International Relations
Peacebuilding Through The United Nations
- 04 Nov 2023
- 16 min read
This editorial is based on “Is the United Nations toothless in ending wars?” which was published in The Hindu on 03/11/2023. It talks about the effectiveness of the United Nations (UN) in addressing the Israel-Hamas conflict and the broader security issues of contemporary international order.
For Prelims: United Nations, United Nations Security Council, International Atomic Energy Agency, Chemical Weapons Convention, Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Kashmir Dispute, Darfur Conflict in Sudan, Iraq Invasion, Rohingya Crisis, P5, African Union, European Union
For Mains: UN role in maintaining international peace and security, Success of the UN in maintaining international peace and security, Limitations of the UN in maintaining international peace and security, India's Contribution in United Nations Peacekeeping Missions, Challenges Faced by United Nations peacekeeping operations, Necessary Reforms in the United Nations.
The United Nation’s capacity to bring a ceasefire in the Israel-Hamas conflict is being questioned due to changing global power dynamics. Over time, the UN's effectiveness inconflict resolution has diminished, and it has seen reduced influence in recent decades. Conflicting interests among major powers often prevent the UN from reaching a consensus on matters related to peacebuilding, security, and ceasefire agreements.
How Does the UN Maintain International Peace and Security?
The United Nations (UN) maintains international peace and security through various mechanisms and actions, as outlined in the UN Charter Chapter VII: Action with Respect to Threats to the Peace, Breaches of the Peace, and Acts of Aggression (Articles 39-51).
Here are the key ways in which the UN fulfils its role in this regard:
- Collective Security: The UN promotes collective security through the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), a principal organ responsible for maintaining international peace and security. The UNSC has the authority to take measures, including the use of force, to address threats to international peace and security.
- Peacekeeping Operations: The UN deploys peacekeeping missions to areas of conflict. These missions are composed of military, police, and civilian personnel from member states who work to monitor ceasefires, facilitate negotiations, and support the implementation of peace agreements.
- Diplomacy and Conflict Resolution: The UN serves as a platform for diplomatic negotiations and conflict resolution. It encourages dialogue and negotiations among parties in conflict and assists in mediating disputes to reach peaceful settlements.
- Sanctions: The UNSC can impose economic and political sanctions, such as trade restrictions and travel bans, against countries or entities that threaten international peace and security.
- Preventive Diplomacy: The UN engages in preventive diplomacy by proactively identifying potential conflicts and working to prevent their escalation.
- Conflict Prevention: The UN works to address the root causes of conflicts, such as poverty, inequality, and human rights abuses, to prevent the outbreak of conflicts.
- Humanitarian Assistance: The UN provides humanitarian aid to populations affected by conflicts and natural disasters. This assistance helps alleviate suffering, save lives, and address the consequences of conflicts.
- International Law: The UN promotes the adherence to international law, treaties, and conventions that govern behavior between states and ensure that countries respect the principles of sovereignty, territorial integrity, and non-interference in the affairs of other states.
- Disarmament and Non-Proliferation: The UN works to reduce the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and promote disarmament efforts.
How Successful has the UN been in Maintaining International Peace and Security?
The success of the UN in maintaining international peace and security:
- Prevention of World Wars:
- The UN was established after World War II with the primary goal of preventing another global conflict.
- The absence of a third world war since the UN's formation can be seen as a success in maintaining international peace at a global level.
- Preventing Nuclear Proliferation:
- For over five decades, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has served as the world’s nuclear inspector.
- IAEA experts work to verify that safeguarded nuclear material is used only for peaceful purposes. To date, the Agency has safeguards agreements with more than 180 States.
- Supporting Disarmament:
- UN treaties are the legal backbone of disarmament efforts:
- Chemical Weapons Convention-1997 has been ratified by 190 States
- Mine-Ban Convention-1997 by 162 states
- Arms Trade Treaty-2014 by 69 states
- UN treaties are the legal backbone of disarmament efforts:
- Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN has conducted numerous peacekeeping missions to mitigate conflict and support post-conflict stability.
- The UN has been more successful in preventing and resolving conflicts at the regional level, particularly in Africa, through peacekeeping missions and diplomatic efforts.
- Resolution of Interstate Conflicts:
- The UN has successfully mediated in some interstate conflicts, preventing or resolving disputes between countries.
- Example: 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis.
- The UN has successfully mediated in some interstate conflicts, preventing or resolving disputes between countries.
- Humanitarian and Relief Efforts:
- The UN has been involved in humanitarian and relief efforts in conflict zones, providing aid to those affected by conflicts.
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP),United Nations Refugee Agency (UNHCR), United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP) and the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) have primary roles in the delivery of relief assistance.
The limitations of the UN in maintaining international peace and security:
- Israeli-Palestinian conflict (1948-Now): The UN has failed to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with Israel maintaining control over historic Palestine and facing little accountability for its actions..
- Cambodia Violence (1975-1979): The UN recognized the Khmer Rouge regime, ignoring human rights violations, and failed to prevent genocide in Cambodia.
- Civil War in Somalia and South Sudan (1991-Now): The UN peacekeeping mission in Somalia failed due to the lack of a government to engage with and repeated attacks against UN officers, resulting in civilian deaths.
- The civil war in South Sudan has killed hundreds of thousands despite the presence of UN peacekeeping forces.
- Darfur Conflict in Sudan (2003-Now): The UN intervened years after the conflict in Darfur began, and the situation remains dire, with millions affected.
- Iraq Invasion (2003-2011): The U.S.-led invasion of Iraq, based on concerns about Weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) under UN Resolution 1483, resulted in instability and later contributed to the rise of ISIS. ISIS took control of territory in Iraq and Syria, triggering a major regional and global crisis.
- Syrian Civil War (2011-Now) : The UNSC limited action in the Syrian war led to a prolonged and devastating conflict in the region with millions of displaced Syrians.
- Yemen Civil War (2014-Now): The UN's efforts to provide humanitarian aid have been hindered by the Saudi-led coalition's intervention in Yemen.
- Rohingya Crisis, Myanmar (2017-Now): The UN failed to prevent the persecution and displacement of the Rohingya in Myanmar.
What are the Challenges Faced by UN Peacekeeping Operations?
Strategic Challenges:
- Lack of Adequate Representation: The UNSC is less effective because it is less representative, the most pertinent absence being that of Africa (a continent of 54 countries).
- Leadership System: The effectiveness of UN peacekeeping operations has been hampered by leadership failures, poor management, discipline issues, and inefficiencies in traditional peacekeeping approaches.
- Legislation: Troop and police-contributing countries often have varying interpretations of Status of Forces Agreements (SOFA), mandates, and Rules of Engagement.
- Global Order: Geopolitical and strategic interests of powerful nations can influence UN decision-making, leading to conflicts of interest.
Operational Challenges:
- Nature of Armed Conflict:. The evolving threats of violent extremism, transnational terrorism, and organized crime have made it challenging for peacekeepers to protect civilians and maintain security, especially in areas where peace and stability are difficult to achieve.
- Misuse of Veto Power: Veto power has been always criticized by many experts as well as by most States calling it a ”self-chosen club of the privileged” and non-democratic. It has been criticized for not allowing the Council to make necessary decisions whenever it displeases any one of the P-5.
- Methods of Operation: Peacekeeping operations now require a wide range of social and military activities to support or restore a host country's government and social institutions.
- Readiness: The UN does not have a standing army or police force, which makes it challenging to mobilize multinational member states' military and police forces for field missions.
Tactical Challenges:
- Geopolitical Rivalry within P5: The geopolitical rivalry among the permanent members of the UNSC (P5) has prevented the UNSC from coming up with effective mechanisms to deal with global issues like the invasion of Afghanistan.
- Lack of Common Understanding of Operations: Lack of a common understanding of operations among peacekeepers can lead to ineffective deployment.
- Multilateral Cooperation: Finding a comprehensive and effective leadership system that integrates UN and non-UN organizations in areas of operation remains a challenge.
- Discipline and Code of Conduct: Peacekeepers, police, and civilian personnel may engage in misconduct and mishandling of UN properties.
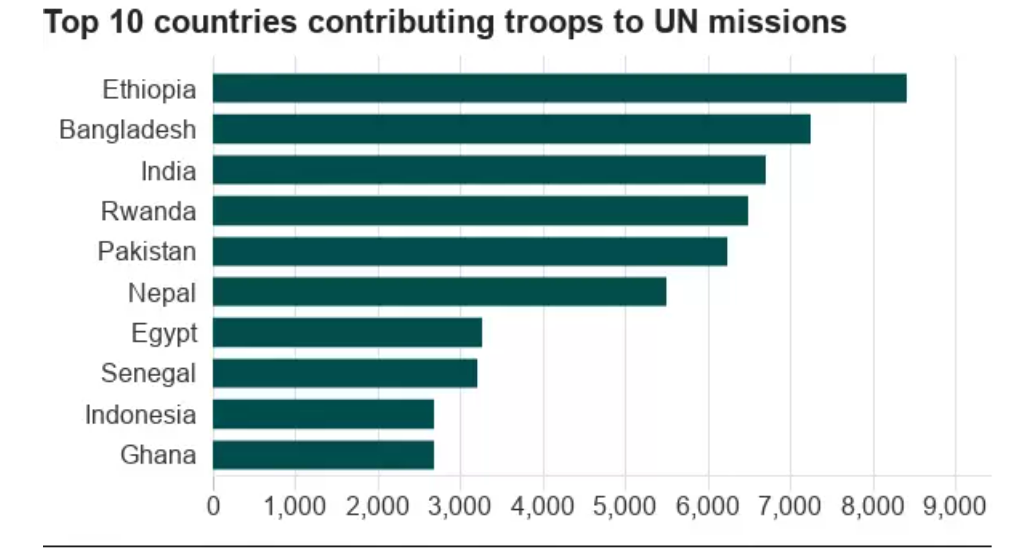
What is India's Contribution in UN Peacekeeping Missions?
- Troop Deployment: India has been actively involved in UN peacekeeping operations since its first commitment in Korea in 1950. Indian troops have served in 49 of the 72 UN missions, totalling over 253,000 personnel deployed worldwide.
- Female Peacekeepers: India has deployed Female Engagement Teams in the United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei, which is the second largest women contingent after Liberia.
- Medical and Engineering Units: India deploys medical teams and engineering units to provide essential services, such as medical care and infrastructure development, in conflict-affected regions.
- Expertise in Training: India's Centre for United Nations Peacekeeping (CUNPK) provides training and expertise in peacekeeping operations.
- Leadership Roles: Indian officers have served in leadership roles within UN missions, including as Force Commanders, contributing to effective mission management.
- Humanitarian Assistance: In addition to military contributions, India has provided humanitarian assistance, including medical aid and disaster relief support, in conflict-affected regions.
What Reforms are Necessary in the United Nations ?
- Improve UNSC Structure and Functioning:
- Expanding the number of permanent members.
- Implementing limitations on veto use in cases of mass atrocities and introducing collective veto consultation.
- Provide adequate resources to the Department of Political and Peacebuilding Affairs (DPPA) and the Department of Peace Operations (DPO).
- Create a single political-operational Structure for streamlining and enhancing coordination
- Strengthen Conflict Prevention Mechanisms:
- Enhance intelligence gathering and developing regional early warning centers.
- Invest in diplomatic efforts and expand the role of special envoys.
- Enhance Peacekeeping Operations:
- Promote a coordinated approach with fostering cross-pillar coordination.
- Provide training in hybrid and unconventional warfare and equipping peacekeepers with advanced technology.
- Addressing misconduct and sexual exploitation issues while strengthening peacekeeper discipline.
- Bolstering Partnerships:
- Strengthen connections with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and promote grassroots participation.
- Leverage resources and expertise from the private sector, aligning business interests with peace and security goals.
- Enhance ties with regional entities such as the African Union (AU) and the European Union (EU) and participate in joint peacekeeping initiatives.
Conclusion:
As the world grapples with conflicts, terrorism, humanitarian crises, and emerging threats, the need for a reinvigorated and more efficient UN peace and security apparatus becomes increasingly evident. However, it is important to acknowledge that implementing UN reforms will require collective commitment from member states as well as consistent monitoring and evaluation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of the United Nations in maintaining international peace and global order in the face of contemporary challenges. What reforms are necessary to enhance its effectiveness in this critical mission? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10 members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in UN Security Council. (2015)