International Relations
India as a Bridge Between the Global North and South
- 17 Feb 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Global South, Non-Alignment Movement, Group of 77, African Union, Belt and Road Initiative, International Solar Alliance, Mission LiFE
For Mains: India’s Foreign Policy and its role in global governance, South-South cooperation in international relations.
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted India’s commitment to amplifying the Global South's voice and leading inclusive global governance reforms, aiming to serve as a bridge between the Global North and South.
How India is Emerging as a Bridge Between North and South?
- Bridging the Global North-South Divide: Many developing nations face economic distress due to debt crises and restrictive International Monetary Fund (IMF) conditions.
- India offers a collaborative development model, unlike Western or Chinese approaches, with its proposed "Global Development Compact" providing an alternative, non-conditional development cooperation framework.
- Unlike Cold War-era diplomacy, India is deepening ties with the West (US, Europe) while expanding engagement with Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia.
- India advocates for a fairer global economic system, aligning with the Global South’s interests.
- India advocates for UN Security Council (UNSC) reform, arguing that developing countries deserve greater representation in global decision-making.
- India supports IMF and World Bank reforms to make financing more accessible for Global South nations.
- India offers a collaborative development model, unlike Western or Chinese approaches, with its proposed "Global Development Compact" providing an alternative, non-conditional development cooperation framework.
- India’s Early Role in the Global South: India played a key role in establishing the Non-Alignment Movement (NAM) to promote self-determination for developing nations.
- It helped form the Group of 77 (G-77) in 1964 to unite developing nations at the United Nations.
- At the Stockholm Conference, 1972, India championed climate justice, leading to the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR).
- Assertive Foreign Policy: Unlike the NAM, India is no longer a passive observer but an active participant in reshaping global governance.
- The inclusion of the African Union in G20 (2023) under India’s presidency showcased its diplomatic leverage.
- India’s Voice of Global South Summit has provided a platform for developing nations to collectively push for reforms.
- India champions the protection of traditional knowledge through initiatives like the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) treaty and advocates for the inclusion of Global South voices in forums like the G20.
- India’s Vaccine Maitri initiative, providing millions of vaccine doses during the pandemic, demonstrates its commitment to the welfare of developing nations.
- India played a key role in establishing the Loss and Damage Fund, ensuring climate financing for vulnerable nations.
- Co-founded the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to promote clean energy in developing nations.
- Strategic Autonomy: India stays independent on global issues, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, strengthens South-South ties.
- India is not strictly anti-West but is engaging with both developed and developing nations without aligning with any bloc.
- Countering China: China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has left many Global South nations in debt distress.
- India is positioning itself as an alternative development partner, focusing on transparent, sustainable cooperation rather than debt-driven infrastructure projects.
- India with the Quad (India, US, Japan, Australia) is countering China’s maritime expansion in the Indo-Pacific.
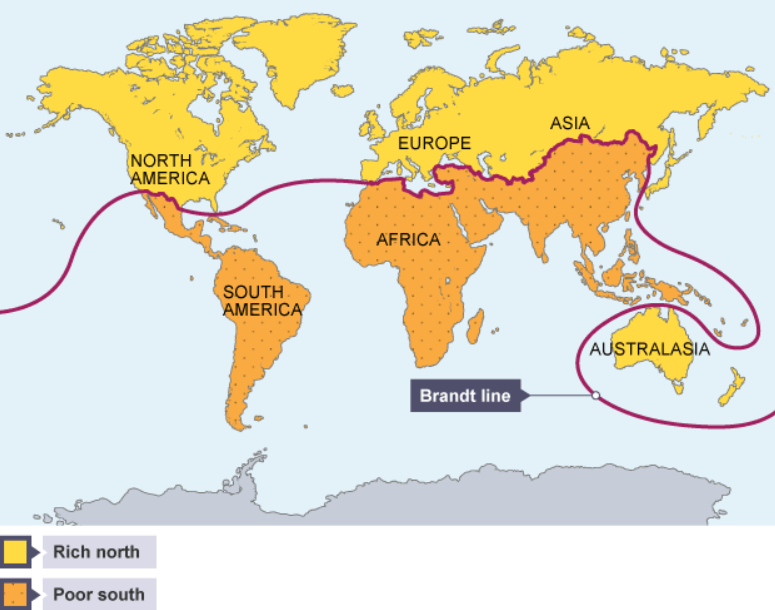
What is Global North and South?
Click here to Read: Global South, Global North
What are the Challenges in India’s Global South Leadership?
- Managing China’s Influence: China’s financial muscle and large-scale investments in Global South nations pose competition.
- India’s own economic and infrastructure challenges could limit its ability to offer large-scale aid as compared to China.
- Delays in Project Implementation India’s infrastructure and development projects often suffer from delays and inefficiencies.
- Kaladan Multimodal Transit Project (Myanmar) remains incomplete after two decades.
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC), a Japan-India initiative, has made slow progress compared to China’s BRI.
- Institutional and Policy Gaps: India lacks a well-defined institutional framework for global development aid.
- Requires a structured long-term vision similar to China’s BRI.
- Additionally, India’s bid for permanent United Nations Security Council (UNSC) membership is opposed by rival Global South nations (e.g., Pakistan).
- Lack of Consistent Engagement: India’s limited engagement with traditional Global South platforms like NAM and G-77, and the absence of an India-Africa Summit since 2015, has created diplomatic gaps and hindered its influence in the developing world.
- Balancing Ties with the Global North: India’s deepening ties with the US and Europe must not alienate Global South allies. Balancing US, EU, and developing country expectations remains a diplomatic challenge.
- Big Brother Attitude: Some Global South nations view India as over-assertive in regional politics, leading to mistrust as evident by the “India Out” campaign in the Maldives accused India of meddling in domestic affairs.
How Can India Become an Effective Global Development Partner?
- Institutionalizing Development Diplomacy: India should set a clear international development assistance policy, similar to China’s BRI and Japan’s Official Development Assistance (ODA).
- Establishing an India International Development Agency can coordinate foreign aid, while the AAGC with Japan offers a viable alternative to the BRI.
- An India-led Global South Development Fund can finance sustainable infrastructure projects.
- North-South Cooperation: India should make trilateral partnerships involving both the Global South and Global North (e.g., India-US-Africa, India- Russia- ASEAN) to enhance its impact.
- Deepening South-South Cooperation: Strengthen regional pacts like IBSA (India-Brazil-South Africa) and BRICS, prioritize trade with Africa, Latin America, and ASEAN, and offer low-cost credit lines to Global South nations for infrastructure.
- Promote the Internationalisation of Indian Currency, RuPay, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and digital payments to boost financial connectivity in the developing world.
- Human-Centric Development: India's Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) should expand to include human capital development in Global South nations through initiatives like Skill India, women entrepreneurship, and ITEC (Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation), along with investments in sustainable development goals (SDGs).
- Enhancing Soft Power: Expand diaspora engagement in Africa, Latin America, and South Asia while strengthening education and research ties through scholarships and technical training programs.
Conclusion
India’s leadership in the Global South is a strategic move to reshape global governance by promoting inclusive development. By addressing internal challenges and fostering strong, transparent partnerships, India can emerge as a key driver for sustainable growth and global equity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: India aspires to be the ‘Voice’ of the Global South, but it must also ‘listen’ to be a good leader." Critically analyze India’s role in reshaping global governance. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.“If the last few decades were of Asia’s growth story, the next few are expected to be of Africa’s.” In the light of this statement, examine India’s influence in Africa in recent years. (2021)
Q.Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post Cold War international scenario. (2016)