International Relations
Call for Reforming UN Security Council
- 30 Sep 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: L69 and C-10 Countries, United Nations Security Council, G4 nations, UN General Assembly, India's participation in the Security Council.
For Mains: Need for UN Security Council Reforms, Procedure of UN Security Council Reforms, Significance of UN Security Council's Permanent Membership.
Why in News?
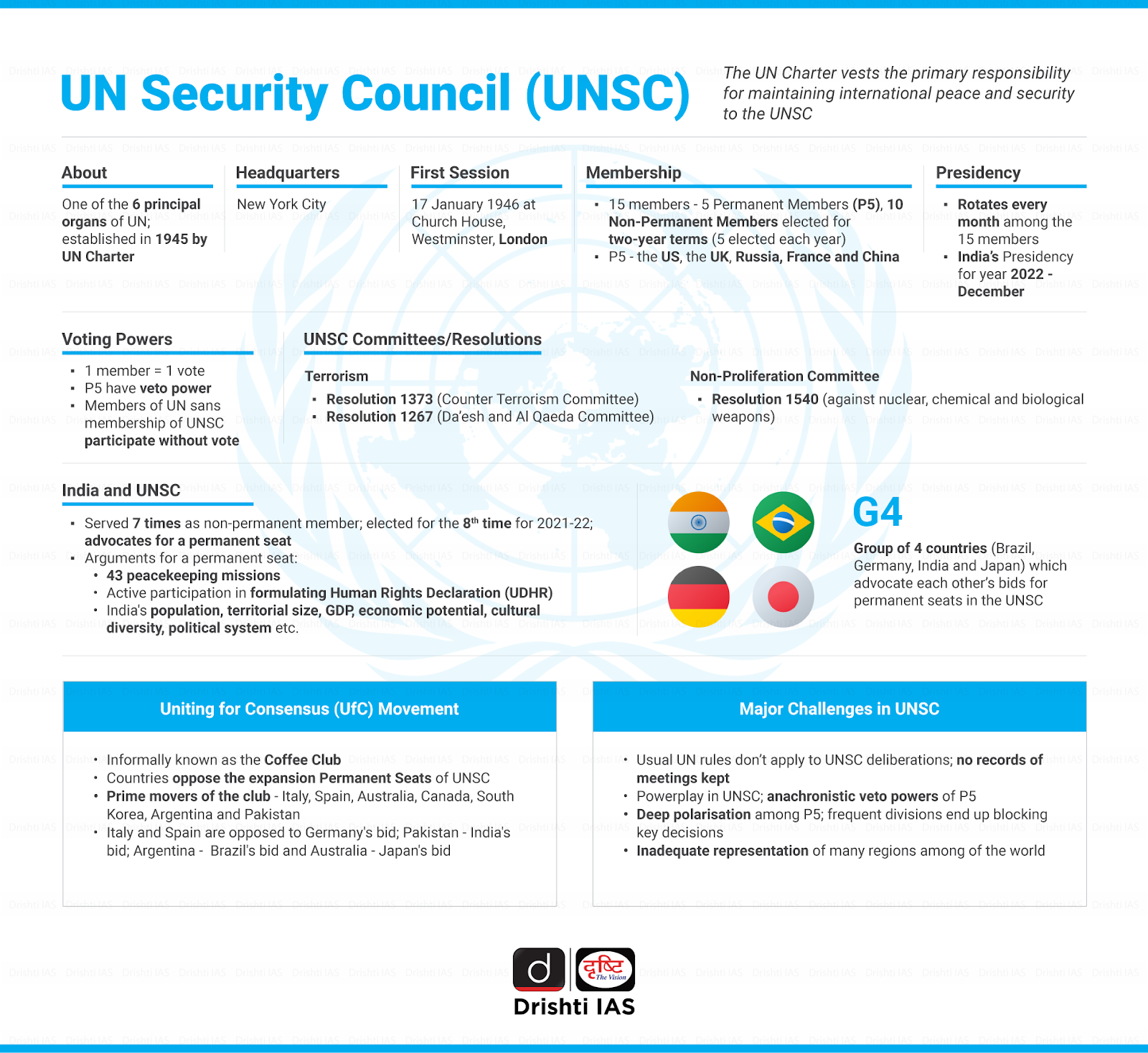
As the United Nations (UN) approaches its 80th anniversary in 2025, the G4 countries (India, Brazil, Germany, and Japan) have reiterated their calls for urgent reforms of the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- This was supported by other plurilateral groupings such as the L69 and C-10.
- Also, India addressed the 79th UNGA summit, sharing its perspectives and recommendations on global development and reforms.
What are G4, L69 and C-10 Groups?
- L69 Group:
- The L69 Group consists of 42 developing nations, including India, from Asia, Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, and the Pacific.
- It advocates for expanding both permanent and non-permanent UNSC membership to reflect current global realities and enhance accountability and representation.
- The Group advocates for a review of the permanent membership composition every 15 years to ensure it reflects evolving global realities.
- The group is named after the "L.69" draft document introduced in 2007-08, which initiated the Intergovernmental Negotiation (IGN) process.
- C-10 Grouping:
- The Committee of Ten (C-10) Heads of State and Government of the African Union consists of 10 African nations.
- It aims to reform the UNSC by advocating for improved representation of Africa and promoting the Common African Position, which is based on the Ezulwini Consensus and the Sirte Declaration.
- The Ezulwini Consensus, agreed by the African Union in 2005, seeks to reform the UNSC by providing Africa with 2 permanent seats with veto power and 5 non-permanent seats, aiming for enhanced representation and democracy.
- The Sirte Declaration (1999) was the resolution adopted to establish the African Union and address peace and security issues across the African continent.
- G-4 Grouping:
- The G4 is a grouping of Brazil, Germany, India and Japan which are aspiring to become permanent members of the UNSC.
- It was created in 2004 and has been promoting UN Security Council Reforms.
- The G4 countries are backing each other's efforts for permanent UNSC membership and typically hold meetings during the annual high-level UN General Assembly (UNGA) session.
Intergovernmental Negotiations (IGN)
- IGN is a group of nation-states working (informally) within the UN to further reform of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
- The IGN is composed of several different international organisations.
- African Union
- G4 nations
- Uniting for Consensus Group (UfC)
- L.69 Group of Developing Countries
- Arab League
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
Procedure for UN Security Council Reforms
- Reforming the UN Security Council requires amending the United Nations Charter, following a 2-stage process outlined in Article 108.
- First Stage: The General Assembly must approve the reform with a two-thirds majority, or at least 128 out of 193 member states. This stage does not permit a veto, as per Article 27.
- Second Stage: After the first stage approval, the UN Charter is treated as an international treaty and is amended.
- The amended Charter needs to be ratified by at least two-thirds of the member states, including all P5 members, following their national procedures.
- During this stage, the ratification can be influenced by the Parliaments of the P5 members, which may impact when the amended Charter takes effect.
What are Key Highlights of External Affairs Minister Speech at the 79th UN General Assembly (UNGA)?
- Reform of Multilateralism: India supported the theme of the 79th UNGA, "Leaving no one behind” by calling for reforming international systems and highlighting the need for equitable contributions and restoring trust to ensure global peace and prosperity.
- India’s Initiatives: India shared its initiatives such as
- Focus on vulnerable groups (women, farmers, youth) through targeted policies.
- Expansion of employment and entrepreneurship opportunities.
- Creation of replicable governance models and digital infrastructure.
- Convening Global South Summits to amplify shared concerns.
- Call for Unity: India called the member states to come together, share resources, and strengthen resolve to create positive change in the world.
- Condemnation of Terrorism: India condemned Pakistan's radicalization and ties to terrorism, emphasising that the central issue is Pakistan's occupation of Indian territory and its long-standing support for terrorism.
- India underscored the need for the United Nations (UN) to sanction terrorists without political interference, hinting at China's role in blocking such actions.
- Economic Practices and Sovereignty: India criticised unfair economic practices and infrastructure projects, particularly the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), stating that connectivity that undermines sovereignty must be approached with caution.
- Calls for Global Solutions: India urged the international community to seek urgent resolutions to ongoing conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine War and Gaza conflict, avoiding a fatalistic mindset.
Read More: UN Summit of the Future and the Reform in UN Institutions
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10 members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)
Q. How is the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference wherein the agreements were signed to set up IBRD, GATT and IMF, commonly known? (2008)
(a) Bandung Conference
(b) Bretton Woods Conference
(c) Versailles Conference
(d) Yalta Conference
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the International Monetary and Financial Committee (IMFC) consider the following statements: (2016)
- IMFC discusses matters of concern affecting the global economy, and advises the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on the direction of its work.
- The World Bank participates as observer in IMFC’s meetings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q. “Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to (2020)
(a) a loan system of the World Bank
(b) one of the operations of a Central Bank
(c) a credit system granted by WTO to its members
(d) a credit system granted by IMF to its members
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in the UN Security Council. (2015)





-min.jpg)