Economy
India's Export Outlook
- 22 Jul 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: India's Export Outlook, Gross Domestic Product, World Trade Organization, Foreign Trade Policy, Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES).
For Mains: India's Export Outlook, challenges and Way forward.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India has decided to adopt a Target Range Approach in announcing Export Goals for FY 2023-24 instead of a single number due to ongoing global uncertainties.
- Despite achieving a record USD 450 billion in merchandise exports during 2022-23, India's outbound shipments have faced significant challenges in the first quarter of 2023-2024.
What is the Target Range Approach Adopted by the Government?
- Targets Based on Four Key Parametres:
- Overall Target of USD 2 Trillion by 2030:
- As per India’s new Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023, it aims to achieve a total export of USD 2 trillion with services and goods exports accounting for a trillion dollars each by 2030.
- This long-term objective will be considered while setting the current year's targets.
- Import to GDP Ratio of Importing Countries:
- The targets will take into account the import to GDP (Gross Domestic Product) ratio of the countries that are major importers of Indian goods.
- This ratio will provide insights into the potential demand for Indian products in various international markets.
- Export to GDP Ratio of India:
- The export to GDP ratio of India itself will be assessed to gauge the country's export potential and capacity.
- Trend Growth of Past Years:
- The past growth trends in exports will be analyzed to understand the trajectory of India's trade performance and consider it in setting achievable targets.
- Overall Target of USD 2 Trillion by 2030:
- Target Range:
- In FY 202-23, exports amounted to USD 450 billion. Based on this figure and assuming a conservative growth rate of 10%, trade experts suggest the following potential target range:
- Lower End of Range: USD 451 billion (Slightly above the previous year's exports)
- Upper End of Range: USD 495 billion (Assuming a 10% growth rate).
- In FY 202-23, exports amounted to USD 450 billion. Based on this figure and assuming a conservative growth rate of 10%, trade experts suggest the following potential target range:
- Monitoring Mechanism:
- The Department of Commerce will use a fixed number to track export performance every month, which could be a mid-value or an average.
- This monitoring mechanism will provide timely insights into progress and help make necessary adjustments if required.
What is the Current Scenario of Indian Export?
- Export Performance:
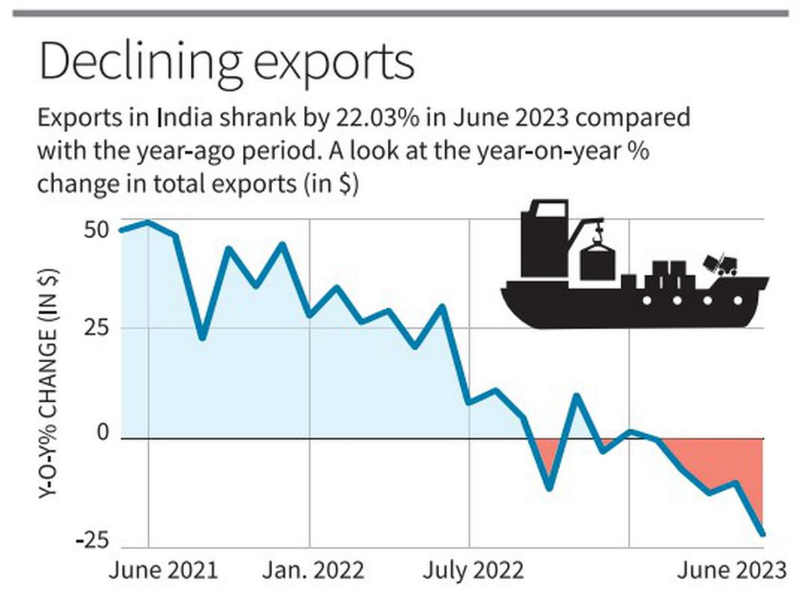
- Goods exports have experienced a series of deceleration in recent months, with a 22% drop in June 2023, marking the steepest fall in 37 months.
- The USD 32.7 billion export tally for June 2023 was the lowest since October 2022.
- Exported services have also witnessed a slowdown, with forex earnings from intangible exports growing by only 5.2% to USD 80 billion in the first quarter of 2023-24, compared to about 28% growth in the previous year 2022-23, where earnings reached USD 325 billion.
- Goods exports have experienced a series of deceleration in recent months, with a 22% drop in June 2023, marking the steepest fall in 37 months.
- Factors Influencing Exports:
- Global Oil Prices:
- Petroleum exports saw a sharp plunge of 33.2% in the first quarter, primarily driven by reduced global oil prices.
- Additionally, price cap sanctions on Russian oil shipments have also contributed to a moderation in demand.
- External Factors:
- The World Trade Organisation's (WTO) forecast of slower global trade growth in 2023 is influencing India's export outlook, prompting the need for a more cautious approach.
- Global Oil Prices:
- Government's Broader Target:
- India's broader target for exports, as per the new Foreign Trade Policy, is to achieve USD 2 trillion by 2030, with services and goods exports each accounting for a trillion dollars.
What is the Status of the Export Sector in India?
- Status of Trade:
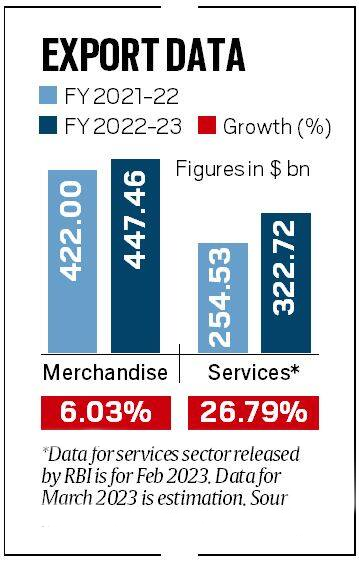
- The merchandise trade deficit, which is the gap between exports and imports, increased by over 39% in 2022-23 to record USD 266.78 billion, as compared to USD 191 billion in 2021-22.
- Merchandise imports increased by 16.51% in 2022-23, while merchandise exports rose by 6.03%.
- India’s Major Export Arenas:
- Engineering Goods: They registered a 50% growth in exports, at USD 101 bn in FY22.
- Agriculture Products: Agricultural exports were buoyed by the government's push to meet global demand for food amid the pandemic. India exports rice worth USD 9.65 bn, the highest among agricultural commodities.
- Textile and Apparels: India’s textile and apparel exports (including handicrafts) stood at USD 44.4 billion in FY22, a 41% increase on a YoY basis.
- Government’s scheme like Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel (MITRA) Park are giving a strong boost to this sector.
- Pharmaceuticals and Drugs: India is the third-largest producer of medicines by volume and the biggest supplier of generic drugs.
- India supplies over 50% of Africa’s requirement for generics, around 40% of generic demand in the US and 25% of all medicine in the UK.
What are the Challenges Related to the Export Sector in India?
- Challenges in Access to Finance:
- Access to affordable and timely finance is crucial for exporters.
- However, many Indian exporters face challenges in obtaining finance due to high interest rates, collateral requirements, and lack of credit availability from financial institutions, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Limited Diversification:
- India's export basket is concentrated in a few sectors, such as engineering goods, textiles and pharmaceuticals, which makes it vulnerable to global demand fluctuations and market risks.
- Limited diversification of exports poses a challenge to India's export sector as it can limit its resilience to changing global trade dynamics.
- Rising Protectionism and Deglobalisation:
- Countries around the globe are moving towards protectionist trade policies due to disrupted global political order (Russia-Ukraine War) and weaponization of supply chain, that is in way shrinking India’s export capacities.
What are the Major Government Initiatives to Promote Export Growth?
- Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES)
- PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP)
- Duty Drawback Scheme
- Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP)
- Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies
Way Forward
- Improved infrastructure and logistics are critical for enhancing export competitiveness.
- India should prioritise investments in transportation networks, ports, customs clearance processes, and export-oriented infrastructure such as export promotion zones and specialised manufacturing zones.
- Skill development programs should be implemented to enhance the availability of skilled labour in export-oriented industries.
- Additionally, incentivizing and promoting technology adoption, such as automation, digitization, and Industry 4.0 technologies, can boost productivity, competitiveness, and innovation in the export sector.