Appointment of CEC and EC
For Prelims: Chief Election Commissioner (CEC), Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023, Anoop Baranwal Case, 2023, Election Commission, LoP, CJI, Goswami Committee, Law Commission.
For Mains: Concerns related to appointment of Chief Election Commissioner and way forward.
Why in News?
Gyanesh Kumar has been appointed as the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) under the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023.
- One of the members of the selection committee objected that the selection process bypassed Supreme Court (SC) guidelines in the Anoop Baranwal Case, 2023.
What are the Key Facts Regarding the 2023 Act?
- About: The Act replaces the Election Commission (Conditions of Service of Election Commissioners and Transaction of Business) Act, 1991 to regulate the appointment, tenure, service conditions of CEC/ECs, and Election Commission procedures.
- Judicial Background: This Act followed SC intervention after several petitions challenged the Centre’s exclusive power in appointing CEC and ECs.
- In the Anoop Baranwal Case, 2023, the SC ruled that a panel of the Prime Minister, LoP, and CJI would select CEC and ECs until Parliament passed a law.
- Before the Judgement, the appointment of the CEC and other ECs was made by the President on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- Key Provisions:
- Selection Committee: The CEC and ECs will be appointed by the President based on the recommendation of a Selection Committee consisting of:
- Prime Minister (Chairperson).
- Leader of the Opposition (LoP) (or leader of the largest opposition party) in the Lok Sabha.
- Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Search Committee: A Search Committee, led by the Law Minister and comprising two other members not below the rank of Secretary to the Government of India, shortlists five candidates.
- Section 8 of the Act gives the Selection Committee the power to consider names beyond the shortlisted five.
- Eligibility Criteria: The CEC and other ECs must have held a Secretary-level post in the Government of India and possess integrity, election management experience.
- Salary, Term, and Reappointment: CEC and ECs receive a SC judge's salary and serve for six years or until age 65, whichever is earlier.
- CEC and ECs cannot be re-appointed. If an EC becomes CEC, their total tenure cannot exceed six years.
- A CEC or EC receiving a government pension (excluding disability pension) will have their salary reduced by the amount of the pension received.
- Removal and Resignation: The CEC can be removed only in the same manner and on the same grounds as a SC Judge, while an EC can be removed on the CEC’s recommendation.
- Both can resign to the President.
- Selection Committee: The CEC and ECs will be appointed by the President based on the recommendation of a Selection Committee consisting of:
What are the Key Concerns Regarding the 2023 Act?
- Exclusion of CJI: The 2023 Act replaces the SC-mandated panel (PM, LoP, CJI) with a committee of the PM, LoP, and a Union Minister allowing the executive to dominate the selection process.
- Violation of Separation of Power: The Act is being challenged in SC by petitioners arguing whether Parliament has the legal authority to override or modify a SC’s Constitution Bench ruling in the Anoop Baranwal Case, 2023 through legislation or ordinance.
- Vacancy in Selection Committee: The Act allows the Selection Committee to function despite vacancies.
- If the LoP post is vacant due to the dissolution of the Lok Sabha, only the PM and a Union Minister will remain for selecting candidates, effectively bypassing both the judgment and the 2023 Act.
- Undermining Free and Fair Elections: With the executive holding two of three votes, the Act raises concerns over ECs' independence and potential alignment with the ruling party that may undermine free and fair elections.
- Impact on Credibility of EC: The Act's Search Committee for CEC and EC candidates faces criticism for increasing executive influence even before appointment.
- Perceived bias in EC selection could significantly impact Indian democracy, as elections determine political power.
Global Practices in the Appointment of Electoral Body Members
- South Africa: The selection process involves key figures such as the President of the Constitutional Court, representatives of the Human Rights Court, and advocates for gender equality.
- United Kingdom: Candidates for the electoral body are subject to approval by the House of Commons.
- United States: The President appoints members to the electoral body, and the appointments require confirmation by the Senate.
Way Forward
- Reviewing Selection Process: Restoring the CJI’s role in the Selection Committee as per the Anoop Baranwal Case, 2023 would introduce a neutral element in the process, reducing the risk of political bias.
- A retired Supreme Court judge or the Speaker of the Lok Sabha can be included in the Selection Committee to dilute executive dominance.
- Strengthening Independence of EC: The Goswami Committee (1990) advised barring CECs and ECs from government posts, including Governor, to prevent conflicts of interest and ensure impartiality.
- Financial Autonomy: The expenditure of the Election Commission should be 'charged' on the Consolidated Fund of India (CFI) so that it cannot be altered or reduced through voting.
- Equality Between CEC and ECs: The 255th Law Commission (2015) report on Electoral Reforms recommended amending Article 324(5) to give ECs the same protection as the CEC, ensuring impartiality and resistance to external influence.
- Article 324(5) mandates impeachment like Supreme Court judges for CEC removal, while ECs can be removed on the CEC’s recommendation, making them more vulnerable.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q.Evaluate the concerns related to executive influence in the appointment process in the Election Commissioners and suggest measures to enhance its autonomy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections.
- Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognised political parties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in the light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)
Rising Stress in India’s Defence Forces
For Prelims: Central Reserve Police Force, National Tele Mental Health Programme, Kiran Helpline
For Mains: Stress and morale issues in armed forces, Mental health concerns and stigma
Why in News?
A Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) soldier in Manipur killed two colleagues before taking his own life, highlighting rising stress among India’s security forces.
- Increasing suicides and resignations across defense personnel emphasize the urgent need for better mental health support and grievance redressal.
What are the Causes of Stress Among Defence Personnel?
- Operational Stressors:
- Prolonged Deployment in Counter-Insurgency/Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT) Operations and continuous exposure to high-risk environments (extreme weather, difficult terrain, and lack of basic amenities in remote postings), contributes significantly to stress.
- A study by United Service Institution of India (USI), highlights that over 50% of Indian Army personnel are under severe stress and officers experience higher cumulative stress compared to Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) and Other Ranks (ORs).
- Frequent and Long Separations from Family during combat operations and field posting limits interaction with loved ones affects mental well-being.
- Unpredictable work hours, irregular shifts, and high operational pressure demand constant vigilance and quick decision-making under stress, increasing strain on officers.
- For non-officers, short-term employment (as seen in Agnipath Scheme) and uncertain career prospects add to job-related anxieties.
- Casualties and Combat Trauma, witnessing injuries or deaths of fellow soldiers leads to psychological distress.
- Prolonged Deployment in Counter-Insurgency/Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT) Operations and continuous exposure to high-risk environments (extreme weather, difficult terrain, and lack of basic amenities in remote postings), contributes significantly to stress.
- Non-Operational Stressors:
- Leadership and Administrative Issues like perceived unfair promotions, lack of recognition, and leadership gaps.
- Conflicts with Seniors and Subordinates including cases of humiliation, lack of dignity, and interpersonal tensions.
- Frequent Transfers and Short Command Tenures causing instability in career progression and family life.
- Pay and Status Concerns like downgradation in rank equivalence and financial dissatisfaction.
- Leave Denial and Excessive Workload due to delayed or rejected leave applications despite emergencies.
- Restrictions on Personal Freedom due to limited use of mobile phones and strict discipline rules.
- Inadequate Infrastructure and Support such as poor quality of rations, lack of recreational facilities, and inefficient administrative support.
- Additionally, the harassment of military personnel's families back home further exacerbates their stress.
- Mental Health Stigma leading to reluctance in seeking psychological help due to fear of being seen as weak.
- Additionally, using alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress, leads to long-term health and social issues.
- Leadership and Administrative Issues like perceived unfair promotions, lack of recognition, and leadership gaps.
How Does Stress Impact Defence Personnel?
- Increased Suicides and Fratricides as stress leads to extreme actions, endangering both the individual and colleagues.
- From 2020 to 2024, as many as 55,555 CAPF personnel either resigned or took voluntary retirement, and 730 personnel died by suicide.
- Decline in Mental and Physical Health with rising cases of hypertension, anxiety, depression, and other stress-related illnesses.
- Lower Morale and Motivation reducing operational effectiveness and commitment to duty.
- Compromised Combat Readiness as stress affects decision-making, alertness, and overall performance in critical situations.
- Higher Attrition Rates with more personnel opting for voluntary retirement, resignations, or early exits.
- Family and Social Struggles as work-related stress strains relationships, leading to domestic conflicts and emotional distress.
- Reduced Trust in Leadership causing dissatisfaction with management decisions, policies, and organizational support.
India’s Initiatives for Mental Well-being in the Army
- Advisory & Guidelines: In August 2023, the Indian Army issued an advisory deploying officers, religious teachers, and trained personnel to address stress and mental health issues.
- Training and Counselling Programs: Officers are trained at the Defence Institute of Psychological Research (DIPR).
- Religious teachers (Pandits, Maulvis, Granthis, Pastors) posted in every unit for support.
- Unit Psychological Counsellor Courses for Junior and Non-Commissioned Officers (12-week duration).
- Counseling Support: Civilian counselors deployed at major military stations and helplines established across all Command Headquarters.
- Psychiatry Centres: Set up under the Directorate General of Medical Service at major military stations.
- Holistic Approaches: Includes yoga, meditation, sports, recreation, improved amenities, and a buddy system for soldiers.
Way Forward
- Conduct Periodic Stress Assessments: Expand ongoing studies like the DIPR initiative to assess and address evolving stress factors.
- Leverage Technology for Mental Health Support: AI-based chatbots, telemedicine services (under National Tele Mental Health Programme and Kiran Helpline), and mobile apps can provide real-time mental health assistance.
- Family Support Programs: Counseling, financial planning workshops, and well-being programs for families of personnel can reduce domestic stress.
- Facilitate the lateral entry of retiring soldiers into paramilitary forces, police, and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) to ensure stable post-service employment and expand the reach of the Self-Employment Scheme for Ex-Servicemen and widows of the servicemen.
- Better Grievance Redressal: Establish a time-bound mechanism similar to the Right to Information Act 2005 for addressing soldiers’ concerns efficiently.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How do rising stress levels among India’s defence personnel impact national security and operational effectiveness? Suggest measures to address these concerns. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Mains
Q. Why suicide among young women is increasing in Indian society? (2023)
Q. What does the following quotation mean to you?
“We can never obtain peace in the outer world until and unless we obtain peace within ourselves.” – Dalai Lama. (2021)
China’s Weaponization of Supply Chains
For Prelims: Make in India initiative, Line of Actual Control, Belt and Road Initiative, Production-Linked Incentive, China Plus One strategy
For Mains: Supply Chain Disruptions and Economic Security, India's Electronics Manufacturing Sector
Why in News?
China has weaponised supply chains by restricting its engineers and technicians at Apple-Foxconn’s India facilities and curbing exports of critical manufacturing equipment.
- This move is seen as an attempt to slow down India’s growing electronics manufacturing sector and impact the country’s broader ambitions under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
How is China Disrupting India’s Supply Chains?
- Control Over Supply Chains: China dominates the global electronics supply chain. By restricting technicians and key equipment exports, it aims to disrupt India’s production and hinder skill transfer to Indian workers.
- This pressure tactic strengthens Beijing’s bargaining position against India.
- India imports a significant share of smartphone components from China. The latest restrictions highlight India’s vulnerability and the need for self-sufficiency.
- Delaying Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs): Since 2019, China has delayed customs clearance for German TBMs imported by India, crucial for metro, rail, road, and strategic mountain tunnels near the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Beijing fears these tunnels enhance Indian military logistics, enabling faster troop movement along the LAC.
- Curbs on Critical Minerals Exports: Since 2023, China has imposed curbs on exports of germanium and gallium, key materials for semiconductors, solar panels, and advanced electronics.
- While gallium can be extracted from India’s bauxite reserves, germanium imports remain a challenge, which is critical for semiconductors and military applications.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Through the BRI and industrial investments, China ensures multinationals remain reliant on its supply chains.
- For example, despite US sanctions, companies like Tesla continue major operations in China due to its cost-effective production ecosystem.
Why is China Weaponising Supply Chains?
- Preventing India as Manufacturing Hub: China’s dominance in high-tech manufacturing and consumer electronics is being challenged as Apple and other firms shift to India.
- India now produces 14% of the world's iPhones, with projections to reach 25-40%.
- With unemployment rising in China, the government fears losing high-value jobs to India, especially in sunrise industries like AI-driven consumer tech.
- Retaliation for India’s Economic Restrictions: Since the 2020 Galwan Conflict, India has banned Chinese apps, restricted Chinese investments and investigated Chinese firms for illegal activities.
- China’s latest export curbs aim to force India into trade negotiations by leveraging supply chain disruptions.
- China uses trade restrictions to punish countries for political disagreements.
- India’s Resilience in Global Trade: China has struggled with effective economic sanctions, unlike the US, which has strong global alliances.
- These selective export denials allow China to assess how India adapts to supply chain disruptions before escalating further restrictions.
India’s Efforts to Counter Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- National Manufacturing Mission
- Duty Reductions on Components: Union Budget 2025 removed import duties on critical mobile phone components (e.g., printed circuit boards, camera modules, connectors, sensors and lithium-ion battery manufacturing machinery).
- Skill Development Initiatives: National Skill Development Mission, Skill India Mission SANKALP Scheme, TEJAS Skilling Project, Model Skill Loan Scheme.
What Challenges Does India Face in Electronics Manufacturing?
- Heavy Dependence on Imports: India imports over 75% of electronic components. Lack of domestic supply chains for high-end manufacturing equipment limits India’s ability to scale up production.
- This reliance on imports makes key industries vulnerable to disruptions despite initiatives like the Semicon India Program.
- Shortage of Skilled Workforce: India lacks specialized talent in chip design, electronics assembly, and automation, critical for high-tech manufacturing.
- Weak Ecosystem for Ancillary Industries: Unlike China, India does not have a strong network of local suppliers for key smartphone and electronics components.
- Lack of R&D: Most high-tech research and development (R&D) in electronics is concentrated in the US, Taiwan, South Korea, and China, with limited innovation in India.
- India must invest in research institutions, industry-academia collaboration, and patent generation to build a competitive edge.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Domestic Manufacturing: Expand the PLI to boost local production of semiconductors, critical components, and high-tech machinery.
- Secure alternative suppliers for germanium and gallium from countries like Japan, South Korea, and the US.
- Fast-track domestic extraction of gallium to meet India’s semiconductor demand.
- Trade Alliances and Technology Partnerships: India should strengthen trade alliances, with collaborations like the Chip 4 Alliance (US, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan) helping to reduce dependency on China and build resilient supply chains.
- Use international forums like World Trade Organisation (WTO) and G20 to highlight China’s supply chain weaponisation.
- Utilising the China Plus One strategy, India must attract global manufacturers by promoting itself as a sustainable business location and capitalizing on its booming economy and startup ecosystem.
- Skilled Workforce: On-site worker training and specialized skill development programs are needed to bridge the talent gap.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyze India's challenges amid China's workforce and export restrictions. Suggest measures to strengthen domestic capabilities. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Belt and Road Initiative’ is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2016)
(a) African Union
(b) Brazil
(c) European Union
(d) China
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (2018)
Q2. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
Neotethys Oceanic Plate and Tectonic Movements
For Prelims: Neotethys oceanic plate, Zagros Mountains, Arabian and Eurasian continental plates, Plate Tectonics Theory, Continent Formation.
For Mains: Role of Plate Tectonics and Geological Processes in Continent Formation, Tectonic Forces and the Evolution of Landforms, The Role of Plate Tectonics in the Formation of Himalayas and Its Ongoing Impact.
Why in News?
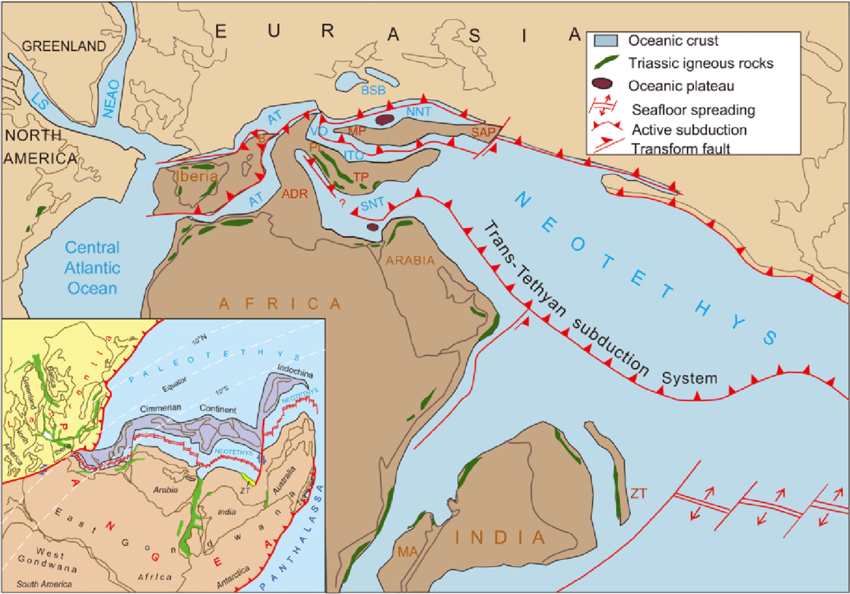
A study has revealed that the ancient Neotethys oceanic plate, which once lay between the Arabian and Eurasian continental tectonic plates, is breaking apart under the Zagros Mountains in West Asia due to plate movement.
- This impacts regional geography, earthquakes, and resource distribution offering valuable insights into the Earth's deep tectonic processes.
What is Neotethys Oceanic Plate?
- The Neotethys Oceanic Plate was an ancient oceanic plate that once formed the seafloor of the Neotethys Ocean, which existed during the breakup of Pangaea.
- Over time, it was subducted into the Earth's mantle beneath the Eurasian continent as the Arabian and Eurasian plates moved closer.
Arabian Plate:
- The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, moving northward along with the African and Indian plates.
- Its collision with the Eurasian Plate has been a major force in mountain formation, contributing to the rise of the Zagros Mountains, Alborz Mountains, Iranian Plateau, Himalayas, and other ranges in Southern Europe and Southeast Asia.
- The heavy weight of the Zagros Mountains has caused the surrounding land to sink, forming the Mesopotamian sedimentary basin.
Eurasian Plate:
- The Eurasian Plate is a major tectonic plate that covers most of Europe, Russia, and parts of Asia, with boundaries shared with the North American, African, Arabian, Indian, and Sunda Plates.
- It has a divergent boundary with the North American Plate in the west and moves at an average rate of 0.25 to 0.5 inches per year, pulling Iceland apart at 2.5 cm per year.
What is Tectonic Plates and its Movement?
- About: A tectonic plate (also called lithospheric plate) is a massive, irregularly shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic plates.
- Continental plates form the Earth's landmasses, while oceanic plates lie beneath the ocean floor.
- Oceanic plates are composed of denser basaltic rocks and subducted beneath continental plates at convergent boundaries, as continental plates consist of lighter granitic rocks.
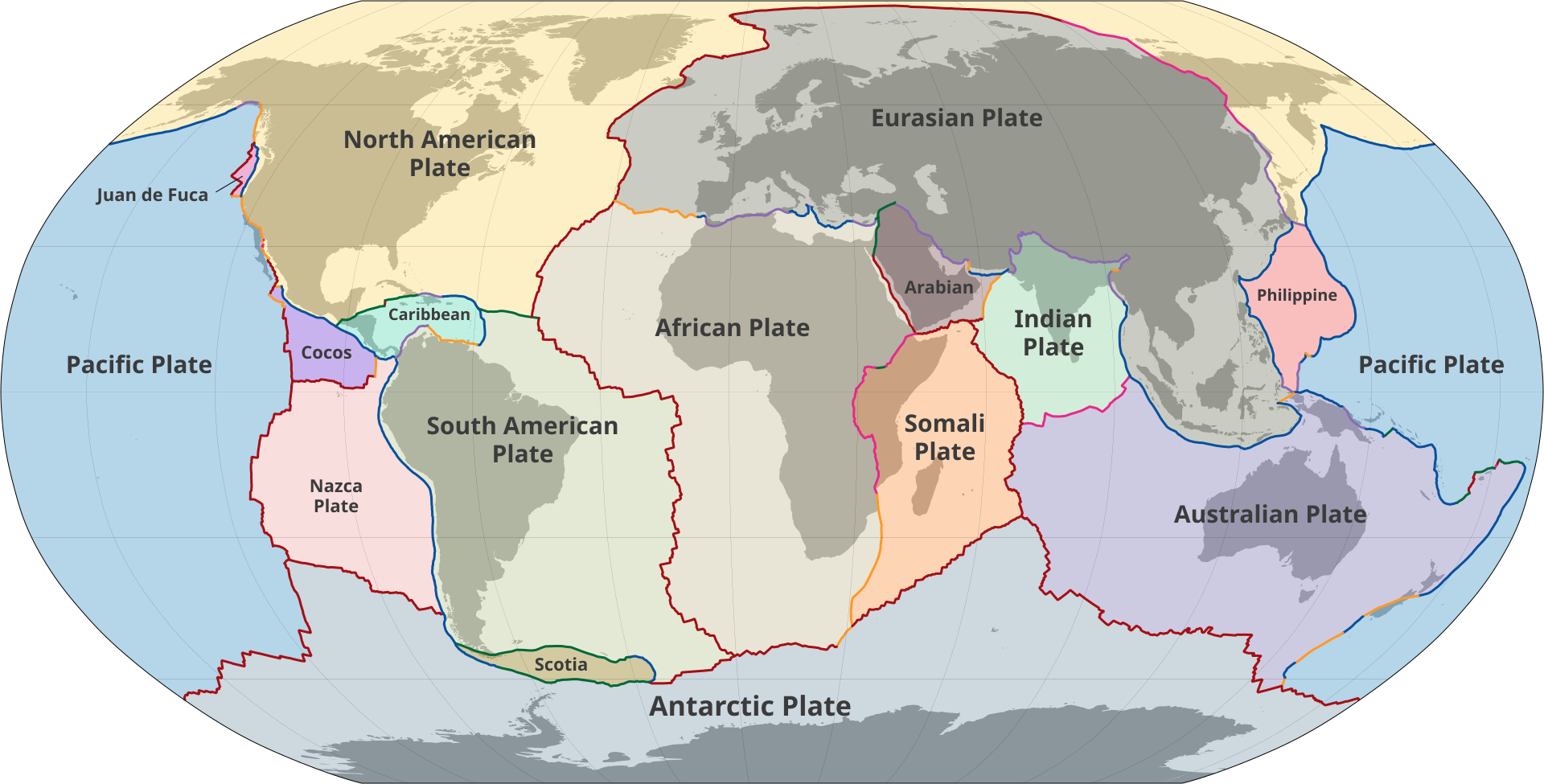
- Major and Minor Tectonic Plates: Earth's lithosphere is divided into 7 major plates and several minor plates.
- Major Plates: Antarctic Plate, North American Plate, South American Plate, Pacific Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, African Plate, Eurasian Plate.
- Minor Plates: Cocos Plate, Nazca Plate, Arabian Plate, Philippine Plate, Caroline Plate, Fiji Plate, Juan de Fuca Plate, etc.
- Tectonic Plate Movement:
- Movement of Plates: The tectonic plates are not fixed but constantly move horizontally over the asthenosphere as rigid units.
- Their interactions- colliding, diverging, or sliding past each other result in geological events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Rate of Movement: Tectonic plates move at varying speeds. The Arctic Ridge has the slowest movement (<2.5 cm/year), while the East Pacific Rise in the South Pacific moves the fastest (>15 cm/year).
- Driving Force: The movement is driven by convection currents in the mantle which occur due to primordial heat from Earth's formation and radioactive decay of isotopes like thorium and uranium.
- Heated material rises, spreads, cools, and sinks, creating a continuous cycle that propels the plates.
- Movement of Plates: The tectonic plates are not fixed but constantly move horizontally over the asthenosphere as rigid units.
- Tectonic Plate Boundaries:
- Convergent Boundaries (Destructive Boundaries): Plates collide, leading to subduction, mountain formation, and volcanic arcs.
- Oceanic-Continental Convergence: The denser oceanic plate subducts beneath the continental plate (e.g., Juan de Fuca Plate subducting under the North American Plate).
- Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence: The denser plate subducts, forming deep trenches and island arcs (e.g., Mariana Trench).
- Continental-Continental Convergence: Collision results in mountain formation (e.g., Himalayas due to the Indian and Eurasian plate collision).
- Divergent Boundaries (Constructive Boundaries): Plates move apart, creating new crust, seafloor spreading, and rift valleys.
- Oceanic Divergence: Mid-ocean ridges form (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge).
- Continental Divergence: Rift valleys emerge (e.g., Great Rift Valley in Africa).
- Transform Boundaries (Conservative Boundaries): Plates slide past each other without creating or destroying crust.
- They often cause earthquakes due to accumulated stress along faults (e.g., San Andreas Fault in California).
- Convergent Boundaries (Destructive Boundaries): Plates collide, leading to subduction, mountain formation, and volcanic arcs.
| Drishti Mains Question: Q. What are convergent, divergent, and transform plate boundaries? Discuss their significance in understanding seismic activity and natural disasters |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following phenomena might have influenced the evolution of organisms? (2014)
- Continental drift
- Glacial cycles
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Mains
Q. What do you understand by the theory of ‘continental drift’? Discuss the prominent evidences in its support. (2013)
Kashi Tamil Sangamam 3.0
Why in News?
The 3rd edition of Kashi Tamil Sangamam (KTS 3.0), a cultural confluence between Tamil Nadu and Kashi, is being held in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh.
What are the Key Highlights of KTS 3.0?
- Kashi Tamil Sangamam (KTS 3.0) coincides with Mahakumbh 2025 in Prayagraj and provides an opportunity to visit the Ram Mandir in Ayodhya for the first time post-inauguration.
- The 1st edition of KTS was held in 2022, while the 2nd in 2023.
- It features around 1,000 delegates from Tamil Nadu across 5 categories, including students, teachers, writers, farmers, artisans, professionals, entrepreneurs, SHGs, and innovation communities.
- Also, joined by 200 Tamil-origin students from Central Universities, enhancing the event’s diversity and engagement.
- Central Theme: “Legacy of Sage Agastya”.
What is Kashi Tamil Sangamam?
- About:
- It is a cultural initiative that aims to celebrate the deep-rooted historical and cultural ties and strengthen the ancient civilizational bond between Tamil Nadu and Kashi (Varanasi).
- The event aligns with the Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat initiative, emphasizing the integration of India’s diverse cultural heritage.
- Historical Significance:
- The historical ties between Kashi (Uttar Pradesh) and Tamil Nadu date back to the 15th century when King Parakrama Pandya of Madurai traveled to Kashi to bring back a sacred lingam for his temple (Sivakasi, Tamil Nadu).
- The Pandya rulers also established the Kasi Viswanathar Temple in Tenkasi, located in southwestern Tamil Nadu, near the Kerala border.
- This deep-rooted spiritual and cultural connection underscores the essence of the Kashi Tamil Sangamam initiative.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Education in collaboration with various ministries and the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
- Objectives:
- Knowledge Sharing: Encouraging interactions between scholars, researchers, artisans, and professionals.
- Academic Collaboration: Facilitating discussions on Indian Knowledge Systems in alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Promoting Traditional Art and Craft: Showcasing classical Tamil art, literature, and cuisine to a national audience.
- Youth Engagement: Providing young participants an immersive experience in India’s civilizational ethos.
Agastya Muni
- He is a revered Saptarishi in Vedic and Puranic texts, considered the father of Tamil language and Siddha medicine, with his works, Agastya Samhita and Naadi Shastra, being foundational to Siddha medicine.
- He composed the first Tamil grammar, Agattiyam, and introduced the Tamil script.
- He is also revered in Java and Sumatra for spreading Indian culture and credited with propagating Vedic culture in South India, Aryanizing the Yadavas, and advancing Tampa Parniyan medicine and spirituality.
- He is mentioned in Ramayana, with his hermitage on the banks of the Godavari River.
4th No Money for Terror Conference
The Union Minister of State for Home Affairs participated in the 4th No Money for Terror (NMFT) Conference in Germany.
- India emphasized global unity in combating terrorism, reiterated its proposal for a permanent NMFT Secretariat at New Delhi.
- No Money for Terror (NMFT) Conference:
- Launch: It was launched in 2018 by France.
- Previous Conferences: France (Paris, 2018), Australia (2019) and India (2022).
- Launch: It was launched in 2018 by France.
- Objective: It aims to enhance international cooperation in curbing terror financing.
- Sub-verticals: The conference focused on global efforts to counter terror financing through 4 key sub-verticals:
- Multilateral cooperation
- Financing methods for terrorism
- Financial inclusion & Risk-based approach
- Terrorist Financing & Organized Crime
- Similar Conferences on Counter-Terrorism & Terror Financing:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Plenary Meetings: Focusing on anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF).
- United Nations Counter-Terrorism Week: Organized by the UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) to discuss global counter-terrorism strategies.
Read More: India’s Contribution to Counter-Terrorism Efforts
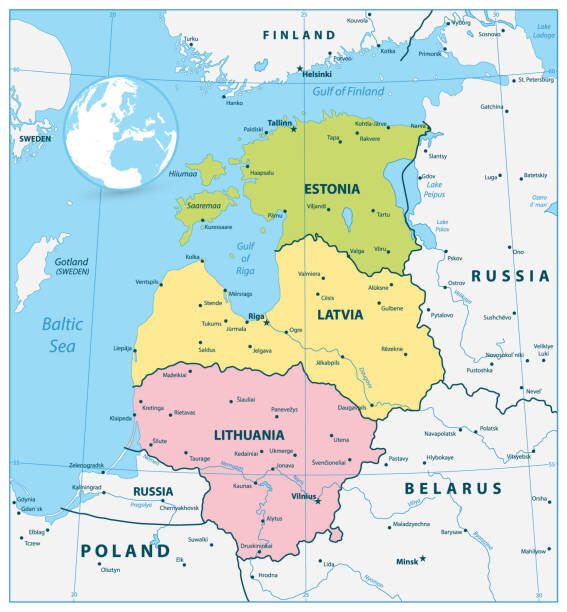
Baltic States Disconnected from Russian Grid
The Baltic Nations (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) have officially disconnected from Russia's Soviet-era electricity grid and integrated into the EU's power network through connections with Finland, Sweden, and Poland.
- Europe’s Energy Dependence on Russia:
- The Baltic States inherited a Soviet-era power grid and remained in Russia's network even after 1991 independence.
- By 2025, they achieved full electricity independence from Russia and Belarus.
- Europe's reliance on Russian energy has declined significantly. Before the 2022 Russia-Ukraine War, it sourced 40% of gas, 30% of oil, and 50% of coal from Russia. By 2023, gas imports fell to 14.8%.
Baltic States:
- The Baltic states are located in northeastern Europe, bordered by the Baltic Sea (west & north), Russia (east), Belarus (southeast), and Poland & Russia (Kaliningrad)(southwest).
- They gained independence from the USSR in 1991.
- They lack natural resources, relying on imports despite Estonia's oil shale production. Agriculture remains vital, with grains, potatoes, fodder crops, and livestock farming.
- All 3 countries are members of NATO (since 2004), the EU, the Eurozone, and the OECD.
Read More: Baltic Nations - Drishti IAS
Meta’s Project Waterworth
Meta has announced plans to launch Project Waterworth, a subsea cable network that will span 50,000 km and will reach depths of up to 7,000 meters.
- It will be the world's longest and most technologically advanced cable system connecting India, the US, Brazil, South Africa, and other regions.
- It is expected to be operational by 2030 and will address increasing demand for AI and digital services.
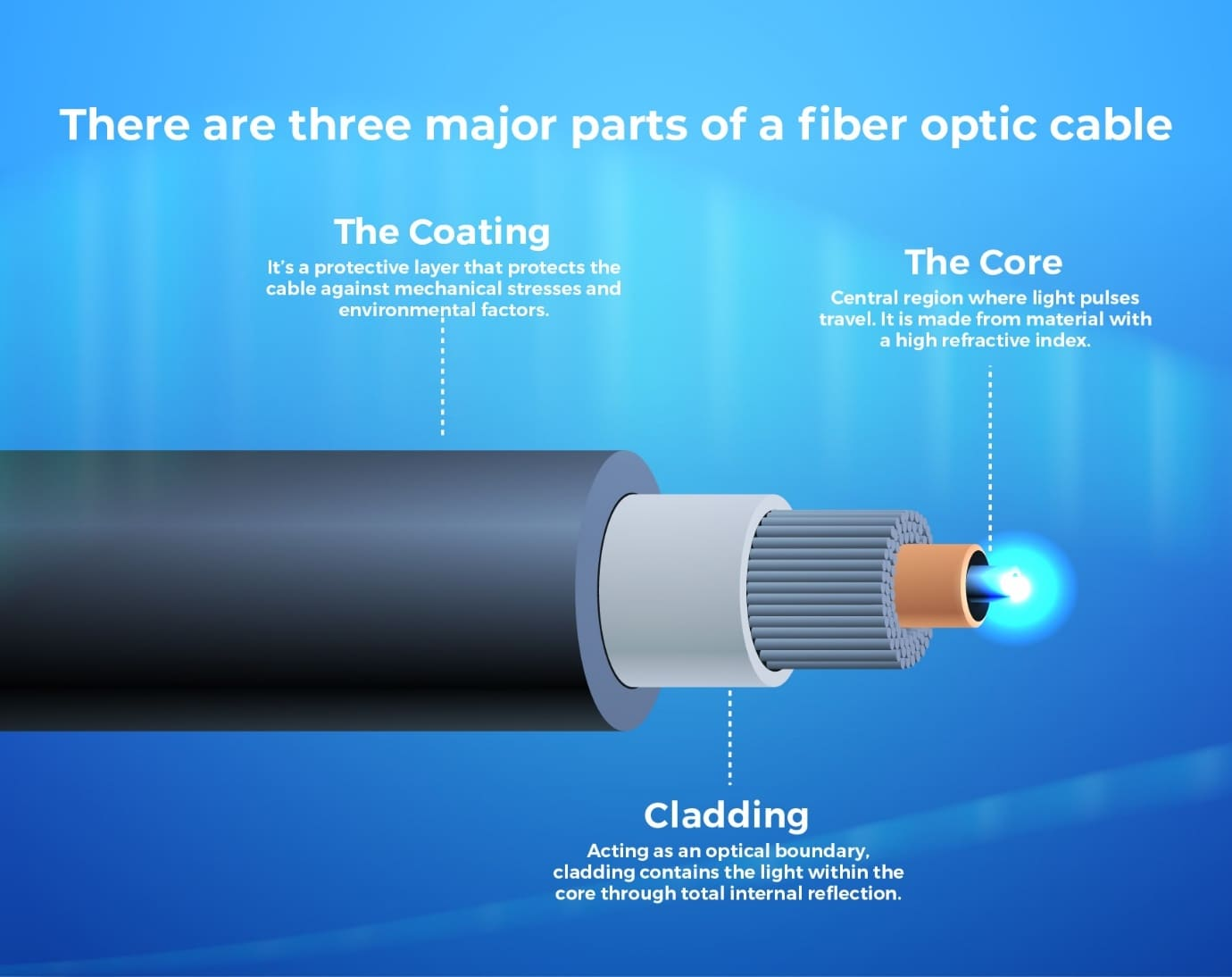
- Subsea Cable (Submarine Cables): They are high-capacity optic fibre cables laid on the ocean floor that play a crucial role in providing global connectivity for high-speed data exchange.
- They use fast-moving light pulses to transmit digital information through total internal reflection.
- The glass fibers are protected by layers of plastic and sometimes steel wire.
- Unlike satellite communication, fiber optics offer unlimited bandwidth and low latency, unaffected by space weather, radiation, or debris.
- India will soon launch two cable systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX) linking Chennai and Mumbai to Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX) linking Chennai and Mumbai to France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
Read More: Undersea Cable Network
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
The birth anniversary of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was commemorated globally on 19th February, reflecting his enduring legacy and influence.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj: Born on 19th February 1630, at Shivneri Fort, Pune was a visionary leader from the Bhonsle clan and the founder of the Maratha Empire, known for resisting the Mughal Empire and striving for self-rule.
- Major Battles: Battle of Pratapgad, Battle of Pavan Khind, Sacking of Surat, Battle of Purandar, Battle of Sinhagad, and Battle of Sangamner.
- The Wagh nakh, was used by Shivaji to kill Afzal Khan in the 1659 Battle of Pratapgad.
- Titles: Chhatrapati, Shakakarta, Kshatriya Kulavantas, and Haindava Dharmodhhaarak.
- Administration: Centralized administration with the Ashtapradhan (Council of Eight Ministers), abolished the Jagirdari System, implemented the Ryotwari System, and built a strong naval force for coastal defense.
- Shivaji is renowned for his innovative guerrilla warfare tactics, which influenced subsequent rulers and shaped the Maratha Military Landscapes.
- Major Battles: Battle of Pratapgad, Battle of Pavan Khind, Sacking of Surat, Battle of Purandar, Battle of Sinhagad, and Battle of Sangamner.
- Other Prominent Maratha Kings: After Shivaji, Sambhaji (1681–1689), Rajaram (1689–1700), and Shahu (1707–1749) fought against the Mughals. Later, the Peshwa administration began with Balaji Vishwanath (1713–1720), who strengthened Maratha governance.
- Peshwa Madhavrao I (1761–1772) revived Maratha power after the Third Battle of Panipat (1761).
Read more: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
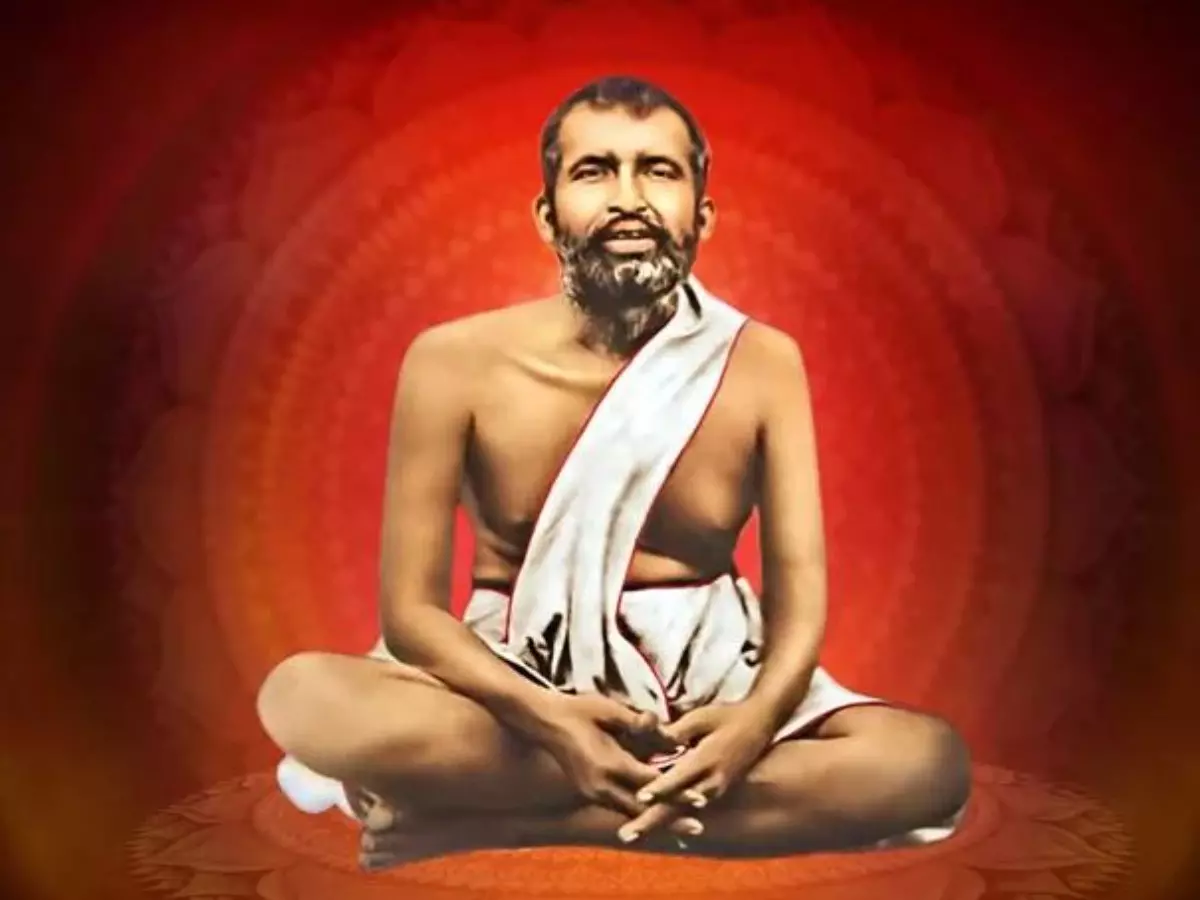
Birth Anniversary of Ramakrishna Paramhansa
The Prime Minister paid tributes to Swami Ramakrishna Paramhansa on his birth anniversary on 18th February 2025.
- About: Ramakrishna Paramahamsa was born as Gadadhar Chattopadhyaya on 18th February 1836 in Bengal.
- Religious Philosophy: He was deeply devoted to Goddess Kali, serving as a priest and worshiping her at Dakshineswar Kali Temple.
- He practiced various spiritual traditions, including Tantric, Bhakti, Vaishnavism, and Advaita Vedanta.
- Ramakrishna preached religious unity, believing all faiths lead to the same truth.
- Spreading Legacy: His foremost disciple, Narendra Nath Datta (later Swami Vivekananda), established the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897 and spread Ramakrishna’s teachings across India, America, and Europe.
- Teaching Documentation: Mahendranath Gupta, his disciple, documented Ramakrishna’s teachings in the book Sri Sri Ramakrishna Kathamrita (Bengali) (The Gospel of Sri Ramakrishna in English in 1942).
Read More: Ramakrishna Mission’s Awakening Programme
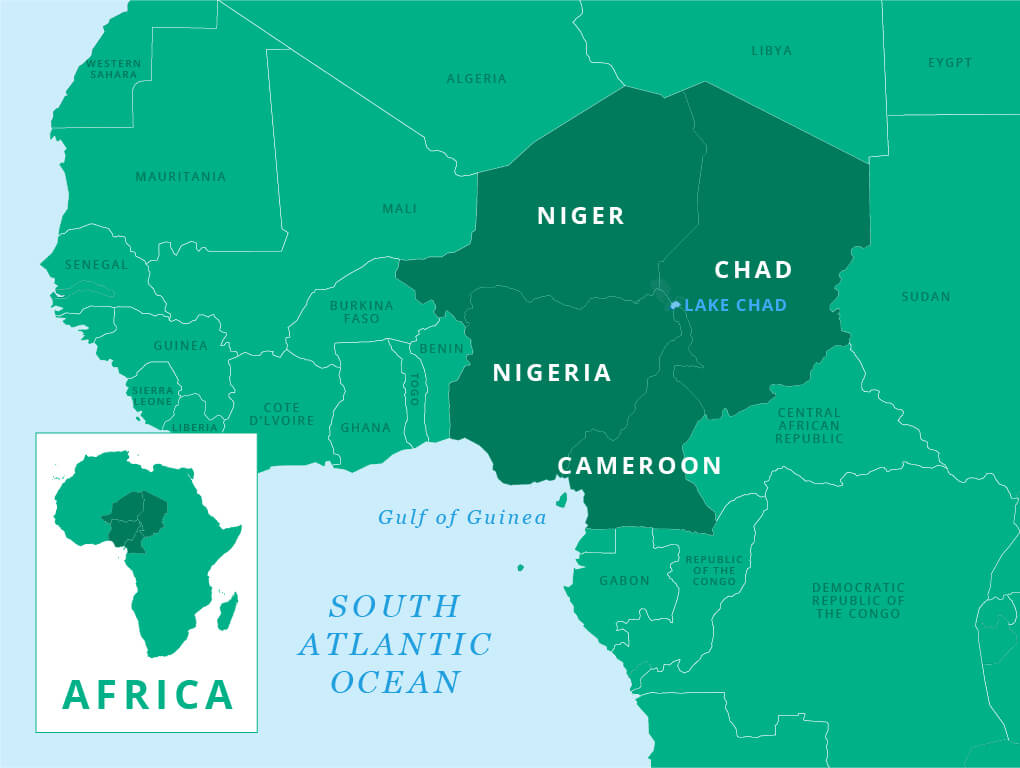
Lake Chad
Chad has concluded a military campaign, Operation Haskanite, against Boko Haram.
- The campaign targeted Boko Haram’s strongholds in the Lake Chad region, a strategic hub for militant activity.
- Boko Haram: It is a Nigeria-based terrorist group aiming to impose Islamic law in the country. Its name means “Western education is forbidden.”
- Lake Chad: Situated in north-west Africa, the Lake Chad region spans Nigeria, Cameroon, Niger, and Chad. It is a dynamic freshwater body with human presence dating back to the Paleolithic era (2.6 million years ago to 10,000 years ago).
- The Sao Civilization (5th century) left rich archaeological remains, showcasing expertise in fishing, hunting and farming.
- Lake Chad faces a humanitarian crisis, with over 10 million in need due to poverty, climate change, and conflict. Boko Haram exploits the instability, worsening the region's challenges.
Read more: Economic Community of West African States