Infographics
Governance
Subsidies and Climate Change
Prelims: World Bank, Gross domestic product, Air pollution, Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi, Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana, Climate change
Mains: Positive and Negative Impacts of Subsidies, Challenges Related to Subsidies
Why in News?
A new World Bank report highlights the negative consequences of inefficiently subsidizing agriculture, fishing, and fossil fuel sectors, both implicitly and explicitly, by spending trillions of dollars, exacerbating climate change.
- In total, the report calculated that subsidy in the three areas exceeded USD 7 trillion, equivalent to 8% of the global gross domestic product.
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- Fossil Fuel Subsidies and Climate Change:
- The report acknowledges the limited effectiveness of reducing incentives for polluting fuels, as energy demand is not highly responsive to price changes.
- In 2021, countries spent USD 577 billion on subsidies aimed at lowering the prices of polluting fuels like oil, gas, and coal.
- These measures incentivize the overuse of fossil fuels and contribute to air pollution, particularly in industrializing middle-income countries with a high health burden.
- The report highlights the disproportionate allocation of funds, as most countries spend six times more on subsidizing fossil fuel consumption than on commitments made under the 2015 Paris Agreement.
- Inefficient Agricultural Subsidies:
- Explicit subsidies in the agricultural sector amount to approximately USD 635 billion annually in countries with accessible data, while global estimates exceed USD 1 trillion.
- These subsidies target farmers for purchasing specific inputs or cultivating particular crops.
- Research published in the report indicates that subsidies tend to favor wealthier farmers, even when programs are designed to target the poor.
- Inefficient subsidy usage has resulted in up to 17% of all nitrogen pollution in water over the past 30 years, leading to health impacts and reducing labor productivity by up to 3.5%.
- Explicit subsidies in the agricultural sector amount to approximately USD 635 billion annually in countries with accessible data, while global estimates exceed USD 1 trillion.
- Damaging Subsidies in the Fisheries Sector:
- The fisheries sector receives an estimated USD 35.4 billion per year in subsidies, of which approximately USD 22.2 billion contributes to overfishing.
- Subsidies play a significant role in driving excess fishing capacity, depleting fish stocks, and reducing fishing rents.
- When fisheries are not managed sustainably and already severely depleted, the negative impacts of subsidies are even more pronounced.
- Repurposing subsidies without incentivizing increased fishing capacity is crucial for safeguarding remaining fish stocks.
- The fisheries sector receives an estimated USD 35.4 billion per year in subsidies, of which approximately USD 22.2 billion contributes to overfishing.
What are the Positive Impacts of Subsidies?
- Agriculture:
- Income Support: Subsidies can provide income support to farmers, helping them cope with price fluctuations, market uncertainties, and production risks.
- For instance, the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme launched in 2019 provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Increased Production: Subsidies on inputs like fertilizers, seeds, and irrigation can promote increased agricultural production.
- The Indian government's support for fertilizers through the Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme ensures the availability of fertilizers at affordable prices to farmers.
- Income Support: Subsidies can provide income support to farmers, helping them cope with price fluctuations, market uncertainties, and production risks.
- Fishery:
- Modernization and Infrastructure Development: Subsidies in the fishery sector can aid in the modernization of fishing practices and the development of infrastructure.
- This can lead to increased productivity, improved safety measures, and better storage facilities.
- The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) aims to enhance fish production and fishermen's welfare through various interventions, including infrastructure development..
- Livelihood Support: Subsidies can provide livelihood support to fishermen, especially during lean seasons and adverse climatic conditions.
- Schemes like the National Scheme of Welfare of Fishermen provide assistance to fishermen for the construction and repair of boats, supply of safety equipment, and training programs.
- Modernization and Infrastructure Development: Subsidies in the fishery sector can aid in the modernization of fishing practices and the development of infrastructure.
- Fossil Fuel:
- Energy Access and Affordability: Subsidies on fossil fuels, such as LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) and kerosene, can ensure energy access and affordability for vulnerable sections of society.
- The Indian government launched the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) to increase LPG usage and reduce air pollution, deforestation, and health disorders
- Energy Access and Affordability: Subsidies on fossil fuels, such as LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) and kerosene, can ensure energy access and affordability for vulnerable sections of society.
What are the Challenges Related to Subsidies?
- Fiscal Burden: Subsidies often impose a significant fiscal burden on the government.
- The cost of subsidies can strain the government's finances and impact its ability to allocate resources to other critical sectors such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development.
- Balancing the need for subsidies with fiscal sustainability is a constant challenge.
- Inefficient Targeting: One of the major challenges is ensuring that subsidies reach the intended beneficiaries effectively.
- There is a risk of subsidies being misdirected or captured by ineligible individuals or entities.
- Proper identification and targeting mechanisms are essential to avoid leakages and ensure that subsidies benefit the intended recipients.
- Market Distortions: Subsidies can distort market dynamics and create inefficiencies. They may lead to overproduction or overconsumption of certain commodities, leading to market imbalances and price distortions.
- These distortions can affect the competitiveness of the sector and hinder the development of a sustainable and market-oriented agricultural, fishery, or energy sector.
- Environmental Implications: Subsidies on fossil fuels can discourage the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
- They can perpetuate the reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental degradation, air pollution, and climate change.
Way Forward
- Targeted Subsidy Reforms: Implement targeted subsidy reforms to ensure that subsidies reach the intended beneficiaries effectively.
- This can be achieved through the use of technology, such as Aadhaar-linked identification systems, to improve targeting accuracy and reduce leakages.
- Gradual Reduction and Rationalization: Gradually reduce and rationalize subsidies to ensure fiscal sustainability and minimize market distortions.
- Instead of across-the-board subsidy cuts, a phased approach can be adopted, focusing on reducing subsidies for the affluent and gradually redirecting funds towards investments in infrastructure, research and development, and capacity building in the respective sectors.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: Encourage the adoption of sustainable practices in agriculture, fishery, and energy sectors through subsidies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.
- Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.
- Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q1. How do subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and the economy of farmers? What is the significance of crop insurance, minimum support price and food processing for small and marginal farmers? (2017)
Q2. In what way could replacement of price subsidy with direct benefit Transfer (DBT) change the scenario of subsidies in India? Discuss. (2015)
Q3. What are the different types of agriculture subsidies given to farmers at the national and at state levels? Critically, analyse the agricultural subsidy regime with reference to the distortions created by it. (2013)
International Relations
U.S.-India initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology
For Prelims: Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), OpenRAN network technology, QUAD, NATO, AI, quantum computing, semiconductors
For Mains: Potential benefits of cooperation in critical and emerging technology, Role of innovation ecosystems
Why in News?
Recently, India and the United States have taken a significant step towards strengthening their strategic partnership and driving technology and defense cooperation. Under the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), the two nations have unveiled a roadmap for enhanced collaboration in high-technology areas.
- The initiative focuses on addressing regulatory barriers, aligning export controls, and fostering deeper cooperation in critical and emerging fields.
What is the iCET?
- About:
- The iCET was announced by India and the US in May 2022 and was officially launched in January 2023 and is being run by the National Security Council of both countries.
- Under iCET, both countries have identified six areas of cooperation which would include co-development and co-production, that would gradually be expanded to QUAD, then to NATO, followed by Europe and the rest of the world.
- Under iCET, India is ready to share its core technologies with the US and expects Washington to do the same.
- It aims to promote collaboration in critical and emerging technology areas, including AI, quantum computing, semiconductors, and wireless telecommunication.
- Focus Areas of the Initiative:
- AI research agency partnership.
- Defense industrial cooperation, defense technological cooperation, and defense startups.
- Innovation Ecosystems.
- Semiconductor ecosystem development.
- Cooperation on human spaceflight.
- Advancement in 5G and 6G technologies, and adoption of OpenRAN network technology in India.
- Progress Made So Far:
- Key achievements include the Quantum Coordination Mechanism, public-private dialogue on telecommunication, important exchanges on AI and space, MoU on establishing a semiconductor supply chain, and conclusion of a roadmap for defense industrial cooperation.
- The two countries are close to finalizing a mega jet engine deal, and a new initiative called the India-U.S. Defence Acceleration Ecosystem (INDUS-X) is set to be launched.
- Strategic Trade Dialogue has been established to address regulatory barriers and review export control norms.
How have been India’s Relations with the US?
- Economic Relations:
- The U.S. has emerged as India's biggest trading partner in 2022-23 on account of increasing economic ties between the two countries.
- The bilateral trade between India and the U.S. has increased by 7.65% to USD 128.55 in 2022-23 as against USD 119.5 billion in 2021-22.
- Exports to the U.S. rose by 2.81% to USD 78.31 billion in 2022-23 as against USD 76.18 billion in 2021-22, while imports grew by about 16% to USD 50.24 billion.
- International Cooperations:
- India and the United States cooperate closely at multilateral organizations, including the United Nations, G-20, Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Regional Forum, International Monetary Fund, World Bank, and World Trade Organization.
- The United States welcomed India joining the UN Security Council in 2021 for a two-year term and supports a reformed UN Security Council that includes India as a permanent member.
- Together with Australia and Japan, the United States and India convene as the Quad to promote a free and open Indo-Pacific and provide tangible benefits to the region.
- India is also one of twelve countries partnering with the United States on the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF).
- India is a member of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), at which the United States is a dialogue partner.
- In 2021, the United States joined the International Solar Alliance headquartered in India, and in 2022 the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
What is OpenRAN Network Technology?
- About:
- It is a non-proprietary version of the Radio Access Network (RAN) system.
- A RAN is a major component of a wireless telecommunications system that connects individual devices to other parts of a network through a radio link.
- Allows interoperability between cellular network equipment from different vendors.
- It is a non-proprietary version of the Radio Access Network (RAN) system.
- Advantages of OpenRAN Network Technology:
- Creates a more open and flexible RAN architecture.
- Based on open interfaces and virtualization.
- Supported by industry-wide standards.
- Cost reduction.
- Increased competition.
- Faster innovation.
- Applications of OpenRAN Network Technology:
- Supporting 5G and 6G networks.
- Enhancing network performance and security.
- Enabling new services and capabilities.
- Bridging the digital divide.
Indian Economy
India Infrastructure Project Development Fund
For Prelims: Infrastructure Finance Secretariat (IFS), IIPDF, PPP, Budget 2023-24, PM Gati Shakti, NIP.
For Mains: Promoting Private Investment in Indian Infrastructure.
Why in News?
To support the Digital India initiative, the Infrastructure Finance Secretariat (IFS), under the Ministry of Finance has launched the IIPDF (India Infrastructure Project Development Fund) Portal.
- This online platform allows the submission of applications under the IIPDF Scheme, reducing processing time, paperwork, and facilitating timely approvals.
What is IIPDF Scheme?
- Background:
- IIPDF was created in the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India with an initial corpus of Rs. 100 crore for supporting the development of Public Private Partnership (PPP) projects that can be offered to the private sector.
- About:
- DEA has restructured the existing fund IIPDF as a Central Sector Scheme with total outlay of Rs.150 Crore for a period of 3 years from 2022-23 to 2024-25.
- It is available to the Sponsoring Authorities for PPP projects for meeting the project development costs.
- It would be necessary for the Sponsoring Authority to create and empower a PPP Cell to undertake PPP project development activities and also address larger policy and regulatory issues.
- Objective:
- It is aimed at providing financial support for quality project development activities.
- Significance:
- The Sponsoring Authority will be able to source funding to cover a portion of the PPP transaction costs, thereby reducing the impact of costs related to procurement on their budgets.
- Financial Outlay:
- The IIPDF will contributes upto 75% of the project development expenses to the Sponsoring Authority as an interest free loan. The balance 25% will be co-funded by the Sponsoring Authority.
- On successful completion of the bidding process, the project development expenditure would be recovered from the successful bidder.
- However, in the case of failure of the bid, the loan would be converted into grant.
- In case the Sponsoring Authority does not conclude the bidding process for some reason, the entire amount contributed would be refunded to the IIPDF.
- Approval Committee (AC):
- The IIPDF scheme shall be administered by the AC. The composition of the AC is as under:
- Joint secretory, DEA- Chairperson
- Representative of NITI Aayog
- Deputy Secretory/Private Investment Unit, DEA- Member Secretary
- The IIPDF scheme shall be administered by the AC. The composition of the AC is as under:
What is the Status of the Infrastructure Sector of India?
- About:
- Infrastructure development plays a crucial role in India's growth trajectory, acting as a catalyst for economic development across various sectors.
- The Indian government has recognized the significance of robust infrastructure and has launched several initiatives and investments to drive progress.
- Current Market Size and Outlook:
- The infrastructure sector in India is poised to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% by 2027.
- The capital investment outlay for infrastructure in Budget 2023-24 is being increased by 33% to Rs. 10 lakh crore (USD 122 billion), accounting for 3.3% of GDP.
- India is expected to be one of the largest economies in the world by 2047 with a GDP of about USD 35- 40 trillion as per CII (Confederation of Indian Industry) estimates from about USD 3.5 trillion in 2022 which increased by about 2 x since 2010.
- In addition, the country’s industrial output has increased by 56% since 2010, which has supplemented the pace of urbanization which is expected to accelerate by 2047.
- Government Initiatives:
Way Forward
- India has to enhance its infrastructure to reach its 2025 economic growth target of USD 5 trillion. India's population growth and economic development requires improved transport infrastructure, including through investments in roads, railways, and aviation, shipping and inland waterways.
- The government has also suggested an investment of USD 750 Billion to strengthen railway infrastructure and envisioned the Maritime India Vision 2030 which estimates massive investments in world-class infrastructure development at Indian ports.
- India, it is estimated, needs to invest USD 840 billion over the next 15 years into urban infrastructure to meet the needs of its fast-growing population. This investment will only be rational as well as sustainable, if we additionally focus on long-term maintenance and strength of our buildings, bridges, ports and airports.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘National Investment and Infrastructure Fund’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an organ of NITI Aayog.
- It has a corpus of Rs 4,00,000 crore at present.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
- The NIIF (National Investment and Infrastructure Fund) is overseen by the Investment Division of Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The NIIF is currently managing three funds which are registered as an Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) under the SEBI Regulations. Those three funds are Master Fund, Strategic Fund and Fund of Funds and the proposed corpus of NIIF is Rs 40,000 crore and not 4,00,000 crore. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Governance
GoI-UNSDCF 2023-2027
For Prelims: NITI Aayog, United Nations, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), GoI-UNSDCF 2023-2027.
For Mains: Government of India - United Nations Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework (GoI-UNSDCF) 2023-2027, Initiatives related to SDGs.
Why in News?
Recently, NITI Aayog and the United Nations in India signed the Government of India - United Nations Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework (GoI-UNSDCF) 2023-2027.
- The United Nations General Assembly designates this framework as the principal planning and implementation instrument for the UN Development System at country level.
- The framework aligns with India's national vision for development and aims to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), emphasizing gender equality, youth empowerment, and human rights.
What are the Key Points of the Framework?
- Strategic Pillars and Outcome Areas:
- The GoI-UNSDCF 2023-2027 is built upon Four Strategic pillars derived from the 2030 Agenda:
- People, Prosperity, Planet, and Participation.
- The four pillars encompass Six Outcome Areas:
- Health and Wellbeing
- Nutrition and Food Security
- Quality Education
- Economic Growth and Decent Work
- Environment, Climate, WASH (Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene), and Resilience
- Empowering People, Communities, and Institutions.
- The GoI-UNSDCF 2023-2027 is built upon Four Strategic pillars derived from the 2030 Agenda:
- Focus:
- The GoI-UNSDCF places specific emphasis on SDG localisation and South-South Cooperation, aligning with India's leadership in implementing and accelerating the SDGs.
- SDG localization is the process of transforming the SDGs into reality at the local level, in line with national frameworks and with communities’ priorities.
- India aims to showcase its development models globally and actively promotes South-South cooperation.
- The GoI-UNSDCF places specific emphasis on SDG localisation and South-South Cooperation, aligning with India's leadership in implementing and accelerating the SDGs.
- Implementation and Monitoring:
- The implementation, monitoring, and reporting of the GoI-UNSDCF 2023-2027 will be jointly led by the Government of India and the United Nations, India through a Joint Steering Committee.
What are Sustainable Development Goals?
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
- It is a set of 17 SDGs which recognize that action in one area will affect outcomes in others and that development must balance social, economic, and environmental sustainability.
- Countries have committed to prioritizing progress for those who are furthest behind.
- The SDGs are designed to end poverty, hunger, AIDS, and discrimination against women.
- India in recent years has made significant efforts in achieving the Goal 13th of the SDGs in particular.
- The goal calls for taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
- The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Governance
Alarming Rise of Non-Communicable Diseases in India
For Prelims: Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), non-communicable diseases, Diabetes, National Health Mission (NHM), Sustainable Development
For Mains: Impacts of Non-Communicable Diseases, National Health Mission
Why in News?
A recent study conducted by the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has shed light on the growing burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in India.
- The study marks the first comprehensive epidemiological research paper to include participants from 31 states and Union Territories. By including data from a wide range of regions, the study provides valuable insights into the prevalence and impact of NCDs, such as diabetes, in the country.
What Were the Key Findings of the Study?
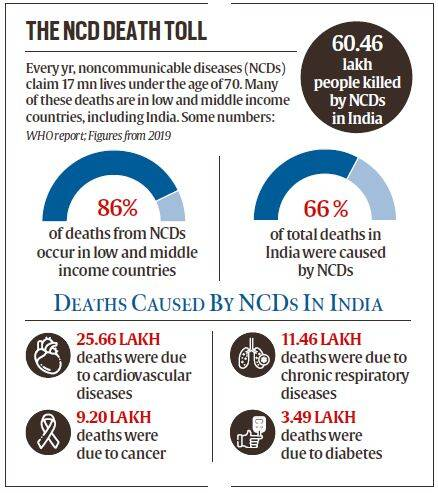
- Findings:
- Goa, Puducherry, and Kerala have the highest prevalence of diabetes, with rates approaching 25-26.4%.
- Diabetes: India now has 101 million individuals with diabetes.
- Prediabetes: The study identified 136 million people with prediabetes.
- High blood pressure: 315 million individuals were found to have hypertension.
- Obesity: 254 million people were classified as generally obese, while 351 million had abdominal obesity.
- The prevalence of generalised obesity stands at 28.6% across the population, while abdominal obesity affects 39.5% of Indians. Female abdominal obesity is particularly high, at 50%.
- Hypercholesterolemia: 213 million individuals had fat accumulation in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- The study reveals that 24% of Indians suffer from hypercholesterolemia.
- High LDL Cholesterol: 185 million individuals had elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
- LDL is the “bad cholesterol” because too much of it in blood can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Cholesterol travels through the blood on proteins called “lipoproteins.
- Significance of the Study:
- The study encompasses a large sample size of 1,13,043 individuals from diverse regions.
- It reveals that diabetes and other metabolic NCDs are more prevalent in India than previously estimated.
- While urban areas currently have higher rates of metabolic NCDs, except for prediabetes, rural regions are expected to experience a surge in diabetes cases in the next five years if left unregulated.
- Interstate and inter-regional variations highlight the need for state-specific policies and interventions.
- Impact of Study on India:
- The study serves as an early warning for the population's increased vulnerability to NCDs and life-altering medical conditions, including strokes.
- India faces the dual challenge of malnutrition and obesity, with exposure to fast food, sedentary lifestyles, lack of sleep, exercise, and stress contributing to NCD prevalence.
- Impact on Quality of Life and Life Expectancy:
- NCDs, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and chronic respiratory diseases, contribute to the overall disease burden in the country.
- NCDs often result in disabilities, reducing individuals' functional abilities and impairing their daily activities.
- The management of NCDs requires long-term medical care, medications, and lifestyle modifications, which can be challenging for individuals and their families.
- NCDs can lead to increased healthcare expenses, impacting the financial well-being of individuals and households.
- The burden of NCDs can hinder individuals' productivity and socioeconomic development, affecting their employment opportunities and economic growth.
- NCDs can significantly reduce life expectancy if not properly managed and controlled.
What are Initiatives Related to NCDs?
- Indian:
- National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD), previously known as National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- The Central Government is implementing the Strengthening of Tertiary Care Cancer facilities scheme to support the setting up of State Cancer Institutes (SCI) and Tertiary Care Centres (TCCC) in different parts of the country.
- Oncology in its various aspects has a focus in case of new AIIMS and many upgraded institutions under Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY).
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal outlets have been opened at 159 Institutions/Hospitals with an objective to make available Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases drugs and implants at discounted prices to the patients.
- Jan Aushadhi stores are set up by the Department of Pharmaceuticals to provide generic medicines at affordable prices.
- Global:
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
- WHO plays a key leadership role in the coordination and promotion of the global fight against NCDs.
- Global Action Plan: In 2019, the World Health Assembly extended the WHO Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020 to 2030 and called for the development of an Implementation Roadmap 2023 to 2030 to accelerate progress on preventing and controlling NCDs.
- It supports actions to achieve a set of nine global targets with the greatest impact towards prevention and management of NCDs.
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
What are Non-Communicable Diseases?
- About:
- NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors.
- The main types of NCD are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
- Causes:
- Tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity and air pollution are the main risk factors contributing to these conditions.
Way Forward
- Wellness and a healthy lifestyle are essential in combating this growing pandemic.
- Emphasizing healthy diets and regular exercise is crucial.
- The Indian Health Ministry has identified cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes as major NCDs, addressing them through programs focusing on health infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, awareness generation, prevention, early diagnosis, and appropriate healthcare referrals.
- State-specific policies allow tailored interventions to address the specific challenges and risk factors of each region, maximizing the effectiveness of efforts to combat NCDs.
- By allocating resources according to the specific needs of each state, state-specific strategies optimize resource utilization, enhance healthcare infrastructure, and ensure maximum impact in the fight against NCDs.
Important Facts For Prelims
Gandhi Peace Prize
Why in News?
Gita Press, Gorakhpur, a 100-year-old institution that publishes Hindu religious texts and promotes Gandhian ideals of peace and social harmony, has been awarded the Gandhi Peace Prize for 2021 by the Government of India.
- The prize was announced by the Ministry of Culture.
What is the Gandhi Peace Prize?
- About:
- Gandhi Peace Prize Awards for Social, Economic and Political transformation through Non-violence was instituted in the year 1995, on the occasion of the 125th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi, as a tribute to his ideals and contributions to humanity.
- Reward:
- The award carries an amount of Rs 1 crore, a citation, a plaque and a traditional handicraft or handloom item.
- The award is conferred by the President of India at a function in Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- The award carries an amount of Rs 1 crore, a citation, a plaque and a traditional handicraft or handloom item.
- Consideration:
- This award is given to individuals, associations, institutions or organizations who have worked selflessly for peace, non-violence and amelioration of human sufferings.
- The award is open to all persons regardless of nationality, race, language, caste, creed or gender.
- The Award may be divided between two persons / institutions who are considered by the Jury to be equally deserving of recognition in a given year.
- Work by a person since deceased cannot be the subject of an Award. If, however, his death occurred subsequent to a proposal having been submitted to the Jury(headed by the Prime Minister) in the manner stipulated in the Code of Procedure, then a Posthumous Award may be made.
- Previous Awardees:
- Organizations: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Ramakrishna Mission, Grameen Bank of Bangladesh, Vivekananda Kendra, Akshaya Patra, Ekal Abhiyan Trust, Sulabh International
- Luminaries: Nelson Mandela, Sultan Qaboos bin Said Al Said, Oman (2019) and Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, Bangladesh (2020).
Gita Press
- Established in 1923 by Jaya Dayal Goyandka and Hanuman Prasad Poddar, Gita Press is one of the world’s largest publishers of Hindu religious texts, having published 41.7 crore books in 14 languages, including 16.21 crore copies of Shrimad Bhagvad Gita.
- Gita Press also runs a monthly magazine called Kalyan, which covers topics such as spirituality, culture, history, ethics and morality.
- It also runs a charitable hospital called Kalyan Chikitsalaya in Gorakhpur, which provides free medical services to the poor and needy.
Mahatma Gandhi
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
(a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
(d) Sarojini Naidu
Ans: (c)
Q2. With reference to the British colonial rule in India, consider the following statements: (2019)
- Mahatma Gandhi was instrumental in the abolition of the system of ‘indentured labour’.
- In Lord Chelmsford’s ‘War Conference’, Mahatma Gandhi did not support the resolution on recruiting Indians for World War.
- Consequent upon the breaking of Salt Law by Indian people, the Indian National Congress was declared illegal by the colonial rulers.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
Impact of US Federal Reserve's Policy on Indian Markets
Why in News?
The recent US Federal Reserve policy meeting, keeping the policy rate unchanged at 5.25% but signaling two rate hikes to reach 6% by end-2023, has sparked speculation on India's interest rates and markets.
- While the Fed chose to maintain the status quo, it hinted at the possibility of two more rate hikes this year to combat inflation.
What is the Impact of Fed’s Policy on the Indian Market?
- The Indian markets fell by 0.49% on June 29, 2023, following the Fed’s policy announcement.
- The Fed’s policy affects the Indian markets through various channels such as:
- Exchange Rate Channel: The Fed’s rate hikes tend to strengthen the US dollar against other currencies, including the Indian rupee.
- A weaker rupee also increases the debt servicing costs for Indian borrowers who have taken loans in foreign currency.
- Capital Flow Channel: The Fed’s rate hikes also reduce the interest rate differential between the US and India, which makes India less attractive for foreign investors who seek higher returns.
- This could lead to capital outflows from India’s equity and debt markets, which could lower asset prices and increase volatility.
- Capital outflows could also reduce India’s foreign exchange reserves and create liquidity crunches in domestic markets.
- Inflation Channel: The Fed’s rate hikes could also affect India’s inflation through two ways.
- First, a weaker rupee could increase the imported inflation for India, as it raises the cost of imported goods such as oil, gold and electronics.
- Second, higher global commodity prices due to strong US demand could also push up India’s domestic inflation, as it affects the input costs for various sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing and services.
- Growth Channel: The Fed’s rate hikes could also have an impact on India’s economic growth through two ways.
- First, a tighter US monetary policy could slow down the global economic recovery from the pandemic, which could hurt India’s export prospects and external demand.
- Second, higher domestic interest rates due to capital outflows and inflation pressures could dampen India’s domestic demand and investment activity.
- Exchange Rate Channel: The Fed’s rate hikes tend to strengthen the US dollar against other currencies, including the Indian rupee.
What are Some of the Possible Scenarios for Indian Markets?
- Best-case Scenario: The Fed’s rate hikes are gradual and moderate, and are accompanied by clear and credible communication.
- The RBI maintains an accommodative stance and supports the liquidity and credit conditions in India.
- India’s economic recovery is robust and resilient, supported by strong domestic and external demand. India’s inflation is contained and manageable, and its fiscal and current account deficits are under control.
- Global risk appetite is high and foreign investors remain positive on India’s growth potential and reforms.
Note: An accommodative stance means the central bank is prepared to expand the money supply to boost economic growth. The central bank, during an accommodative policy period, is willing to cut the interest rates.
- Worst-case Scenario: The Fed’s rate hikes are sudden and aggressive, and are driven by unexpected inflation shocks.
- The RBI is forced to tighten its policy to defend the rupee and curb inflation. India’s economic recovery is weak and uneven, hampered by pandemic-related uncertainties and structural bottlenecks.
- India’s inflation is high and persistent, and its fiscal and current account deficits are unsustainable.
- Global risk appetite is low and foreign investors flee from India’s markets due to geopolitical tensions, policy uncertainty and governance issues.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
- Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
- Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Tight monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
- Capital flight may increase cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBs
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
Impact of Spaceflight on Brain Fluid Dynamics
Why in News?
Recently, a study was published in Scientific Reports, which sheds light on the effects of Spaceflight on the Brain, particularly concerning Longer Missions and the recovery period between flights.
- The study involved MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans of 30 astronauts before and after spaceflight. These participants encompassed various mission durations, including two-week missions, six-month missions, and longer expeditions.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Spaceflight-Induced Brain Changes:
- The extended stays in space lead to fluid changes in the brain, with ventricles—cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid—expanding progressively.
- Cerebrospinal fluid is a clear, colorless fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord. It is produced in the ventricles of the brain and circulates throughout the central nervous system.
- The extended stays in space lead to fluid changes in the brain, with ventricles—cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid—expanding progressively.
- Recovery Time between Missions:
- Astronauts who had over three years of recovery time experienced an increase in ventricular volume after their most recent mission.
- Conversely, those with shorter recovery periods demonstrated minimal to no ventricular enlargement after spaceflight.
- Association between Inter-Mission Delay and Brain Changes:
- Longer inter-mission delays were linked to greater increases in left and right lateral and third ventricle volumes following spaceflight.
- However, the fourth ventricle exhibited the opposite pattern, with longer inter-mission intervals correlating with greater volumetric decreases after space travel.
What is the Significance of the Study?
- Understanding the influence of both previous and current spaceflight experiences on brain changes is crucial for safeguarding astronauts' health.
- There is a need to consider adequate recovery periods between missions, exceeding three years, to enable the brain's compensatory mechanisms to normalize intracranial fluid levels.
- By addressing these factors, future space missions can better protect astronauts from potential long-term neurological implications and enhance their overall well-being.
What are Brain Ventricles?
- About:
- Brain ventricles are cavities within the brain that produce and store Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF), which surrounds the brain and spinal cord, cushioning them and protecting them from trauma.
- They are also responsible for removing waste and delivering nutrients to your brain.
- There are Four Brain Ventricles:
- The first and second ventricles are lateral ventricles. These C-shaped structures are located on each side of the cerebral cortex, the wrinkly outer layer of Brain.
- The third ventricle is a narrow, funnel-shaped structure situated between the right and left thalamus, just above your brain stem.
- The fourth ventricle is a diamond-shaped structure that runs alongside the brain stem.
- It has four openings through which cerebrospinal fluid drains into an area surrounding the brain (subarachnoid space) and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- Functions:
- CSF Circulation: The ventricles, specifically the lateral ventricles, are interconnected with the third ventricle in the midline of the brain. CSF flows through these ventricles and circulates around the brain and spinal cord, helping to remove waste products and regulate the extracellular environment.
- Maintenance of Intracranial Pressure: The ventricles help maintain the appropriate pressure within the brain. Any disruption in the production, circulation, or absorption of CSF can lead to an imbalance in intracranial pressure, which may result in conditions like hydrocephalus.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Dugdh Sankalan Sathi App
Recently, the Indian dairy industry witnessed a significant milestone with the unveiling of the "Dugdh Sanakalan Sathi Mobile App" by the Union Minister of Heavy Industries. This ground breaking mobile application, developed by Rajasthan Electronics & Instruments Limited (REIL), is poised to revolutionize the milk collection process and address key challenges faced by the industry. With a focus on improving milk quality, fostering transparency among stakeholders, and streamlining operations at the grassroots village level, including Milk Cooperative Societies, this app marks a significant step towards digitization in the dairy sector. The app also provides real-time updates on milk prices from the cloud server, eliminating human errors and ensuring transparency in payment calculations. Additionally, it facilitates direct beneficiary transfers of milk payments and government subsidies to the bank accounts of milk producers, promoting financial inclusion and empowerment.
Read more: India’s Dairy and Livestock Sector
NTPC's Rooftop Solar Project Empowers IIT Jodhpur
NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam Limited (NVVN), a wholly owned subsidiary of National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPC), has commissioned its first Rooftop Solar Photovoltaic Project at IIT Jodhpur, Rajasthan. The one MW Grid-connected Solar Project has been implemented by NVVN under the RESCO model, with a Power Purchase Agreement duration of 25 years. Under the RESCO model for implementing rooftop solar installation, a renewable energy service company ("RESCO"), designs, builds, funds, and operates the entire solar power plant (roof or ground-mounted), the consumer pays the developer against assured monthly unit generation per kW and DISCOMs adjusts generated units in consumer’s electricity bill.
NVVN Limited was formed by NTPC in the year 2002 to tap the potential of power trading in the country. NVVN holds the highest Category 'I' power trading license as per the latest regulation of Central Electricity Regulatory Commission.
NTPC Ltd. is a central Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under the Ministry of Power. It is India’s largest energy conglomerate with roots planted way back in 1975 to accelerate power development in India. It became a Maharatna company in May 2010. It is located in New Delhi.
Read more: National Thermal Power Corporation Limited, India’s Solar Power Dream
The Right to Change One’s Name
In recent rulings, the High Courts of Allahabad and Delhi emphasized the right to change one's name as an integral part of the right to life under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution. The Allahabad High Court stated that every citizen has the fundamental right to keep or change their name. The courts found that the denial of name-change requests by the authorities violated the fundamental rights of the petitioners under Articles 19(1)(a), 21, and 14 of the Constitution.
Similarly, the Delhi High Court, asserted that the right to identity is an intrinsic part of the right to life under Article 21. Both cases highlight the significance of personal identity and the recognition that individuals have the right to a name that reflects their self-worth and protects them from social stigmas.
While the right to change one's name is considered a fundamental right, it is not an absolute right and is subject to reasonable restrictions. The Allahabad High Court clarified that these restrictions must be fair, just, and reasonable.
Read more: Article 21 of the Indian Constitution
Common Annual Confidential Report (ACR) in Armed Forces
To foster integration and jointness within the armed forces, a common Annual Confidential Report (ACR) will be implemented, starting with senior officers.
This reform aims to establish common parameters, procedures, and assessments, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced uniformity in HR practices. The implementation of a common ACR for two- and three-star officers has been approved.
Currently, selection for combined or tri-services appointments is based on parent service-specific parameters, but recent cross-services postings have been initiated as a step towards achieving greater integration.
With the ongoing transformation towards joint structures and organizations, the employment of officers in tri-service appointments is expected to increase. Consequently, there is a need to streamline the appraisal system to ensure effectiveness in undertaking tasks within these appointments. The move towards a common ACR aligns with the broader goal of establishing integrated theater commands and reflects the commitment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) to drive organizational reforms.
Read more: Theaterisation-of-Armed-Forces, Chief of Defence Staff.