Female Genital Mutilation
For Prelims: Female Genital Mutilation, International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, United Nations Population Fund, United Nations Children's Fund
For Mains: Challenges Related to Women, Challenges in Eradicating FGM
Why in News?
Recently, the UN agencies stated that in 2024, nearly 4.4 million girls are at risk of female genital mutilation around the world.
What is Female Genital Mutilation?
- About: Female genital mutilation (FGM) comprises all procedures that involve altering or injuring the female genitalia for non-medical reasons and is recognised internationally as a violation of the human rights, the health and the integrity of girls and women.
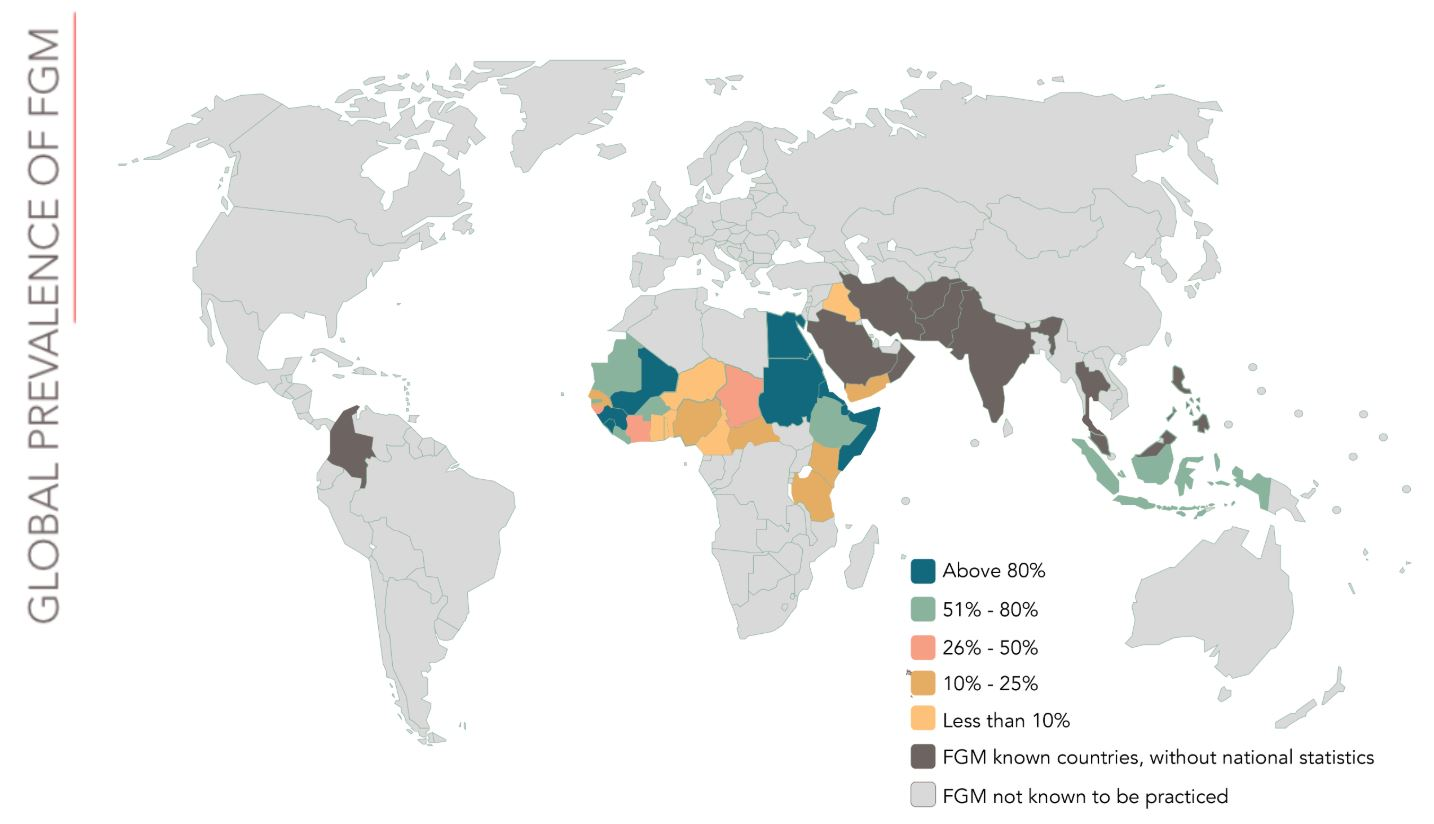
- Prevalence: It is concentrated primarily in Western, Eastern, and North-Eastern Africa, as well as select Middle Eastern and Asian nations.
- However, with increased migration, FGM has become a global concern, affecting girls and women in Europe, Australia, and North America as well.
- Impacts: Girls who undergo female genital mutilation face short-term complications such as severe pain, shock, excessive bleeding, infections, and difficulty in passing urine, as well as long-term consequences for their sexual and reproductive health and mental health.
- Status in India: Presently, there is no legislation that bans the FGM practice in the country.
- In 2017, in response to a petition in the Supreme court, the Ministry of Women and Child Development had said that “at present there is no official data or study which supports the existence of FGM in India.”
- However, according to some other unofficial reports, procedures of FGM are prevalent amongst the Bohra community, primarily in the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Challenges in Eradicating FGM:
- Cultural and Social Norms: FGM is often deeply rooted in cultural and social norms, with communities practicing it as a tradition passed down through generations.
- Changing these deeply ingrained beliefs and practices can be challenging.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: Many individuals within communities where FGM is practiced may not fully understand the harmful consequences of the practice.
- Lack of awareness and education about the physical and psychological health risks associated with FGM can perpetuate its continuation.
- Lack of Adequate Data Collection and Reporting: Limited data collection and reporting on FGM prevalence hinder efforts to understand the scope of the issue and target interventions effectively.
- Cultural and Social Norms: FGM is often deeply rooted in cultural and social norms, with communities practicing it as a tradition passed down through generations.
- Global Initiatives Towards Eradication:
- United Nations Population Fund and United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), have co-led the largest global programme on the elimination of female genital mutilation (FGM) since 2008.
- In 2012, the UN General Assembly designated 6th February as the International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, with the aim to amplify and direct the efforts on the elimination of this practice.
- 2024 Theme: Her Voice. Her Future
- The United Nations strives for its full elimination by 2030, following the spirit of Sustainable Development Goal 5.
- SDG 5.3 aims to eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilations.
Way Forward
- Legislation and Policy Enforcement: Strengthening existing laws to explicitly bans FGM and imposes penalties for those who perform or facilitate it.
- Governments should ensure effective enforcement of these laws through law enforcement agencies.
- Awareness and Education: Launching a comprehensive awareness campaigns to educate communities about the harmful effects of FGM on physical, psychological, and sexual health.
- These campaigns should target not only individuals within practicing communities but others as well.
- Inclusion in Human Rights Framework: There is a need to ensure that efforts to combat FGM are grounded in human rights principles and respect the rights of women and girls.
- Advocating for the inclusion of FGM prevention and response measures in international human rights framework is the need of the hour.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalisation on women in India? (2015)
Bharat Ratna Awardees 2024
For Prelims: Bharat Ratna, Karpoori Thakur, MS Swaminathan, P. V. Narasimha Rao, Lal Krishna Advani, Green Revolution, Liberalization
For Mains: Important Personalities, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
The prestigious Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honour, is set to be conferred upon five eminent personalities who have made remarkable contributions to politics, governance, and agriculture. They are Karpoori Thakur, Mankombu Sambasivan (MS) Swaminathan, Pamulaparthi Venkata (P. V.) Narasimha Rao, Lal Krishna Advani, and Chaudhary Charan Singh.
What are the Notable Contributions of Bharat Ratna Awardees (2024)?
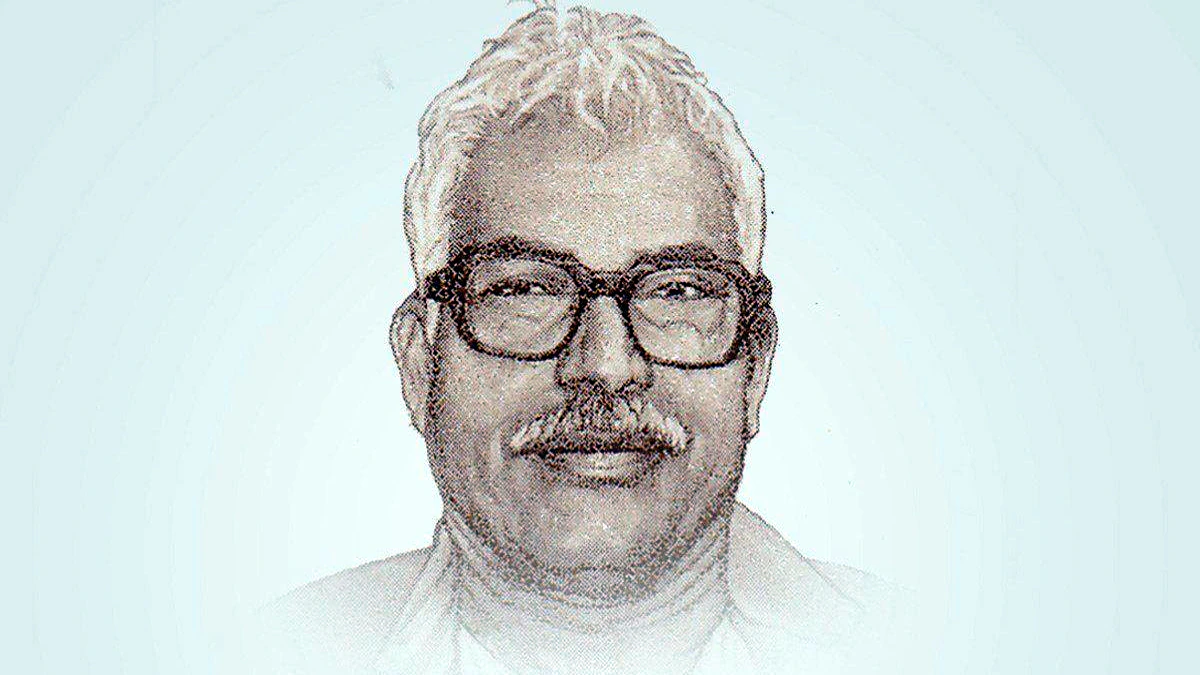
- Karpoori Thakur:
- Karpoori Thakur, known as "Jan Nayak," served as Bihar's 11th Chief Minister twice, from 1970-71 and 1977-79. He will be conferred the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
- Karpoori Thakur was the pioneer in providing the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) with the benefit of reservation as he implemented the recommendations of the Mungeri Lal Commission during his tenure as Bihar CM from 1977 to 1979.
- In 1978, he introduced a groundbreaking reservation model, allocating 26% of reservations with specific quotas for OBCs, Economically Backward Classes (EBCs), women, and economically backward classes among upper castes.
- Thakur advocated for marginalised communities' rights, emphasising social justice and inclusive development.
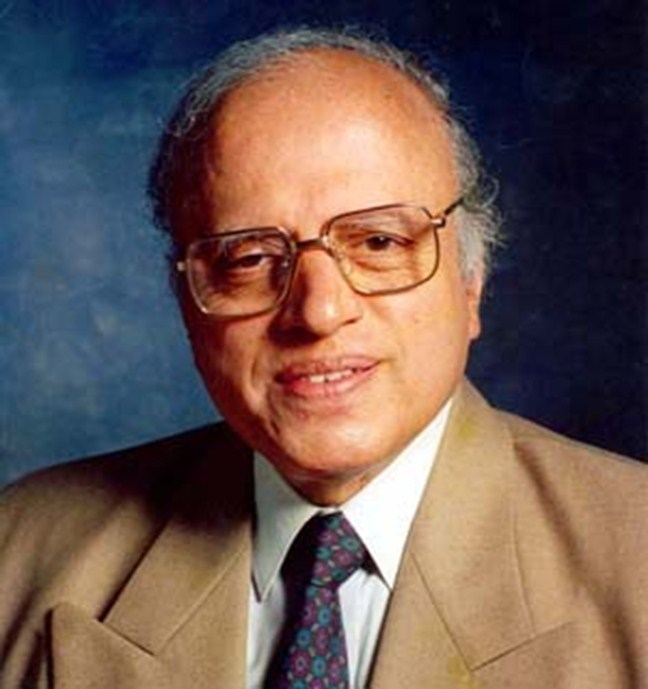
- Mankombu Sambasivan (MS) Swaminathan:
- MS Swaminathan, the ‘Father of India’s Green Revolution,’ helped India become self-reliant in agriculture and modernised it. He will be conferred the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
- Developed high-yielding wheat and rice varieties with Norman Borlaug, revolutionising agriculture in India in the 1960s and '70s.
- He Advocated for fair prices for agricultural produce and sustainable farming practices, leading the National Commission of Farmers.
- He played a pivotal role in developing the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Right Act, 2001.
- Swaminathan received numerous prestigious awards, including the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award in 1961, the Ramon Magsaysay Award in 1971, and the Albert Einstein World Science Award in 1986.
- Recognised with the Padma Shri (1967), Padma Bhushan (1972) Padma Vibhushan (1989).
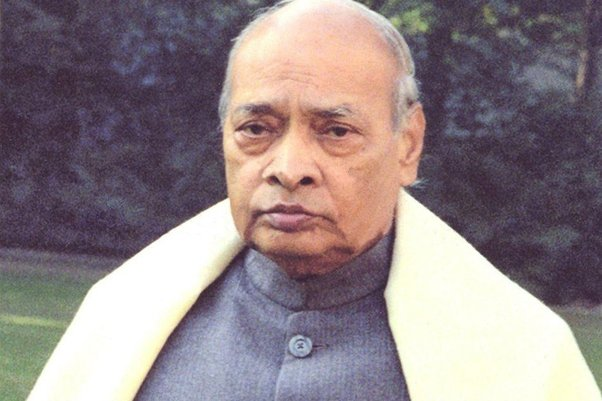
- Pamulaparthi Venkata (P. V.) Narasimha Rao:
- P. V. Narasimha Rao served as the 9th Prime Minister of India from 1991 to 1996, he will be conferred the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
- As Prime Minister, P.V. Narasimha Rao reset India’s foreign policy, improving ties with the United States and establishing relations with Israel.
- He maintained national independence by refusing to give up India’s right to pursue its nuclear strategy.
- Rao’s tenure left behind a polity more confident, with India on a path of economic liberalization and resurgence, following the LPG reforms of 1991 that opened up the economy to globalisation, reduced trade barriers, and initiated privatisation in various sectors.
- He published ‘SahasraPhan’, a Hindi translation of the famous Telugu Novel ‘Veyi Padagalu’.
- The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments Acts were enacted during the tenure of P.V. Narasimha Rao.
- The 73rd and 74th Amendment Acts mandate the reservation of one-third of seats for women in Panchayati Raj institutions and urban local bodies (ULBs).
- Lal Krishna Advani:
- Advani through the years has served as the 7th Deputy Prime Minister of India (1999-2004) and as the President of the Bharatiya Janata Party for the longest period since its inception in 1980.
- Advani is widely regarded as an individual of great intellectual ability, strong principles, and unwavering support for the idea of a strong and prosperous India.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh:
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was an Indian politician and a freedom fighter. He served as the 5th prime minister of India and former Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh.
- In 1952, as agriculture minister, he led Uttar Pradesh in abolishing the zamindari system.
- He advocated for the interests and rights of the peasants and introduced several measures to improve their conditions and welfare. He also promoted the values of democracy, secularism, and social justice.
- Charan Singh followed Mahatma Gandhi in a non-violent struggle for independence from the British Government and was imprisoned several times.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was an Indian politician and a freedom fighter. He served as the 5th prime minister of India and former Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh.
Note
- The rule of maximum three awards in a year is a guideline for the Bharat Ratna. The rule was broken for the first time in 1999, when four recipients were conferred the award: Jayaprakash Narayan, Amartya Sen, Gopinath Bordoloi, and Ravi Shankar.
- The rule was broken again in 2024, when five recipients were conferred the award.
Read more: Bharat Ratna to Karpoori Thakur, Bharat Ratna to LK Advani
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards: (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titles under the Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements are not correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
UPI Services in Sri Lanka and Mauritius
For Prelims: Unified Payment Interface, RuPay card, National Payments Corporation of India, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Aadhaar, DigiYatra, DigiLocker
For Mains: Digital Public Infrastructure, India- Sri Lanka- Mauritius Relations, Economic and Strategic Significance, Measures to boost bilateral relations.
Why in News?
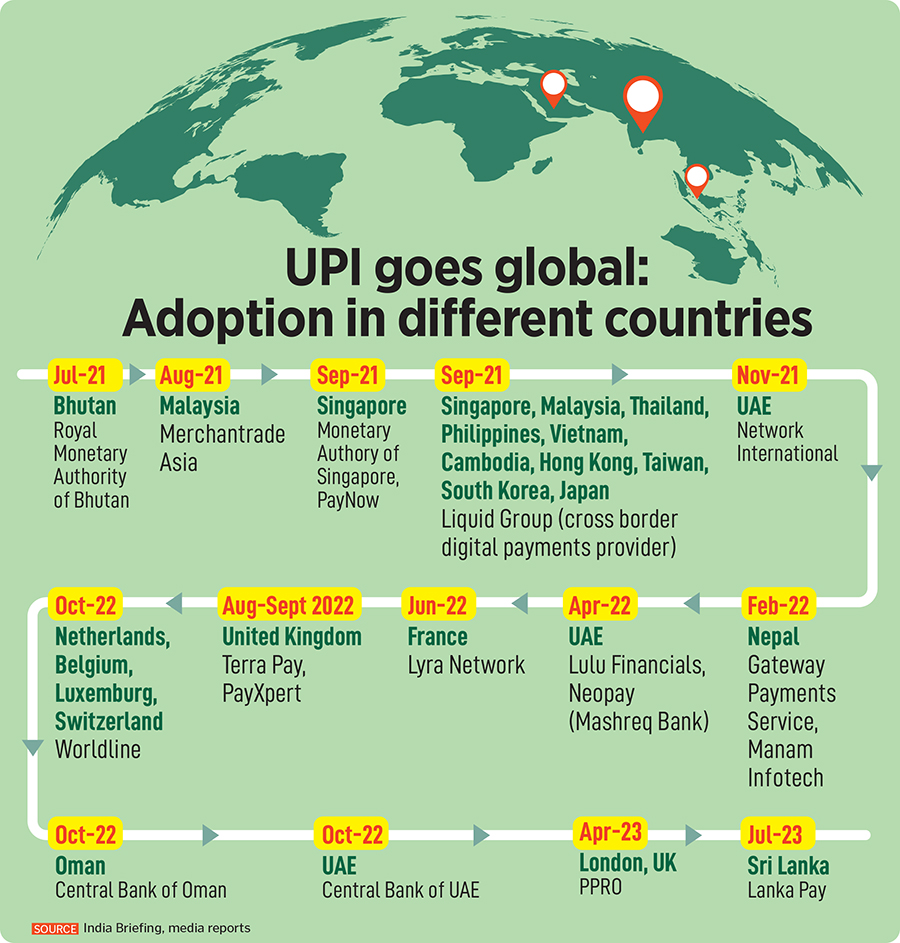
Recently, the Prime Minister of India along with the President of Sri Lanka, Mr Ranil Wickremesinghe and the Prime Minister of Mauritius, Mr Pravind Jugnauth jointly inaugurated the launch of Unified Payment Interface (UPI) services in Sri Lanka and Mauritius, and also RuPay card services in Mauritius.
- This move aims to facilitate seamless digital payments among citizens of the three countries, fostering stronger economic ties.
- These projects have been developed and executed by NPCI International Payments Ltd (NIPL), along with partner banks/non-banks from Mauritius and Sri Lanka, under the guidance and support of the Reserve Bank of India.
What are RuPay and UPI?
- RuPay:
- RuPay is a payment system and financial services product developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- It is a domestic card payment network that can be used at automated teller machines (ATMs), point of sale (POS) devices, and e-commerce websites across India.
- The provision under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007, empowered the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) to create a secure electronic payment and settlement system in India.
- RuPay has launched various card variants catering to the different segments of society.
- In addition to the Government scheme cards, RuPay Classic, Platinum & Select variant cards are designed for the masses and affluent customers.
- After Nepal, Bhutan, Singapore and UAE, the RuPay card is now available in Africa through Mauritius, the first non-Asian country to issue it.
- The use of RuPay technology will allow banks in Mauritius to issue RuPay cards locally through the Mauritius Central Automated Switch (MauCAS) card network.
- MauCAS is a novel state-of-the-art digital hub fully owned and operated by the Bank of Mauritius for routing payments among operators.
- The use of RuPay technology will allow banks in Mauritius to issue RuPay cards locally through the Mauritius Central Automated Switch (MauCAS) card network.
- UPI:
- The UPI is a digital and real-time payment system developed by the NPCI in 2016.
- UPI is built over the IMPS (Immediate Payment Service) infrastructure and allows users to instantly transfer money between any two parties' bank accounts.
- UPI allows merging several banking features, seamless fund routing, and merchant payments into one mobile application.
- More than 100 billion transactions took place via UPI in 2023 worth Rs 2 lakh crores.
- The countries that accept UPI payments are France, UAE, Mauritius, Sri Lanka, Singapore, Bhutan, and Nepal.
How will RuPay and UPI Benefit the Users in Mauritius and Sri Lanka?
- Facilitating Seamless Transactions:
- Users in Mauritius and Sri Lanka will experience convenience in making transactions, both domestically and internationally, through the adoption of RuPay and UPI.
- With RuPay cards and UPI connectivity, individuals travelling between India, Mauritius, and Sri Lanka can conduct transactions seamlessly, eliminating the need for currency exchange and reducing transactional complexities.
- Users in Mauritius and Sri Lanka will experience convenience in making transactions, both domestically and internationally, through the adoption of RuPay and UPI.
- Enhanced Financial Access:
- RuPay cards will be accepted at ATMs and PoS terminals in Mauritius, expanding the accessibility of digital payments for users in the region.
- UPI connectivity in Sri Lanka enables users to make QR code-based payments at merchant locations, providing a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods.
- Promotion of Financial Inclusion:
- The availability of RuPay cards and UPI services empowers individuals from diverse socio-economic backgrounds to participate in the digital economy, fostering financial inclusion.
- UPI transactions offer a cost-effective solution for users, reducing the expenses associated with traditional banking services and facilitating affordable financial transactions.
- Strengthened Economic Ties:
- Seamless payment solutions contribute to the growth of trade and tourism between India, Mauritius, and Sri Lanka, fostering economic cooperation and collaboration.
- Increased digital transactions support local businesses by promoting cashless transactions, enhancing transparency, and reducing reliance on cash-based transactions.
- The launch of UPI and RuPay services will also strengthen the economic and strategic ties between the three countries, as part of India’s “neighbourhood first” policy and “SAGAR” (Security and Growth for All in the Region) vision.
- Seamless payment solutions contribute to the growth of trade and tourism between India, Mauritius, and Sri Lanka, fostering economic cooperation and collaboration.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement:
- The introduction of RuPay and UPI reflects a commitment to embracing digital innovation, positioning Mauritius and Sri Lanka as progressive economies in the global digital landscape.
- By leveraging advanced payment technologies, users gain access to innovative financial solutions that empower them to manage their finances more efficiently and securely.
- The introduction of RuPay and UPI reflects a commitment to embracing digital innovation, positioning Mauritius and Sri Lanka as progressive economies in the global digital landscape.
India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- India's DPI also known as the India Stack, is a set of open and interoperable platforms yet independent "blocks" that provide identity, payment, data sharing, and consent mechanisms for various digital applications.
- These platforms are built on the principles of user-centric design, policy objectives, developing use cases, and engagement.
- Some of the key components of India’s DPI are Aadhaar, DigiYatra, DigiLocker, and Account Aggregator (AA).
- The DPI holds the promise of driving economic transformation and fostering inclusive growth. The modular layers of India Stack create opportunities for innovation, inclusion, and competition in the digital realm.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (2017)
(a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
(b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades.
(c) FDI inflows will drastically increase.
(d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans: (a)
Q3. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) helps in promoting the financial inclusion in the country.
- NPCI has launched RuPay, a card payment scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) based Projects/ Programmes usually suffers in terms of certain vital factors. Identify these factors, and suggest measures for their effective implementation. (2019)
Smart Gram Panchayat
For Prelims: PM-WANI, Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan, Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs), Sustainable Development Goals, BharatNet
For Mains: Role of PM-WANI in India's Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), Improving Rural Digital Literacy, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj inaugurated the ‘Smart Gram Panchayat: Revolution towards Digitization of Gram Panchayat’ Project at Paprour Gram Panchayat of Begusarai District, Bihar signalling a significant leap towards digital empowerment in rural India.
What is the Smart Gram Panchayat Project?
- The project aims to extend the PM-WANI (Prime Minister’s Wi-Fi Access Network Interface) Service to Gram Panchayats in Begusarai, marking a paradigm shift in rural connectivity.
- Begusarai leads the digital transformation in Bihar by equipping all Gram Panchayats with Wi-Fi services under the PM-WANI Scheme.
- It is funded under the revamped Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA), the project targets 455 Gram Panchayats across 37 Blocks in Begusarai and Rohtas Districts in Bihar. The Ministry of Panchayati Raj implements it.
- Emphasis is placed on using technology to enhance access to online services in critical sectors like health, education, and skilling, improving the quality of life in rural areas.
- Students, farmers, artisans, and Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) are among the beneficiaries of this initiative.
- Robust mechanisms for Operation & Maintenance (O&M) will be instituted to sustain the project's impact over time.
- The project aims to bridge the rural-urban divide, foster accountability, and efficiency in local self-governance, and empower communities through digital footprints.
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA)
- The RGSA is a scheme of the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, launched in, 2018. Later it was revamped and the Centrally Sponsored Scheme of RGSA was approved for implementation from 2022-23 to 2025-26 for capacity building of elected representatives (ERs) of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- The primary objective of Revamped RGSA is to develop the governance capabilities of the Panchayats to deliver on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) which are covered within the purview of Panchayats.
- Under the scheme basic orientation training for ERs of Panchayats is to be ensured within 6 months of election and refresher training within 2 years. The funding pattern for the State components is in the ratio of 60:40 among Central and States respectively, except Northeast Hilly States and UT of J & K where Central and State Share is in the ratio of 90: 10. For other UTs, the Central share is 100%.
- RGSA focuses on:
- Strengthening Panchayat-SHG convergence and training at various levels on e-Governance and Localization of SDGs.
- Utilising emerging technologies for interactive capacity building and standardised training. Capacitating PRIs on digital literacy and leadership roles.
What is PM-WANI?
- About:
- PM-WANI, launched by the Department of Telecom (DoT) in December 2020, promotes public WiFi hotspots for nationwide digital connectivity. Any entity can set up hotspots, aligning with the National Digital Communications Policy, 2018 (NDCP) aims for robust digital infrastructure in rural areas.
- PM-WANI Ecosystem:
- Public Data Office (PDO):
- PDOs set up and manage PM-WANI Wi-Fi hotspots, providing last-mile broadband connectivity to subscribers by procuring internet bandwidth.
- Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA):
- PDOA will provide aggregation services such as authorisation and accounting to PDOs, thereby facilitating PDOs in providing services to the end consumer.
- App Provider:
- App Providers develop apps for user registration, Wi-Fi hotspot discovery, and authentication for accessing PM-WANI compliant services.
- Central Registry:
- It will maintain the details of App Providers, PDOAs, and PDOs. It is currently maintained by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT).
- Public Data Office (PDO):
- Benefits:
- PM-WANI will boost broadband availability and affordability in rural areas, fostering entrepreneurship and digital inclusion. It complements BharatNet initiatives.
- It can provide an affordable and convenient option for internet access, as compared to mobile technologies like 5G, which require high investment and subscription costs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. The fundamental object of Panchayati Raj system is to ensure which among the following? (2015)
- People’s participation in development
- Political accountability
- Democratic decentralisation
- Financial mobilisation
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Q. Assess the importance of the Panchayat system in India as a part of local government. Apart from government grants, what sources can the Panchayats look out for financing developmental projects? (2018)
India’s Act East Policy
For Prelims: India’s Act East Policy, Inland Water Transport, Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), Look East Policy.
For Mains: India’s Act East Policy, India and its neighborhood- relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways has flagged off the first batch of trial Cargo Vessels from Maia Inland Custom Port in West Bengal to Sultanganj Port in Bangladesh, marking a significant step under India’s Act East Policy, with a focus on enhancing Inland Water Transport.
- It has been organised by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), marking a new beginning for improved connectivity and cooperation between India and Bangladesh.
What is the Significance of this Trial Shipment?
- Operationalization of Maia Terminal is expected to be a game-changer as it would shift 2.6 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) of Bangladesh-bound export cargo from road to waterways.
- The Maia-Aricha route (Protocol Route 5 & 6) will reduce the distance from NW1 (National Waterways 1) to Bangladesh and the North Eastern Region by 930 kilometres.
What is Inland Water Transport (IWT)?
- About:
- IWT refers to the transportation of goods and passengers via navigable rivers, canals, lakes, and other inland waterways.
- This mode of transport utilises watercraft such as boats, barges, and ships to move cargo and people within a country's interior regions, connecting various ports and terminals along the water routes.
- Significance:
- IWT is a highly cost-effective mode of transportation, particularly for bulk cargo like coal, iron ore, cement, food grains, and fertiliser.
- Despite its advantages, its current share in India's modal mix is only 2%. The government aims to increase this share to 5% by 2030 under the Maritime India Vision (MIV)-2030.
- To achieve this goal, the IWAI has identified 25 new National Waterways (NWs) through feasibility studies to make them navigable for transportation.
What is Act East Policy?
- About:
- The ‘Act East Policy’ announced in November, 2014 is the upgrade of the “Look East Policy”.
- It is a diplomatic initiative to promote economic, strategic and cultural relations with the vast Asia-Pacific region at different levels.
- It involves intensive and continuous engagement with Southeast Asian countries in the field of connectivity, trade, culture, defence and people-to-people-contact at bilateral, regional and multilateral levels.
- Aim:
- To promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and developing a strategic relationship with countries in Indo-pacific region with a proactive and pragmatic approach and thereby improving the economic development of the North Eastern Region (NER) which is a gateway to the South East Asia Region.
What is the Look East Policy?
- In order to recover from the loss of the strategic partner -USSR (end of the Cold war 1991), India sought to build up a relationship with the USA and allies of the USA in Southeast Asia.
- In this pursuit, former Prime minister of India P V Narasimha Rao launched Look East policy in 1992, to give a strategic push to India’s engagement with the South-East Asia region, to bolster its standing as a regional power and a counterweight to the strategic influence of the People’s Republic of China.
What is the Difference Between Look East Policy and Act East Policy?
- Look East:
- Look East policy focused on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries+Economic Integration.
- India became a dialogue partner of ASEAN in 1996 and summit level partner in 2002.
- In 2012 the relationship got up-graded into a Strategic Partnership.
- The time when India launched the Look East Policy in 1992, India's trade with ASEAN was USD 2 billion. After signing the Free Trade Agreement in 2010 with ASEAN, the trade has grown to USD 72 billion (2017-18).
- India is also an active participant in several regional forums like the East Asia Summit (EAS), ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) etc.
- Act East:
- Act East Policy focused on ASEAN countries + Economic Integration + East Asian countries + Security cooperation.
- Prime minister of India highlighted 4C's of Act East Policy.
- Culture
- Commerce
- Connectivity
- Capacity building
- Prime minister of India highlighted 4C's of Act East Policy.
- Security is an important dimension of India's Act East Policy.
- In the context of growing Chinese assertiveness in the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean, securing freedom of navigation and India's own role in the Indian Ocean is a key feature of Act East Policy.
- In pursuance of this, India has been engaged under the narrative of Indo-pacific and informal grouping called Quad.
- Act East Policy focused on ASEAN countries + Economic Integration + East Asian countries + Security cooperation.
- Look East policy focused on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries+Economic Integration.
What are the Initiatives to Enhance Connectivity under Act East Policy?
- Agartala-Akhaura Rail Link between India and Bangladesh.
- Intermodal transport linkages and inland waterways through Bangladesh.
- Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project and the Trilateral Highway Project connecting the North East with Myanmar and Thailand.
- Under India-Japan Act East Forum, projects such as Road and Bridges and modernization of Hydro-electric power projects have been undertaken.
- India-Japan Act East Forum was established in 2017 which aims to provide a platform for India-Japan collaboration under the rubric of India’s "Act East Policy” and Japan’s "Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy”.
- The Forum will identify specific projects for economic modernization of India’s North-East region including those pertaining to connectivity, developmental infrastructure, industrial linkages as well as people-to-people contacts through tourism, culture and sports-related activities.
- Other Initiatives:
- Assistance extended in the form of medicines/medical supplies to ASEAN countries during the pandemic.
- Scholarships with offers of 1000 PhD fellowships have been offered at IITs for ASEAN countries participants.
- India is also implementing Quick Impact Projects in Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar and Vietnam to provide development assistance to grass-root level communities in the fields of education, water resources, health etc.
- Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) are small-scale, low cost projects that are planned and implemented within a short timeframe.
- To enhance the modal share of coastal shipping and inland water transport, 46 initiatives have been identified in Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
- Key initiatives include the creation of port-based agglomeration centres, coastal berths near production/demand centers, and projects to improve road, rail, and inland waterway connectivity.
- The plan also aims to operationalize 50 waterways by 2047 and introduce low-draft vessel designs with possible tug-barge combinations to enhance efficiency and accessibility.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the five countries (Australia, China, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand) with which ASEAN has existing FTAs.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q.2 In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Analyze internalsecurity threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (2020)
Q. How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? (2013)
APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Card
Why in News?
Recently, the National Conference on APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Card was held in New Delhi.
- Vital interconnection between APAAR IDs, the Academic Bank of Credit, and Digilocker, facilitating streamlined operations, was also highlighted in the event.
What is APAAR?
- About: APAAR, an acronym for Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, is a specialised identification system designed for all students in India, beginning from an early age.
- It is introduced in accordance with the National Education Policy (NEP) of 2020 and the National Credit and Qualifications Framework (NCrF).
- Registration for an APAAR ID is voluntary, not mandatory.
- Objective: It aims to streamline and enhance the academic experience for students throughout India by assigning a unique and permanent 12-digit ID to each student, consolidating their academic records into a single accessible platform.
- It is emphasised as not only a vital tool for tracking the educational progress of 260 million students in India but also as an aspirational and globally recognized document for students.
- Benefits:
- APAAR ensures accountability and transparency in education by tracking student progress and streamlining academic records.
- It enhances efficiency, combats fraud, and includes co-curricular achievements for holistic student development.
- With multiple use cases, APAAR facilitates a smooth transfer process and supports data-driven decision-making in educational institutions.
- It also enables students to easily share their academic records for enhanced access to employment.
- Related Concerns:
- Privacy Concerns: Consolidating academic records into a centralised database raises concerns about the privacy and security of student data.
- The proliferation of digital identities through APAAR IDs may increase the risk of identity theft or fraudulent activities, requiring robust security measures.
- Digital Divide: There is a risk that students from marginalised or remote communities may not have equal access to digital platforms, potentially widening existing educational disparities.
- Privacy Concerns: Consolidating academic records into a centralised database raises concerns about the privacy and security of student data.
What is the Academic Bank of Credits and DigiLocker?
- Academic Bank of Credits: As per NEP 2020, the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) has been envisaged to facilitate the academic mobility of students with the freedom to study across the education Institutions in the country with an appropriate "credit transfer" mechanism from one programme to another.
- If the student changes schools, whether within the state or to another state, all their data in the ABC gets transferred to her/his new school just by sharing the APAAR ID.
- DigiLocker: It is a cloud-based platform that allows users to store, issue, and verify documents and certificates digitally.
- It is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY) under Digital India programme.
- The issued documents in DigiLocker system are deemed to be at par with original physical documents as per Rule 9A of the Information Technology (Preservation and Retention of Information by Intermediaries providing Digital Locker facilities) Rules, 2016.
Read more: CBSE to Introduce Credit System
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)
SC Strikes Down Electoral Bonds Scheme
Recently, the Supreme Court(SC) struck down the electoral bonds scheme that allows anonymous donations to political parties, citing it as unconstitutional.
- SC asserted that transparency regarding funding to political parties is crucial for informed electoral decisions, affirming that the scheme infringes upon the right to information as enshrined in Article 19(1)(a).
- Electoral bonds are money instruments that act as promissory notes or bearer bonds that can be purchased by individuals or companies in India.
- They are issued specifically for the contribution of funds to the political parties.
- The SBI is the only bank authorized to issue and encash electoral bonds.
- The donations made under this scheme enjoyed 100% tax exemption.
- SC has directed the State Bank of India to stop issuing electoral bonds immediately and submit all the details to the Election Commission by 6th March, 2024.
Read more: Electoral Bonds
Gold ETF Inflows Surge Amidst Economic Uncertainty
In January 2024, Gold Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) witnessed a remarkable surge in inflows, reaching Rs 657 crore. This influx contributed to a 1.6% rise in the assets under management (AUM) of gold funds.
- Experts attribute this surge to the enduring appeal of gold as a safe haven and hedge against inflation, particularly amidst ongoing geo-political tensions and elevated inflation in the US.
- Gold ETFs are passive investment instruments representing physical gold which may be in paper or dematerialised form. Each unit of a Gold ETF usually represents a fixed amount of gold, often 1 gram.
- Gold ETFs combine the flexibility of stock investment and the simplicity of gold investments.
- Investing in Gold ETFs entails acquiring gold in an electronic format, allowing individuals to engage in buying and selling activities just like stock trading.
- They offer liquidity and exposure to gold prices without the hassle of owning and storing physical gold.
Read more: Gold Exchange Traded Funds
Indo-Dutch Collaboration for Energy Transition
Recently, NITI Aayog and the Embassy of the Kingdom of the Netherlands released a report titled ‘LNG as a Transportation Fuel in Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicle’ during India Energy Week.
- It addresses the potential of LNG as a fuel source and suggests strategies for its utilisation in commercial vehicles.
- LNG is natural gas that has been converted to a liquid form for the ease and safety of natural gas transport.
- Natural gas is cooled to approximately -260°F, creating a clear, colourless, and non-toxic liquid that can be transported from areas with a large supply of natural gas to areas that demand more natural gas.
Read more: Natural Gas: A Stepping Stone
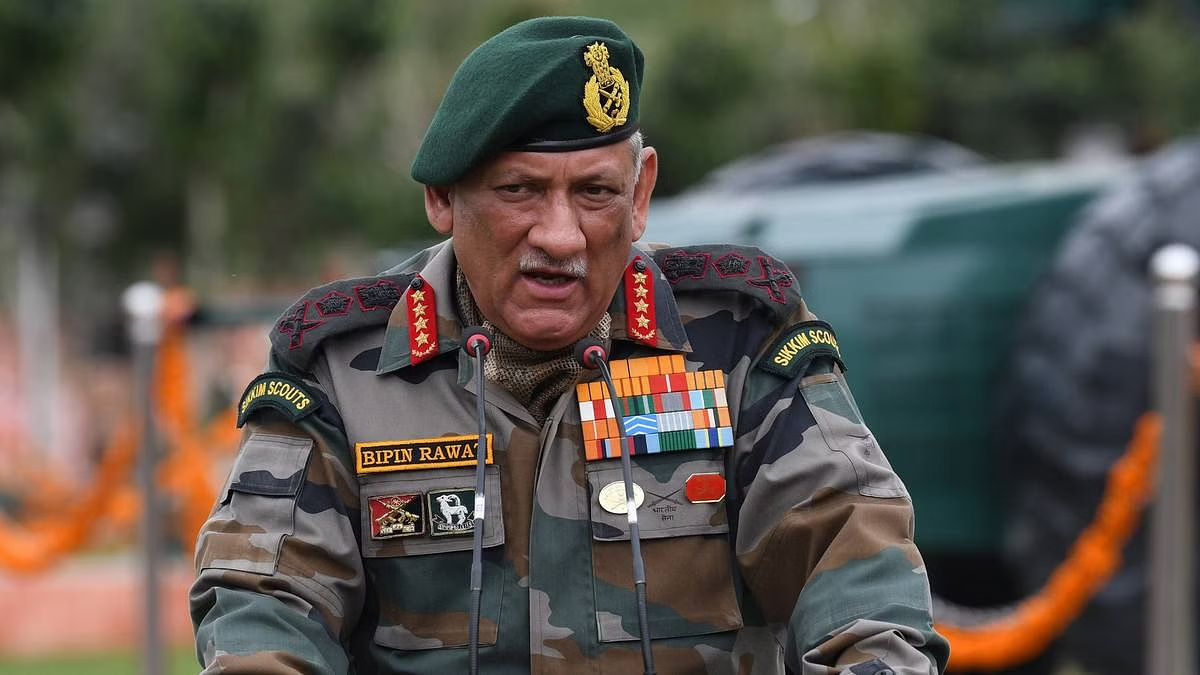
General Bipin Rawat
Source: PIB
Recently, the Minister of Defence of India unveiled a life-size statue of the late General Bipin Rawat (1958-2021), the country's first Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), at TonsBridge School, Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- Bipin Rawat was born in Pauri, Uttarakhand on 16th March 1958. He is an alumnus of the National Defence Academy (NDA) and the Indian Military Academy (IMA).
- Military Career Highlights:
- Served in various capacities including General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-C) Southern Command, and General Staff Officer Grade 2 at the Military Operations Directorate.
- Commanded a multinational brigade in the Democratic Republic of Congo as part of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force.
- Became Vice-Chief of Army Staff before assuming the role of Chief of Army Staff (COAS).
- Key Achievements:
- Played a significant role in reducing militancy in the Northeast.
- Instrumental in planning the 2016 surgical strikes across the Line of Control into Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which was a response to terrorist activities.
- Decorations and Awards:
- During his service, he was decorated with the Param Vishisht Seva Medal, Uttam Yudh Seva Medal, Ati Vishisht Seva Medal, Vishisht Seva Medal, Yudh Seva Medal, and Sena Medal.
Read more: Role of the Chief of Defence Staff, Theaterisation-of-Armed-Forces