Governance
Government Programme for NCD Renamed
- 08 May 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: NPCDCS programme, National Health Mission, NP-NCD, Non-Communicable Diseases
For Mains: National Health Mission, Non-Communicable Diseases
Why in News?
The existing National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) programme has been renamed National Programme for Prevention & Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD).
- It has been renamed to subsume all types of NCDs.
- Further, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has renamed the Comprehensive Primary Healthcare Non-Communicable Disease (CPHC NCD IT) system as the National NCD Portal to cover a wider population for screening and management of non-communicable diseases.
What is NPCDCS/NP-NCD?
- About:
- NPCDCS is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) across the country.
- Aim:
- It was launched in 2010 with a focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- Management:
- Under NPCDCS, NCD Cells are being established at National, State and District levels for programme management, and NCD Clinics are being set up at District and Community Health Centres (CHC) levels, to provide services for early diagnosis, treatment and follow-up for common NCDs.
- Achievement:
- Under NPCDCS, 677 NCD district-level clinics, 187 District Cardiac Care Units, 266 District Day Care Centres and 5,392 NCD Community Health Centre-level clinics have been set up.
What is National Health Mission?
- NHM was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission and the National Urban Health Mission.
- The main programmatic components include Health System Strengthening in rural and urban areas for - Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), and Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases. The NHM envisages achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people's needs.
- The National Health Mission seeks to ensure the achievement of the following indicators:
- Reduce Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) to 1/1000 live births
- Reduce Infant Mortality rate (IMR) to 25/1000 live births
- Reduce Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 2.1
- Prevention and reduction of anaemia in women aged 15–49 years
- Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non- communicable; injuries and emerging diseases
- Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure
- Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half
- Reduce the prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts
- Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000
- Less than 1 per cent microfilaria prevalence in all districts
- Kala-azar Elimination by 2015, <1 case per 10000 population in all blocks
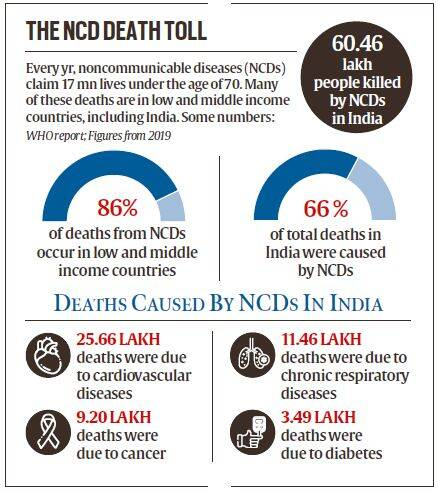
What are Non-Communicable Diseases?
- About:
- NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors.
- The main types of NCD are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes.
- Causes:
- Tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity and air pollution are the main risk factors contributing to these conditions.
- Indian Initiatives:
- The Central Government is implementing the Strengthening of Tertiary Care Cancer facilities scheme to support the setting up of State Cancer Institutes (SCI) and Tertiary Care Centres (TCCC) in different parts of the country.
- Oncology in its various aspects has a focus in case of new AIIMS and many upgraded institutions under Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY).
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal outlets have been opened at 159 Institutions/Hospitals with an objective to make available Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases drugs and implants at discounted prices to the patients.
- Jan Aushadhi stores are set up by the Department of Pharmaceuticals to provide generic medicines at affordable prices.
- Global:
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).
- WHO plays a key leadership role in the coordination and promotion of the global fight against NCDs.
- Global Action Plan: In 2019, the World Health Assembly extended the WHO Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020 to 2030 and called for the development of an Implementation Roadmap 2023 to 2030 to accelerate progress on preventing and controlling NCDs.
- It supports actions to achieve a set of nine global targets with the greatest impact towards prevention and management of NCDs.
- Agenda for Sustainable Development: As part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, heads of state and government committed to develop ambitious national responses, by 2030, to reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment (SDG target 3.4).