Indian Polity
Curative Petition
For Prelims: Supreme Court of India, Curative Petition, Contempt of Court, Article 145 of the Indian Constitution
For Mains: Special Powers of the Supreme Court of India, Curative Petition and its Significance.
Why in News?
In a significant move, the Supreme Court of India has exercised its "extraordinary powers" through a curative petition to overturn its previous judgement from 2021.
- This judgement overturns an arbitral award of nearly Rs 8,000 crore that the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) was ordered to pay to Delhi Airport Metro Express Private Limited (DAMEPL), led by Reliance Infrastructure Ltd-consortium.
What is Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Ltd. v Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt. Ltd. Case, 2024?
- Background:
- In 2008, the DMRC partnered with DAMEPL to construct, operate, and maintain the Delhi Airport Metro Express.
- Disputes led to the termination of the agreement by DAMEPL in 2013, citing safety concerns and operational issues.
- Legal battles ensued, resulting in an arbitration panel ruling in favour of DAMEPL, ordering DMRC to pay nearly Rs 8,000 crore. However, the Delhi High Court directed DMRC to deposit 75% of the amount in an escrow account. The government appealed, and in 2019, the High Court's decision was overturned in favour of DMRC.
- DAMEPL then approached the Supreme Court, which initially upheld the arbitral award in 2021.
- Judgement:
- Recent judgement of the SC ruled in favour of DMRC, citing a "fundamental error" in its previous judgement.
- The SC's decision is significant as it highlights the importance of curative petitions, provides clarity on legal frameworks for public-private partnerships in infrastructure projects, and demonstrates the court's willingness to correct errors and ensure justice, even years after a final verdict.
What is a Curative Petition?
- Definition: A curative petition is a legal recourse available after the dismissal of a review plea against a final conviction.
- Constitutionally, a final ruling of the Supreme Court can typically be challenged only through a review petition, and even then, only on narrow procedural grounds.
- However, the curative petition serves as a sparingly used judicial innovation to rectify a grave miscarriage of justice.
- Constitutionally, a final ruling of the Supreme Court can typically be challenged only through a review petition, and even then, only on narrow procedural grounds.
- Objective: It aims to prevent miscarriage of justice and deter abuse of the legal process.
- Decision Process: Curative petitions are typically decided by judges in chambers, though open-court hearings may be granted upon specific request.
- Legal Basis: Principles governing curative petitions were established by the Supreme Court in the case of Rupa Ashok Hurra Vs Ashok Hurra & another Case, 2002.
- Criteria for Entertaining a Curative Petition:
- Violation of Natural Justice: It must be demonstrated that there was a breach of principles of natural justice, such as the petitioner not being heard before the court passed an order.
- Apprehension of Bias: It may be admitted if there are grounds to suspect bias on the part of the judge, such as failure to disclose relevant facts.
- Guidelines for Filing a Curative Petition:
- Certification by Senior Advocate: The petition must be accompanied by a certification from a senior advocate, highlighting substantial grounds for its consideration.
- Initial Review: It is first circulated to a bench comprising the three senior-most judges, along with the judges who passed the original judgement, if available.
- Hearing: Only if a majority of the judges deem it necessary for a hearing, it is listed for consideration, preferably before the same bench that passed the initial judgement.
- Role of Amicus Curiae: The bench may appoint a senior counsel to assist as amicus curiae at any stage of the consideration of the curative petition.
- Cost Implications: If the bench determines that the petition lacks merit and is vexatious, it may impose exemplary costs on the petitioner.
- Judicial Discretion: The Supreme Court emphasises that curative petitions should be rare and reviewed with caution to maintain the integrity of the judicial process.
Other Cases Related to Curative Petition:
- Union of India v Union Carbide Case (Bhopal Gas Tragedy):
- The Union Govt. filed a curative petition in 2010 for more compensation for the Bhopal Gas Tragedy victims. In 2023, a 5-judge Bench rejected the petition, stating that the previously decided compensation was sufficient.
- The Bench emphasised that a curative petition can only be entertained in cases of gross miscarriage of justice, fraud, or suppression of material facts, none of which were present in this case.
- Navneet Kaur v State of NCT of Delhi Case, 2014:
- This case marked a shift in capital punishment cases. The petitioner, sentenced to death, successfully argued through a curative petition that mental illness and an unreasonably long wait for a mercy petition constituted grounds for commuting the sentence to life imprisonment.
What are the Special Powers of the Supreme Court of India?
- Dispute Resolution: Article 131 of the Indian Constitution gives the Supreme Court exclusive original jurisdiction in disputes between the Government of India and one or more States, or between States themselves, involving legal rights.
- Discretionary Jurisdiction: Article 136 of the Indian Constitution grants the Supreme Court the power to grant special leave to appeal from any judgement, decree, or order made by any court or tribunal in India.
- This power does not apply to military tribunals and court-martials.
- Advisory Jurisdiction: The Supreme Court has advisory jurisdiction under Article 143 of the Constitution, where the President of India can refer specific matters to the Court for its opinion.
- Contempt Proceedings: Under Articles 129 and 142 of the Constitution, the Supreme Court has the authority to punish for contempt of court, including contempt of itself, either suo motu or petition by the Attorney General, Solicitor General, or any individual.
- Review and Curative Powers:
- Article 145 gives the Supreme Court authority, with the President's approval, to make rules for regulating the practice and procedure of the Court, including rules for persons practising before the Court, hearing appeals, enforcing rights, and entertaining appeals.
- It also includes rules for reviewing judgments, determining costs, granting bail, staying proceedings, and conducting inquiries.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the role of the Supreme Court in safeguarding the principles of natural justice and evaluate the effectiveness of curative petitions in rectifying judicial errors. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Indian judiciary, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither I nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Critically examine the Supreme Court’s judgement on ‘National Judicial Appointments Commission Act, 2014’ with reference to the appointment of judges of higher judiciary in India. (2017)


International Relations
Asia Development Outlook Report 2024
For Prelims: Asian Development Bank, India's Gross Domestic Product, Capital expenditure, Current account deficit, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, International North-South Transport Corridor, India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, International Solar Alliance.
For Mains: Sectors Driving Asia’s Development, India’s Contribution in Asia’s Development.
Why in News?
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) recently released the Asia Development Outlook Report in April 2024 and revised India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth forecast for the fiscal year (FY) 2024 and FY 2025, citing various factors contributing to this optimistic outlook.
What are the Key Highlights of Asia Development Outlook Report 2024?
- Asia’s Growth Outlook:
- About: Despite uncertain external prospects, Asia is projected to maintain resilient growth in the coming years.
- Factors such as the conclusion of interest rate hiking cycles in most economies and a sustained recovery in goods exports, particularly driven by improving semiconductor demand, contribute to the region's broadly positive outlook.
- GDP Growth Forecast: Asia's GDP growth forecast for 2024 stands at 4.9%, with a similar projection maintained for 2025.
- This steady growth trajectory reflects the region's ability to navigate external challenges and sustain economic momentum.
- Inflation Trends: Inflation in Asia is expected to moderate, with a forecast of 3.2% for 2024 and a further decrease to 3.0% in 2025.
- This trend indicates a relatively stable pricing environment, which can support consumer confidence and spending.
- About: Despite uncertain external prospects, Asia is projected to maintain resilient growth in the coming years.
- India’s Growth Forecast:
- Growth Forecast: India's investment-driven growth is highlighted as a significant factor in positioning the country as a major economic engine within Asia.
- ADB now projects India's GDP growth to reach 7% in FY 2024 and 7.2% in FY 2025, up from the previous forecast of 6.7% for FY 2024.
- Factors Fueling Growth in FY 2024:
- Higher capital expenditure on infrastructure development by central and state governments is a major driver of growth.
- Private corporate investment is expected to rise, supported by stable interest rates and improved consumer confidence.
- The service sector's performance, including financial, real estate, and professional services, is contributing significantly to economic expansion.
- Growth Momentum in FY 2025: FY 2025 is expected to witness increased momentum, driven by improved goods exports, enhanced manufacturing productivity, and higher agricultural output.
- The forecast reflects a positive outlook for India's economy, buoyed by its strong domestic demand and supportive policies.
- Risks and Challenges: Despite the positive forecast, unanticipated global shocks like supply disruptions in crude oil markets and weather-related impacts on agriculture remain key risks.
- The current account deficit is projected to widen moderately due to rising imports to meet domestic demand.
- However, according to recent RBI data, the current account deficit (CAD) decreased sequentially from 1.3% of GDP in Quarter 2 FY24 to 1.2% in Quarter 3 FY24.
- Growth Forecast: India's investment-driven growth is highlighted as a significant factor in positioning the country as a major economic engine within Asia.
What is the Asian Development Bank?
- About: Established in 1966, ADB is a regional development bank that envisions a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty in the region.
- ADB supports its members and partners through the provision of loans, technical assistance, grants, and equity investments aimed at advancing social and economic development.
- Headquarters: Manila, Philippines
- Members: It currently has 68 members of which 49 are from within Asia and the Pacific and 19 outside.
- ADB and India: India is a founding member of ADB and the bank’s fourth-largest shareholder.
- ADB supports India's priorities for robust, climate resilient, and inclusive growth, aligned with ADB's Strategy 2030 and the country partnership strategy, 2023–2027.
What are the Sectors Driving Asia’s Growth?
- Economic Powerhouse: Asia is home to several of the world's fastest-growing economies. With China, Japan and India being in the top 5 economies of the world.
- Fueled by economic growth, a burgeoning middle class across Asia is creating a vast pool of consumers, driving demand for goods and services.
- Example: Vietnam is expected to add 36 million people to its middle class by 2030.
- Fueled by economic growth, a burgeoning middle class across Asia is creating a vast pool of consumers, driving demand for goods and services.
- Home to Manufacturing Hubs: For decades, Asia has been a dominant manufacturing centre. From China's dominance in electronics to Vietnam's rise in footwear production, Asian countries benefit from skilled labour forces and efficient infrastructure, making them cost-competitive and crucial to global supply chains.
- Rising Trade & Investment: Asian nations are actively involved in international trade. Regional trade agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) create significant trade blocs, boosting intra-Asian trade and foreign investment.
- Rising Financial Centers: Asian cities such as Tokyo, Hong Kong and Singapore have emerged as major financial centres, attracting investments, fostering entrepreneurship, and facilitating cross-border capital flows.
- The growing influence of Asian financial institutions like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) reflects the region's increasing role in shaping global economic policies.
What is India’s Contribution to Asia’s Growth?
- Regional Connectivity: India has been a key player in promoting regional connectivity in Asia through initiatives like the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor.
- These projects aim to improve transportation networks, trade routes, and economic cooperation between Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Renewable Energy: India is actively promoting renewable energy initiatives that contribute to sustainable development in Asia.
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA), launched by India and France, aims to promote solar energy adoption globally, especially in sun-rich countries in Asia and Africa, thereby addressing energy security and climate change challenges.
- Capacity Building: India engages in capacity-building efforts across Asia through initiatives like the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program.
- It offers training, education, and skill development opportunities to professionals and students from Asian countries, fostering human resource development and cultural exchanges.
- Unifying Asia with UPI: India’s UPI (Unified Payments Interface) services are becoming increasingly popular in Asia due to their convenience and efficiency in digital transactions.
- UPI services have already been launched in Sri Lanka and Mauritius.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the role of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) in fostering economic growth and development in Asia-Pacific countries especially India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Which one among the following South Asian countries has the highest population density? (2009)
(a) India
(b) Nepal
(c) Pakistan
(d) Sri Lanka
Ans: (a)
Q. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)


Governance
Government Reviews RERA Functioning
For Prelims: Government Reviews RERA Functioning, Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, State Level Regulatory Authorities, Real Estate Appellate Tribunal.
For Mains: Government Reviews RERA Functioning, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016.
What is RERA?
- About:
- The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA), is a significant legislation enacted by the Government of India in 2016.
- Its primary objective is to regulate the real estate sector and promote transparency, accountability, and efficiency in real estate transactions.
- RERA aims to protect the interests of homebuyers and promote fair practices in the real estate industry.
- Need:
- Securing the Largest Investment Sector: Regulation of the real estate sector has been under discussion since 2013, and the RERA Act eventually came into being in 2016.
- Data show that more than 77% of the total assets of an average Indian household are held in real estate, and it’s the single largest investment of an individual in his lifetime.
- Creating Accountability: Before the law, the real estate and housing sector was largely unregulated, with the consequence that consumers were unable to hold builders and developers accountable.
- The Consumer Protection Act of 1986 was inadequate to address the needs of homebuyers.
- RERA was introduced to ensure greater accountability towards consumers, to reduce frauds and delays, and to set up a fast track dispute resolution mechanism.
- Securing the Largest Investment Sector: Regulation of the real estate sector has been under discussion since 2013, and the RERA Act eventually came into being in 2016.
- Major Provisions:
- Establishment of State-Level Regulatory Authorities, i.e. Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA): The Act provides for State governments to establish more than one regulatory authority with the following mandate:
- Register and maintain a database of real estate projects; publish it on its website for public viewing,
- Protection of interest of promoters, buyers and real estate agents
- Development of sustainable and affordable housing,
- Render advice to the government and ensure compliance with its Regulations and the Act.
- Establishment of Real Estate Appellate Tribunal: Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals.
- Mandatory Registration: All projects with a plot size of a minimum of 500 sq. mt or eight apartments need to be registered with Regulatory Authorities.
- Deposits: Depositing 70% of the funds collected from buyers in a separate escrow bank account for construction of that project only.
- Liability: Developer’s liability to repair structural defects for five years.
- Penal interest in case of default: Both promoter and buyer are liable to pay an equal rate of interest in case of any default from either side.
- Cap on Advance Payments: A promoter cannot accept more than 10% of the cost of the plot, apartment or building as an advance payment or an application fee from a person without first entering into an agreement for sale.
- Carpet Area: Defines Carpet Area as net usable floor area of flat. Buyers will be charged for the carpet area and not the super built-up area.
- The built-up area refers to the total floor area of a building, including all interior and exterior spaces such as walls, balconies, common areas, and amenities.
- Punishment: Imprisonment of up to three years for developers and up to one year in case of agents and buyers for violation of orders of Appellate Tribunals and Regulatory Authorities.
- Establishment of State-Level Regulatory Authorities, i.e. Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA): The Act provides for State governments to establish more than one regulatory authority with the following mandate:
- Implementation:
- All States/ UTs have notified Rules under RERA except the State of Nagaland.
- 32 States/UTs have set up a Real Estate Regulatory Authority and 28 States/UTs have set up a Real Estate Appellate Tribunal.
- 1,01,304 Real Estate Projects & 72,012 Real Estate Agents have been registered under the provisions of RERA and 1,06,657 complaints have been successfully disposed of by the Real Estate Regulatory Authorities across the country.
What is the Status of Home Buyers and Builders under the IBC?
- Under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), homebuyers have been granted certain rights and provisions, primarily through amendments made to the code over the years. Legal provisions for homebuyers under the IBC are:
- Classification as Financial Creditors: Through amendments, particularly the 2018 Amendment Act, homebuyers have been categorised as Financial Creditors. This means that the money advanced by a homebuyer to a real estate project is considered a financial debt, granting them the status of a creditor under the IBC.
- Right to Initiate Insolvency Proceedings: Homebuyers have the right to initiate insolvency proceedings against a defaulting builder company under the IBC.
- However, the process involves certain conditions. As per the 2020 Amendment, homebuyers must jointly file an application for initiation of corporate insolvency with either at least 100 homebuyers or at least 10% of the homebuyers in the same real estate project.
- Position in Liquidation Stage: In case the insolvency process fails and the company is pushed into liquidation, homebuyers are treated as unsecured financial creditors.
- This places them in the fourth position under the waterfall mechanism of Section 53 of the IBC.
- Homebuyers' claims are considered after the dues of insolvency process costs, secured creditors, workmen, and employees are satisfied.
Why is the Government Reviewing RERA?
- Assessment of Effectiveness:
- The government wants to assess the effectiveness of RERA in achieving its objectives.
- This includes evaluating its impact on transparency, accountability, information dissemination, and grievance redressal in the real estate sector.
- By holding regular meetings with homebuyers and other stakeholders, the government aims to gather feedback on their experiences with RERA.
- This feedback can help identify any shortcomings or areas for improvement in the implementation of the Act.
- Data Collection:
- The Ministry is setting up a data collection unit to gather data on the functioning of the RERAs over the years.
- This data would provide insights into the number of projects approved, their progress, delays, and other relevant information, helping in assessing RERA's overall impact.
- Uniformity and Compliance:
- The government is focusing on ensuring uniformity in the information available on RERA websites across different states.
- This indicates a push for greater compliance with the provisions of the Act, such as mandatory publication of annual reports and quarterly progress reports of builders.
- During the meeting, the issue of lack of information on the RERA websites was raised which as per the Act should have annual reports and quarterly progress reports of builders.
- It was also found that there were instances where RERAs had registered projects without verification of documents.
- Possible Amendments:
- The government's review process lays the groundwork for any future changes.
- This suggests a proactive approach towards addressing any shortcomings identified during the review process and improving the effectiveness of RERA.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Analyse the major provisions of RERA and assess its effectiveness in achieving transparency, accountability, and consumer protection in the real estate industry. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. “The growth of cities as I.T. hubs has opened up new avenues of employment, but has also created new problems”. Substantiate this statement with examples. (2020)
Q. Discuss the various social problems which originated out of the speedy process of urbanisation in India. (2013)


Important Facts For Prelims
134th Dr. Ambedkar Jayanti
Why in News?
The 134th Dr Ambedkar Jayanti was celebrated on 14th April 2024, by the Dr. Ambedkar Foundation (DAF) on behalf of the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- B.R. Ambedkar played a key role in drafting the Constitution of independent India. His lesser-known contribution to the Hindu Code Bill, aimed at reforming Hindu personal laws, is equally significant in understanding his vision for a more equitable society.
What was the Hindu Code Bill?
- As the Law Minister in the newly formed government, Ambedkar embarked on drafting the Hindu Code Bill in 1950. It was Ambedkar's attempt to reform Hindu personal laws that would codify and modernise Hindu law, giving greater rights to women.
- Before drafting the bill, Ambedkar appointed Sanskrit scholars to translate important texts and shlokas, ensuring the reforms were rooted in Hindu tradition.
- The bill faced strong resistance from within the Congress party and the opposition, leading Nehru to delay its passage.
- After Ambedkar resigned from the Cabinet, Nehru took over the initiative and championed four separate bills that encompassed the same content as the Hindu Code Bill.
- These bills, namely the Hindu Marriage Act (1955), Hindu Succession Act (1956), Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act (1956), and Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act (1956) were enacted, realising Ambedkar's vision for Hindu reform.
Dr. Ambedkar Foundation (DAF)
- DAF was constituted to disseminate the message and ideologies of Babasaheb Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, aiming to further his visions and thoughts on a pan-Indian scale.
- Established in 1992, under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, DAF operates as an autonomous body dedicated to preserving and propagating the legacy of Dr Ambedkar.
- The Dr Ambedkar National Memorial (DANM) museum showcases the life, work, and contributions of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar through a collection of personal belongings, photographs, letters, and documents.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following parties were established by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar? (2012)
- The Peasants and Workers Party of India
- All India Scheduled Castes Federation
- The Independent Labour Party
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, despite having divergent approaches and strategies, had a common goal of amelioration of the downtrodden. Elucidate. (2015)


Important Facts For Prelims
3-D Map of the Universe
For Prelims: Dark Energy, space Technology, lunar mission, Radio Telescopes, optical telescope, ISRO, NASA, ESA, TIFR, DESI
For Mains: Discuss the type and nature of Dark Energy.
Why in News?
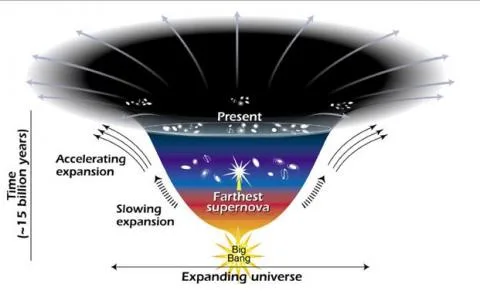
Recently, the most comprehensive three-dimensional map of the universe has been released by an international team of researchers.
- Scientists believe that this development could reveal some clues about Dark Energy.
- This map, derived from the first year of observations by the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), offers insights into the spatial distribution of galaxies and holds promise in unravelling the mysteries of Dark Energy.
What are the Universe's Fundamental Components?
- The universe is made up of three components:
- Normal or visible matter (5%)
- Dark matter (27%),
- Dark energy (68%)
- Normal Matter:
- Normal matter makes up everything we can directly observe.
- It is composed of atomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- It can exist as gas, solid, liquid, or plasma of charged particles.
- Dark Matter:
- Like ordinary matter, dark matter takes up space and holds mass.
- Dark matter is invisible and does not interact with light, making it impossible to directly observe.
- It exerts gravitational influence, as evidenced by its impact on the motion of stars, gas, and galaxies.
- Dark matter is believed to form halos around galaxies, and it is more prevalent in dwarf galaxies compared to larger ones.
- Dark Energy:
- Dark energy is a mysterious force that counteracts gravity, causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate.
- Despite being invisible like dark matter, dark energy has a different effect, pushing galaxies apart instead of pulling them together.
- The discovery of dark energy in 1998 was based on measurements of cosmic expansion, which revealed an increasing rate of expansion.
- Nature of Dark Energy:
- The recent findings have raised the tantalising possibility that dark energy – a mysterious, repulsive force that drives the process – is not constant throughout time as has previously been suggested.
- Dark Energy is detected by its effect on the rate at which the universe expands and its effect on the rate at which large-scale structures such as galaxies and clusters of galaxies form through gravitational instabilities.
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI):
- DESI is a unique piece of equipment that, once fitted over a telescope, can capture light from 5,000 galaxies at the same time.
- It is a collaboration of more than 900 researchers in institutions across the world. From India, TIFR (Tata Institute of Fundamental Research) is the only participating institution.
- Using DESI, which is mounted over the Mayall 4-Meter Telescope in Arizona, US, researchers have been able to measure light from six million galaxies — some of which existed as far back as 11 billion years ago.
- This was used to prepare the most detailed map of the universe as yet.
Read more: Dark Energy, Dark Matter
UPSC Civil Services Examinations, Previous Year Questions
Q.1 Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidence for the continued expansion of the universe? (2012)
- Detection of microwaves in space
- Observation of redshift phenomenon in space
- Movement of asteroids in space
- Occurrence of supernova explosions in space
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a)
Q.2. In the year 2008, which one of the following conducted a complex scientific experiment in which sub-atomic particles were accelerated to nearly the speed of light? (2008)
(a) European Space Agency
(b) European Organization for Nuclear Research
(c) International Atomic Energy Agency
(d) National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Ans: b


Important Facts For Prelims
India Developing Early Warning Systems in Partner Nations
Why in News?
India is taking proactive steps to assist neighbouring countries and small island nations in developing early warning systems to mitigate the impact of extreme weather events.
- This initiative aims to reduce the loss of life and property, aligning with the United Nations' 'Early Warnings for All' initiative.
How does India Plan to Help Partner Countries?
- About:
- Since, many countries lack the capacity to establish early warning systems, particularly those that are poor, least developed, or small island nations like Maldives and Seychelles.
- Therefore India aims to play a crucial role in helping countries like Nepal, Maldives, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Mauritius.
- Since, many countries lack the capacity to establish early warning systems, particularly those that are poor, least developed, or small island nations like Maldives and Seychelles.
- Role of India in Developing Early Warning System (EWS):
- India is providing technical expertise and financial aid to five partner countries, utilising public-private partnerships for financial support, with technical assistance from India and other contributing nations.
- India will assist in setting up meteorological observatories in partner countries.
- Partner nations will have access to India's numerical models to enhance their forecasting capabilities.
- India will aid in creating decision support systems to facilitate timely responses to extreme weather events.
- Ministries of communication in respective nations will collaborate to establish data exchange and warning dissemination systems.
What are the Trends Related to the Extreme Weather Events?
- Global Trends:
- A report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) highlights that natural disasters have surged over five times between 1970 and 2019, with water-related disasters becoming the most prevalent globally.
- Impact on Asia:
- Human and Economic Toll:
- From 1970 to 2021, nearly 12,000 weather, climate, or water-related disasters occurred, resulting in over two million deaths and economic losses exceeding USD 4.3 trillion.
- The Role of Climate Change:
- Climate change exacerbates the frequency and intensity of disasters, making them more likely and more challenging to manage effectively.
- Future Projections:
- By 2030, it is estimated that the world could face 560 medium- to large-scale disasters annually.
- India As a Key Player:
- India's initiative to bolster early warning systems underscores the importance of international cooperation in addressing the growing threat of natural disasters and climate change.
India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- IMD was established in 1875.
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting, and seismology.
Early Warnings for All Initiatives:
- The Early Warnings for All initiative is co-led by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR), with other partners.
- The Early Warnings for All initiative is built on four pillars to deliver effective and inclusive multi-hazard early warning systems:
- Disaster risk knowledge and management
- Detection, observation, monitoring, analysis, and forecasting
- Warning dissemination and communication
- Preparedness and response capabilities
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The 2004 Tsunami made people realize that mangroves can serve as a reliable safety hedge against coastal calamities. How do mangroves function as a safety hedge? (2011)
(a) The mangrove swamps separate the human settlements from the sea by a wide zone in which people neither live nor venture out
(b) The mangroves provide both food and medicines which people are in need of after any natural disaster
(c) The mangrove trees are tall with dense canopies and serve as an excellent shelter during a cyclone or tsunami
(d) The mangrove trees do not get uprooted by storms and tides because of their extensive roots
Ans:(d)
Mains:
Q. Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. (2021)


Rapid Fire
Dispelling Myths Around Bats in Kerala
Recently, researchers from Kerala have training programs on bat taxonomy, acoustics, and biogeography.
- Myth, superstition, and zoonotic diseases such as Covid-19 and the Nipah virus infection, have created a negative impression of bats.
- The project aims to address the challenges posed by emerging zoonotic diseases and the ongoing threats faced by bat populations, including habitat loss and the cutting down of fruit bat roosts.
- Researchers in Kerala are also supporting the ongoing National Bat Monitoring Programme, which has been running since 1996.
- It gives us the information needed to help bat conservation.
Bats:
- India is home to 135 bat species. Bats are nocturnal animals.
- Bats normally feed on fruits, helping in pollination by seed dispersal but also cause agricultural losses and hence are regarded as vermin.
- The population of bats has declined worldwide due to poaching, meat consumption, use in traditional medicines, climate change, environmental pollution, and biological invasions.
Read more: Invasive Alien Species


Place In News
India Gains Sittwe Port Access
Recently, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) has approved a proposal for India Ports Global Ltd (IPGL) to take over the operations of the entire Sittwe port located on the Kaladan River, Myanmar. It will be India’s 2nd overseas port after Chabahar Port.
- IPGL is a company 100% owned by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
Sittwe Port:
- The Sittwe Port, located in the Rakhine State of Myanmar, is a crucial component of the Kaladan multi-modal transit transport project.
- The deep-water port offers a significant connectivity advantage for cargo to reach from Vizag and Kolkata to the Northeastern states, bypassing Bangladesh.
- It will also reduce dependency on the Siliguri Corridor (or the chicken’s neck) squeezed between Bhutan and Bangladesh.
- India’s operational control over these 2 overseas ports, Chabahar and Sittwe, will strengthen India’s maritime influence to counter China’s String of Pearls policy with ports like Hambantota in Sri Lanka, Djibouti in Africa, etc.
Read more: India-Myanmar Ties: Fencing The Free Movement, India-Bangladesh Relations


Rapid Fire
Artificial Reefs to be installed in Mumbai
India's second-ever installation of artificial reefs (after Pondicherry) to boost marine life is being deployed near Worli Koliwada, Mumbai.
- 210 reef units made from recycled concrete and steel are installed 500 meters offshore, and it will take 3 months to show initial signs of a thriving ecosystem.
Artificial Reefs:
- These are structures built by humans through biorock technology and placed on the seabed in freshwater or saltwater environments.
- Biorock technology was invented by Wolf Hilbertz. In this technology, a low electrical current is passed through the water using electrodes placed near a steel structure.
- This current acts like a magnet, attracting dissolved minerals, particularly calcium and carbonate ions, forming a calcium carbonate (CaCO3) layer similar to natural coral reefs.
- These reefs offer crucial hard surfaces to which algae, barnacles, corals, and oysters can firmly attach themselves.
- These reefs will create habitats for fish, absorb carbon dioxide, and benefit local fishing communities.
Read More: Coral reefs, Biorock technology


Rapid Fire
Cryogenics
Cryogenics is defined as the science of materials at temperatures below negative 153 degrees Celsius. It deals with extremely low temperatures where common gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and air become liquid.
- Cryogenics, typically uses helium and nitrogen as the cryogenic fluid, the thing that cools a substance.
- Nitrogen has a boiling point of negative 196 degrees C and helium has a negative 269 degrees C. Below these temperatures they are liquid.
- These liquids need to be stored in vacuum flasks or they could leak and damage their surroundings.
Use of Cryogenics:
- For example, hydrogen is one of the best rocket fuels but it can only be used as a liquid, so it needs to be cryogenically cooled.
- Cryogenic hydrogen and cryogenic oxygen power the third stage of ISRO’s LVM-3 rocket.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) devices used in medical diagnostics use cryogenic fluids to cool their magnets.
Read more: 3D Printed Cryogenic Engine and Space Sector Privatisation


Rapid Fire
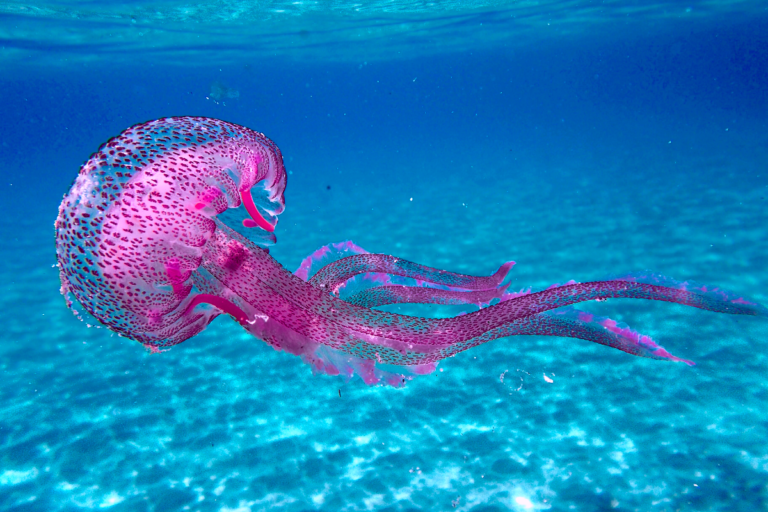
Venomous Jellyfish
Recently, a bloom of venomous jellyfish was reported across the Visakhapatnam coast.
- The species, Pelagia noctiluca, also known as the mauve stinger or purple-striped jellyfish, has a painful sting and causes different degrees of illnesses such as diarrhoea, extreme pain, vomiting and anaphylactic shock and can be life-threatening.
- It is a purple-coloured translucent species resembling a floating balloon.
- It is found worldwide in tropical and warm-temperature seas.
- Unlike other jellyfish species, it has stingers not just on the tentacles, but on the bell too.
- These are bioluminescent, having an ability to produce light in the dark.
- A jellyfish bloom is when the population of the species increases dramatically within a short period of time, usually due to a higher reproduction rate. It occurs frequently as a result of rising ocean temperatures.
- These have in the past been known to have caused massive damage to the fishing industry and impacted tourism.
Read more: 505-Million Year Old Jellyfish Fossils


Rapid Fire
Piezoelectric Bone Conduction Hearing Implants
Command Hospital Pune has achieved a significant milestone by successfully performing two piezoelectric bone conduction hearing implants, marking the first instance of such procedures in a government hospital in India.
- The piezoelectric bone conduction hearing implant system is an expensive implantable medical device designed for patients with hearing impairments, including those with conductive loss (such as aural atresia), mixed hearing loss, and single-sided deafness (SSD).
- Aural atresia is a congenital condition that affects the development of the ear, specifically the ear canal.
- In individuals with aural atresia, the ear canal fails to form properly or is completely absent, leading to significant hearing impairment or deafness in the affected ear.
- Single-sided deafness is a condition in which an individual experiences complete or near-complete hearing loss in one ear, while the other ear has normal or near-normal hearing.
- Aural atresia is a congenital condition that affects the development of the ear, specifically the ear canal.
- Piezoelectricity is a property of certain materials that induces an electric current when mechanically stressed.
Read more: Piezoelectric Effect, Empowering Persons with Disabilities