violations .
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is the mandate of the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes? Analyze its effectiveness in protecting tribal rights. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ
Prelims
Q. If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Ans: (a)
Mains
What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)


International Relations
India - US COMPACT Initiative
For Prelims: India - US COMPACT Initiative, Tiger Triumph, International Energy Agency, Mission 500' initiative, TRUST, India-Middle East-Europe Corridor.
For Mains: India-US Relations, Multilateral and Regional Cooperation, Challenges and way forward
Why in News?
The US-India COMPACT (Catalyzing Opportunities for Military Partnership, Accelerated Commerce & Technology) for the 21st Century was launched by President Donald Trump and Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
What are the Highlights of the India - US COMPACT Initiative?
- Defence Collaboration: A new 10-year Framework for the US - India Major Defence Partnership (2025-2035) will be signed, expanding Defence sales and co-production of Javelin Anti-Tank Guided Missiles, and enhancing joint exercises like Tiger Triumph.
- The initiative includes the Reciprocal Defence Procurement (RDP) Agreement for seamless Defence trade and Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA) to boost AI-driven autonomous Defence cooperation.
- Trade and Investment Expansion: Under the COMPACT Initiative, the 'Mission 500' initiative was launched to increase bilateral trade to USD 500 billion by 2030, supported by negotiations for a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA).
- Efforts include reducing trade barriers, such as tariff cuts on beverages, vehicles, and Information and communication technology (ICT) products, while increasing market access for agricultural goods and industrial exports.
- Energy Security: Strengthens energy ties, boosting oil, gas, and nuclear cooperation, with the US supporting India's International Energy Agency (IEA) membership.
- Technology Advancement: The Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) was rebranded as TRUST (Transforming the Relationship Utilizing Strategic Technology), focusing on semiconductors, quantum computing, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Efforts will expand critical mineral supply chains, including lithium and rare earth recovery projects.
- Civil space cooperation will advance through NASA-ISRO initiatives, including an Indian astronaut's mission to the International Space Station (ISS) and the NISAR launch.
- Multilateral and Regional Cooperation: Strengthen Quad partnerships, enhance counterterrorism efforts, Indo-Pacific security and advance connectivity projects like the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor.
- People-to-People Engagement: The COMPACT initiative boosts academic and workforce mobility, eases legal migration, and strengthens law enforcement cooperation against trafficking and transnational crime.
India - US Relations
- Trade and Investment: India-US ties have evolved into a "global strategic partnership".
- In 2024, India's total goods trade with the U.S. reached USD 129.2 billion. India's exports to the U.S. stood at USD 87.4 billion, while imports from the US were USD 41.8 billion. India has a USD 45.7 billion trade surplus with the US in 2024.
- USA is the 3rd largest investor in India with cumulative Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows of USD 65.19 billion from 2000- 2024.
- International Cooperations: India and the US collaborate in multilateral forums like the United Nations, G-20, Association of Southeast Asian Nations, World Trade Organization, I2U2 group and Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF).
- Defence Cooperation: India-US defense ties strengthened with the 2005 Defense Framework, renewed in 2015.
- India is a Major Defense Partner of the US with Strategic Trade Authorization-1 (STA‑1) status (allowing easier access to US defense technologies).
- Joint exercises: Ex VAJRA PRAHAR (Army), SALVEX (Indian Navy), Cope India (Air Force) and Malabar Exercise (Quadrilateral naval exercise of India, USA, Japan and Australia).
- People to people Ties: The 3.5 million Indian American community plays a key role in US society, strengthening India-US ties.
What are the Key Challenges in India-US Relations?
- Tariff Disputes: President Trump criticized India's "onerous tariffs" (burdensome and excessively high import duties) and reinforced his policy of "reciprocal tariffs" (tariffs imposed in response to similar tariffs by another country), which could increase costs for Indian exporters. Further, the absence of a Free Trade Agreement increases tariffs, and restricts trade.
- India’s current trade surplus with the US may shrink as it increases imports to reach the USD 500 billion trade target, potentially requiring selective tariff reductions that favor US interests over broader India’s economic efficiency.
- Immigration Policies: India agreed to facilitate the return of 2,20,000–7,00,000 undocumented Indians immigrants, a move seen as aligning with Trump’s stricter immigration stance.
- Despite India's reliance on H-1B visas for IT professionals, no clear commitments were made, reflecting ongoing tensions between Silicon Valley and Trump’s nationalist policies.
- Technology Transfer: Despite growing Defence ties, US restrictions on AI, drones, and missile technology hinder India's access to advanced Defence systems.
- Data Localization: The US opposes India’s data sovereignty laws, arguing they hurt American tech firms, while India insists on national security and user privacy protections.
- Geopolitical and Multilateral Differences: Despite US support for India's permanent UNSC membership, differences in global governance persist, with the US urging India to leverage its ties with Russia to end the war, while India maintains neutrality.
- India's historical Defence and energy ties with Russia conflict with US efforts to isolate Moscow.
Way Forward
- BTA: Finalize the BTA to ease trade tensions, improve supply chain integration in semiconductors and pharmaceuticals, and harmonize regulatory standards with US norms to attract investments.
- Workforce Mobility: India should push for higher H-1B quotas, and faster visa processing to support professionals and tech talent and mutual recognition of qualifications is essential to enhance workforce integration.
- Data Governance: India should selectively ease data localization norms, facilitate US tech investments in India, and develop joint cybersecurity frameworks to enhance trust in digital governance.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Strengthening US-India engagement in multilateral forums like Quad, IPEF while leveraging India’s strategic role in the Global South to address global governance differences and enhance economic and security influence.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the India-US COMPACT Initiative in strengthening bilateral relations. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- deer
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Mains
‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)


Governance
Draft UGC Regulations 2025
For Prelims: National Education Policy, Concurrent List, University Grants Commission
For Mains: Higher Education Policies, Education Governance, Equity in Education
Why in News?
Six Indian states called for the withdrawal of the draft University Grants Commission (Minimum Qualifications for Appointment and Promotion of Teachers and Academic Staff in Universities and Colleges and Measures for the Maintenance of Standards in Higher Education) Regulations, 2025, citing concerns over federal autonomy and educational standards.
What are the Key Provisions of Draft UGC Regulations 2025?
- The draft centralizes the selection process for Vice Chancellors (VCs) by removing the role of State governments in the appointment.
- Universities failing to comply could be debarred from UGC schemes and denied funding.
- The draft proposes increasing the tenure of VCs from three years to five years.
- The draft allows the appointment of non-academics with at least 10 years of senior-level experience in public administration and public policy.
- The draft proposes making entrance exams mandatory for undergraduate courses.
- The draft strengthens academia-industry collaboration, promotes Indian languages in academic publication, enhances transparency, and includes sportspersons in teaching roles.
What are the Key Facts About UGC?
- Genesis: India's first effort to establish a national education system began with the 1944 Sargeant Report, which recommended creating a University Grants Committee.
- Formed in 1945, the committee initially supervised Aligarh, Banaras, and Delhi universities. By 1947, its scope expanded to include all existing universities.
- In 1948, the University Education Commission, led by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, recommended its restructuring based on the UK model.
- In 1952, the Union Government designated the University Grants Commission (UGC) to oversee grants for Central Universities and higher education institutions.
- Formally inaugurated by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad in 1953 , it became a statutory body in 1956. The head office of the UGC is located in New Delhi.
- Composition: UGC is made up of a Chairman, a Vice-Chairman, and 10 other members. The Central Government appoints all members of the UGC.
- Key Functions: Assess universities' financial needs, and allocate and disburse grants for maintenance, development, and other purposes.
- Recommends improvements in higher education and assists in implementation.
Regulation of Education in India
- The 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976 shifted Education from the State List to the Concurrent List, allowing the central government greater involvement in policymaking while preserving state autonomy in local education administration.
- Policies like National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the role of bodies like UGC, and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) derive their authority from the Concurrent List.
- Education in 7th Schedule:
|
Union List (List I) |
State List (List II) |
Concurrent List (List III) |
|
|
|
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)


Facts for UPSC Mains
2nd All-India State Water Ministers’ Conference
Why in News?
The 2nd All-India State Water Ministers’ Conference, organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti concluded in Udaipur, Rajasthan suggested a number of initiatives for water management issues.
- The conference, themed "India@2047 – A Water Secure Nation’’.
Note: The First All India State Ministers Conference on Water held in Bhopal (January 2023) focussed on five key areas i.e., water security, water use efficiency, governance, climate resilience, and water quality.
What are Key Initiatives Suggested by 2nd All-India State Water Ministers’ Conference?
- Agricultural Water Management: Adoption of micro-irrigation techniques such as drip and sprinkler irrigation, expanding Pressurized Irrigation Networks (PIN), Evapotranspiration (ET)-based irrigation performance assessment to improve water efficiency in agriculture.
- ET combines soil evaporation and plant transpiration to assess whether crops receive adequate water for optimal growth.
- River Rejuvenation: Implementing floodplain zoning, rejuvenating water sources such as springs to augment river flows, and promoting quantification of water consumption can augment river restoration projects.
- Strengthening Drinking Water Supply: Sustaining the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) through Village Water & Sanitation Committees (VWSCs).
- Enhancing urban water security through AMRUT by improving water supply infrastructure promoting grey water management under Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 for wastewater reuse.
- Improving Water Storage: Prioritizing Extension, Renovation, and Modernization (ERM) of water storage systems to maximize efficiency and lifespan while restoring smaller water bodies to enhance availability in rural and urban areas.
- Implementing automated reservoir operations for better management of water storage and distribution.
- Strengthening Water Governance: Implementing Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) with state-specific solutions and strengthening grassroots participation in water governance.
- Scaling up the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative nationwide to promote community-driven water conservation efforts.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What initiatives can be taken to ensure sustainable water management? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. What are the salient features of the Jal Shakti Abhiyan launched by the Government of India for water conservation and water security? (2020)
Q. What is water stress? How and why does it differ regionally in India? (2019)


Rapid Fire
BTR and BUR under Paris Agreement
India is set to submit its first-ever Biennial Transparency Report (BTR) under the Paris Agreement, which will be subject to an independent expert review by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- BTR: Under the Paris Agreement, 2015, countries must submit BTRs every two years to enhance transparency in climate action. Small Islands Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) can submit at their discretion.
- These reports track progress on national greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories, Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and climate adaptation measures.
- BUR: India has previously submitted Biennial Update Reports (BUR), with the last one in 2024 (BUR- 4), covering data till 2020.
- Key Highlights of BUR 4:
- India’s Emissions by Gas: Carbon dioxide (80.53%), Methane (13.32%), Nitrous oxide (5.13%), and others 1.02%.
- Emissions by sector: Energy (75.66%), Agriculture(13.72%), Industrial Process and Product Use (IPPU) (8.06%), and Waste(2.56%).
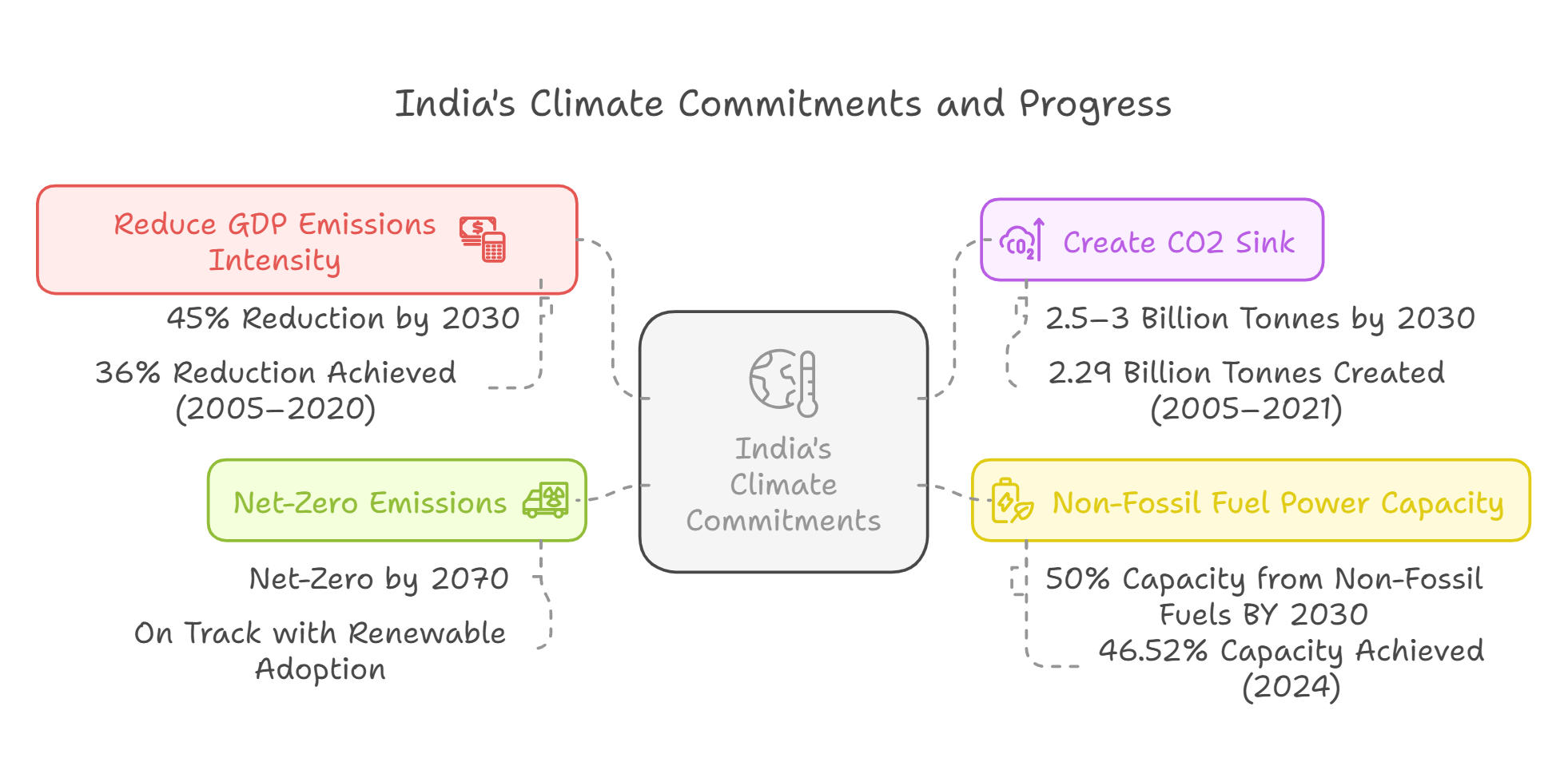
- Forests & Tree Cover: Sequestered 522 million tonnes (mt) of CO₂, equivalent to reducing 22% of the country's total carbon dioxide emissions in 2020.
- Emission Intensity Reduction: 36% decrease in emissions intensity (2005–2020), with India on track to achieve its target of a 45% reduction by 2030.
- As of 2020, India’s emissions, excluding land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF), stood at 2,959 mt of CO2e. Including LULUCF, net emissions were at 2,437 mt of CO2e.
Read more: WMO's Greenhouse Gas Bulletin 2023


Rapid Fire
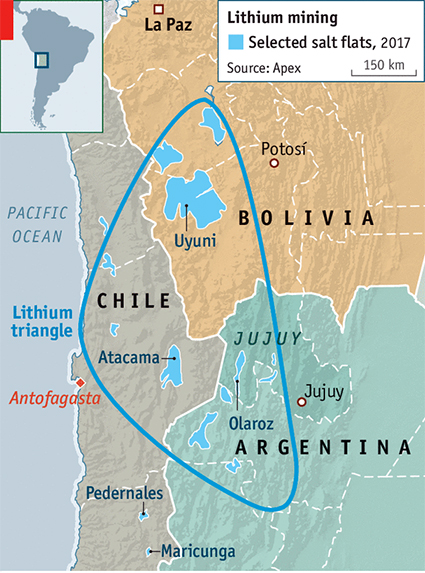
India-Argentina Lithium Partnership
India and Argentina signed an MoU for lithium exploration and investment opportunities in Argentina.
- Argentina is known for its vast lithium reserves and is part of the 'Lithium Triangle' along with Bolivia and Chile.
- About Lithium: It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal and is also known as white gold.
- It is the lightest metal and solid element, and classified as both an alkali and a rare metal.
- It is mined from ores of petalite, lepidolite, spodumene and also subsurface brines.
- It is highly reactive and flammable and must be stored in mineral oil.
- It is an essential mineral required for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy storage.
- Chile (1st), China (2nd) and Australia (3rd) have the largest reserves of lithium.
- In India, Salal-Haimna areas (Reasi district of J&K), Koderma and Giridih (Jharkhand), and Mandya (Karnataka) have lithium reserves.
- It is the lightest metal and solid element, and classified as both an alkali and a rare metal.
Read More: Lithium-Deal with Argentina


Rapid Fire
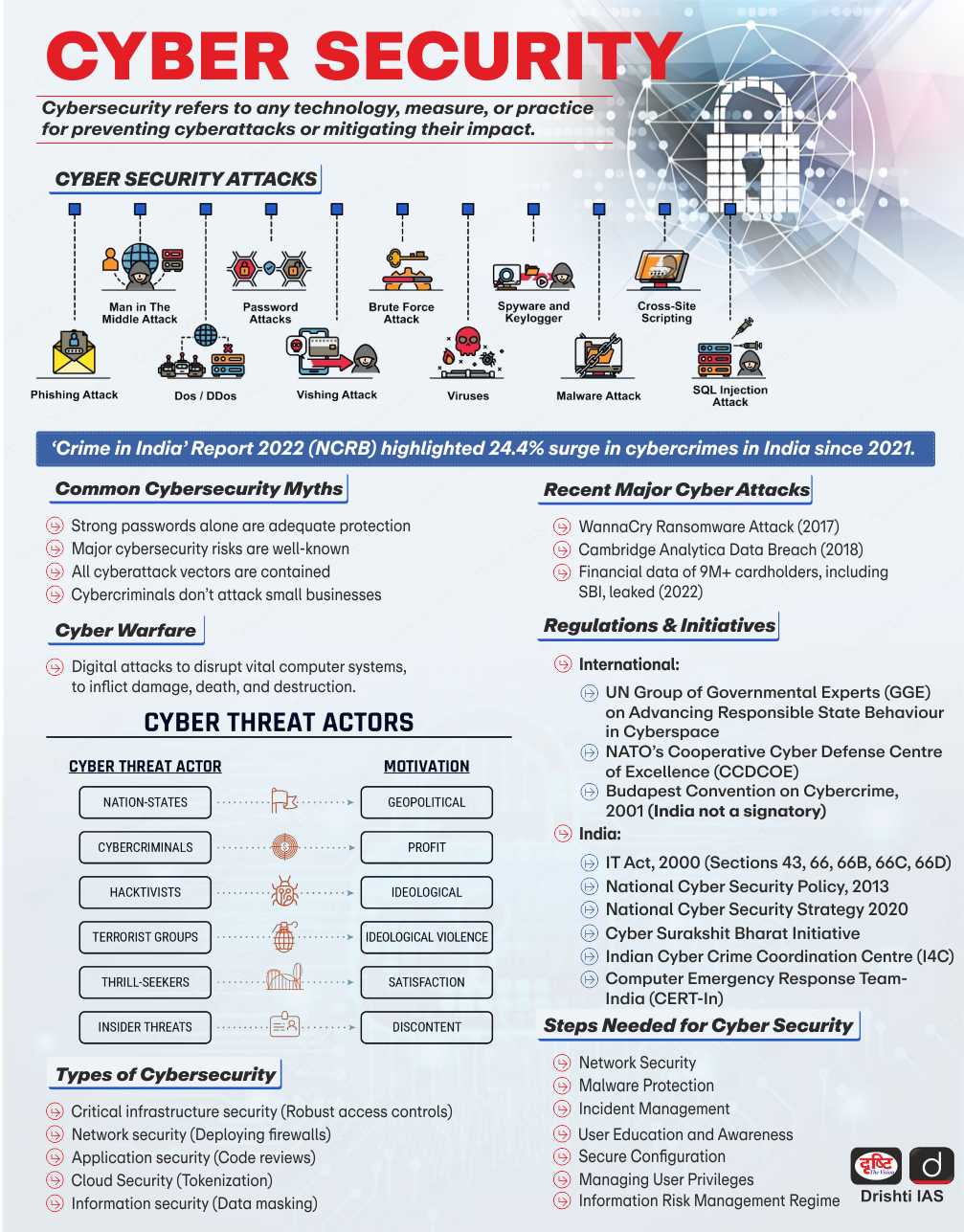
DDoS Cyber-Attack
Karnataka's Kaveri 2.0 portal that deals with property registration faced severe disruptions due to a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
- This overloaded the system with fake accounts and automated requests, causing downtime.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack:
- About: DDoS attack is a cyberattack that floods a website or network with malicious traffic making it inaccessible.
- DDoS attacks are large-scale versions of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks that use multiple compromised systems (botnets) instead of a single source to overload the target.
- Types:
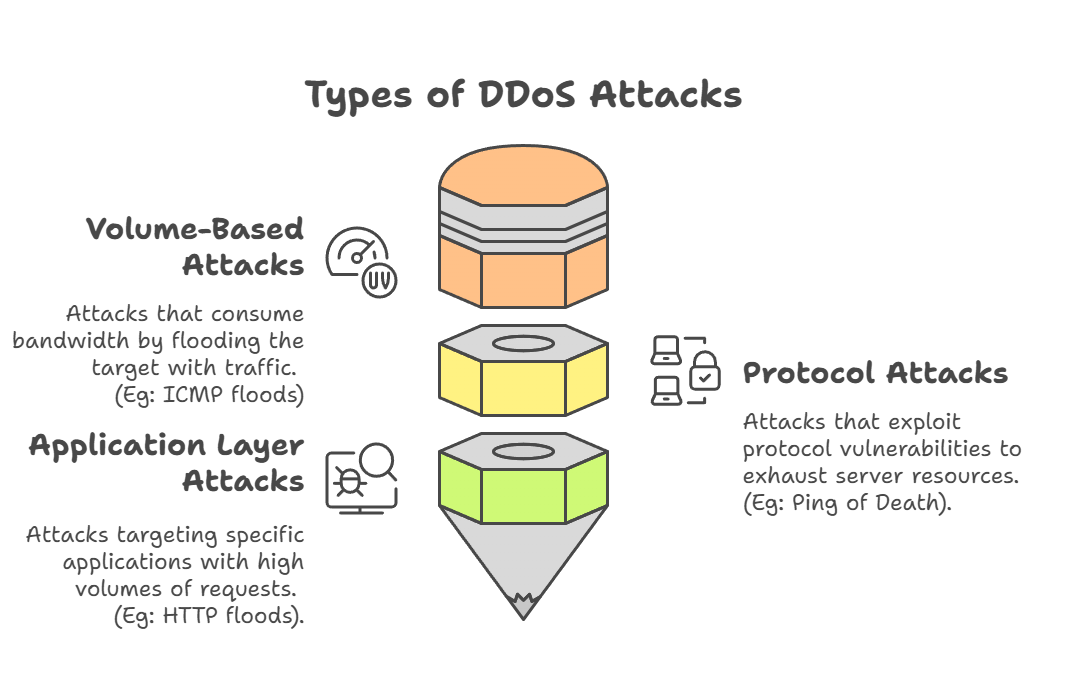
- Impact:
- DDoS attacks disrupt services, impact revenue, and expose cybersecurity vulnerabilities, damaging an organization's reputation.
- Mitigation Strategies
- Traffic filtering, rate limiting, bot detection (CAPTCHA, behavioral analysis), security audits, incident response plans, and multi-factor authentication enhance defense against DDoS attacks.
- About: DDoS attack is a cyberattack that floods a website or network with malicious traffic making it inaccessible.
Read More: Denial of Service (DoS) Attack


Rapid Fire
Colour Revolutions
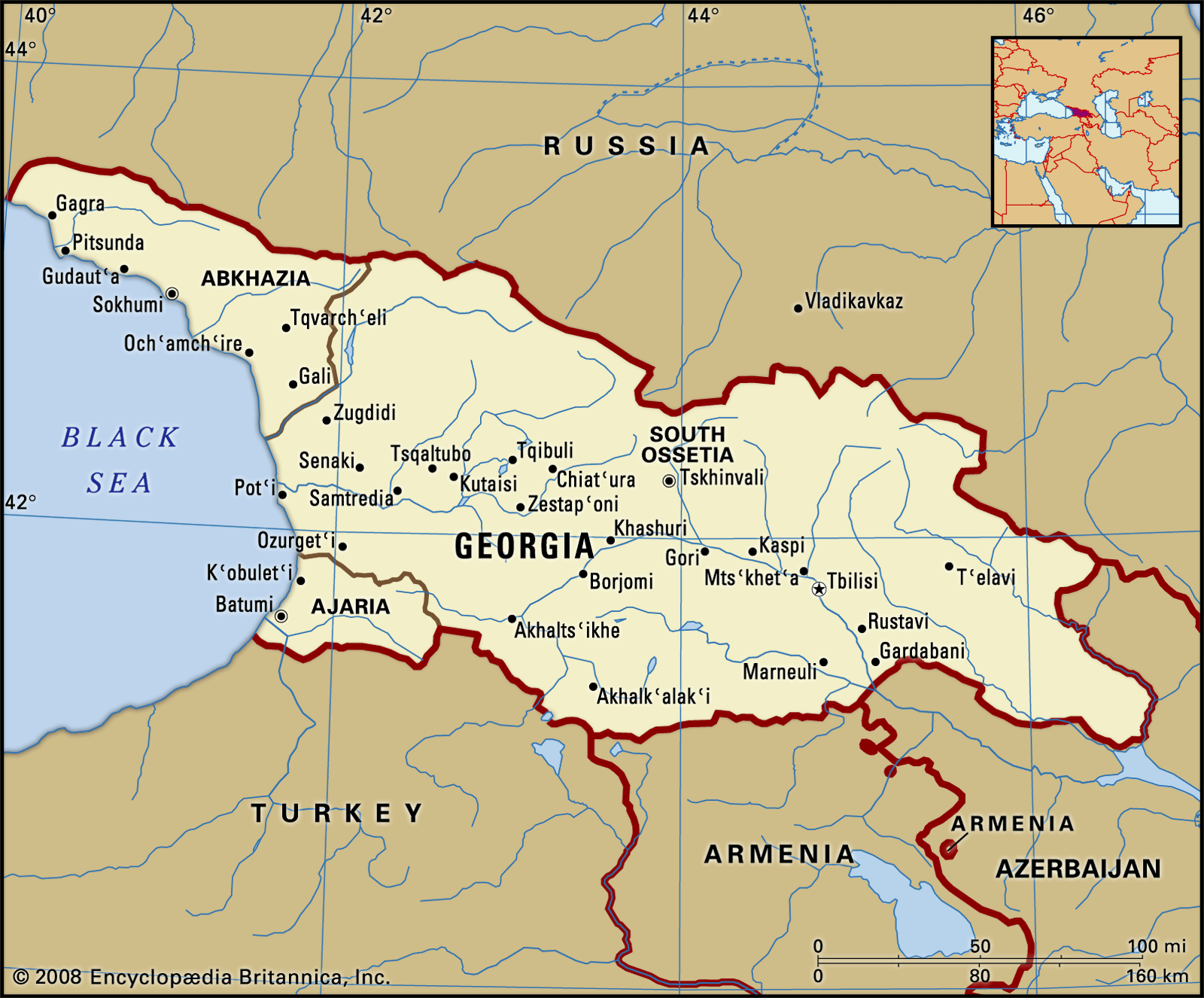
Georgia’s 2024 elections have reignited discussions on colour revolutions, with allegations of Western interference in ongoing political protests, as the former President refused to vacate office, citing electoral malpractices, while the elected President assumed power.
- Colour Revolutions:
- About: It refers to peaceful, mass protest uprisings in post-Soviet states, characterized by symbolic colours, aiming to replace pro-Moscow regimes with peaceful and democratic governments.
- Though initially successful in creating pro-Western governments, these revolutions often resulted in instability, corruption, and disillusionment.
- Examples:
- Georgia’s Rose Revolution (2003)
- Ukraine’s Orange Revolution (2004)
- Kyrgyzstan’s Tulip Revolution (2005)
- Russia sees these movements as Western interference threatening its regional influence.
- About: It refers to peaceful, mass protest uprisings in post-Soviet states, characterized by symbolic colours, aiming to replace pro-Moscow regimes with peaceful and democratic governments.
- Georgia: It is a country located in Eastern Europe and West Asia, bordered by Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia and Turkey. It has a sea boundary with Black Sea.